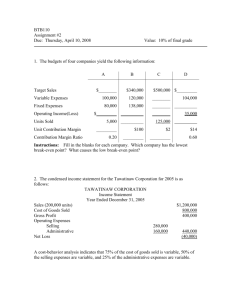
Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport Graduate School of Business Course Title: Managerial Accounting Instructor name: Dr. Mohammed Mostafa Student Name: Karem Abdel Hamid Mohammed Mohammed Registration: 21126473 1 True/False Questions 1. Managerial accounting is a branch of financial accounting and serves essentially the same purposes as financial accounting. False. Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting 1. Users External persons who make financial decisions; Stockholders, Creditors, Regulators. Internal Users Managers who plan for and control an organization; Managers, Supervisors, Offecirs and any employees. 2. Type Of Reports Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statements, .. Etc Internal reports, Job Cost Sheet, Cost of Goods Manufactured, Porduction Cost Report, …. Etc 3. Frequency Of Reports Quarterly & annually as Frequently as Needed 4. Time focus Historical perspective Future emphasis Emphasis on verifiability Emphasis on relevance for planning and control Emphasis on precision Emphasis on timeliness 7. Subject Primary focus is on the whole organization Focuses on segments of an organization 8. GAAP Must follow GAAP and prescribed formats Need not follow GAAP or any prescribed format 5. Verifiability versus relevance 6. Precision versus timeliness 2. Managerial accounting places greater emphasis on the future than financial accounting, which is primarily concerned with the past. TRUE 3. Manufacturing overhead is an indirect cost with respect to units of product. TRUE 2 4. Depreciation on office equipment would not be included in the cost of goods manufactured. TRUE Manufacturing cost is the sum of costs of all resources consumed in the process of making a product. The manufacturing cost is classified into three categories: direct materials cost, direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead.[1] It is a factor in total delivery cost.[ 5. Rent on a factory building used in the production process would be classified as a period cost and as a fixed cost. FALSE Rent on a factory building used in the production process would be classified as a product cost and as a fixed cost. A fixed cost remains constant if expressed on a unit basis. Total variable cost is expected to remain unchanged as activity changes within the relevant range. 6. Variable costs per unit are affected by changes in activity. FALSE Total variable cost increases and decreases in proportion to changes in the activity level. 7. The amount that a manufacturing company could earn by renting unused portions of its warehouse is an example of an opportunity cost. TRUE 8. To estimate what the profit will be at various levels of activity, a manager can simply take the number of units to be sold over the break-even point and multiply that number by the unit contribution margin. TRUE 9. To facilitate decision-making, fixed expenses should be expressed on a per-unit basis. False 3 10. An increase in the number of units sold will decrease a company's break-even point. False If any change in the sales the break-Even point doesn’t change. An increase in the variable cost per unit will decrease a company's break-even point 11. The break-even point is the point where the total contribution margin equals total variable expenses. False At Break-Even Point, …… Total Contribution margin = Total Fixed Expenses. Total Fixed Expenses/Contribution Margin Per Unit 12. If a company has high operating leverage, then profits will be very sensitive to changes in sales. TRUE The company's degree of operating leverage = Contribution margin / Net Operating Income. Multiple Choice Questions 1. Management accounting focuses primarily on providing data for: (A) A) internal uses by managers. B) external uses by stockholders and creditors. C) external uses by the Internal Revenue Service. D) external uses by the Securities and Exchange Commission. 2. Managerial accounting: (A) A) is more future oriented than financial accounting. B) tends to summarize information more than financial accounting C) is primarily concerned with providing information to external users. D) is more concerned with precision than timeliness. 3. Which of the functions of management involves overseeing day-to-day activities? (B) A) Planning B) Directing and motivating C) Controlling D) Decision making. 4. Indirect labor is a part of: (B) 4 A) Prime cost. B) Conversion cost. C) Period cost. D) Nonmanufacturing cost. Types of Conversion Costs , Examples of costs that may be considered conversion costs are: Direct labor and related benefits and payroll taxes Equipment depreciation Equipment maintenance Factory rent Factory supplies Factory insurance Machining Inspection Production utilities Production supervision Small tools charged to expense 5. The cost of lubricants used to grease a production machine in a manufacturing company is an example of a(n): (C) A) period cost. B) direct material cost. C) indirect material cost. D) none of the above. 6. The salary paid to the president of King Company would be classified on the income statement as a(n): (A) A) administrative expense. B) direct labor cost. C) manufacturing overhead cost. D) selling expense. 7. Direct labor cost is a part of: (C) Conversion cost Prime cost 5 A) No No B) No Yes C) Yes Yes D) Yes No Prime cost = Direct raw materials + Direct labor Conversion Costs = Direct Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overheads 8. Direct material cost is a: (B) Conversion cost Prime cost A) No No B) No Yes C) Yes Yes D) Yes No 9. Prime cost consists of: (C) A) direct labor and manufacturing overhead. B) direct materials and manufacturing overhead. C) direct materials and direct labor. D) direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead. 10. Property taxes on a company's factory building would be classified as a(n): (A) A) product cost. B) opportunity cost. C) period cost. D) variable cost. 11. Fixed costs expressed on a per unit basis: (B) A) will increase with increases in activity. B) will decrease with increases in activity. C) are not affected by activity. D) should be ignored in making decisions since they cannot change. 6 12. A cost incurred in the past that is not relevant to any current decision is classified as a(n): (C) A) period cost. B) opportunity cost. C) sunk cost. D) differential cost. A sunk cost is money that has already been spent and cannot be recovered. In business 13. The following costs were incurred in January: (A) - Direct materials ................................... $33,000 - Direct labor ......................................... $28,000 - Manufacturing overhead ..................... $69,000 - Selling expenses ................................ $16,000 - Administrative expenses ..................... $21,000 Conversion costs during the month totaled: A) $97,000 B) $167,000 C) $102,000 D) $61,000 Conversion Costs = Direct Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overheads = 28,000 + 69,000 = 97,000 $ 14. The following costs were incurred in January: (B) Direct materials ............................ $39,000 Direct labor ................................... $26,000 Manufacturing overhead ............... $21,000 Selling expenses .......................... $14,000 Administrative expenses .............. $27,000 Prime costs during the month totaled: 7 A) $86,000 B) $65,000 C) $47,000 D) $127,000 Prime cost = direct materials cost + direct labor cost = 39,000 + 26,000 = 65,000 $ 15. Aable Company's manufacturing overhead is 20% of its total conversion costs. If direct labor is $45,000 and if direct materials are $53,000, the manufacturing overhead is: (A) A) $11,250 B) $13,250 C) $180,000 D) $24,500 Conversion Costs = Direct Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overheads Conversion Costs = 45,000 + Manufacturing Overheads Conversion Costs = 45,000 + 20% Conversion Costs Conversion Costs - 20% Conversion Costs = 45,000 80% Conversion Costs = 45,000 Conversion Costs = 54250 $ So , 54,250 = 45,000 + Manufacturing Overheads Manufacturing Overheads = 54,250 - 45,000 = 11,250 $ 16. A manufacturing company prepays its insurance coverage for a three-year period. The premium for the three years is $3,000 and is paid at the beginning of the first year. Three-fourths of the premium applies to factory operations and one-fourth applies to selling and administrative activities. What amounts should be considered product and period costs respectively for the first year of coverage? (D) 8 Product Period A) $1,000 $0.0 B) $250 $750 C) $2,250 $750 D) $750 $250 Total Insurance expense for the year = $3,000 / 3 year Total Insurance expense for the year = $1000 Product cost (Manufacturing cost) = $1000 * 3/4 = $ 750 Period Cost (Selling and administrative cost) = $1000 * 25% = $ 250 17. Last month a manufacturing company had the following operating results: (A) Beginning finished goods inventory ................ $72,000 Ending finished goods inventory..................... $66,000 Sales .............................................................. $465,000 Gross margin ................................................. $88,000 What was the cost of goods manufactured for the month? A) $371,000 B) $459,000 C) $383,000 D) $377,000 Goods Manufactured=Total Sales-Gross margin-(Beginning finished goods inventory-Ending finished goods inventory Goods Manufactured = 465,000 – 88,000 – (72,000 – 66,000) = 371,000 $ 18. During February, the cost of goods manufactured was $83,000. The beginning finished goods inventory was $14,000 and the ending finished goods inventory was $13,000. What was the cost of goods sold for the month? (D) A) $83,000 B) $110,000 C) $82,000 D) $84,000 Cost of Goods Sold a Month = Cost of goods manufactured+(beginning Goods inventory - ending Goods inventory) Cost of Goods Sold a Month = 83,000 + (14,000 – 13,000) = 84,000 $ 9 19. Use the following to answer questions 19-22: The following data (in thousands of dollars) have been taken from the accounting records of Karsen Corporation for the just-completed year. Sales ................................................................... $930 Raw materials inventory, beginning ..................... $70 Raw materials inventory, ending .......................... $40 Purchases of raw materials ................................. $190 Direct labor .......................................................... $150 Manufacturing overhead ...................................... $210 Administrative expenses...................................... $90 Selling expenses ................................................. $120 Work in process inventory, beginning .................. $80 Work in process inventory, ending ....................... $70 Finished goods inventory, beginning ................... $90 Finished goods inventory, ending ........................ $140 Use these data to answer the following series of questions. 19.The cost of the raw materials used in production during the year (in thousands of dollars) was: (B) A) $230 B) $220 C) $160 D) $260 The cost of raw material = Purchases of raw materials +(Raw materials inventory, beginning - Raw materials inventory, ending) The cost of raw material = 190 + (70-40) = 220,000 $ 20. The cost of goods manufactured (finished) for the year (in thousands of dollars) was: (A) A) $590 B) $650 C) $660 D) $570 Cost of Goods Manufactured. 10 = The Cost of raw Material + Direct labor Cost + Manufacturing overhead + (Work in process inventory, beginning - Work in process inventory, ending) Cost of Goods Manufactured = 220 + 210 + 150 + (80-70) = 590,000 $ 21. The cost of goods sold for the year (in thousands of dollars) was: : (B) A) $680 B) $540 C) $640 D) $730 22. The net operating income for the year (in thousands of dollars) was: : (A) A) $180 B) $170 C) $390 D) $190 Net operating income for the year = 23. The contribution margin ratio is equal to: : (B) A) Total manufacturing expenses/Sales. B) (Sales - Variable expenses)/Sales. C) 1 - (Gross Margin/Sales). D) 1 - (Contribution Margin/Sales). Contribution Margin Ratio = (Sales Income - Total Variable Costs) / Sales Revenue 24. In the middle of the year, the price of Lake Corporation's major raw material increased by 8%. How would this increase affect the company's break-even point and margin of safety? (B) Break-even point Margin of safety A) Increase Increase B) Increase Decrease C) Decrease Decrease D) Decrease Increase 11 25. The break-even point in unit sales is found by dividing total fixed expenses by: (D) A) the contribution margin ratio. B) the variable expenses per unit. C) the sales price per unit. D) the contribution margin per unit. The contribution margin per unit = Selling price per unit – Variable cost per unit. 26. Which of the following would not affect the break-even point? (A) A) Number of units sold B) variable expense per unit C) total fixed expenses D) selling price per unit 27. If a company increases its selling price by $2 per unit due to an increase in its variable labor cost of $2 per unit, the break-even point in units will: (C) A) decrease. B) increase. C) Not change. D) change but direction cannot be determined If any change in the sales the break even point doesn’t change. 28. Carver Company produces a product which sells for $40. Variable manufacturing costs are $18 per unit. Fixed manufacturing costs are $5 per unit based on the current level of activity, and fixed selling and administrative costs are $4 per unit. A selling commission of 15% of the selling price is paid on each unit sold. The contribution margin per unit is: (D) A) $7 B) $17 C) $22 D) $16 Variable Cost per unit=$18 per unit+ (0.15 x 40 per unit)=$24 per unit Unit CM=Sales of 40-Variable cost of 24=16 So the CM is $16 29. Mason Company's selling price was $20.00 per unit. Fixed expenses totaled $54,000, variable expenses were $14.00 per unit, and the company reported a profit of $9,000 for the year. The break-even point for 12 Mason Company is: (D) A) 10,500 units B) 4,500 units C) 8,500 units D) 9,000 units Fixed expense at 54,000/ CM at 6.00= 9,000 units 30. Given the following data: (A) Selling price per unit ........................... $2.00 Variable production cost per unit ........ $0.30 Fixed production cost ......................... $3,000 Sales commission per unit .................. $0.20 Fixed selling expenses ....................... $1,500 The break-even point in dollars is: A) $6,000 B) $4,500 C) $2,647 D) $4,000 CM RATIO = TOTAL CM/TOTAL SALES CM RATIO=1.5/2=0.75 BREAK-EVEN=FIXED EXPENSE/CM RATIO BREAK-EVEN=4500/.75=6000 31. Darwin, Inc., sells a particular textbook for $20. Variable expenses are $14 per book. At the current volume of 50,000 books sold per year the company is just breaking even. Given these data, the annual fixed expenses associated with the textbook total: (A) A) $300,000 13 B) $1,000,000 C) $1,300,000 D) $700,000 TOTAL SALES =20*50000=1000000$ TOTAL VARIABLE EXPENSES= 14*50,000=700,000$ PROFIT = ZERO FIXED EXPENSES=100,0000-700,000=300,000$ 32. Company X sold 25,000 units of product last year. The contribution margin per unit was $2, and fixed expenses totaled $40,000 for the year. This year fixed expenses are expected to increase to $45,000, but the contribution margin per unit will remain unchanged at $2. How many units must be sold this year to earn the same net operating income as was earned last year: (B) A) 22,500 B) 27,500 C) 35,000 D) 2,500 Net Profit (Net Operation Income) = Sales − Variable Expenses − Fixed Expenses = Contribution margin = Net Sales - variable expenses 33. Alpha Company reported the following data for its most recent year: sales, $500,000; variable expenses, $300,000; and fixed expenses, $150,000. The company's degree of operating leverage is: (C) A) 10 14 B) 2 C) 4 D) 2.5 Net Profit (Net Operation Income) = Sales − Variable Expenses − Fixed Expenses Net Operating Income = 500,000 – 300,000 – 150,000 = 50,000 $ Contribution margin = Net Sales - variable expenses = 500,000 – 300,000 = 200,000 $ The company's degree of operating leverage = Contribution margin / Net Operating Income The company's degree of operating leverage = 200,000/50,000 = 4 Essay Questions 1. Baker Company has a product that sells for $20 per unit. The variable expenses are $12 per unit, and fixed expenses total $30,000 per year. Required : a. What is the total contribution margin at the break-even point? b. What is the contribution margin ratio for the product? c. If total sales increase by $20,000 and fixed expenses remain unchanged, by how much would net operating income be expected to increase? d. The marketing manager wants to increase advertising by $6,000 per year. How many additional units would have to be sold to increase overall net operating income by $2,000? 15 The Solution a) What is the total contribution margin at the break-even point? Solution The Unit Price = $ 20 per unit The variable expenses = $12 per unit. Fixed Expenses total $30,000 per year Break Even Point = Fixed Cost Selling Price Per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit At the Breakeven Point … Total Contribution Margin = Total Fixed Cost So that Total Contribution Margin = 30,000 $ b) What is the contribution margin ratio for the product? Solution Contribution Margin = Selling Price - Variable Expenses Contribution Margin Ratio = Contribution Margin / Selling Price Contribution Margin = 20 – 12 = 8 $ Contribution Margin Ratio = 8/20 = 0.4 = 40% 16 c) If total sales increase by $20,000 and fixed expenses remains unchanged, by how much would the net operating income be expected to increase? Solution The Increased sold by Unit = increased by income / unit price = 20,000/20 = 1000 units net operating income be expected to increase = increased sold by unit x Contribution Margin = 1000 x 8 = 8000 $ d) The marketing manager wants to increase advertising by $6,000 per year. How many additional units would have to be sold to increase overall net operating income by $2,000? Solution Advertising is fixed cost = 6000 $ per Year. Break Even Point as unit = (30,000)/(20-8) = 3750 Units. Additional Break Even Point as unit = (6000+2000)/(20-12) = 1000 Units. 17