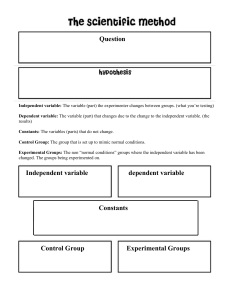
Variables in Science Objectives: • - Students will be able to identify: The independent variable The dependent variable The controlled variable or constants in an experiment What are variables? Variables are things that vary and change. 3 Types of Variables • In an experiment there are 3 variables: 1. An independent variable 2. A dependent variable 3. Controlled variables that are sometimes called constants Let’s look at each type. Independent Variable • The independent variable is the part of the experiment that you decide to change. Think Independent = I change For example: • An experiment testing to see if temperature of water effects the amount of sugar that will dissolve • Ask - what am I changing? • You would change the temperature of the water • Water temperature is the independent variable Another example: • An experiment testing the effect of different amounts of fertilizer on plant height • Ask - what am I changing? • You would change the amount of fertilizer • The amount of fertilizer is the independent variable Dependent Variable • The dependent variable changes because of the independent variable. • The dependent variable is what is measured in the experiment. • Think Dependent Variable = Data • What is the data you are collecting in the experiment? What is being measured? For example: • An experiment testing to see if temperature of water effects the amount of sugar that will dissolve • Ask – what is the data? • You would collect data on the amount of sugar that dissolves • The amount of sugar is the dependent variable Another example: • An experiment testing the effect of different amounts of fertilizer on plant height • Ask - what is the data? • You would collect data about the height of the plant • The plant height is the dependent variable Controlled Variables or Constants • Controlled variables or constants are the parts of the experiment that must stay the same. • The controlled variables make the experiment a fair test. • Think of controlled variables as the unchanging parts of the experiment. • Think constant = No Change change For example: • An experiment testing to see if temperature of water effects the amount of sugar that will dissolve • Ask – what must stay the same to be fair? • Same container, same amount of water, same type of sugar Another example: • An experiment testing the effect of different amounts of fertilizer on plant height • Ask – what must stay the same to be fair? • Same fertilizer brand, same type of plant, same measurement standard, same amount of water and light Your turn: • A test to determine which type of ball (golf, basketball, ping pong, or tennis) bounces the highest when dropped What is the independent variable? What is the dependent variable? What are some of the controlled variables or constants? Discuss your answer with your shoulder partner. Answers • Independent variable = I change The type of ball • Dependent variable = data The height of the bounce • Controlled variable or constants = no change for a fair test All balls must be dropped from the same height in the same way Graphing • When graphing the data, think DRY MIX – the Dependent variable goes on the Y axis and the Independent variable goes on the X axis Dry dependent Mix - independent No monkey-ing around! You are ready to identify variables.