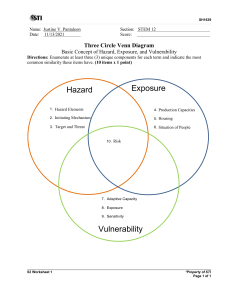
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST IN DISASTER READINESS AND RISK REDUCTION Third Quarter Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer and shade the corresponding letter in your answer sheet. 1. What causes a serious disruption of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic or environmental losses and impacts, which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources according to the Food and Agriculture Organization? a. disaster b. hazard c. phenomenon d. risk 2. Which of the following is an example of natural hazard that causes disaster? a. genocide b. typhoon c. bombs or explosions d. oil spills from shipping boat 3. What category of man-made disaster increase the risk for possible contamination of fresh water due to leak of hazardous chemical like aluminum oxide near a residential area? a. Terrorism disaster b. Violence disaster c. Complex humanitarian emergencies d. Technological/industrial disasters 4. What is the process or circumstance, usually connected to development, that increases catastrophe risk by increasing exposure and susceptibility or diminishing capacity? a. risk factor b. disaster risk c. natural hazard d. man-made hazard 5. Which of the following risk factors BEST describes the cause of COVID-19 pandemic? a. climate change b. weak governance c. poverty and inequality d. globalized economic development 6. The cause of landslides in one of the residential communities at Barangay Maanus is due to illegal logging. This kind of disaster will fall under which of the following risks? a. climate change b. weak governance c. poverty and inequality d. environmental degradation 7. Why should individuals prepare for the worst-case scenarios that may occur in the event of a disaster? a. So that others might learn from their mistakes. b. So that individuals can demonstrate their own ability. c. In order for individuals to be able to plan ahead of time. d. As a result, individuals will be less likely to be affected by calamities. 8. What do you characterize a disaster's effect on a group of individuals who are forced to flee their homes? a. health risk b. food scarcity c. displaced population d. emotional aftershock 9. COVID19 has infected millions of individuals worldwide, resulting in thousands of fatalities or death. What steps could you take to lessen the effect of a calamity that may strike your life? a. Stay away from the crowd. b. Establish positive ties with your neighbors. c. To stay informed, keep an eye on the news. d. Get in the appropriate frame of mind and make the necessary preparations. 10. What perspective of disaster is mostly unpredictable, which leave the victims in a state of shock and they tend to deny the loss and try to escape from reality? a. physical perspective b. economic perspective c. psychological perspective d. socio-cultural perspective 11. As a student, how can you best help your family and other people fight against COVID-19? a. I can volunteer as a frontliner. b. I can practice health protocols. c. I can donate cash and/or goods to the needy. d. I can wave cash assistance or goods from the government. 12. Which statement best describes vulnerability? a. Vulnerability can result in death, injury, or property damage. b. Vulnerability may lead to social and economic upheaval as well as environmental damage. c. Vulnerability is a physical occurrence, phenomenon, or human behavior that has the potential to cause harm. d. The term "vulnerability" refers to the ability to be vulnerable or susceptible. 13. Which of the following groups is the most vulnerable? a. teacher rendering services in a far-flung area b. elder leader in a community c. health care workers in the barrio d. fruit and vegetable vendor 14. What could be the possible reason why urban place like the City of Manila is more vulnerable to COVID-19 than the rural place like the Municipality of Balbalan? a. The urban area has a larger population than the rural area. b. Rural areas have a higher population density than metropolitan areas. c. The population density in rural areas is higher than that of metropolitan areas. d. The population density of urban areas is higher than that of rural areas. 15. What will most likely happen when the human population grows? a. a decreased risk b. fewer exposures c. hazard reduction d. heightened susceptibility 16. The COVID 19 pandemic had an economic impact, with several companies closing as a result of the increased community quarantine. What element is mostly affected? a. social b. physical c. economical d. environmental 17. Kaingin is a human practice that involves converting a forest into agriculture. This is the main source of income for people living in Sitio Malalaw. What element is most likely exposed to hazard? a. social b. physical c. economical d. environmental 18. What occurrence results in a dangerous condition, substance, human behavior, or situation that can result in death, injury, or other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihood and services, social and economic disruption, or environmental degradation? a. risk b. hazard c. exposure d. vulnerability 19. What are the possible ways to lessen the vulnerability of the exposed elements to hazard? a. Construction of poor designed comfort rooms. b. Housing relocation near emergency shelters and schools. c. Installation of waste segregation bin without labels. d. Land use planning that is uncontrolled. 20. Which is an example of natural hazard? a. dam failures b. plane crashes c. water pollution d. floods 21. Which hazard arise directly as a result of human activities? a. fires b. landslides c. tsunami 22. Which is an example of quasi- natural hazards? a. fog b. storm surge c. landslides d. leakage of ammonia d. toxic 23. During the identification of hazard and risk assessment, what method you are useful for identifying hazards and recommending solutions? a. observation b. safety audits c. discussion groups d. hazard and risk survey 24. Which of the following should be given consideration in risk assessment? a. probability and impact b. type of hazard and impact c. severity and type of hazard d. impact and type of damage/ harm 25. Landslides may cause flooding, river blockages, fatalities, and damage to land and natural resources, among other things. As a student, what will you suggest to improve areas prone to landslide? a. Plant trees on slope areas. b. Construct a concrete canal along slope area. c. Construction of relocation house on top of the mountain. d. Fill slope areas with soil and gravel. 26. Which of these can assist in reducing the danger of an earthquake for 100 families living in 20storey building condominium? a. landslide hazard map b. building earthquake resistant infrastructures c. monthly simulation of earthquake drill d. home owner association quarterly meeting 27. Which secondary effect of an earthquake is described as collapse of buildings caused by earthquake vibrating water-saturated fill or unconsolidated soil? a. flood b. landslide c. tsunami d. liquefaction 28. How could you determine that there is impeding sign of tsunami? a. As a tsunami approaches shorelines, water may recede from the coast, exposing the ocean floor, reefs and fish. b. Tsunamis may not be caused by severe ground shaking caused by local earthquakes. c. Abnormal Ocean activity, a wall of water, and an approaching tsunami create a musical sound. d. An approaching tsunami is a slow and expected recession of water levels below the expected low tide. 29. What would you recommend to your friend asking for help who cannot escape from tsunami? a. Go to an upper storey of a sturdy building or climb onto a roof. b. Tell your friend to call emergency hotlines. c. Grab a floating object and hang on until help arrives. d. Just wait for the rescuer to come. 30. What effect of earthquake hazard cause the deformation on the ground that marks the intersection of the with the earth's surface? a. ground rupture b. ground shaking c. liquefaction d. tsunami 31. What will likely happen when an area affected with earthquake experiences liquefaction or when solid materials acting non-solid due to vibration or saturation, typically from earthquakes? a. sinking and or titling of infrastructure b. drowning of people and damage to properties c. coastal erosion c. flood and landslide 32. When creating an earthquake hazard map, you can acquire which of the following? a. evacuation b. information c. mitigation d. transformation 33. Which of the following parts of the map will give you direction? a. compass rose b. grid reference c. color d. title 34. Which of the following color describe the strongest shaking of the ground during an earthquake? a. brown b. gray c. red d. white 35. What volcano-related hazard when hot or cold mixtures of water and volcanic debris that form when volcanic materials interact with water, ice, snow, or loose wet sediments? a. lava b. lahar c. tephra falls d. mud pools 36. What is the most dangerous volcanic hazard for persons with respiratory problems, over a distance of 270 miles (170km)? a. tephra falls b. mud pools c. lava d. lahar 37. Which of the following statements is true? I. One warning sign observed is enough to predict an eruption. II. One warning sign observed is not enough to predict an eruption. III. Small changes recorded from an instrument is enough to predict an eruption. IV. Small changes recorded from an instrument is not enough to predict an eruption. a. I and III b. I and IV c. II and III d. II and IV 38. What do you call the molten rocks found beneath the Earth? a. elements b. lava c. magma d. minerals 39. What form of hazard map depicts visual, geographical representations of regions that might be influenced by numerous volcanic phenomena during or after an eruption? a. volcanic hazard map b. earthquake hazard map c. landslide hazard map d. typhoon hazard map 40. During the information education campaign about volcano-related hazard at one of the barangays near Mayon Volcano at Legaspi, Albay. What will you tell to the community people on importance of volcanic hazard map? a. To communicate a complex array of hazard information to those at risk, or those responsible for managing those at risk. b. To help you understand the areas that may be affected by volcanic related hazard. c. To show areas that can be impacted and where it is safe. d. To evaluate areas prone to accident. Prepared by: JAY ANN T. TOLENTINO/GENEVA KARILL D. MILLAN Subject Teachers SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST IN DISASTER READINESS AND RISK REDUCTION Third Quarter ANSWER KEY 1. A 11. B 21. D 31. A 2. B 12. D 22. A 32. B 3. D 13. B 23. C 33. B 4. A 14. A 24. A 34. C 5. D 15. D 25. A 35. B 6. B 16. C 26. B 36. A 7. D 17. D 27. D 37. D 8. C 18. B 28. A 38. C 9. D 19. B 29. A 39. A 10. A 20. D 30. A 40. A Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating 3 Describe the effects of disasters on one’s life. Understanding Differentiate the risk factors underlying disasters. Remembering 2 NO. OF ITEMS 1 Explain the meaning of disaster. LEARNING TARGETS WEIGHT PERCENTAGE CONTENT AREA/OBJECTIVES NO. OF LESSONS TABLE OF SPECIFICATION in DISASTER READINESS & RISK REDUCTION - THIRD QUARTER 18 6 7 5 3 1 1 3 1, 2 1 3 4 5 6 1 3 8 7 9 1 2 10 11 1 2 12 13 100 3 Analyze disaster from the different perspectives 4 (physical, psychological, socio-cultural, economic, political, and biological). 5 Explain the meaning of vulnerability. 6 Explain why certain sectors of society are more vulnerable to disaster than others. 1 2 14 7 Recognize vulnerabilities of different elements exposed to specific hazards. 1 2 16 1 2 18 20, 21, 22 15 17 Differentiate among hazards, exposure, and 8 vulnerabilities and explain the relationship of 19 the three to disaster risk. 9 Define and cite examples of the types of hazards. 1 3 10 Explain the impact of various hazards on people and the environment. 1 2 1 3 11 Identify various potential earthquake hazards. 23 27 12 Recognize the natural signs of an impending tsunami. 1 2 13 Analyze the effects of the different earthquake hazards. 1 2 30 1 3 32, 33, 34 14 Interpret different earthquake hazard maps. 24 26 25 28, 29 31