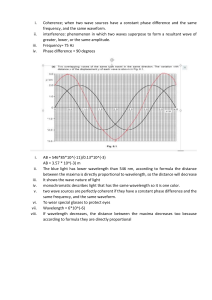
AIR ENERGIZED HEAT HOT TIRED JAN JERICHO C. BATINGA HEAT These atoms and molecules are always in motion, and they have kinetic energy What is LIGHT? • Transparent object - the objects that allow all light rays to travel through. • Opaque object – the objects that light cannot pass through. • Translucent object– the objects that light pass through them partially WHO AM I? Nature of light the theory supports Theory of Light 1. Corpuscular Theory of Light Scientist who proposed the theory Isaac Newton wave particle ∕ Wave and particle HOW LIGHT BEHAVES? UNDERSTANDING HOW LIGHT BEHAVES ISAAC NEWTON CHRISTIAN HUYGENS LOUIS DE BROGLIE JAMES CLERK MAXWELL “light behaves like a particle ” “light behaves like a wave ” “light can be a particle and a wave” Dual-Nature of Light “light as a propagating wave of electric and magnetic fields” “corpuscles” Corpuscular Theory of Light Wave Theory of Light Electromagnetic Theory of Light Bring the following materials by group on Thursday, March 30 • • • • • Cardboard Sando bag (green, blue, red) 3 flashlights Button fastener (pushpin/thumbtacks) Glue and scissor “Colors of Light – Color of Life!” Color Spectrum Red Orange Yellow Frequency Wavelength (THz) (nm) (× 1012 /𝑠) (× 10−9 𝑚) 422 482 517 Frequency x Wavelength (m/s) 700 (422 × 1012 /𝑠)(700 × 10−9 m) 295 400 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s 620 (482 × 1012 /𝑠)(620 × 10−9 m) 300, 080 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s 580 (517 × 1012 /𝑠)(580 × 10−9 m) 299, 860 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s Color Spectrum Green Blue Violet Frequency Wavelength (THz) (nm) (× 1012 /𝑠) (× 10−9 𝑚) 566 638 744 Frequency x Wavelength (m/s) 530 (566 × 1012 /𝑠)(530 × 10−9 m) 299, 980 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s 470 (638 × 1012 /𝑠)(470 × 10−9 m) 299, 860 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s 400 (744 × 1012 /𝑠)(400 × 10−9 m) 297, 600 × 103 m/s 3 × 108 m/s Color Spectrum Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet Frequency (THz) (× 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟐 /𝐬) 422 482 517 566 638 744 Wavelength (nm) (× 𝟏𝟎−𝟗 𝐦) 700 Frequency x Wavelength (m/s) (422 × 1012 /𝑠)(700 × 10−9 m) 𝟐𝟗𝟓 𝟒𝟎𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 620 (482 × 1012 /𝑠)(620 × 10−9 m) 𝟑𝟎𝟎, 𝟎𝟖𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 580 (517 × 1012 /𝑠)(580 × 10−9 m) 𝟐𝟗𝟗, 𝟖𝟔𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 530 (566 × 1012 /𝑠)(530 × 10−9 m) 𝟐𝟗𝟗, 𝟗𝟖𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 470 (638 × 1012 /𝑠)(470 × 10−9 m) 𝟐𝟗𝟗, 𝟖𝟔𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 400 (744 × 1012 /𝑠)(400 × 10−9 m) 𝟐𝟗𝟕, 𝟔𝟎𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟑 𝐦/𝐬 Question 1. s: Which color registers the highest frequency? Shortest wavelength? 2. Which color registers the lowest frequency? Longest wavelength? 3. What do you observe with the wavelength and frequency of different colors? 4. What did you observe with the product of wavelength and frequency for each color? What is the significance of this value? 5. What can you say about the speed of the different colors of light in air? 6. Give a plausible explanation as to why white light separate into different colors? Color Plastic Filters Color that you see projected on the screen Green GREEN Blue BLUE Red RED Color Combination Resulting Color Green + Blue CYAN Blue + Red MAGENTA Red + Green YELLOW Red + Green + Blue WHITE TRIVIA TIME!!! It takes 499 seconds or approximately 8 minutes. TRIVIA TIME!!! • It has a speed of 299, 792, 458 8𝑚 meters per second or 3 × 10 𝑠 What is LIGHT? • • It is an electromagnetic wave It does not need a medium to propagate SOURCES OF LIGHT Natural source of light Luminous body Artificial sources of light An object capable of producing its own light LIGHT DUAL NATURE: particle nature and wave nature LIGHT vibration of electric and magnetic field Visible Spectrum – WHITE LIGHT PRISM WHITE LIGHT DISPERSION – The phenomenon which a prism separates white light in component colors. LIGHT form of energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Parts of a wave CHARACTERISTIC OF LIGHT LIGHT INTENSITY • the power of light • it is the quantity that measures the amount of light illuminating a surface • PHOTOMETRY – the science of measuring the intensity or brightness of light. “Photo” – light “metry” - measure LIGHT INTENSITY BRIGHTNESS • qualitative expression of light intensity. • visual perception in which a light source appears to be emitting light or a surface to be reflecting light. LIGHT INTENSITY LUMINOUS INTENSITY • it is the amount of light that the objects produce • candela (cd) LIGHT INTENSITY The brightness of light depends on how far you are from the source. LIGHT INTENSITY The closer you are to the source of light, the brighter is the light that you will see. LIGHT INTENSITY If you are farther from the source, the dimmer is the light that you will see. LIGHT INTENSITY The intensity of light depends upon the amount of light or the number of photons that pass a certain area or space., LIGHT INTENSITY The higher amplitude corresponds to a brighter light while the lower amplitude corresponds to dimmer light. COLOR COLOR COLOR Wavelength range 400 nanometers to 750 nanometers COLOR As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases. COLOR In terms of Wavelength Red has the longest wavelength, and violet has the shortest wavelength COLOR In terms of Frequency Violet has the highest frequency, and Red has the lowest frequency COLOR • Frequency and Wavelength are inversely proportional • The color white represents the combination of all the wavelengths of visible light, while black is the absence of the wavelength THANK YOU FOR LISTENING! ALTERNATIVE RESOURCES