MITSUBISHI CNC
700 Series
Setup Manual
IB-1500124(ENG)-A
MELDAS is a registered trademark of Mitsubishi Electric Corporation.
Other company and product names that appear in this manual are trademarks or
registered trademarks of the respective companies.
Introduction
This manual is the alarm/parameter guide required to use the MITSUBISHI CNC700 Series.
This manual is prepared on the assumption that your machine is provided with all of the MITSUBISHI
CNC700 Series functions. Confirm the functions available for your NC before proceeding to operation by
referring to the specification issued by the machine tool builder.
Notes on Reading This Manual
(1) This manual explains general parameters as viewed from the NC.
For information about each machine tool, refer to manuals issued from the machine tool builder.
If the descriptions relating to "restrictions" and "allowable conditions" conflict between this manual
and the machine tool builder's instruction manual, the later has priority over the former.
(2) This manual is intended to contain as much descriptions as possible even about special operations.
The operations to which no reference is made in this manual should be considered impossible.
(3) The "special display unit" explained in this manual is the display unit incorporated by the machine
tool builder, and is not the MELDAS standard display unit.
Caution
If the descriptions relating to the "restrictions" and "allowable conditions" conflict between this
manual and the machine tool builder’s instruction manual‚ the latter has priority over the former.
The operations to which no reference is made in this manual should be considered
"impossible".
This manual is complied on the assumption that your machine is provided with all optional
functions. Confirm the functions available for your machine before proceeding to operation by
referring to the specification issued by the machine tool builder.
In some NC system versions‚ there may be cases that different pictures appear on the screen‚
the machine operates in a different way or some function is not activated.
Precautions for Safety
Always read the specifications issued by the machine tool builder, this manual, related manuals and attached
documents before installation, operation, programming, maintenance or inspection to ensure correct use.
Understand this numerical controller, safety items and cautions before using the unit.
This manual ranks the safety precautions into "DANGER", "WARNING" and "CAUTION".
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
When the user may be subject to imminent fatalities or major injuries if handling is
mistaken.
When the user may be subject to fatalities or major injuries if handling is mistaken.
When the user may be subject to injuries or when physical damage may occur if
handling is mistaken.
Note that even items ranked as "
CAUTION", may lead to major results depending on the situation. In any
case, important information that must always be observed is described.
DANGER
Not applicable in this manual.
WARNING
Not applicable in this manual.
CAUTION
1. Items related to product and manual
If the descriptions relating to the "restrictions" and "allowable conditions" conflict between this
manual and the machine tool builder's instruction manual‚ the latter has priority over the former.
The operations to which no reference is made in this manual should be considered impossible.
This manual is complied on the assumption that your machine is provided with all optional
functions. Confirm the functions available for your machine before proceeding to operation by
referring to the specification issued by the machine tool builder.
In some NC system versions‚ there may be cases that different pictures appear on the screen‚
the machine operates in a different way on some function is not activated.
2. Items related to faults and abnormalities
If the battery low alarm is output, save the machining programs, tool data and parameters to an
input/output device, and then replace the battery. If the BATTERY alarm occurs, the machining
programs, tool data and parameters may be damaged. After replacing the battery, reload each
data item.
[Continued on next page]
CAUTION
[Continued]
3. Items related to maintenance
Do not replace the battery while the power is ON.
Do not short-circuit, charge, heat, incinerate or disassemble the battery.
Dispose of the spent battery according to local laws.
4. Items related to servo parameters and spindle parameters
Do not adjust or change the parameter settings greatly as operation could become unstable.
In the explanation on bits, set all bits not used, including blank bits, to "0".
CONTENTS
I Procedures for Starting up
1. Outline ..................................................................................................................................... I-1
2. Outline of Hardware Configuration ....................................................................................... I-1
3. Setup Procedures ................................................................................................................... I-2
3.1 Connecting the Control Unit and Peripheral Devices .......................................................... I-3
3.2 Erasing the Backed up Data (SRAM) .................................................................................. I-4
3.3 Inputting the Parameters ..................................................................................................... I-5
3.3.1 When There is No Parameter File................................................................................. I-5
3.3.2 When a Parameter File is Available .............................................................................. I-7
3.4 Formatting the File System.................................................................................................. I-8
3.5 Inputting the Ladder Program.............................................................................................. I-9
II Explanation of Alarms
1. List of Alarms .........................................................................................................................II-1
1.1 Operation Alarms................................................................................................................ II-1
1.2 Stop Codes ......................................................................................................................... II-8
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms ....................................................................................................... II-12
1.4 MCP Alarm ....................................................................................................................... II-21
1.5 System Alarms.................................................................................................................. II-25
1.6 Absolute Position Detection System Alarms..................................................................... II-29
1.7 Messages during Emergency Stop................................................................................... II-32
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms ........................................................................................................ II-34
1.9 Computer Link Errors........................................................................................................ II-41
1.10 User PLC Alarms ............................................................................................................ II-42
1.11 Network Service Errors................................................................................................... II-44
2. Operation Messages ............................................................................................................II-45
2.1 Search-related Operation Messages ................................................................................ II-45
2.2 Graphic Display-related Operation Messages .................................................................. II-46
2.3 Variable (Common variables, local variables) - related Operation Messages .................. II-47
2.4 PLC Switch-related Operation Messages......................................................................... II-47
2.5 Compensation-related (Tool compensation, coordinate system offset)
Operation Messages......................................................................................................... II-47
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages ............................................................... II-48
2.7 Parameter-related Operation Messages........................................................................... II-52
2.8 Measurement-related (Workpiece, rotation) Operation Messages ................................... II-53
2.9 Tool (Tool registration, tool life) -related Operation Messages......................................... II-54
2.10 Editing-related Operation Messages .............................................................................. II-55
2.11 Diagnosis-related Operation Messages.......................................................................... II-57
2.12 Maintenance-related Operation Messages..................................................................... II-58
2.13 Data Sampling-related Operation Messages.................................................................. II-60
2.14 Absolute Position Detection-related Operation Messages ............................................. II-61
2.15 Other Operation Messages............................................................................................. II-62
3. Program Error ......................................................................................................................II-63
4. Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................II-79
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting.......................................................................................... II-79
4.1.1 Troubleshooting at Power ON .................................................................................... II-79
4.1.2 Troubleshooting for Each Alarm No. .......................................................................... II-80
4.1.3 Troubleshooting for Each Warning No. .................................................................... II-108
4.1.4 Parameter Numbers during Initial Parameter Error .................................................. II-112
4.1.5 Troubleshooting the Spindle System when There Is No Alarm or Warning ............. II-113
III Explanation of Parameters
1. Outline .................................................................................................................................. III-1
1.1 Screen Transition Chart..................................................................................................... III-1
1.2 Unit .................................................................................................................................... III-1
2. User Parameters .................................................................................................................. III-2
2.1 Process Parameters .......................................................................................................... III-2
2.2 Control Parameters ......................................................................................................... III-10
2.3 Axis Parameters .............................................................................................................. III-12
2.4 Operation Parameters ..................................................................................................... III-14
2.5 Barrier Data (For L system only) ..................................................................................... III-15
2.6 I/O Parameters ................................................................................................................ III-16
2.7 Ethernet Parameters ....................................................................................................... III-19
2.8 Computer Link Parameters.............................................................................................. III-21
2.9 Subprogram Storage Designation Parameters................................................................ III-23
3. Setting the Machine Parameters. ..................................................................................... III-24
4. Base Specifications Parameters ...................................................................................... III-25
5. Axis Specifications Parameters ....................................................................................... III-81
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters ....................................................................................... III-81
5.2 Zero Point Return Parameters......................................................................................... III-88
5.3 Absolute Position Parameters ......................................................................................... III-90
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2 .................................................................................... III-92
6. Servo Parameters .............................................................................................................. III-99
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series ........................................................................................................... III-99
6.2 Supplement ................................................................................................................... III-134
6.2.1 D/A Output No. ........................................................................................................ III-134
6.2.2 Electronic Gears...................................................................................................... III-135
6.2.3 Lost Motion Compensation...................................................................................... III-136
7. Spindle Parameters ......................................................................................................... III-137
7.1 Spindle Specification Parameters.................................................................................. III-137
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series ......................................................................................................... III-145
7.3 Supplement ................................................................................................................... III-173
7.3.1 D/A Output Numbers ............................................................................................... III-173
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters.......................................................................... III-174
9. Machine Error Compensation......................................................................................... III-178
9.1 Function Outline ............................................................................................................ III-178
9.2 Setting Compensation Data........................................................................................... III-181
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis ......................................................... III-183
9.4 Example in Using a Rotary Axis as the Base Axis ........................................................ III-187
10. PLC Constants ............................................................................................................... III-188
10.1 PLC Timer ................................................................................................................... III-188
10.2 PLC Integrated Timer .................................................................................................. III-189
10.3 PLC Counter................................................................................................................ III-189
10.4 PLC Constants ............................................................................................................ III-190
10.5 Selecting the PLC Bit................................................................................................... III-190
11. Macro List ....................................................................................................................... III-193
12. Position Switch .............................................................................................................. III-195
12.1 Canceling the Position Switch .....................................................................................III-197
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter............................................................................................... III-198
I
Procedures for Starting Up
1. Outline
1. Outline
"I Procedures for Starting Up" explains the normal work required to newly start up the MITSUBISHI CNC 700
Series.
Start up the system following these setup procedures.
2. Outline of Hardware Configuration
The names of the hardware used in this manual's explanations are explained below.
Display unit
Next
Back
Keyboard
IC card interface on front of
display unit
Tab right
Control unit
LED1
SW1
LED2
CS1
E
D
C
B
A
F 0 1
9 8 7
2
6
3
4
5
Upper rotary switch
CS2
E
D
C
B
A
I-1
F 0 1
9 8 7
Lower rotary switch
2
6
3
4
5
INPUT
3. Setup Procedures
3. Setup Procedures
The procedures for setting up are explained with a flow chart.
Start
Refer to section 3.1
Connecting the control unit
and peripheral devices
Connect the control unit with the peripheral devices (servo/spindle drive,
auxiliary axis, remote IO).
Erasing the backed up data (SRAM)
Refer to section 3.2
Erase the backed up data (SRAM).
Set CS1 to "0" and CS2 to "C" to erase the SRAM.
Turning the power ON again.
Refer to section 3.3
Inputting the parameters
If there is no parameter file, input the parameters manually.
If there is a parameter file, input the parameters with input/output screen.
Turning the power ON again.
Refer to section 3.4
Formatting the file system
Format the file system
Turning the power ON again.
Refer to section 3.5
Inputting the ladder program
Input the ladder program using "GX Developer" or "PLC Onboard".
Inputting the machining program
End
I-2
3. Setup Procedures
3.1 Connecting the Control Unit and Peripheral Devices
3.1 Connecting the Control Unit and Peripheral Devices
Connect the control unit with the peripheral devices (servo/spindle drive, auxiliary axis, remote IO).
Refer to "Mitsubishi CNC 700 Series Connection Manual" (IB-1500034), "MDS-D Specifications Manual" (IB15000011), and "MDS-DH Specifications Manual" (IB-1500003) for details.
Control unit
Operation panel I/O unit
Machine operation
panel
Servo drive
Spindle drive
Auxiliary axis
I-3
3. Setup Procedures
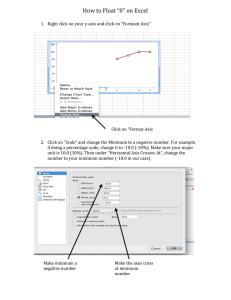
3.2 Erasing the Backed up Data (SRAM)
3.2 Erasing the Backed up Data (SRAM)
Use the following procedure if the backed up data (SRAM) needs to be cleared after the control unit is
replaced, etc.
(1) With the NC power OFF, set the upper rotary switch (CS1) on the
control unit to "0" and the lower rotary switch (CS2) to "C". Then,
turn the power ON.
LED1
SW1
LED2
CS1
E
D
C
B
A
F 0 1
9 8 7
CS2
F 0 1
E
D
C
B
A
9 8 7
2
6
2
6
3
4
5
3
4
5
(2) The LED display will change from "08." → "00" → "01" ... "9.0". The process is completed when the NC
starts up. (Required time: 30 seconds)
(3) Turn the NC power OFF.
(4) Set the lower rotary switch (CS2) to "0".
LED1 LED2
SW1
CS1
E
D
C
B
A
F0 1
9 8 7
2
6
3
4
5
CS2
E
D
C
B
A
F 0 1
9 8 7
2
6
3
4
5
(Note) After the SRAM is cleared and the NC power is turned ON, the IP addresses are initialized to the
following values.
<Base common parameters>
#1926 Global IP address : 192.168.200. 1
#1927 Global Subnet mask : 255.255.255. 0
#1928 Global Gateway
: 0. 0. 0. 0
To communicate with the screen, the parameter value and the "C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini" setting value
must match. Confirm that "C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini" is set to the above value.
Last line of C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini
•••
[HOSTS]
TCP1=192.168.200.1,683
I-4
3. Setup Procedures
3.3 Inputting the Parameters
3.3 Inputting the Parameters
3.3.1 When There is No Parameter File
If there is no parameter file (ALL.PRM), input the parameters manually.
(1) Select "MAINTENANCE (Mainte)" → "Mainte" → "Psswd input", and input "MPARA". Then, press
INPUT.
(2) Select the "Retn" menu
→ "Param", and set the various parameters such as the base
specifications parameters and axis specification parameters according to the machine configuration.
The minimum required parameters are listed below. Refer to "III Explanation of Parameters" for details
on each parameter.
(2-1) Set the number of NC axes, number of spindles and number of auxiliary axes, and then turn the
power ON again.
Type
Base system
parameter
Base common
parameters
#
1002 axisno
Item
Number of axes
1039 spinno
1044 auxno
Number of spindles
MR-J2-CT connections
(2-2) Set the minimum required parameters such as the axis name.
Type
Base axis specification
parameters
Base common
parameters
#
1013
1021
1022
1155
axname
mcp_no
axname2
DOOR_m
1156 DOOR_s
1240 set12/bit4
Axis specification
parameters
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
2007
2008
2102
2103
rapid
clamp
smgst
G0tL
G0t1
G1tL
G1t1
skip_tL
skip_t1
Zero point return
parameter
Servo parameters
2029 grspc
2201 SV001
:
:
2456 SV256
Item
Axis name
Drive unit I/F channel No. (Servo)
2nd axis name
Signal input device 1 for door interlock II common for part
systems
Signal input device 2 for door interlock II common for part
systems
Optical communication automatic station detection invalid
(Set to "1" for M700 Version A0.)
Rapid traverse rate
Cutting federate for clamp function
Acceleration/deceleration modes
G0 time constant (linear)
G0 time constant (primary delay)
G1 time constant (linear)
G1 time constant (primary delay)
Skip time constant linear
Skip time constant primary delay acceleration/
deceleration by software 2nd stage
Grid interval
Servo parameters
I-5
3. Setup Procedures
3.3 Inputting the Parameters
Type
Spindle specification
parameters
Spindle parameters
#
3001
3005
3024
3025
3031
3105
3107
3109
13001
:
13240
Item
slimt1
smax1
sout
enc_on
smcp_no
sut
ori_spd
zdetspd
SP1001
:
SP1240
Limit rotation speed
Maximum rotation speed
Spindle connection
Spindle encoder
Drive unit I/F channel No. (Spindle)
Speed reach range
Orientation command speed
Z phase detection speed
Spindle parameters
(Setting example) For 3 NC axes (X, Y, Z) and 1 spindle axis (S)
Power supply
unit
NC
X
Drive unit rotary switch
No.
#1021 mcp_no
#3031 smcp_no
Y
Z
S
0
1
2
1001
1002
1003
P
3
1004
3rd axis for 1st channel
I-6
3. Setup Procedures
3.3 Inputting the Parameters
3.3.2 When a Parameter File is Available
If a parameter file is available, input the parameters using the input/output function.
(Example) When files are available on a compact flash (CF) card
(1) Insert the CF card into the IC card interface on the front of the display unit.
Display unit
Adapter
CF card
Select "MAINTENANCE (EDIT)" → "Input/Output".
Confirm that device A is selected, and then select "Device select" → "Memory card".
Select "File name" → "From list" → "ALL.PRM", and then press INPUT.
Press "Area change", and select device B.
Select "Device select" → "Memory".
Select "Dir" → "Param".
* "ALL.PRM" is directly input as the file name.
(8) Press "Transfr A → B", and execute parameter input.
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(Note) To communicate with the screen, the IP address parameter value and the "C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini"
setting value must match. After inputting the parameters, confirm that "C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini" is set
to the above value.
<Base common parameter>
#1926 Global IP address
: 192.168.200. 1
#1927 Global Subnet mask : 255.255.255. 0
#1928 Global Gateway
:
0. 0. 0. 0
These must match.
<Last line of C:\WINDOWS\melcfg.ini>
•••
[HOSTS]
TCP1=192.168.200.1,683
I-7
3. Setup Procedures
3.4 Formatting the File System
3.4 Formatting the File System
The base specification parameter "#1037 cmdtyp" must be set before the file system is formatted.
M System specifications : Set 1 or 2 according to the tool compensation type.
L System specifications : Select and set from 3 to 8 according to the G code list.
→ "Format".
(1) Select "MAINTENANCE (Mainte)" → "NEXT" menu
(2) The message "Format NC memory (Y/N)?" will appear. Press "Y".
(3) When the memory is correctly formatted, the message "Format complete" will appear.
I-8
3. Setup Procedures
3.5 Inputting the Ladder Program
3.5 Inputting the Ladder Program
The ladder program can be created and input using the GX Developer installed in an external personal
computer or with the PLC onboard editing screen.
Refer to the "MITSUBISHI CNC 700 Series PLC Programming manual" (IB-1500036) for details.
The ladder program creation and input procedures are explained below with a flow chart.
Start
Creation methods
Create with GX Developer
Create with PLC onboard
Writing method
Write to NC temporary
memory
Write with GX Developer
Write with PLC onboard
Save ladder program on
IC card
Connection method
Write to NC temporary
memory with Ethernet
communication
Write to NC temporary
memory with RS-232-C
Open ladder program in IC
card with PLC onboard
Write to NC temporary
memory
Write ladder program to NC ROM
End
I-9
II
Explanation of Alarms
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
MUU Message {{{{
Error No.
Message
Class
(1) Class: M01 Operation error
Alarms occurring due to incorrect operation by the operator during NC operation and those by machine
trouble are displayed.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0001
Dog overrun
When returning to the reference position‚ the
near-point detection limit switch did not stop
over the dog‚ but overran the dog.
•
•
Increase the length of the near-point dog.
Reduce the reference position return speed.
0002
Some ax does not pass Z phase
One of the axes did not pass the Z-phase
during the initial reference position return after
the power was turned ON.
•
Move the detector one rotation or more in the
opposite direction of the reference position‚ and
repeat reference position return.
0003
R-pnt direction illegal
When manually returning to the reference
position‚ the return direction differs from the
axis movement direction selected with the AXIS
SELECTION key.
•
The selection of the AXIS SELECTION key's
+/- direction is incorrect. The error is canceled
by feeding the axis in the correct direction.
0004
External interlock axis exists
The external interlock function has activated
(the input signal is "OFF") and one of the axes
has entered the interlock state.
•
As the interlock function has activated‚ release
it before resuming operation.
Check the sequence on the machine side.
Check for broken wires in the interlock signal
line.
The servo OFF function is valid‚ so release it
first.
An axis that can be removed has been issued‚
so perform the correct operations.
The command is issued in the same direction
as the direction where manual skip turned ON‚
so perform the correct operations.
During the manual/automatic simultaneous
mode‚ the axis commanded in the automatic
mode became the manual operation axis. Turn
OFF the manual/automatic valid signal for the
commanded axis.
Turn ON the power again‚ and perform
absolute position initialization.
0005
Internal interlock axis exists
The internal interlock state has been entered.
The absolute position detector axis has been
removed.
A command for the manual/automatic
simultaneous valid axis was issued from the
automatic mode.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
0006
H/W stroke end axis exists
The stroke end function has activated (the input
signal is "OFF") and one of the axes is in the
stroke end status.
II - 1
•
•
•
Move the machine manually.
Check for broken wires in the stroke end signal
wire.
Check for trouble in the limit switch.
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0007
S/W stroke end axis exists
The stored stroke limit I‚ II‚ IIB or IB function has
activated.
•
•
Move it manually.
If the stored stroke limit in the parameter is
incorrectly set‚ correct it.
0008
Chuck/tailstock stroke end ax
The chuck/tail-stock barrier function turned ON‚
and an axis entered the stroke end state.
•
Reset the alarm with reset‚ and move the
machine in the reverse direction.
0009
Ref point return No. invalid
Return to the No. 2 reference position was
performed before return to the No. 1 reference
position was completed.
•
Execute No. 1 reference position return.
0019
• Turn the tool measurement mode signal input
Sensor signal illegal ON
OFF, and move the axis in a safe direction.
The sensor signal was already ON when the tool
measurement mode (TLM) signal was validated. • The operation alarm will turn OFF even when
the sensor signal is turned OFF.
The sensor signal turned ON when there was no
axis movement after the tool measurement mode (Note) When the tool measurement mode signal
(TLM) signal was validated.
input is turned OFF, the axis can be
The sensor signal turned ON at a position within
moved in either direction. Pay attention to
100µm from the final entry start position.
the movement direction.
0020
Ref point retract invalid
Return to the reference position was performed
before the coordinates had not been established.
•
Execute reference position return
0021
Tool ofs invld after R-pnt
Reference position return was performed during
tool retract return, and therefore the tool
compensation amount became invalid after
reference position return was completed.
•
The error is cleared if the operation mode is
changed to other than reference position return
before the axis performs reference position
return.
The error is cleared when reference position
return is completed.
The error is cleared if reset 1 is input or the
emergency stop button is pushed.
•
•
0024
R-pnt ret invld at abs pos alm
A zero point return signal was input during an
absolute position detection alarm.
•
Reset the absolute position detection alarm‚
and then perform zero point return.
0025
R-pnt ret invld at zero pt ini
A zero point return signal was input during zero
point initialization of the absolute position
detection system.
•
Complete zero point initialization‚ and then
perform zero point return.
0030
Now skip on
The skip signal remains input when the skip
return operation changed to the measurement
operation.
•
Increase the skip return amount.
0031
No skip
Even though 1st skip was to the correct position,
the 2nd skip could not be found.
•
Check whether the measurement target has
moved.
0050
Chopping axis R-pnt incomplete
The chopping axis has not completed zero point
return before entering the chopping mode.
All axes interlock will be applied.
•
Reset or turn the chopping signal OFF, and
then carry out zero point return.
II - 2
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0051
Synchronous error excessive
The synchronization error of the master and
slave axes exceeded the allowable value under
synchronous control.
A deviation exceeding the synchronization error
limit value was found with the synchronization
deviation detection.
•
•
•
•
0101
•
No operation mode
•
•
0102
Cutting override zero
"The cutting feed override" switch on the
machine operation panel is set to zero.
The override was set to "0" during a single
block stop.
•
•
•
0103
External feed rate zero
"The manual feed speed" switch on the
machine operation panel is set to zero when
the machine is in the jog mode or automatic dry
run mode.
The "Manual feedrate B speed" is set to zero
during the jog mode when manual feedrate B is
valid.
The "each axis manual feedrate B speed" is set
to zero during the jog mode when each axis
manual feedrate B is valid.
•
•
•
Select the correction mode and move one of
the axes in the direction in which the errors are
reduced.
Increase the allowable value or reset it to 0
(check disabled).
When using simple C-axis synchronous
control, set the contents of the R435 register to
0.
Check the parameter (#2024 synerr).
Check for a broken wire in the input mode
signal wire.
Check for trouble in the mode selector switch.
Check the sequence program.
Set "the cutting feed override" switch to a value
other than zero to release the error.
If "the cutting feed override" switch is set to a
value other than zero‚ check for a short circuit
in the signal wire.
Check the sequence program.
Set "the manual feed speed" switch to a value
other than zero to release the error.
If "the manual feed speed" switch is set to a
value other than zero‚ check for a short circuit
in the signal wire.
Check the sequence program.
0104
F 1-digit feed rate zero
The F1-digit feedrate is set to zero when the
F1-digit feed command is being executed.
•
Set the F1-digit feedrate on the setup
parameter screen.
0105
Spindle stop
The spindle stopped during the synchronous
feed command.
•
•
•
Rotate the spindle.
If the workpiece is not being cut‚ start dry run.
Check for a broken wire in the spindle encoder
cable.
Check the connections for the spindle encoder
connectors.
Check the spindle encoder pulse.
Reconsider the program. (Command, address)
•
•
•
0106
Handle feed ax No. illegal
An axis not found in the specifications was
designated for handle feed or the handle feed
axis was not selected.
•
•
•
Check for broken wires in the handle feed axis
selection signal wire.
Check the sequence program.
Check the No. of axes listed in the
specifications.
0107
Spindle rotation speed over
The spindle rotation speed exceeded the axis
clamp speed during the thread cutting
command.
•
Lower the commanded spindle rotation speed.
0108
Fixed pnt mode feed ax illegal
An axis not found in the specifications was
designated for the fixed point mode feed or the
fixed point mode feedrate is illegal.
•
Check for broken wires in the fixed mode feed
axis selection signal wire and fixed point mode
feedrate wire.
Check the fixed point mode feed specifications.
II - 3
•
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0109
Block start interlock
An interlock signal that locks the start of the
block has been input.
•
Check the sequence program.
0110
Cutting block start interlock
An interlock signal that locks the start of the
cutting block has been input.
•
Check the sequence program.
0111
Restart switch ON
The restart switch was turned ON before the
restart search was completed, and the manual
mode was selected.
•
•
Search the block to be restarted.
Turn OFF the restart switch.
0112
Program check mode
The automatic start button was pressed during
program check or in program check mode.
•
Press the reset button to cancel the program
check mode.
0113
Auto start in buffer correct
The automatic start button was pressed during
buffer correction.
•
Press the automatic start button after buffer
correction is completed.
0115
In reset process
The automatic start button was pressed during
resetting or tape rewinding.
•
When rewinding the tape‚ wait for the winding
to end‚ or press the reset button to stop the
winding‚ and then press the automatic start
button.
During resetting‚ wait for resetting to end‚ and
then press the automatic start button.
•
0117
Playback not possible
The playback switch was turned ON during
editing.
•
During editing‚ cancel the function by pressing
the input or previous screen key‚ and then turn
ON the playback switch.
0118
Turn stop in normal line cntrl
The turning angle at the block joint exceeded
the limit during normal line control.
•
•
•
Check the program.
Set the normal line control axis turning speed.
(Parameter "#1523 C_feed")
Set the C axis turning diameter smaller than the
arc radius, or check the setting value of the C
axis turning diameter.
(Parameter "#8041 C rot. R")
Normal line control type I
The normal line control axis turning speed
(#1523 C_feed) has not been set.
Normal line control type II
When turning in the inside of the arc, the
parameter "#8041 C-rot. R" setting value is
larger than the arc radius.
0120
In synchronous correction mode
The synchronous correction mode switch was
pressed in a non-handle mode.
•
•
Select the handle or manual feed mode.
Turn OFF the correction mode switch.
0121
No synchronous control option
The synchronous control system (register
R2589) was set with no synchronous control
option.
•
Set 0 in register R2589.
0123
Computer link B not possible
The cycle start was attempted before resetting
was completed.
An attempt was made to perform computer link
B operation at the second part system and
following in a multi-part system.
•
Perform the cycle start after resetting is
completed.
Set 0 in "#8109 HOST LINK", and then set 1
again before performing the cycle start.
The computer link B operation cannot be
performed at the second part system and
following in a multi-part system.
II - 4
•
•
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
0124
X/Z axes simultaneous prohibit
The basic axis corresponding to the inclined
axis was started simultaneously in the manual
mode while the inclined axis control was valid.
•
0126
Program restart machine lock
Machine lock was applied on the return axis
while manually returning to the restart position.
•
Release the machine lock before resuming
operations.
0127
Rot axis parameter error
The orthogonal coordinate axis name does not
exist.
The rotary axis name does not exist.
The orthogonal coordinate axis name is
duplicated.
The number of axes that were selected to
change tool length compensation along the tool
axis amount exceeds the maximum number of
axes.
The orthogonal coordinate axis name is that of
the rotary axis name.
•
Review the rotational axis configuration
parameters.
0150
Chopping override zero
The override became "0" while performing the
chopping operation.
•
•
Check the chopping override (R2530).
Check the rapid traverse override (R2502).
0151
Command axis chopping axis
A chopping axis movement command was
issued from the program during the chopping
mode. (This alarm will not occur when the
movement amount is commanded as 0.)
(All axes interlock state will be applied.)
•
Reset, or turn OFF the chopping signal. When
the chopping signal is turned OFF, the axis will
return to the reference position, and then the
program movement command will be executed.
0153
Bottom dead center pos. zero
The bottom dead center position is set to the
same position as the upper dead center
position.
•
Correctly set the bottom dead center position.
0154
Chopping disable for handle ax
Chopping was started when the chopping axis
was selected as the handle axis.
•
Select an axis other than the chopping axis as
the handle axis, or start chopping after
changing the mode to another mode.
0160
No speed set out of soft limit
Returned from the outside of the soft limit range
for the axis with no maximum speed set for the
outside of the soft limit range.
•
Set the maximum speed for the outside of the
soft limit range. (Parameter "#2021 out_f")
Change the soft limit range.
(Parameter "#2013 OT-" "#2014 OT+")
0170
Ill. op during T tip control
An attempt was made to perform an incorrect
operation during tool tip center control.
•
Change to the previous operation mode and
reboot.
1005
G114.n command illegal
An attempt was made to execute G114.n
during execution of G114.n.
G51.2 was commanded when the G51.2
spindle-spindle polygon machining mode was
already entered with a separate part system.
•
•
Cancel with G113.
Issue the spindle synchronous cancel signal
(Y18B8: SPSYC).
Cancel with G50.2.
Cancel with the spindle-spindle polygon cancel
signal (YCD1).
1007
Remedy
Spindle in-use by synchro tap
The spindle is being used in synchronized
tapping.
II - 5
•
•
•
•
•
Turn the inclined axis and basic axis start OFF
for both axes. (This also applied for
manual/automatic simultaneous start.)
Invalidate the basic axis compensation, or
command one axis at a time.
Cancel synchronized tapping.
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
Remedy
1026
SP-C ax ctrl runs independntly
C axis mode command was issued for polygon
machining spindle.
C axis mode command was issued for
synchronized tapping spindle.
Polygon command was issued for
synchronized tapping spindle.
Spindle is being used as spindle/C axis.
•
•
•
Cancel the C axis command.
Cancel the polygon machining command.
Cancel the C axis with servo OFF.
1030
Synchronization mismatch
Different M codes were commanded in the two
part systems as the synchronization M codes.
Synchronization with the "!" code was
commanded in another part system during M
code synchronization.
Synchronization with the M code was
commanded in another part system during
synchronization with the "!" code.
•
Correct the program so that the M codes
match.
Correct the program so that the same
synchronization codes are commanded.
•
1031
Multiple C axes select invalid
The C axis selection signal was changed when
multiple C axes could not be selected.
An axis that cannot be controlled as the
multiple C axes selection was selected.
•
Check and correct the parameters and
program.
1032
Tap retract Sp select illegal
Tap return was executed when a different
spindle was selected. Cutting feed will wait until
synchronization is completed.
•
Select the spindle for which tap cycle was
halted before the tap return signal was turned
ON.
1033
Sp-Sp polygon cut interlock
Cutting feed will wait until synchronization is
completed.
•
Wait for synchronization to end.
1034
Cross machining cmnd illegal
Cross machining control exceeding the number
of control axes was attempted.
Cross machining control with duplicated axis
addresses was attempted.
•
Check the parameter settings for cross
machining control.
1035
Cross machining disable modal
Cross machining control was commanded for a
part system in which cross machining control is
disabled as shown below.
• During nose R compensation mode
• During pole coordinate interpolation mode
• During cylindrical interpolation mode
• During balance cut mode
• During fixed cycle machining mode
• During facing turret mirror image
•
Check the program.
II - 6
1. List of Alarms
1.1 Operation Alarms
Error No.
Details
Remedy
•
Set the R2589 register to 0.
Mirror image disable state
The external mirror image or parameter mirror
image was commanded during facing turret
mirror image.
•
Check the program and parameters.
1037
Synchro start/cancel disable
Synchronous control was started or canceled
when synchronous control could not be started
or canceled.
•
Check the program and parameters.
1038
Move cmnd invld to synchro ax
A movement command was issued to a
synchronous axis in synchronous control.
•
Check the program.
1106
Sp synchro phase calc illegal
The spindle synchronization phase alignment
command was issued while the spindle
synchronization phase calculation request
signal was ON.
•
•
Check the program.
Check the sequence program.
1036
Synchro ctrl setting disable
The synchronous control operation method
selection (R2589 register) was set when the
mode was not the C axis mode.
The synchronous control operation method
selection (R2589 register) was set in the zero
point not set state.
(2) Class: M90 Message: Parameter set mode
M90 Messages output when the setup parameter lock function is enabled are displayed.
Error No.
-
Details
Remedy
Setup parameter lock released
The setup parameter lock is released.
Automatic start is disabled when setup
parameters can be set.
Refer to the manual issued by the machine tool
builder.
II - 7
1. List of Alarms
1.2 Stop Codes
1.2 Stop Codes
These codes indicate a status that caused the controller to stop for some reason.
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
TUU Message {{{{
Error No.
Message
Class
(1) Class: T01 Cycle start prohibit
This indicates the state where automatic operation cannot be started when attempting to start it from the
stop state.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0101
Axis in motion
Automatic start is not possible as one of the
axes is moving.
•
Try automatic start again after all axes have
stopped.
0102
NC not ready
Automatic start is not possible as the NC is not
ready.
•
Another alarm has occurred. Check the details
and remedy.
0103
Reset signal ON
Automatic start is not possible as the reset
signal has been input.
•
•
Turn OFF the reset input signal.
Check that the reset switch is not ON
constantly due to trouble.
Check the sequence program.
•
0104
Auto operation pause signal ON
The FEED HOLD switch on the machine
operation panel is ON (valid).
•
•
•
•
0105
H/W stroke end axis exists
Automatic start is not possible as one of the
axes is at the stroke end.
•
•
•
Check the FEED HOLD switch.
The feed hold switch is the B contact.
Check for broken wires in the feed hold signal
wire.
Check the sequence program.
If one of the axis' ends is at the stroke end‚
move the axis manually.
Check for broken wire in the stroke end signal
wire.
Check for trouble in the stroke end limit switch.
0106
S/W stroke end axis exists
Automatic start is not possible as one of the
axes is at the stored stroke limit.
•
•
Move the axis manually.
If an axis is not at the end‚ check the parameter
details.
0107
No operation mode
The operation mode has not been selected.
•
•
Select the automatic operation mode.
Check for broken wires in the automatic
operation mode (memory‚ tape‚ MDl) signal
wire.
0108
Operation mode duplicated
Two or more automatic operation modes are
selected.
•
Check for a short circuit in the mode selection
signal wire (memory‚ tape‚ MDl).
Check for trouble in the switch.
Check the sequence program.
Return to the original automatic operation
mode‚ and start automatic start.
0109
Operation mode changed
The automatic operation mode changed to
another automatic operation mode.
II - 8
•
•
•
1. List of Alarms
1.2 Stop Codes
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0110
Tape search execution
Automatic start is not possible as tape search is
being executed.
•
Begin automatic start after the tape search is
completed.
0112
Restart pos. return incomplete
Automatic start is not possible as the axis has
not been returned to the restart position.
•
•
Manually return to the restart position.
Turn the automatic restart valid parameter ON,
and then execute automatic start.
0113
CNC overheat
Automatic start is not possible because a
thermal alarm (Z53 CNC overheat) has
occurred.
•
The NC controller temperature has exceeded
the specified temperature.
Take appropriate measures to cool the unit.
•
0115
Cycle st. prohibit(Host comm.)
Automatic start cannot be executed as the NC
is communicating with the host computer.
•
Execute automatic start after the
communication with the host computer is
completed.
0116
Cycle st prohibit(Battery alm)
Automatic start cannot be executed because
the voltage of the battery inserted in the NC
control unit has dropped.
•
•
Replace the battery of the NC control unit.
Contact the service center.
0138
In absolute position alarm
A start signal was input during an absolute
position detection alarm.
•
Reset the absolute position detection alarm‚
and then input the start signal.
0139
In abs posn initial setting
A start signal was input while initializing the
absolute position detector's zero point.
•
Complete zero point initialization before
inputting the start signal.
0190
Cycle start prohibit
Automatic start is disabled because setup
parameters can be set.
•
Refer to the manual issued by the machine tool
builder.
0191
Cycle start prohibit
Automatic start was caused during file deletion
or writing.
•
Cause automatic start after file deletion or
writing is completed.
II - 9
1. List of Alarms
1.2 Stop Codes
(2) Class: T02 Feed hold
The feed hold state been entered due to a condition in the automatic operation.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
•
0201
H/W stroke end axis exists
An axis is at the stroke end.
•
Manually move the axis away from the stroke
end limit switch.
The machining program must be corrected.
0202
S/W stroke end axis exists
An axis is at the stored stroke limit.
•
•
Manually move the axis.
The machining program must be corrected.
0203
Reset signal ON
The reset signal has been input.
•
The program execution position has returned to
the start of the program. Execute automatic
operation from the start of the machining
program.
0204
Auto operation pause signal ON
The FEED HOLD switch is ON.
•
Resume automatic operation by pressing the
"CYCLE START" switch.
0205
Operation mode changed
The operation mode changed to another mode
during automatic operation.
•
Return to the original automatic operation
mode‚ and resume automatic operation by
pressing the "CYCLE START" switch.
0206
Acc/dec time cnst too large
The acceleration and deceleration time
constants are too large. (This problem occurs
at the same time as system alarm Z59.)
•
Increase the set value of the parameter "#1206
G1bF".
Decrease the set value of the parameter
"#1207 G1btL".
Lower the cutting speed.
Reset the absolute position detection alarm.
•
•
0215
Abs posn detect alarm occurred
An absolute position detection alarm occurred.
•
(3) Class: T03 Block stop
This indicates that automatic operation stopped after executing one block of the program.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0301
Single block stop signal ON
The SINGLE BLOCK switch on the machine
operation panel is ON.
The single block or machine lock switch
changed.
•
Automatic operation can be resumed by turning
the CYCLE START switch ON.
0302
Block stop cmnd in user macro
The block stop command was issued in the
user macro program.
•
Automatic operation can be resumed by turning
the CYCLE START switch ON.
0303
Operation mode changed
The automatic mode changed to another
automatic mode.
•
Return to the original automatic operation
mode‚ and resume automatic operation by
turning the CYCLE START switch ON.
0304
MDI completed
The last block of MDI was completed.
•
Set MDI again‚ and turn the CYCLE START
switch ON to resume MDl operation.
0305
Block start interlock
The interlock signal that locks the block start is
entered.
•
Check the sequence program.
0306
Cutting blck start interlock
The interlock signal that locks the block cutting
start is entered.
•
Check the sequence program.
0310
Inclined Z offset change
Whether to validate the offset of the inclined
Z-axis switched during program operation.
•
Automatic operation can be restarted by turning
ON the CYCLE START switch.
II - 10
1. List of Alarms
1.2 Stop Codes
(4) Class: T04 Collation stop
This indicates that collation stop was applied during automatic operation.
Error No.
0401
Details
Remedy
•
Collation stop
Collation stop occurred.
Automatic operation can be restarted with
automatic start.
(5) Class: T10 Fin wait
This indicates the operation state when an alarm did not occur during automatic operation‚ and nothing
seems to have happened.
Error No.
0
Details
The error number is displayed while each of the completion wait modes listed in the table below is
ON. It disappears when the mode is canceled.
0
Alarm
No.
Unclamp In dwell
signal
execuwait
tion
Alarm
No.
(Note 2)
Door
open
(Note 1)
0
Waiting
for
spindle
position
to be
looped
0
×
1
8
×
9
×
×
Alarm
No.
Waiting
for
spindle
orientation to
complete
Waiting
for
cutting
speed
deceleration
Waiting
for rapid
traverse
deceleration
Waiting
for MSTB
completion
0
×
1
8
×
9
×
×
×
1
2
×
3
×
4
×
5
×
6
×
×
7
×
×
×
×
8
×
9
×
A
×
×
B
×
×
C
×
×
D
×
×
E
×
×
×
F
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
(Note 1) This mode is enabled by the door interlock function.
(Note 2) The system is waiting for the index table indexing unclamp signal to turn ON or OFF
II - 11
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
This section describes alarms occurred by the errors in the servo system such as the drive unit‚ motor and
encoder, etc. The alarm message‚ alarm No. and axis name will display on the alarm message screen. The
axis where the alarm occurred and the alarm No. will also display on the servo monitor screen and the spindle
monitor screen respectively. If several alarms have occurred‚ up to two errors per axis will display on the
servo monitor screen and the spindle monitor screen respectively.
(Note 1) The alarm class and alarm reset class combinations are preset.
Alarm class
Alarm reset class
Resetting methods
S01
PR
After removing the cause of the alarm, reset the
alarm by turning the NC power ON again.
S02
Again after removing the cause of the alarm, reset
the alarm by turning OFF the controller power and
then turning it ON.
S03
NR
After removing the cause of the alarm, reset the
alarm by inputting the NC RESET key.
S04
AR
After removing the cause of the alarm, reset the
alarm by turning the drive unit power ON again.
S51
This is cleared if a correct value is set.
S52
(Note 2) The resetting method may change according to the alarm class.
For example, even if "S03 SERVO ALARM: NR" is displayed, it may be necessary to turn the NC
power ON again.
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
S{{
Message
:
∆∆∆∆
xx
Servo : Axis name
Axis name
Spindle : "S", "T", "M", "N"
Alarm No. (Parameter No.)
Alarm reset class
Message
Alarm class
(1) Class: S01/S03/S04 Servo alarm
Alarm No.
0010
Message
Insufficient voltage
Meaning
Insufficient PN bus voltage was detected in main circuit.
0011
Axis selection error
Setting of the axis No. selection switch is incorrect.
0012
Memory error 1
A CPU error or an internal memory error was detected during the
power ON self-check.
0013
Software processing Software processing has not finished within the specified time.
error 1
Software processing Software processing has not finished within the specified time.
error 2
A CPU error or an internal memory error was detected during the
Memory error 2
power ON self-check.
0014
0015
0016
0017
0018
Magnet pole pos
detect error
A/D converter error
Initial magnetic pole for motor control has not been formed yet.
Motor side dtc: Init
commu err
Initial communication with the motor end detector failed.
An error was detected in the A/D converter for detecting current FB.
II - 12
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Alarm No.
0019
Message
Meaning
Detector commu err Initial communication with the motor end detector on master axis
failed when setting closed-loop current synchronous control. Or
in syn cont
the communication was interrupted.
001A
Machine side dtc:
Init comu er
Initial communication with the linear scale or the ball screw end
detector failed.
001B
Machine side dtc:
Error 1
001C
Machine side dtc:
Error 2
The machine side detector detected an error.
As details defer from detector to detector, refer to the separate table
(1).
001D
Machine side dtc:
Error 3
001E
Machine side dtc:
Error 4
001F
Machine side dtc:
Commu error
An error was detected in communication data with the linear scale or
the ball screw end detector. Or the communication was
interrupted.
0020
Motor side dtc: No
signal
It was detected that the motor side detector cables are incorrectly
connected.
0021
Machine side dtc:
No signal
No ABZ phase signal was returned from the machine side detector,
or the detector cables are incorrectly connected.
0023
Excessive speed
error
A difference between the speed command and speed feedback was
continuously exceeding 50 r/min for longer than the setting time.
0024
Grounding
The motor power cable is in contact with FG (Frame Ground).
0025
Absolute position
data lost
Unused axis error
The absolute position was lost, as the backup battery voltage
dropped in the absolute position detector.
A power module error occurred in the axis whose axis No. selection
switch was set to "F"(free axis).
0027
Machine side dtc:
Error 5
The machine side detector detected an error.
As details defer from detector to detector, refer to the separate table
(1).
0028
Machine side dtc:
Error 6
Machine side dtc:
Error 7
0026
0029
002A
002B
Machine side dtc:
Error 8
Motor side dtc:
Error 1
The motor side detector (linear scale in the case of linear motor)
detected an error.
As details defer from detector to detector, refer to the separate table
(1).
002C
Motor side dtc:
Error 2
002D
Motor side dtc:
Error 3
002E
Motor side dtc:
Error 4
002F
Motor side dtc:
Commu error
An error was detected in communication data with the motor end
detector or with the linear scale of a linear servo system. Or the
communication was interrupted.
0030
Over regeneration
Over-regeneration detection level became over 100%. The
regenerative resistor is overloaded.
0031
Overspeed
The motor was detected to rotate at a speed exceeding the
allowable speed.
II - 13
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Alarm No.
0032
Power module
overcurrent
Meaning
Overcurrent protection function in the power module has started its
operation.
0033
Overvoltage
PN bus voltage in main circuit exceeded the allowable value.
0034
NC-DRV commu:
CRC error
An error was detected in the data received from the CNC.
0035
NC command error
The travel command data that was received from the CNC was
excessive.
0036
NC-DRV commu:
Commu error
Initial parameter
error
The communication with the CNC was interrupted.
NC-DRV commu:
Protocol error 1
NC-DRV commu:
Protocol error 2
An error was detected in the communication frames received from
the CNC.
An error was detected in the axis information data received from the
CNC.
003A
Overcurrent
Excessive current was detected in the motor drive current.
003B
Power module
overheat
Thermal protection function in the power module has started its
operation.
003C
Regeneration circuit An error was detected in the regenerative transistor or in the
regenerative resistor.
error
The spindle motor failed to rotate faster than 45 r/min, even when
Spindle speed
the max. torque command was given.
blocked
0037
0038
0039
003D
Message
An incorrect parameter was detected among the parameters
received from the CNC at the power ON.
1. The spindle motor speed feedback was detected to be
accelerated exceeding the commanded speed.
2. The spindle motor was detected to be rotated at a speed
exceeding the parameter value, while the speed command was
"0" (including the case of operation stoppage during the position
control).
003E
Spindle speed
overrun
0040
Detector select unit An error was detected in the motor switching signals that were
received from the detector selection unit, while controlling one drive
swtch err
unit and two motors.
0041
0042
Detector select unit An error was detected in the communication with the detector
selection unit, while controlling one drive unit and two motors.
commu err
An error was detected in the feedback signals of the pulse position
Feedback error 1
detector in a servo system, or in PLG's feedback signals in a spindle
system.
0043
Feedback error 2
Excessive difference was detected in position data between the
motor end detector and the machine end detector in a servo system.
In a spindle system, an error was detected in the encoder feedback
signals.
0044
Inappropriate coil
for C axis
When using a coil changeover motor, C-axis was controlled while
the high-speed coil was selected.
0045
Fan stop
A cooling fan built in the drive unit stopped, and the loads on the unit
exceeded the specified value.
0046
Motor overheat
Thermal protection function of the motor or in the detector, has
started its operation.
0047
Regenerative
resistor overheat
Thermal protection function of the regenerative resistor, has started
its operation.
II - 14
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Alarm No.
Message
Meaning
The motor side detector (linear scale in the case of linear motor)
detected an error.
As details defer from detector to detector, refer to the separate
table (1).
0048
Motor side dtc:
Error 5
0049
Motor side dtc:
Error 6
004A
Motor side dtc:
Error 7
004B
Motor side dtc:
Error 8
004C
Current err at mag
pole detect
004E
NC command mode The mode outside the specification was input in spindle control
mode selection.
error
The power was momentarily interrupted.
Instantaneous
power interrupt
Overload detection level became over 100%. The motor or the
Overload 1
drive unit is overloaded.
004F
0050
A current error was detected in the IPM spindle motor when the
initial magnetic pole was being formed.
0051
Overload 2
Current command of more than 95% of the unit's max. current was
being continuously given for longer than 1 second in a servo system.
In a spindle system, the load over the continuous rating was being
applied for longer than 30 minutes.
0052
Excessive error 1
A difference between the actual and theoretical motor positions
during servo ON exceeded the setting value in a servo system. In a
spindle system, a difference between the position command and
position feedback exceeded the setting value.
0053
Excessive error 2
A difference between the actual and theoretical motor positions
during servo OFF exceeded the setting value.
0054
Excessive error 3
When an excessive error 1 occurred, detection of the motor current
failed.
0055
External emergency
stop error
Collision detection
1: G0
There is no contactor shutoff command, even after 30 seconds has
passed since the external emergency stop was input.
When collision detection function was valid, the disturbance torque
in rapid traverse (G0) exceeded the collision detection level.
0058
0059
005A
Collision detection When collision detection function was valid, the disturbance torque
in cutting feed (G1) exceeded the collision detection level.
1: G1
Collision detection 2 When collision detection function was valid, the command torque
reached the max. motor torque.
005C
Orientation
feedback error
After orientation was achieved, a difference between the command
and feedback exceeded the parameter setting.
005D
Speed monitor:
Input mismatch
005E
Speed monitor: FB
speed error
As for door state signal of speed monitoring control, a mismatch
between the external input signal and the control signal received
from the CNC was detected.
In speed monitoring control, the spindle speed was exceeding the
setting speed with the door open.
005F
External contactor
error
A contact of the external contactor is welding. Or the contactor fails
to be ON during ready ON.
II - 15
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Alarm No.
Message
Meaning
It was detected that the 24VDC power supply lowered.
0060
Pw sply:Inst pw
interpt(DC24V)
0061
Pw sply: Pwr
module overcurnt
0062
Pw sply: Frequency The input power supply frequency increased above the specification
range.
error
The supplementary regenerative transistor is being ON.
Pw sply:
Supplement regen
err
Pw sply: Rush relay A resistor relay for rush short circuit fails to be ON.
error
An open-phase condition was detected in input power supply circuit.
Pw sply: Phase
interruption
Pw sply: Watchdog The system does not operate correctly.
0063
0065
0067
0068
0069
006A
006B
006C
Overcurrent protection function in the power module has started its
operation.
Pw sply: Grounding The motor power cable is in contact with FG (Frame Ground).
A contact of the external contactor is welding.
Pw sply: Ext
contactor weld
Pw sply: Rush relay A resistor relay for rush short circuit fails to be OFF.
welding
An error was detected in charging operation of the main circuit
Pw sply: Main
capacitor.
circuit error
006D
Pw sply: Parameter
error
The capacity of the power supply unit and the regenerative resistor
type that was set in the parameter are mismatched.
006E
Pw sply: Memory
error
An internal memory error was detected.
006F
Power supply error
A power supply unit is not connected. Or an error was detected in
A/D converter of the power supply unit.
0071
Pw sply: Instant pwr The power was momentarily interrupted.
interrupt
Over-regeneration detection level became over 100%. The
Pw sply: Over
regenerative resistor is overloaded. This alarm cannot be reset for
regeneration
15 min from the occurrence. Leave the drive system emergized for
more than 15 min, then turn the power ON to reset the alarm.
0073
Pw sply: Regen
resist ovheat
Pw sply:
Overvoltage
Thermal protection function of the regenerative resistor, has started
its operation.
L+ and L- bus voltage in main circuit exceeded the allowable value.
As the voltage between L+ and L- is high immedialtey after this
alarm, another alarm may occur if this alarm is reset in a short time.
Wait more than 5 min before resetting so that the voltage drops.
0076
Pw sply: Ext EMG
stop set err
As for the external emergency stop settings, the setting on the rotary
switch and the parameter setting are mismatched.
0077
Pw sply: Power
module overheat
Thermal protection function in the power module has started its
operation.
007F
0087
Drv unit pw supply
restart req
Drive unit
communication
error
A mismatch of program mode selection was detected. Turn the
drive unit power ON again.
Answers from a drive unit connected to the power supply stopped.
0088
Watchdog
The system does not operate correctly.
0074
0075
II - 16
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Separate table (1)
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
OSA105
Detector type
OSA166
MDS-B-HR
002B
002C
002D
002E
001B
001C
001D
001E
Data error
Deterioration of the
LED was detected.
-
An error was
detected in the data.
-
0048
0049
004A
004B
0027
0028
0029
002A
-
-
Judgment error
Magnetic error
The linear scale
analog frequency
cycle could not be
judged.
An error was
detected in the
magnetic data for
the linear servo
system.
CPU error
A CPU initial error
was detected.
Meaning of data
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
OSA105
OSA166
Detector type
MDS-B-HR
Meaning of data
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
TS5690
Detector type
TS5691
LED error
-
Communication
Connection error
error
An error was
An error was
detected in the
detected in the
connection with the communication with
analog output linear the serial output
scale.
linear scale.
002B
002C
002D
002E
001B
001C
001D
001E
Initialization error
Waveform error
-
-
An initialization error
was detected when
the power was
turned ON.
An error was
detected in the A, B,
Z analog signal
waveform.
-
-
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
0048
0049
004A
004B
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
0027
0028
0029
002A
-
Relative position
data error
Meaning of data
Detector type
Meaning of data
TS5690
-
TS5691
-
Overspeed
The tolerable
rotation speed was
exceeded.
II - 17
-
An error was
detected in the
relative position
data.
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
002B
002C
002D
002E
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
001B
001C
001D
001E
Detector type
Manufacturer
name
AT342
AT343
Photo-electric type,
static capacity data
mismatch
Mitsutoyo
AT543
LC191M
Initialization error
LC491M
RCN723
EEPROM error
Heidenhain
ROM/RAM error
Relative/absolute
position data
mismatch
RCN223
ERM280
MJ831
-
-
Sony
-
-
-
-
ADB-20J60
MHI
Faulty mounting
accuracy
-
Detection position
deviated
Scale disconnected
FMD
Futaba
Denshi
Kogyo
-
-
-
-
Alarm number when motor
end is connected
0048
0049
004A
004B
Alarm number when machine
end is connected
0027
0028
0029
002A
Photo-electric type
overspeed
Static capacity type
error
Photo-electric type
error
Overspeed
Absolute position
data error
Detector type
Manufacturer
name
AT342
AT343
Mitsutoyo
AT543
LC191M
CPU error
LC491M
RCN723
Heidenhain
Absolute position
data error
RCN223
ERM280
MJ831
Sony
-
-
-
Encoder error
ADB-20J60
MHI
-
-
Gain fault
Phase fault
FMD
Futaba
Denshi
Kogyo
-
-
Waveform error
Excessive speed
II - 18
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
(2) Class: S02 Message: Initial parameter error
An error was found in the parameters transmitted from the controller to the drive unit when the power
was turned ON.
Remove the cause of the alarm, and then reset the alarm by turning the controller power OFF once.
Alarm
No.
Details
Remedy
2201
to
2264
The servo parameter setting data is illegal.
The alarm No. is the No. of the servo parameter
where the error occurred.
Check the descriptions for the appropriate servo
parameters and correct them.
2301
The number of constants to be used in the
following functions is too large:
• Electronic gears
• Position loop gain
• Speed feedback conversion
Check that all the related parameters are
specified correctly.
sv001:PC1, sv002:PC2, sv003:PGN1
sv018:PIT, sv019:RNG1, sv020:RNG2
2302
When high-speed serial incremental detector
Check that all the related parameters are
(OSE104, OSE105) is connected, parameters for specified correctly.
absolute position are set to ON.
sv017:SPEC, sv025:MTYP
Set the parameters for absolute position
detection to OFF.
To detect an absolute position, replace the
incremental specification detector with an
absolute position detector.
2303
No servo option is found.
The closed loop (including the ball screwend detector) or dual feedback control is an
optional function.
Check that all the related parameters are
specified correctly.
sv025:MTYP/pen
sv017:SPEC/dfbx
2304
No servo option is found.
The SHG control is an optional function.
Check that all the related parameters are
specified correctly.
sv057:SHGC
sv058:SHGCsp
2305
No servo option is found.
The adaptive filtering is an optional function.
Check that all the related parameters are
specified correctly.
sv027:SSF1/aflt
13001
to
13256
Parameter error
The spindle parameter setting data is illegal.
The alarm No. is the No. of the spindle
parameter where the error occurred.
Check the descriptions for the appropriate
spindle parameters and correct them.
Refer to Alarm No.37 in Spindle Drive
Maintenance Manual.
(3) Class: S51 Message: Parameter error
This warning is displayed if a parameter outside the tolerance range is set.
Illegal settings will be ignored.
This alarm will be reset when a correct value is set.
Alarm
No.
Details
Remedy
2201
to
2264
Servo parameter setting data is illegal.
The alarm No. is the No. of the servo parameter
where the warning occurred.
Check the descriptions for the appropriate servo
parameters and correct them.
13001
to
13256
Spindle parameter setting data is illegal.
The alarm No. is the No. of the spindle
parameter where the warning occurred.
Check the descriptions for the appropriate
spindle parameters and correct them.
Refer to Spindle Drive Maintenance Manual.
II - 19
1. List of Alarms
1.3 Servo/Spindle Alarms
(4) Class: S52 Servo warning
Displays servo and spindle tool warnings.
Alarm No.
Message
0093
Init abs pos fluctuation
0096
Scale feedback error
0097
Scale offset error
009B
An error was detected in the shift distance of the magnetic pole in a
Detector converting
unit: Magnetic pole shift linear servo system.
warning
An error was detected in the revolution counter of the absolute
Absolute position
position detector. The absolute position data cannot be
detector: Revolution
compensated.
counter error
009E
Meaning
The position data have fluctuated during the absolute position
initializing.
An excessive deviation was detected between the motor end
detector and MP scale feedback data in a MP scale absolute
position detection system.
An error was detected in the offset data received from the MP scale
in a MP scale absolute position detection system.
The battery voltage that is supplied to the absolute position detector
dropped. The absolute position data is retained.
009F
Battery voltage drop
00A6
00A8
A cooling fan built in the drive unit stopped.
Fan stop warning
Turret indexing warning The designated position shift amount of turret indexing is outside
the setting range.
00A9
Orientation feedback
warning
As an orientation feedback error occurred, the retrial has been
conducted.
00E0
Overregeneration
warning
Over-regeneration detection level exceeded 80%.
00E1
Overload warning
Overload detection level exceeded 80%.
00E2
Continuous high-speed The motor was continuously rotated at a speed exceeding the rated
speed.
revolution warning
Deviation between the absolute and relative position data was
Absolute position
detected.
counter warning
Set parameter warning A parameter setting was outside the setting range.
00E3
00E4
00E6
Control axis
detachment warning
Control axis detachment was commanded.
00E7
In NC emergency stop
state
Emergency stop was input from the CNC.
00E8
Regeneration that are beyond the power supply limitation has
Power supply: Over
frequently occurred.
supplementary
regeneration frequency
The power was momentarily interrupted.
Instantaneous power
interruption warning
In external emergency External emergency stop signal was input.
stop state
Over-regeneration detection level exceeded 80%.
Power supply: Over
regeneration warning
00E9
00EA
00EB
II - 20
1. List of Alarms
1.4 MCP Alarm
1.4 MCP Alarm
An error has occurred in the drive unit and other interfaces. (The bold characters are the messages displayed
on the screen.)
YUU Message {{{{
{{{{
Alarm No.
Error No.
Message
Class
(1) Class: Y02 System alarm
An error occurred in the data transmitted between the MCP and drive unit after the power was turned
ON.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0050
System alm: Process time over
The software or hardware may be damaged.
Contact the service center.
0051
Alarm No.
A communication error has occurred between the
controller and drive unit.
• Take measures against noise.
• Check that the communication cable connector
between the controller and drive unit and one
between the drive units are tight.
• Check whether the communication cable
between the controller and drive unit and one
between the drive units are disconnected.
• A drive unit may be faulty. Take a note of the
7-segment LED contents of each drive unit and
report to the Service Center.
0000
SV commu er: CRC error 1
(10 times/910.2 ms)
0001
SV commu er: CRC error 2
(2 continuous times)
0002
SV commu er: Recv timing err
(2 continuous times)
xx03
SV commu er: Data ID error
(2 continuous times)
xx: Axis No.
xx04
SV commu er: Recv frame No.
(2 continuous times)
xx: Axis No.
0005
SV commu er: Commu error
(No error classification)
0006
SV commu er: Connect error
xx10
SV commu er: Packet esc error
Packet was skipped twice in
succession during communication
cycle
xx: Axis No.
0020
SV commu er: Init commu error
The drive unit could not shift to the
initial communication run time and
stopped.
0030
SV commu er: Node detect error
No response from drive unit to the
request from NC when setting
network configuration.
xx: Channel No.
II - 21
1. List of Alarms
1.4 MCP Alarm
(2) Class: Y03 Message: Drive unit unequipped
The drive unit is not correctly connected.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
Check the drive unit mounting state.
• Check the end of the cable wiring.
• Check the cable for broken wires.
• Check the connector insertion.
• The drive unit input power is not being input.
• The drive unit axis No. switch is illegal.
Alphabet Servo axis drive unit not mounted
(axis
name)
1 to 4 PLC axis drive unit not mounted
S
No.1 spindle axis drive unit not mounted
T
No.2 spindle axis drive unit not mounted
M
N
No.3 spindle axis drive unit not mounted
No.4 spindle axis drive unit not mounted
(3) Class : Y05 Message: Initial parameter error
Details
Remedy
There is a problem in the value set for the number of axes or Check the value set for the corresponding
the number of part systems.
parameters.
#1001 SYS_ON
#1002 axisno
#1039 spinno, etc.
(4) Class: Y06 Message: mcp_no setting error
There are differences in the MCP and axis parameters when the NC power is turned ON.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0001
There is a skipped number in the channels.
0002
The random layout setting is duplicated.
0003
The drive unit fixed setting "0000" and random
layout setting "∗∗∗∗" are both set.
The spindle/C axis "#1021 mcp_no" and "#3031
smcp_no" are not set to the same values.
0004
0005
A random layout is set for the "#1154 pdoor" =1
two-part system.
0006
The channel No. parameter is not within the
setting range.
II - 22
Check the values set for the following
parameters.
#1021 mcp_no
#3031 smcp_no
1. List of Alarms
1.4 MCP Alarm
(5) Class: Y51 Parameter error
An error occurred in a parameter that causes an alarm while the control axis was operating.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
0001
Parameter G0tL illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2004 G0tL".
0002
Parameter G1tL illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2007 G1tL".
0003
Parameter G0t1 illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2005 G0t1".
0004
Parameter G1t1 illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2008 G1t1".
0009
Parameter grid space illegal
•
Check "#2029 grspc".
0012
Parameter stapt1-4 illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check spindle parameters" #3017 stapt1" to
"#3020 stapt4".
0015
Parameter skip_tL illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2102 skip_tL".
0016
Parameter skip_t1 illegal
The time constant has not been set or the
setting exceeded the setting range.
•
Check "#2103 skip_t1".
0017
Parameter G0bdcc illegal
"#1205 G0bdcc" for the 2nd part system is set
to acceleration/deceleration before G0
interpolation.
•
Check "#1205 G0bdcc".
0018
OMR-II parameter error
The OMR-II related parameter settings are
incorrect. In this case, the OMR-II is disabled.
•
Check the related parameter settings.
0101
Values of PC1/PC2 too large
The PC1 and PC2 settings used for the rotary
axis are too large.
•
Check "#2201 PC1" and "#2202 PC2".
II - 23
1. List of Alarms
1.4 MCP Alarm
(6) Class: Y90 Message: No spindle signal
(Alarm No.)
Alarm No.
0
1
0
No.1 spindle
No.2 spindle
No.3 spindle
No.4 spindle
Z open
phase
B open
phase
×
×
×
2
3
4
5
6
7
A open
phase
×
×
×
×
Alarm
No.
Details
0001
to
0007
There is an error in the spindle encoder signal.
The data transmission to the drive unit is stopped
when this error occurs.
×
×
×
×
×
Remedy
II - 24
•
Check the spindle encoder's feedback cable
and the encoder.
1. List of Alarms
1.5 System Alarms
1.5 System Alarms
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
Z31 DataServer error
{{{{
Warning No.
Message
Warning No.
0001
Socket open error(socket)
Explanation
0002
Socket bind error(bind)
0003
Connection wait queue error(listen)
0004
Connection request error(accept)
0005
Data recv error(socket error)
0006
0007
Data recv error(data error)
Data send error(socket error)
0008
Data send error(data error)
000A
Socket close error(close)
(Note) If warning No. 0001, 0002, 0003, or 000A is displayed, set the parameters, then turn power OFF and
turn it ON again.
II - 25
1. List of Alarms
1.5 System Alarms
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
Message
Details
Remedy
Z40
Format
mismatch
Z51
E2PROM error
00xx
This appears when the parameter MemVal
is formatted at 0, and MemVal is set to 1.
•
Either return the MemVal setting, or format
and restart.
<Type>
Z51 E2PROM error 0011: Read error
Z51 E2PROM error 0012: Write error
•
If the same alarm is output by the same
operation, the cause is an H/W fault.
Contact the Service Center.
Z52
Battery fault
The voltage of the battery inserted in the NC
control unit has dropped. (The battery used
to save the internal data.)
•
•
Replace the battery of the NC control unit.
After treating the battery‚ check the
machining program.
Z53
CNC overheat
The controller or operation board
temperature has risen above the designated
value.
(Note 1)
•
•
Cooling measures are required.
Turn OFF the controller power‚ or lower
the temperature with a cooler‚ etc.
This occurs when an error occurs in the
communication between the controller and
remote l/O unit.
• Cable breakage
• Remote l/O unit fault
• Power supply to remote l/O unit fault
(Note 2)
The program memory capacity setting value
Z57
System warning cannot be formatted.
The expansion cassette (HR437) is not
mounted after formatting.
An expansion cassette different from the
expansion cassette (HR437) mounted
during formatting is mounted.
(Note 3)
The machine tool builder macro program
Z58
was not written to the FROM after being
ROM write not
registered, edited, copied, condensed,
completed
merged, the number changed, or deleted.
•
•
•
Check and replace the cables.
Replace the remote I/O unit.
Check the power supply. (existence of
supply‚ voltage)
Z55
RIO
communication
stop
Z59
Acc/dec time
cnst too large
Acceleration and deceleration time
constants are too large.
(This alarm is output at the same time as
"T02 Acc/dec time cnst too large 0206.")
II - 26
Check the state of the following items.
• Program memory capacity
• Status of expansion cassette (HR437)
mounting
• APLC open option
• Write the machine tool builder macro
program to the FROM.
* If the operations, such as editing, done
while the NC power was OFF can be
invalidated, the program does not need to
be written to the FROM.
• Increase the value specified as the "#1206
G1bF" parameter.
• Decrease the value specified as the
"#1207 G1btL" parameter.
• Lower the feedrate.
1. List of Alarms
1.5 System Alarms
!
CAUTION
If the battery low warning is issued, save the machining programs, tool data and parameters
in an input/output device, and then replace the battery. When the battery alarm is issued, the
machining programs, tool data and parameters may be destroyed. Reload the data after
replacing the battery.
Do not replace the battery while the power is ON.
Do not short circuit, charge, heat, incinerate or disassemble the battery.
Dispose of the spent battery following local laws.
(Note 1) Temperature warning
If the alarm is displayed when an overheat alarm is detected‚ the overheat signal will be output
simultaneously. If the machine is in automatic operation‚ the operation will be continued‚ but
restarting will not be possible after resetting or stopping with M02/M30. (Starting will be possible
after block stop or feed hold.) The alarm will be reset and the overheat signal will turn OFF when the
temperature drops below the specified temperature.
Z53 CNC overheat
000x
↑
0001 : The temperature in the controller is high.
0002 : The temperature around the communication terminal
(setting and display unit) is high.
0003 : The temperature in the controller and around the communication
terminal (setting and display unit) is high.
The ambient temperature must be lowered immediately when a "Z53 CNC overheat" alarm occurs‚
but if machining must be continued‚ the alarm can be invalidated by turning the following parameter OFF.
PLC parameter bit selection #6449
76543210
Communication terminal
(setting and display unit)
Controller
II - 27
0: Detection invalid
1: Detection valid
1. List of Alarms
1.5 System Alarms
(Note 2) RIO communication interrupt
If communication between the control unit and remote I/O unit fails, the alarm and remote I/O unit
number are displayed.
Board connection remote I/O
communication interrupted station
(a)(b)
Z55 RIO communication stop
↓↓
Remote I/O 3rd part system
communication interrupted station
Remote I/O 1st part system
communication interrupted station
Remote I/O 2nd part system
communication interrupted station
(a) and (b) above indicate the following matters.
Alarm
number
RIO
(seventh
station)
RIO
(sixth
station)
RIO
(fifth
station)
RIO
(fourth
station)
0
×
×
×
2
3
×
×
×
×
4
5
6
7
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
RIO
(third
station)
RIO
(second
station)
RIO
(first
station)
RIO
(0th
station)
0
1
8
Alarm
number
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
2
×
3
×
×
×
×
4
×
×
×
5
6
×
7
8
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
1
9
A
×
B
C
×
×
×
D
E
×
F
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
×
This also applies for the remote I/O 1st part system communication interrupted station, remote I/O 3rd part
system communication interrupted station and board connection remote I/O communication interrupted
station.
II - 28
1. List of Alarms
1.6 Absolute Position Detection System Alarms
1.6 Absolute Position Detection System Alarms
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
ZUU Message {{{{
Axis name
Error No.
Message
Class
(1) Class: Z70 Abs data error
This error is displayed if the absolute position data is lost in the absolute position detection system.
Error
No.
Details
Remedy
Alarm reset
Zero point
when power
initialization
is turned OFF
Required
-
Servo
alarm
No.
-
0001 Abs posn base set
incomplete
Zero point initialization is
incomplete.
Otherwise, the spindle was
removed.
Complete zero point
initialization.
0002 Absolute position lost
The absolute position
reference point data saved in
the NC has been destroyed.
Input the parameters. If the
reference point data cannot be
restored‚ perform zero point
initialization.
(Required)
-
-
0003 Abs posn param changed
The parameters used to
detect the absolute position
have been changed.
Correctly set the parameters.
Turn the power on again‚ and
perform zero point initialization.
Required
-
-
0004 Abs posn initial set illegal
The zero point initialization
point is not at the grid
position.
Reperform zero point
initialization.
Required
-
-
0005 Abs posn param restored
Restoration was possible
with parameter input in the
above No.0002 state.
Turn the power on again‚ and
operation will be possible.
Not required
-
-
Required
-
(9E)
etc.
#1003
#1016
#1017
#1018
#1040
#2049
iunit
iout
rot
ccw
M_inch
type
#2201
#2202
#2218
#2219
#2220
#2225
PC1
PC2
PIT
RNG1
RNG2
MTYP
Replace the detector and
0080 Abs posn data lost
The absolute value data was complete zero point
initialization.
lost, because the
multi-rotation counter data in
the detector was incorrect,
etc.
II - 29
1. List of Alarms
1.6 Absolute Position Detection System Alarms
Error
No.
Details
Remedy
0101 Abs posn error(servo alm 25) Reperform zero point
initialization.
The power was turned ON
again after the servo alarm
No. 25 displayed.
0106 Abs posn error(servo alm
E3)
The power was turned ON
again after the servo alarm
No. E3 displayed.
Reperform zero point
initialization.
Alarm reset
Zero point
when power
initialization
is turned OFF
Required
-
Required
-
Servo
alarm
No.
(25)
(E3)
(Note) To release alarm "Z70 Abs data error", enter the parameter data output when establishing the
absolute position and turn ON the power again. For the rotary axis, however, the alarm cannot be
released by entering the parameter data.
(2) Class: Z71 Abs encoder failure
This alarm is displayed if an error is found in the detector for the absolute position detection system.
Alarm reset
Zero point
when power
initialization
is turned OFF
Required
0001 AbsEncoder:Backup voltage Replace the battery‚ check the
cable connections‚ and check
(Z70-0101
drop
the detector. Turn the power
displays after
The backup voltage in the
ON again‚ and perform zero
power is
absolute position detector
point initialization.
turned ON
dropped.
again.)
Error
No.
Details
Remedy
Servo
alarm
No.
25
0003 AbsEncoder: Commu error
Communication with the
absolute position detector
was not possible.
Check and replace the cables‚
card or detector. Turn the
power ON again‚ and perform
zero point initialization.
(Required)
Only when
detector is
replaced.
Reset
91
0004 AbsEncoder: Abs data
changed
The absolute position data
fluctuated when establishing
the absolute position.
Check and replace the cables‚
card or detector. Turn the
power ON again‚ and perform
zero point initialization.
(Required)
Only when
detector is
replaced.
Reset
93
0005 AbsEncoder: Serial data
error
An error was found in the
serial data from the absolute
position detector.
Check and replace the cables‚
card or detector. Turn the
power ON again‚ and perform
zero point initialization.
(Required)
Only when
detector is
replaced.
Reset
92
0006 AbsEncoder: Abs/inc posn
diffr
Servo alarm E3
Absolute position counter
warning
Operation is possible until the
power is turned off.
0007 AbsEncoder: Initial commu
err
Initial communication with the
absolute position detector
was not possible.
Check and replace the cables‚
card or detector. Turn the
power ON again‚ and perform
zero point initialization.
II - 30
(Required)
Reset
When power
(Z70-0106
is turned ON displays after
again.
power is
turned ON
again.)
(Required)
Only when
detector is
replaced.
Reset
E3
18
1. List of Alarms
1.6 Absolute Position Detection System Alarms
(3) Class: Z72 Message: Position check error
This alarm is displayed if an error is detected when comparing the detector's absolute position and
controller coordinate values in the absolute position system.
(4) Class: Z73 Message: Absolute position data warning
This warning is displayed for the absolute position detection system.
Alarm
No.
0001
Details
Remedy
Battery for abs data fault
Servo alarm 9F
Low battery voltage
If the battery voltage is low or the cable is
damaged, there is no need to initialize the
absolute position.
II - 31
1. List of Alarms
1.7 Messages during Emergency Stop
1.7 Messages during Emergency Stop
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
EMG
Emergency stop
Error items
Error Item
Details
Remedy
PLC
The user PLC has entered the emergency stop
state during the sequence process.
• Investigate and remove the cause of the user
PLC emergency stop.
EXIN
The emergency stop input signal is significant
(open).
• Cancel the emergency stop input signal.
• Check the wiring to see if any wiring is broken.
SRV
An alarm occurred in the servo system causing
an emergency stop.
• Investigate and remove the cause of the servo
alarm.
STOP
The user PLC (ladder sequence) is not running.
• Check if the rotary switch CS2 on the top of the
controller front panel is set to 1.
• Check if the PLC edit file save screen (onboard
function) [4RUN/SP] (run/stop) switch is turned
ON.
SPIN
Spindle drive unit not mounted
The spindle drive unit is not mounted.
• Cancel the causes of the other emergency
stop.
• Check emergency stop signal input in the
spindle drive unit.
PC_H
High-speed PC processing abnormal
• Check the sequence program.
(To stop monitoring the high-speed PC
processing temporarily, set 1 in "#1219
aux03/bit1". Disable the monitoring function
only as a temporary measure.)
PARA
Setting of the door open II fixed device is illegal.
The dog signal random assignment parameter
setting is illegal.
• Specify the "#1155 DOOR_m" and "#1156
DOOR_s" parameters correctly.
(When the door open II fixed device is not
used, set "#1155 DOOR_m" and "#1156
DOOR_s" to "100".)
• Correctly set the "#2073 zrn_dog", "#2074
H/W_OT+", "#2075 H/W_OT-" and "#1226
aux10/bit5" parameters.
II - 32
1. List of Alarms
1.7 Messages during Emergency Stop
Error No.
LINK
Details
Remedy
If the FROM/TO instruction is not executed within • Try to execute the FROM or TO instruction one
500 ms, an emergency stop occurs.
or more times every 500 ms.
* Measure the time in which no interrupt request
is issued from MELSEC and store the result in
the R register.
R10190: Current time-out counter
R10191: Counter for maximum time-out after
power-on
R10192: Counter for maximum time-out after
system start-up (backed up)
MELSEC is held in error and reset states.
• Check the MELSEC states.
The contents of MELSEC-specific code area in
buffer memory have been destroyed.
• Check the MELSEC states.
PLC serial link communication has stopped.
WAIT
• Check that HR571 card wiring and external
sequencer transmission are normal.
(Note) When "WAIT" is entered for the PLC
• Check the diagnostic screen for link
serial link, only the preparation sequence
communication errors.
has been established before the
• Check whether the basic specification
communication stops. Therefore, it is
parameters related to serial link parameters are
supposed that the basic specification
specified correctly.
parameters related to serial link
parameters #1902 and #1903 are
incorrect or the #1909 set-time is too
short.
• Check that the HR571 card rotary switch and
The preparation sequence is not sent from the
wiring and the external sequencer transmission
master station. Otherwise, the contents of the
are normal.
received preparation sequence are inconsistent
• Check the diagnostic screen for link
with those of the parameters, so that the usual
communication errors.
sequence cannot be started.
(Note) When "LINK" is also entered for the PLC
serial link, refer to "Note" in the section,
"LINK".
XTEN
LAD
The HR571 card operates abnormally or the
rotary switch is set incorrectly.
• Check the HR571 card rotary switch and
replace the HR571 card if required.
The user PLC (ladder sequence) has an illegal
code.
• Check the user PLC (ladder sequence) to see if
it uses illegal device numbers or constants.
II - 33
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
Refer to "1.3 Servo/spindle alarms" for details of the alarm class and alarm clear class combination.
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
S{{ Message UUUU
Axis No. 1 to 4
Alarm information
(Follows MR-J2-CT alarm information)
Message
Alarm class
(1) Class: S01 Aux ax servo alarm
Alarm
information
Details
Remedy
0011
Aux ax PCB err (Drive circuit)
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal PCB.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0013
Aux ax S/W processing error
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal reference
clock.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0016
Aux ax motor/detector type err
Motor type error.
•
Use a correct drive unit and motor
combination.
Detector initial communication error.
•
•
•
Connect correctly.
Replace the motor.
Replace or repair cable.
Detector CPU error.
•
0017
Aux ax PCB error(A/D err)
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal A/D converter.
•
Replace the motor (detector).
Replace servo drive unit.
0025
Aux ax absolute posn lost
An error occurred in the detector's internal absolute
position data.
•
•
Turn the power ON for 2 to 3
minutes while the alarm is
occurring, and then turn the power
ON again.
Replace the battery, and initialize
the absolute position again.
0034
Aux ax CRC error
An error occurred in the communication with the NC.
•
Take countermeasures against
noise.
0036
Aux ax communication timeout
Communication with the NC was cut off.
•
•
•
Connect correctly.
Turn the NC power ON.
Replace the drive unit or NC.
0037
Aux ax parameter error
The parameter setting value is incorrect.
•
Set the parameter correctly.
0038
Aux ax frame error
An error occurred in the communication with the NC.
•
Take countermeasures against
noise.
0039
Aux ax commu INFO error
Undefined data was transferred from the NC.
•
Change the NC software version to
a compatible version.
II - 34
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
(2) Class: S02 Aux ax servo alarm
Alarm
Details
information
0011
Aux ax PCB err (Drive circuit)
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal PCB.
Remedy
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0013
Aux ax S/W processing error
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal reference
clock.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0015
Aux ax EEROM error
A write error occurred to the EEROM in the drive unit.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0017
Aux ax PCB error(A/D err)
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal A/D converter.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0018
Aux ax PCB error(LSI err)
An error occurred in the drive unit's internal LSI.
•
Replace servo drive unit.
0020
Aux ax detector error
An error occurred in the communication between the servo
drive unit and detector.
•
•
Connect correctly.
Replace or repair cable.
0024
Aux ax ground fault detection
A ground fault of the output was detected when the power
was turned ON.
•
•
Repair the ground fault section.
Replace the cable or motor.
(3) Class: S03 Aux ax servo alarm
Alarm
information
Details
0010
Aux ax under voltage
The power voltage is 160V or less.
0030
Aux ax regeneration error
Remedy
The tolerable regeneration power of the internal
regenerative resistor or external regenerative option was
exceeded.
•
•
Review the power supply.
Replace the servo drive unit.
•
•
•
•
Set the parameter #50002 correctly.
Connect correctly.
Lower the positioning frequency.
Change the regenerative option to
a larger capacity.
Lower the load.
Review the power supply.
Replace the servo drive unit.
•
•
0031
0032
Regenerative transistor error
•
Aux ax overspeed
The motor's rotation speed exceeded the tolerable
momentary speed.
•
Aux ax overcurrent
A current exceeding the servo drive unit's tolerable current
flowed.
•
•
•
II - 35
•
•
Increase the acceleration/
deceleration time constant.
Review the gear ratio.
Replace the detector.
Repair the wiring.
Replace the servo drive unit.
Take countermeasures against
noise.
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
Alarm
Details
information
0033
Aux ax overvoltage
The voltage of the converter in the servo drive unit was
400V or more.
Remedy
•
•
•
•
Wire correctly.
Replace the servo drive unit.
For the internal regenerative
resistor, replace the drive unit.
For the external regenerative option,
replace the regenerative option.
0046
Aux ax motor overheating
An operation state causing the motor to overheat
continued.
•
•
Reduce the motor load.
Review the operation pattern.
0050
Aux ax overload 1
The servo drive unit or servomotor overload protection
function activated.
•
•
•
Reduce the motor load.
Review the operation pattern.
Change to a motor or drive unit
with large output.
Change the setting of the
automatic tuning response
characteristics.
Correct the connection.
Replace the servomotor.
•
•
•
0051
Aux ax overload 2
The max. output current flowed for several seconds due to
a machine collision or overload.
•
•
•
•
0052
Aux ax excessive error
A position deflection exceeding the excessive error
detection setting value occurred.
II - 36
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Review the operation pattern.
Change the setting of the
automatic tuning response
characteristics.
Correct the connection.
Replace the servomotor.
Increase the acceleration/
deceleration time constant.
Increase the torque limit value.
Review the power facility capacity.
Review the operation pattern.
Replace the servomotor.
Connect correctly.
Repair or replace the cable.
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
(4) Class: S52 Message: Aux ax servo warning
Alarm
Details
information
Aux ax battery voltage drop
0092
The absolute position detection battery voltage dropped.
00E0
00E1
00E3
00E9
Remedy
•
•
Mount a battery.
Replace the battery and initialize
the absolute position.
Aux ax overregeneration warning
The regeneration power may have exceeded the tolerable
range of the built-in regenerative resistor or external
regenerative option.
•
•
•
Lower the positioning frequency.
Change the regenerative option to
a larger one.
Lower the load.
Aux ax overload warning
The overload alarm 1 could occur.
Aux ax abs position counter warning
There is an error in the absolute position detector internal
data.
•
Refer to the items for S03 0050.
•
•
Take countermeasures against
noise.
Replace the servomotor.
Aux ax main circuit OFF warning
The servo ON signal was input while the main circuit
power was OFF.
The contactor operation is faulty.
•
Turn ON the main circuit power.
(5) Class: Z70 Message: Aux ax abs position error
Alarm
information
Details
Remedy
0001
Aux ax abs posn base set incomplete
The zero point (reference point) has not been initialized in
the absolute position system.
•
Initialize the zero point (reference
point).
0002
Aux ax absolute position lost
The absolute position coordinate data in the drive unit has
been lost.
•
Initialize the zero point (reference
point).
0003
Aux ax abs posn param changed
The absolute position system related parameters have
been changed or lost.
•
Correctly set the parameters and
then initialize the zero point
(reference point).
(6) Class: Z71 Message: Aux ax drop voltage
Alarm
information
0001
Details
Remedy
Aux ax abs encoder: back up voltage drop
The data in the detector has been lost.
Battery voltage drop.
Detector cable wire breakage or looseness.
II - 37
•
Check the battery and detector
cable and then initialize the zero
point (reference point).
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
(7) Class: Z73 Message: Aux ax system warning
Alarm
information
Details
Remedy
0001
Aux ax battery for abs data fault
Battery voltage drop.
Detector cable wire breakage or looseness.
•
Check the battery and detector
cable. The zero point does not
need to be initialized.
0003
Aux ax absolute position counter warning
An error occurred in the detector's absolute position
counter.
•
Replace the detector.
(8) Class: M00 Aux ax operation error
Alarm
information
Details
Remedy
0001
Aux ax dog overrun
When executing dog-type reference position, the zero
point return speed is too fast or the dog length is too short.
•
Lower the zero point return speed
or increase the dog length.
0003
Aux ax R-pnt direction illegal
When executing reference position return, the axis was
moved in the opposite of the designated direction.
•
Move the axis in the correct
direction.
0004
Aux ax external interlock
The axis interlock function is valid.
•
Cancel the interlock signal
0005
Aux ax internal interlock
An interlock was established by the servo OFF function.
•
Cancel the servo OFF.
0007
Aux ax soft limit
The soft limit was reached.
•
Check the soft limit setting and
machine position
0024
Aux ax R ret invld at abs alm
Reference position return was executed during an
absolute position alarm.
•
Initialize the absolute position
reference point and then fix the
absolute position coordinates.
0025
Aux ax R ret invld at ini
Reference position return was executed while initializing
the absolute position.
•
Initialize the absolute position
reference point and then fix the
absolute position coordinates.
II - 38
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
(9) Class: M01 Aux ax operation error
Alarm
information
Details
Remedy
0101
Aux ax no operation mode
The operation mode is not designated, or the operation
mode was changed during axis movement.
•
Correctly designate the operation
mode.
0103
Aux ax feedrate 0
The operation parameter's feedrate setting is zero.
The operation parameter feedrate setting is zero.
Or, the override is valid, and the override value is zero.
•
Set a value other than zero in the
feedrate setting or override value.
0160
Aux ax sta No. illegal
A station No. exceeding the No. of indexed divisions was
designated.
•
Correctly designate the station No.
0161
Aux ax R-pnt ret incomplete
Automatic/manual operation was started before reference
position return was executed with the incremental system.
•
Execute the reference position
return.
0162
Aux abs position initializing
The start signal was input while initializing the absolute
position reference point.
•
Complete the absolute position
reference point initialization.
0163
Aux ax abs position error
The start signal was input during an absolute position
alarm.
•
Initialize the absolute position
reference point and then fix the
absolute position coordinates.
0164
Aux ax arbitrary positioning
The manual operation mode was started during the
random positioning mode.
•
Turn the random positioning mode
OFF before switching to the
manual operation mode.
0165
Aux uneven index sta No. ilgl
The commanded station No. was higher than 9 or the
number of indexing stations during uneven indexing.
•
Check the commanded station No.
and the parameter "#50100 station"
setting.
II - 39
1. List of Alarms
1.8 Auxiliary Axis Alarms
(10) Class: Y02 Auxiliary axis MCP alarms
An error occurred during data transfer between the MCP and auxiliary axis drive unit after turning on the
power.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
The software or hardware may be damaged.
0050
Aux ax sys alm: Proc time over
Contact the service center.
0051
0000
Aux ax commu er:CRC error 1
(10 times/910.2ms)
0001
Aux ax commu er:CRC error 2
(2 continuous times)
0002
Aux ax commu er:Recv timing
(2 continuous times)
xx03
Aux ax commu er:Data ID
(2 continuous times)
xx: Axis No.
xx04
Aux ax commu er:Recv frame no.
(2 continuous times)
xx: Axis No.
A communication error has occurred between the
controller and drive unit.
• Take measures against noise.
• Check that the communication cable connector
between the controller and drive unit and one
between the drive unit are tight.
• Check whether the communication cable
between the controller and drive unit and one
between the drive units are disconnected.
• A driving drive unit may be faulty. Take a note of
the 7-segment LED contents of each driving
drive unit and report to the Service Center.
(11) Class: Y03 Message: Aux ax drive unit unequipped
The drive unit is not properly connected.
Error No.
Details
Remedy
Axis No. bit correspondence (bit 0: 1st axis, bit 1: 2nd axis, Check the auxiliary axis drive unit mounting
state.
1 to 4 bit 2: 3rd axis, bit 3: 4th axis)
• Check the end of the cable wiring.
• Check the cable for broken wires.
• Check the connector insertion.
The auxiliary axis drive unit input power is not
being input.
The auxiliary axis drive unit axis No. switch is
illegal.
II - 40
1. List of Alarms
1.9 Computer Link Errors
1.9 Computer Link Errors
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
LUU Message
{{{{
Error No.
Message
Alarm class
(1) Class: L01 Computer link error
Error
No.
0004
0010
Details
Remedy
Timeout error
Communication ends with timeout
CNC has a 248-byte receive buffer.
The time during which CNC receives 248
bytes exceeds the "TIME-OUT" value set in
the I/O device parameter.
•
Host ER signal OFF
HOST ER (CNC DR) signal is not turned ON.
•
•
•
•
•
Set a greater timeout value in the input/output
device parameter.
Recheck the HOST software as to whether or not
the HOST transmits data in response to DC1
from CNC (data request).
Check whether or not start code of computer link
parameter is set to 0.
Check whether or not the cable is disconnected
from the connector.
Check whether or not the cable is broken.
Check whether or not the HOST power is turned
ON.
Recheck the HOST software as to whether or not
the data to be transmitted to CNC is ISO code.
0015
Parity H error
Communication ends with parity H.
•
0016
Parity V error
Communication ends with parity V.
•
Recheck the data to be transmitted to CNC.
0017
Overrun error
Although CNC transmits DC3 (request to stop
data transfer) to the HOST, it receives data of
10 bytes or more from the HOST, thus
terminates communication.
When CNC is transmitting data to the HOST, it
receives data of 10 bytes or more from the
HOST.
•
Recheck the software as to whether or not the
HOST stops transmitting data within 10 bytes
after receiving DC3.
Recheck the HOST software as to whether or not
the HOST transmits data such as a command or
header to CNC during receiving a work program.
II - 41
•
1. List of Alarms
1.10 User PLC Alarms
1.10 User PLC Alarms
(The bold characters are the messages displayed on the screen.)
UUU Message {{{{ {{{{
Sub-status 2
Sub-status 1
Message
Alarm class
Message
U01
No user
PLC
Sub-status
1
-
2
-
Details
Remedy
The ladder is not a GPPW ladder or
PLC4B ladder.
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) will
be applied.
Download the ladder of the format
selected with the PLC
environment selection parameters
(bit selection #51/bit 4).
U10
0x0010
Illegal PLC
-
PLC scan time error
The scan time is 1 second or
longer.
Edit the ladder size to a smaller
size.
0x0040
-
Ladder operation mode illegal
A ladder different from the
designated mode was
downloaded.
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) will
be applied.
Download the ladder having the
same format as when the power
was reset or turned ON.
0x0080
-
GPPW ladder code error
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) will
be applied.
Download the correct GPPW
format ladder.
0x008x
-
PLC4B ladder code error
An illegal circuit was found in the
PLC4B ladder.
bit1: PC medium-speed circuit
illegal
bit2: PC high-speed circuit illegal
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) will
be applied.
Download the correct PLC4B
format ladder.
Software illegal interrupt
0x0400 Number of
ladder steps
The ladder process stopped
abnormally due to an illegal
software command code.
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) will
be applied.
II - 42
Turn the power ON again.
If the error is not reset, download
the correct ladder.
1. List of Alarms
1.10 User PLC Alarms
Message
Sub-status
Details
Remedy
2
Software exception
U10
0x800x Number of
ladder steps
Illegal PLC
The ladder process stopped
abnormally due to a bus error, etc.
bit 0: BIN command operation error Refer to the methods for using the
bit 1: BCD command operation
BCD and BIN function
error
commands.
1
bit6: CALL/CALLS/RET
command error
bit7: IRET command execution
error
(Note) Emergency stop (EMG) is
applied for bit 6/7.
Turn the power ON again.
If the error is not reset, download
the correct ladder.
U50
PLC
stopped
The ladder is stopped.
Start the ladder.
U55
PLC
stopped /
is not
saved
The ladder is stopped and not written Write the ladder into ROM.
into ROM.
U60
Ladder is
not saved
The ladder is not written into ROM.
Write the ladder into ROM.
(Note) The number of ladder steps displayed on the screen may not match the actual number of error
occurrence steps because of the ladder timing. Use this as a guideline of the occurrence place.
II - 43
1. List of Alarms
1.11 Network Service Errors
1.11 Network Service Errors
Message
N001
Modem initial
error
Details
• There is an error in the modem
connection when the power is turned
ON.
N002
Redial over
• The dial transmission failed more than • Wait a while, and then transmit again.
the designated No. of redial times.
N003
TEL unconnect
• The phone line is not connected.
• Check the modem's phone line connection.
N004
Net
communication
error
• An error other than the above errors
occurred during communication.
• Note down the circumstances under which
this error occurred, and contact the Service
Center.
N005
Invalid net
communication
• The modem connection port is being
used for another function such as
input/output.
• The modem connection port settings
are incorrect.
• Quit using the modem connection port with
the other function, and then turn the power
ON again.
• Check the modem connection port settings.
II - 44
Remedy
• Check the connection between the NC and
modem, connection port and modem power.
2. Operation Messages
2.1 Search-related Operation Messages
2. Operation Messages
The following messages display on each screen.
2.1 Search-related Operation Messages
Message
Searching
Details
• The operation search is being executed.
Search completed
•
The operation search was completed correctly.
Verifying
•
The data is being verified correctly.
Verifying stopped
•
The data comparison completed correctly.
Search error
•
Setting error
•
Restart search is completed
•
The restart search was completed.
Executing restart search
•
The restart search is being executed.
Can't cancel verify stop
•
The compare stop cannot be canceled because the operation is not
in a compare stop.
Executing top search
•
The top search is being executed correctly.
Top search completed
•
The top search was completed correctly.
Can't input data
•
Data input was attempted during M, S, T, B history display.
Input some of ONB
• Awaiting
Verifying stop posn already
registered
•
The verify stop position has already been registered.
No searched program
•
The program has not been searched.
Program restarting
•
The program is being restarted.
Could not find the designated ONB number.
Review the ONB number or machining program settings.
• The operation search could not be completed correctly.
The directory name exceeded the display range.
A directory path for which the entire directory cannot be displayed
cannot be designated in the directory name area.
• The search is not possible because ONB number is not designated.
ONB number input
II - 45
2. Operation Messages
2.2 Graphic Display-related Operation Messages
2.2 Graphic Display-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Searching
•
Search error
•
Executing automatic operation
•
Setting error
•
Execute checksearch
•
Checking
•
The program check is being executed.
Check stopped
•
The program check is being stopped.
Push [Check reset] menu
•
An error occurred in the graphic check.
Press the [Check reset] menu key to reset the error.
Executing trace
•
The trace mode is valid.
Program check completed
•
The trace in the program check completed with an M02/M30 code.
Reset complete
•
The program check was reset.
Tool interfere with work
•
The tool contacted the workpiece when performing rapid traverse
(G0) movement with the interference check enabled.
Program checking
•
The program check is being executed.
Executing reset operation
•
The program check is being reset.
Executing trace(tip posn)
•
The tip position trace mode is valid.
The check search is being executed.
Could not find the designated ONB number.
Review the ONB number or machining program settings.
• The checl search could not be completed correctly.
An attempt was made to peform operatins such as parameter, tool
compensation amount data and coordinate system offset settings
during auto operation. (Input/output also possible during auto
operation)
• The machining program and MDI data that the operator is attempting
to edit cannot be edited during auto operation.
• It is not possible to be executed a check search or check start-up
during auto operation.
• An attempt was made to set the verify stop position during auto
operation.
The directory name exceeded the display range.
A directory path for which the entire directory cannot be displayed
cannot be designated in the directory name area.
• The check search is not possible because ONB number is not
designated.
• A non-existent axis name or setting that does not exist in the format
was made when making the display mode settings.
Set using an existing axis name.
The check could not be started.
Execute a check search.
II - 46
2. Operation Messages
2.3 Variable (Common variables, local variables) - related Operation Messages
2.3 Variable (Common variables, local variables) - related Operation Messages
Message
Erase? (Y/N)
Details
•
Message to confirm the line erase.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Variables are deleted.
[N]
: Variables are not deleted.
2.4 PLC Switch-related Operation Messages
Message
Set up parameter ?(Y/N)
Details
•
Message to confirm the parameter setup.
[Y] or [INPUT] : It will be possible to make settings.
[N]
: It will not be possible to make settings.
2.5 Compensation-related (Tool compensation, coordinate system offset) Operation
Messages
Message
Details
Erase? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the erasing.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Erase the data.
[N]
: Do not erase the data.
Clear all axes? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the all axes clear.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Clear the data for all axes.
[N]
: Do not clear the data.
Cannot return to origin
•
Operations other than line paste, paste and data input cannot be
undone.
Clear all? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the clearing the all data.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Clear all data.
[N]
: Do not clear the data.
Input P number
•
•
The coordinate system [Coord G54.1 P] menu was pressed.
The expansion workpiece coordinate system P No. was input.
Data clear complete
•
Clearing of the collection data is complete.
Execute the collection data
clear?
•
Determines whether to clear the collection data. Press [Y] or [INPUT]
to clear the data.
II - 47
2. Operation Messages
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Overwrite this file?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the overwriting.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Overwrite the file.
[N]
: Do not overwrite the file.
Over run error
•
The buffer overran or overflowed.
Memory over
•
The program cannot be written, because the memory capacity will be
exceeded. (Occurs when copying a program during tape input.)
Can't make directory on this
device
•
Creation of a directory was attempted for a device that cannot have a
directory.
Designated file does not exist
•
The file specified in device A, and B does not exist.
The applicable file does not exist in the specified directory.
•
The file name is a directory
•
A directory was designated for the file transfer. A directory cannot be
transferred.
Change complete
•
The data conversion completed correctly.
Changing
•
The data is being converted.
Erase complete
•
The file has been erased.
Erase ended. Some file not
erased
•
The file erasing completed, but there are some files that could not be
erased.
Verify error
• An
Compare error. Compare next
file?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the comparison
[Y] or [INPUT] : Compare the next file.
[N]
: Do not compare the next file.
Compare complete
•
The data comparison completed.
Verifying
•
The data is being compared.
The file already exists
•
•
The input file name already exists.
The file name after renaming already exists.
Can't erase designated file
•
Erasing was attempted of a file that cannot be erased.
Can't rename designated file
•
An attempt was made to change the name of a file that cannot be
renamed.
Can't condense designated file
•
Condensing of a file that cannot be condensed was attempted.
error occurred when performing a file verification.
II - 48
2. Operation Messages
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Designated file is locked
•
Changing was attempted of a locked file.
Can't open file for dev A
•
Could not find the file for device A.
Or, the file is in a state in which it cannot be accessed.
Can't open file for dev B
•
Could not find the file for device B.
Or, the file is in a state in which it cannot be accessed.
Can't read file for dev A
•
Could not read in the file for device A.
Recheck the connection status for device A or the input/output
parameter setting.
Can't read file for dev B
•
Could not read in the file for device B.
Recheck the connection status for device B or the input/output
parameter setting.
Can't close file for dev A
•
Contact the service center
Can't close file for dev B
•
Contact the service center.
Can't write file for dev A
•
Could not write in the file for device B.
Recheck the connection status for device A or the input/output
parameter setting.
Can't write file for dev B
•
Could not write in the file for device B.
Recheck the connection status for device B or the input/output
parameter setting.
Can't seek file for dev A
•
Contact the service center.
Can't seek file for dev B
•
Contact the service center.
File name not designated for dev
A
•
A file name was not designated for device A.
File name not designated for dev
B
•
A file name was not designated for device B.
Can't open directory for dev A
•
Could not find a directory corresponding to device A.
Can't open directory for dev B
•
Could not find a directory corresponding to device B.
Different devices designated in A
and B
•
The same device must be designated for devices A and B, but
differing devices were designated.
Timeout error
•
A timeout error occurred when communicating with the external
device.
Checking
•
Cannot be executed during a check
Make directory complete
•
Creation of the directory has been completed.
Dir create Complete
•
Creation of the directory has been completed.
II - 49
2. Operation Messages
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Can't make directory
•
The directory is not empty
• A file
Directory pass is illegal
•
The designated directory path name is illegal.
→Input a correct directory path name.
Data protect
•
Setting, erasing, parameter setting, etc., of the various data is
prohibited, because the data protect key is validated.
Transfer complete
•
The data transfer completed correctly.
Transferring
•
The data is being transferred.
Parity H error
•
A parity H error was detected.
Parity V error
•
A parity V error was detected.
File entry over
•
The No. of registration files designated in the specifications was
exceeded, so the file could not be registered.
Program No. not found in the file
•
There is no program number in the selected file.
Executing format
•
The formatting is being executed.
Format complete
•
The formatting completed.
Format error
•
The formatting failed.
Framing error
•
An error occurred between the NC and the external device.
Variable conversion error
•
An error occurred during the M2 macro conversion, and the
conversion failed.
Merge complete
•
The data merge completed.
Merge execution
•
The data merge is being executed.
Memory alloc error
•
Securing of the communication data range failed.
Rename complete
•
OK? (Y/N)
An error occurred while creating the directory.
was found in the directory.
→Erase the file in the directory.
The rename has been completed.
• Message to confirm the operation.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Execute the operation
[N]
: Cancel the operation.
II - 50
2. Operation Messages
2.6 Data Input/Output-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
I/O not ready
•
An error occurred between the NC and the external device.
I/O parameter error
•
The external device settings and input/output parameters do not
match.
I/O port busy
•
Input/output was not possible as the I/O port is busy.
FLD write protect
•
The FLD is write-protected.
→Release the write protection.
PLC running
• An
•
attempt was made to input a user PLC during PLC RUN.
Stop the PLC on the maintenance screen.
FLD not ready
•
MemoryCard not ready
• An
attempt was made to perform operations with no memory card.
DS not ready
• An
attempt was made to perform operations with no data server.
IC not ready
• An
attempt was made to perform operation without at IC card.
Can't write in READ-ONLY file
•
Contact the service center.
Condense complete
•
Condensing has been completed.
A directory does not exist
•
The specified directory does not exist.
An attempt was made to perform an FLD operation search with no
FLD.
• An attempt was made to display the FLD list with no FLD.
II - 51
2. Operation Messages
2.7 Parameter-related Operation Messages
2.7 Parameter-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Designate copy end posn
•
The copy start position was specified using the cursor. Continue and
specify the copy end position using the cursor.
Copy start posn and end posn
reversed
•
When the copy range was designated, a position before the start
position was designated as the end position.
Columns of copy start and end
different
•
A different column (axis or part system) was specified for the copy
start/end position at the screen with the arrangement configuration
for each axis and part system.
Copy range is inadequate
•
Could not find the parameter No. for the copy start position.
A value larger than the last parameter No. was designated as the
copy end position parameter No.
Check the designated copy range.
•
Setting error: column n
• The nth column setting data is inappropriate when multiple axes were
set at the same time (/ division). (Settings have been made up to the
(n-1)th column.)
Password is illegal
• The password designated for displaying the Machine
Parameter screen is illegal.
Input the password
•
The menu key for first displaying the Machine Parameter
screen was pressed after the power was turned ON.
Paste position is illegal
•
An attempt was made to paste in a different parameter from the copy
parameter.
Paste? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the operation when pasting.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Paste the data at the current cursor position.
[N]
: Do not paste the data.
Data protect
•
Setting, erasing , parameter settings, etc., of the various data is
prohibit, because the data protect key is validated.
Executing automatic operation
•
An attempt was made to make parameter settings during auto
operation.
Can't select
•
The password designated for displaying the machine parameters has
not been input.
• Display of the machine parameters was attempted on the [Param
No.] menu, but the password has not been input.
Press the [Machine param] menu, and input the password for
displaying the machine parameters.
II - 52
2. Operation Messages
2.8 Measurement-related (Workpiece, rotation) Operation Messages
2.8 Measurement-related (Workpiece, rotation) Operation Messages
Message
Details
TLM switch OFF
•
Can't take-in skip posn
•
Can't write coordinates data
•
Sensor take in not possible
•
Could not retrieve the position measured with the touch sensor.
Measure again.
Can't write compensation data
•
The cursor position and the cell for writing the compensation amount
(length dimension, radius dimension) do not match.
Match the cursor position with the cell for writing the compensation
amount.
Measurement was attempted when the TLM switch was OFF.
Could not retrieve the skip position.
Check the following:
< When measuring the workpiece >
1. Is the name of the axis to be measured designated in the basic axis
(I, J, K)?
2. Is the axis that executed the axis movement a measurement axis?
< When measuring the rotation >
1. Is the name of the axis to be measured designated in the coordinate
rotation plane (horizontal axis, vertical axis)?
2. Is the axis that executed the axis movement a measurement axis?
Could not obtain the measured axis No.
• The measured angle was illegal.
• Could not write into the coordinate system offset.
Measure again.
II - 53
2. Operation Messages
2.9 Tool (Tool registration, tool life) -related Operation Messages
2.9 Tool (Tool registration, tool life) -related Operation Messages
Message
Designated group already exists
Details
•
•
An already existing group No. was designated when changing the
group No. (Tool life screen (grp))
An already existing group No. was designated when newly creating
the group. (Tool life screen (grp list))
Designate a group No. that does not already exist.
Designated group does not exist
•
Erasing was attempted on the Tool life screen (grp list) of a group that
does not exist.
Can't register group
•
The group registration process on the Tool life screen (grp list) failed.
Can't delete group
•
The group deleition process on the Tool life screen (grp list) failed.
Erase? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the erasing.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Erase the data
[N]
: Do not erase the data.
Pot number not exist
•
The set pot number does not exist.
Check the pot number.
Create new file? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the operation when newly creating data, files,
etc.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Newly create.
[N]
: Cancel the operation.
Input the tool number
•
Waiting tool number input.
Clear not possible
•
The clear range is incorrect.
II - 54
2. Operation Messages
2.10 Editing-related Operation Messages
2.10 Editing-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Buffer correct not possible
•
Buffer correction cannot be performed for this program.
Can't write into file
•
Could not write the data to the memory with the buffer correction.
Contact the service center.
Overwrite this file?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm when registering MDI
[Y] or [INPUT] : Overwrite the file.
[N]
: Do not overwrite the file.
Memory over
•
The program cannot be written, because the memory capacity will be
exceeded.
Designated character string not
found
•
Could not find the search results and character string in the program.
Save current file ?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the saving.
[Y] : Save the changes to the current file.
[N] : Do not save the changes to the current file.
A file does not exist
• An
attempt was made to select and edit a non-existent file.
Designated file does not exist
• An
attempt was made to select and erase a non-existent file.
Erase complete
•
The data erasing completed.
Can't erase designated file
•
The selected file cannot currently be erased.
Designated file does not exist
•
A file that does not exist was designated when file editing.
Designated file already exists
•
When creating a new file, a file name was designated that already
exists.
Replace? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the character string replacement.
[Y] or [INPUT] : Replace the character string.
[N]
: Do not replace the character string.
File access error
•
Contact the Service Center.
File open error
•
The designated file is already open.
Editing
•
A program is being edited on the screen.
Save the program to write it into the memory.
Program entry over
•
The program could not be registered in the memory when attempted,
because the No. of registrations designated in the specifications
would be exceeded.
Paste position is illegal
•
Pasting was attempted within the copy range of the same file.
Designated line is out of
program range
•
Designation was attempted of a line No. larger than the No. of lines in
the entire program.
II - 55
2. Operation Messages
2.10 Editing-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
MDI no setting
•
Editing of the MDI was started, but the MDI setting was incomplete.
MDI search complete
•
The MDI search completed.
MDI search error
•
Could not execute the MDI search.
Can't edit except in MDI mode
•
"#1144 mdlkof" (MDI setting lock) is "0" and therefore it is not possible
to edit the MDI program in a mode other than MDI mode.
Input miss was detected
• An
Input miss was not detected
• A search
Can't edit a file except in NC
memory
•
Save not possible
• A special
input miss was detected.
was performed for an input miss, however, none was found.
Editing cannot be performed at the edit window for programs other
than those in the NC memory.
file (history file etc.) that cannot be saved was edited and an
attempt was made to save it. Perform an operation to quit editing.
II - 56
2. Operation Messages
2.11 Diagnosis-related Operation Messages
2.11 Diagnosis-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Erase? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm alarm history clear operation
[Y] or [INPUT] : Erase the data
[N]
: Do not erase the data.
Can't write data
•
The data cannot be written.
Device is illegal
•
The designated device is inadequate.
Modal output not possible
•
The modal output process failed.
Modal clear not possible
•
The modal cancel process failed.
Continue display not possible
•
Continuous display is not possible because data is not set at the
cursor position.
One-shot output not possible
•
The one-shot output process failed.
Select a menu
•
A device No. was set without selecting a menu operation.
Press any operation menu and input the device No. with a menu
highlighted.
Change Ope. test mode
•
Operation of the Operation test screen was attempted when the
operation adjustment mode was not selected.
II - 57
2. Operation Messages
2.12 Maintenance-related Operation Messages
2.12 Maintenance-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Password is illegal
•
The input password is incorrect.
Input password
•
The [Password] menu key was pressed, and the password input
mode was entered.
Input a password.
Now making back-up
•
Currently backing up system data and the user PLC ladder to a
specified device.
Backupping
•
The SRAM data is being backed up on the HD.
Backup complete
•
Backup error
•
An error occurred while backing up the SRAM data on the HD.
Executing format
•
The formatting is being executed correctly.
Format complete
•
The formatting completed correctly.
Format error
•
The NC memory formatting failed.
Contact the nearest service center.
Quit HMI ?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the HMI quitting
[Y] or [INPUT] : Quit the HMI.
[N]
: Do not quit the HMI.
Format NC memory?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the NC memory formatting
[Y] or [INPUT] : Start formatting the NC memory.
[N]
: Do not format the NC memory.
Execute SRAM backup ?(Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the SRAM back up
[Y] or [INPUT] : The SRAM data is backed up to the HD.
[N]
: The SRAM data is not backed up to the HD.
PLC running. Does it stop? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the PLC STOP
[Y] or [INPUT] : Backup the SRAM data on the HD.
[N]
: Do not backup the SRAM data on the HD.
Restoring
•
The system data and user PLC ladder are now being restored to the
NC from a specified device.
Restore complete
•
Restoration of system data and user PLC ladder to the NC from a
specified device has been completed.
Auto adjust error
•
Backup of the SRAM data on the HD has been completed.
• Back up of system data and user PLC ladder to a specified device
has been completed.
The H/W status cannot be read properly, and therefore it is not
possible to perform auto adjustments.
Check the remote I/O unit.
Perform manual adjustments.
• The unit is defective. Replace the unit.
II - 58
2. Operation Messages
2.12 Maintenance-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Auto adjust complete
• Analog
Auto adjust execution
•
Performing analog output adjustment normally.
Execute? (Y/N)
•
Message to confirm the operation
[Y] or [INPUT] : The currently selected operation is performed.
[N]
: The currently selected operation is not performed.
Unit not equipped
•
The machine is not equipped with an analog output unit.
A serial number is inaccurate
•
The system data to be restored and the serial number in the NC do
not match, and therefore it is not possible to restore.
Check to ensure that the serial number in the NC has been set and
that the system data to be restored matches.
•
Operating aux axis
•
•
output adjustment completed normally.
it is not possible to set parameter and input/output data during
auxiliary axis operation.
It is not possible to change the display axis during auxiliary axis
operation.
II - 59
2. Operation Messages
2.13 Data Sampling-related Operation Messages
2.13 Data Sampling-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Executing sampling
•
The waveform data is being sampled.
Input the axis name
•
This appears when the data type is selected in the Ch1 or Ch2 data
setting area.
Input the name of the axis to be sampled.
Input axis name/signal No./bit
•
This appears when the data type is selected in the Ch1 or Ch2 data
setting area.
Set the sampling conditions common for Ch1 and Ch2.
Input file/sub-ID/item/data
•
This appears when an NC file is selected in the Ch1 or Ch2 data
setting area.
Sampling conditions are illegal
•
The data cannot be sampled as the setting conditions are illegal.
Review the data, vertical scale, sampling rate and horizontal scale on
the Condition setting screen.
Can't start sampling
•
"#1224 aux08 bit0" is "0" and sampling start-up cannot be performed.
The collection invalid
•
The parameters are set to prevent data being collected. Check the
parameters.
The collection begin?
•
Determines whether to start data collection. Press [Y] or [INPUT] to
start data collection.
The collection stop?
•
Determines whether to stop data collection. Press [Y] or [INPUT] to
stop data collection.
The collection is being executed
•
An attempt was made to start data collection while data collection
was being performed.
The collection is stopping
• An
attempt was made to stop data collection while data collection was
stopped.
II - 60
2. Operation Messages
2.14 Absolute Position Detection-related Operation Messages
2.14 Absolute Position Detection-related Operation Messages
Message
Details
Setting absolute position set
•
Setting from the screen was attempted of absolute position detection
data when the "Absolute Position Set" was not ON.
Press the menu key [Absolute Position Set] to turn it ON.
Not the abs position detection
system
•
An absolute position detection system has not been selected for the
currently selected axis.
The machine parameter (Axis specification parameter "#2049 type")
must be set.
Axis name inappropriate
•
The set axis name is inappropriate. Check the axis name.
II - 61
2. Operation Messages
2.15 Other Operation Messages
2.15 Other Operation Messages
Message
Details
Launching application
•
The application is running.
Executing automatic operation
•
Cannot be performed during automatic operation.
Perform the operation again after automatic operation has been
completed.
Setting error
•
Data range error
•
The input data exceeded the range.
Set the value again within the range.
Data protect
•
Setting, erasing, parameter setting, etc., of the various data is
prohibited, because the data protect key is validated.
Reconsider the data protect key setting.
Edit lock B
•
It is not possible to change machining program B (8000 to 8999: user
standard subprogram) or machining program C (9000 to 9999:
machine tool builder custom program) as edit lock B is enabled.
Edit lock C
•
It is not possible to change machining program C (9000 to 9999:
machine tool builder custom program) as edit lock C is enabled.
Origin set not possible
•
Can′t command manual value
•
The setting data is inadequate. (Alphabetic characters were set
where only numeric characters can be set, etc.)
• The data has not been set.
The operation is in a state in which origin set is not possible.
Check the parameter "#1123 origin (Origin set prohibited)" setting.
• Check that the axis has stopped.
• Check that idling (post-reset status) is currently being performed.
The manual numerical value protect is valid and therefore it is not
possible to perform a manual numerical value command.
II - 62
3. Program Error
3. Program Error
(The bold characters are the message displayed in the screen.)
These alarms occur during automatic operation‚ and the causes of these alarms are mainly program errors
which occur‚ for instance‚ when mistakes have been made in the preparation of the machining programs or
when programs which conform to the specification have not been prepared.
Error No.
P 10
Details
Remedy
• Divide the alarm block command into two.
No. of simultaneous axes over
The number of axis addresses commanded in • Check the specifications.
the same block exceeds the specifications.
• Revise the axis names in the program.
P 11
Illegal axis address
The axis address commanded by the
program and the axis address set by the
parameter do not match.
P 20
• Check the program.
Division error
An axis command which cannot be divided by
the command unit has been issued.
P 29
Not accept command
The normal line control command (G40.1,
G41.1, G42.1) has been issued during the
modal in which the normal line control is not
acceptable.
• Check the program.
P 30
Parity H error
The number of holes per character on the
paper tape is even for EIA code and odd for
ISO code.
• Check the paper tape.
• Check the tape puncher and tape reader.
P 31
Parity V error
The number of characters per block on the
paper tape is odd.
• Make the number of characters per block on
the paper tape even.
• Set the parameter parity V selection OFF.
P 32
• Check and revise the program address.
Illegal address
An address not listed in the specifications has • Check and correct the parameters values.
• Check the specifications.
been used.
P 33
Format error
The command format in the program is not
correct.
P 34
• Check and correct the G code address in the
Illegal G code
program.
A G code not listed in the specifications has
been used.
An illegal G code was commanded during the
coordinate rotation command (G68).
• Check the program.
G51.2 or G50.2 was commanded when the
• Check the parameter setting values.
rotary tool axis No. (#1501 polyax) was set to
"0".
G51.2 or G50.2 was commanded when the
tool axis was set to the linear axis (#1017 rot
"0").
P 35
• Check the program.
Setting value range over
The setting range for the addresses has been
exceeded.
P 36
Program end error
"EOR" has been read during tape and
memory mode.
II - 63
• Enter the M02 and M30 command at the end
of the program.
• Enter the M99 command at the end of the
subprogram.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• The program Nos. are designated across a
range from 1 to 99999999.
• The sequence Nos. are designated across a
range from 1 to 99999.
P 37
O, N number zero
A zero has been specified for program and
sequence Nos.
P 39
No specifications
• A non-specified G code was specified.
• The selected operation mode is not used.
• Check the specifications.
P 40
Pre-read block error
When tool radius compensation is executed‚
there is an error in the pre-read block and so
the interference check is disabled.
• Reconsider the program.
P 49
Invalid restart search
• Restart search was attempted for the
3-dimensional circular interpolation.
• Restart search was attempted during the
cylindrical interpolation, polar coordinate
interpolation, and tool tip center control.
• Reconsider the program.
• Reconsider the restart search position.
P 60
Compensation length over
The commanded movement distance is
excessive. (Over 231)
• Reconsider the axis address command.
P 62
No F command
• No feed rate command has been issued.
• There is no F command in the cylindrical
interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation immediately after the G95
mode is commanded.
• The default movement modal command at
power ON is G01. This causes the machine
to move without a G01 command if a
movement command is issued in the
program, and an alarm results. Use an F
command to specify the feed rate.
• Specify F with a thread lead command.
P 65
No spec: High speed mode 3
• Check the high-speed mode III specifications.
P 70
• Check the numerical values of the addresses
Arc end point deviation large
that specify the start and end points, arc
• There is an error in the arc start and end
center as well as the radius in the program.
points as well as in the arc center.
• The difference of the involute curve through • Check the "+" and "-" directions of the
address numerical values.
the start point and the end point is large.
• When arc was commanded, one of the two
axes configuring the arc plane was a
scaling valid axis.
P 71
• Check the numerical values of the addresses
in the program.
• Check whether the start point or end point is
on the inner side of the base circle for involute
interpolation. When carrying out tool radius
compensation, check that the start point and
end point after compensation are not on the
inner side of the base circle for involute
interpolation.
• Check whether the start point and end point
are at an even distance from the center of the
base circle for involute interpolation.
• Check the helical specifications.
No spec: Herical cutting
A helical command has been issued though it • An Axis 3 command was issued by the
circular interpolation command. If there is
is not included in the specifications.
no helical specification, the linear axis is
moved to the next block.
P 72
Arc center error
• The arc center is not sought during
R-specified circular interpolation.
• The curvature center of the involute curve
cannot be obtained.
II - 64
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P 74
Can't calculate 3DIM arc
The end block was not specified during
3-dimension circular interpolation
supplementary modal, and therefore it is not
possible to calculate the 3-dimension circular
interpolation.
Furthermore, it not possible to calculate the
3-dimension circular interpolation due to an
interruption during 3-dimension circular
interpolation supplementary modal.
P 75
3DIM arc illegal
An unusable G code was issued during
3-dimension circular interpolation modal.
Or, a 3-dimension circular interpolation
command was issued during a modal for
which a 3-dimension circular interpolation
command cannot be issued.
P 76
• Check the specifications.
No spec: 3DIM arc interpolat
G02.4/G03.4 was commanded even although
there is no 3-dimension circular interpolation
specification.
P 90
• Check the specifications.
No spec: Thread cutting
A thread cutting command was issued even
although there is no thread cutting command
specification.
• Set the correct thread lead command for the
Illegal pitch vaule
thread cutting command.
The thread lead (thread pitch) when
performing the thread cutting command is
incorrect.
P 93
Remedy
• Reconsider the program.
• Reconsider the program.
P100
No spec: Cylindric interpolat
A cylindrical interpolation command was
issued even although there is no cylindrical
interpolation specification.
• Check the specifications.
P111
Plane selected while coord rot
Plane selection commands (G17, G18, G19)
were issued during a coordinate rotation
command (G68).
• After command G68, always issue a plane
selection command following a G69
(coordinate rotation cancel) command.
P112
• Issue plane selection commands after
Plane selected while R compen
completing (axis movement commands
• Plane selection commands (G17, G18,
issued after G40 cancel command) tool
G19) were issued while tool radius
radius compensation and nose R
compensation (G41, G42) and nose R
compensation commands.
compensation (G41, G42, G46) commands
were being issued.
• Plane selection commands were issued
after completing nose R compensation
commands when there are no further axis
movement commands after G40, and
compensation has not been cancelled.
P113
Illegal plane select
The circular command axis differs from the
selected plane.
P122
• Check the specifications.
No spec: Auto corner override
An auto corner override command (G62) was • Delete the G62 command from the program.
issued even although there is no auto corner
override specification.
II - 65
• Issue a circular command after correct plane
selection.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Reconsider the program.
P126
Invalid cmnd in high-accuracy
An illegal command was issued during the
high-accuracy control mode.
• A G code group 13 command was issued
during the high-accuracy control mode.
• Milling, cylindrical interpolation or pole
coordinate interpolation was commanded
during the high-accuracy control mode.
P130
2nd M function code illegal
The 2nd miscellaneous function address
commanded in the program differs from the
address set in the parameters.
miscellaneous function.
• Check and correct the 2nd miscellaneous
function address in the program.
P131
No spec: Cnst surface ctrl G96
A constant surface speed control command
(G96) was issued even although there is no
specification.
• Check the specifications.
• Change the constant surface speed control
command (G96) to a rotation speed
command (G97).
P132
Spindle rotation speed S=0
No spindle rotation speed command has
been issued.
• Reconsider the program.
P133
• Reconsider the parameter specified for the
Illegal P-No. G96
An invalid constant surface speed control axis constant surface speed control axis.
has been specified.
P140
No spec: Pos compen cmd
The position compensation command (G45
to G48) specifications are not available.
• Check the specifications.
P141
Pos compen during rotation
Position compensation was commanded
during the figure rotation or coordinate
rotation command.
• Reconsider the program.
P142
Pos compen invalid arc
A position compensation invalid arc
command was commanded.
• Reconsider the program.
P150
No spec: Nose R compensation
• Even though there were no tool radius
compensation specifications, tool radius
compensation commands (G41 and G42)
were issued.
• Even though there were no nose R
compensation specifications, nose R
compensation commands (G41, G42, and
G46) were issued.
• Check the specifications.
P151
Radius compen during arc mode
A compensation command (G40‚ G41‚ G42‚
G43‚ G44‚ G46) has been issued in the arc
modal (G02‚ G03).
P152
No intersection
In interference block processing during
execution of a tool radius compensation (G41
or G42) or nose R compensation (G41‚ G42‚
or G46) command‚ the intersection point after
one block is skipped cannot be determined.
• Issue the linear command (G01) or rapid
traverse command (G00) in the
compensation command block or cancel
block.
(Set the modal to linear interpolation.)
• Reconsider the program.
II - 66
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P153
Compensation interference
An interference error has arisen while the tool
radius compensation command (G41‚ G42) or
nose R compensation command (G41‚ G42‚
G46) was being executed.
P155
Fixed cyc exec during compen
A fixed cycle command has been issued in
the radius compensation mode.
P156
• Change the vector to that with which the
R compen direction not defined
compensation direction is defined.
At the start of G46 nose R compensation‚ the
• Exchange with a tool having a different tip
compensation direction is undefined if this
point No.
shift vector is used.
P157
R compen direction changed
During G46 nose R compensation‚ the
compensation direction is inverted.
• Change the G command to that which allows
inversion of the compensation direction (G00‚
G28‚ G30‚ G33‚ or G53).
• Exchange with a tool having a different tip
point No.
• Turn ON the "#8106 G46 NO REV-ERR"
parameter.
P158
Illegal tip point
During G46 nose R compensation‚ the tip
point is illegal (other than 1 to 8).
• Change the tip point No. to a legal one.
P170
No offset number
The compensation No. (DOO‚ TOO‚ HOO)
command was not given when the radius
compensation (G41‚ G42‚ G43‚ G46)
command was issued. Alternatively‚ the
compensation No. is larger than the number
of sets in the specifications.
• Add the compensation No. command to the
compensation command block.
• Check the number of compensation No. sets
a correct it to a compensation No. command
within the permitted number of tool
compensation sets.
P172
G10 L number error
(G10 L-No. error)
The L address command is not correct when
the G10 command is issued.
• Check the address L-No. of the G10
command and correct the No.
P173
• First check the number of compensation sets
G10 P number error
and then set the address P designation to
(G10 compensation error)
within the permitted number of sets.
When the G10 command is issued‚ a
compensation No. outside the permitted
number of sets in the specifications has been
commanded for the compensation No.
command.
P177
• The tool life management data cannot be
Tool life count active
Registration of tool life management data with registered when counting the used data. Turn
G10 was attempted when the used data count the used data count valid signal OFF.
valid signal was ON.
P178
Tool life data entry over
The number of registration groups‚ total
number of registered tools or the number of
registrations per group exceeded the
specifications range.
II - 67
Remedy
• Reconsider the program.
• The radius compensation mode is established
when a fixed cycle command is executed and
so the radius compensation cancel command
(G40) should be issued.
• Review the number of registrations.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P179
Illegal group No.
• When registering the tool life management
data with G10‚ the group No. was
commanded in duplicate.
• A group No. that was not registered was
designated during the T
99
command.
• An M code command must be issued as a
single command but coexists in the same
block as that of another M code command.
• The M code commands set in the same
group exist in the same block.
P180
No spec: Drilling cycle
A fixed cycle command was issued though
there are not fixed cycle (G72 - G89)
specifications.
P181
• Issue the spindle rotation speed command
No spindle command (Tap cycle)
(S) when the fixed cycle for drilling command
The spindle rotation speed command has not
G84‚ G74 (G84‚ G88) is given.
been issued when the fixed cycle for drilling
command is given.
P182
Synchronous tap error
Connection to the main spindle unit was not
established.
P183
• Specify the pitch data and the number of
No pitch/thread number
The pitch or thread number command has not threads by F or E command.
been issued in the tap cycle of a fixed cycle
for drilling command.
P184
• Check the pitch or the number of threads per
Pitch/thread number error
The pitch or the number of threads per inch is inch.
illegal in the tap cycle of the fixed cycle for
drilling command.
P190
No spec: Turning cycle
A lathe cutting cycle command was input
although the lathe cutting cycle was
undefined in the specification.
P191
• The radius set value in the lathe cycle
Taper length error
command must be smaller than the axis shift
In the lathe cutting cycle‚ the specified length
amount.
of taper section is illegal.
P192
Chamfering error
Chamfering in the thread cutting cycle is
illegal.
• Set a chamfering amount not exceeding the
cycle.
P200
No spec: MRC cycle
The compound type fixed cycle for turning
machining I (G70 to G73) was commanded
when the compound type fixed cycle for
turning machining I specifications were not
provided.
• Check the specification.
II - 68
Remedy
• The group No. cannot be commanded in
duplicate. When registering the group data‚
register it in group units.
• Correct to the correct group No.
• Check the specifications.
• Correct the program.
• Check connection to the main spindle.
• Check that the main spindle encoder exists.
• Check the specification.
• Delete the lathe cutting cycle command.
3. Program Error
Error No.
P201
Details
Remedy
• Delete the following G codes from this
Program error (MRC)
subprogram that is called with the compound
• When called with a compound type fixed
type fixed cycle for turning machining I
cycle for turning machining I command, the
commands (G70 to G73): G27‚ G28‚ G29,
subprogram contained at least one of the
G30‚ G31‚ G33‚ G34, and fixed cycle G
following commands:
codes.
• Reference position return command
• Remove G2 and G3 from the first move block
(G27, G28, G29, G30)
of the finish shape program in compound type
• Thread cutting (G33, G34)
fixed cycle for turning machining I.
• Fixed cycle skip-function (G31, G31.n)
• The first move block of the finish shape
program in compound type fixed cycle for
turning machining I contains an arc
command.
P202
Block over (MRC)
The number of blocks in the shape program
of the compound type fixed cycle for turning
machining I is over 50 or 200 (this differs
according to the model).
• Specify 50 or a less value. The number of
blocks in the shape program called by the
compound type fixed cycle for turning
machining I commands (G70 to G73) must be
decreased below 50 or 200 (this differs
according to the model).
P203
D cmnd figure error (MRC)
The compound type fixed cycle for turning
machining I (G70 to G73) shape program
could not cut the work normally because it
defined an abnormal shape.
• Check the compound type fixed cycle for
turning machining I (G70 to G73) shape
program.
P204
• Check the compound type fixed cycle for
E cmnd fixed cycle error
A command value of the compound type fixed turning machining (G70 to G76) command
value.
cycle for turning machining (G70 to G76) is
illegal.
P210
No spec: Pattern cycle
A compound type fixed cycle for turning
machining II (G74 to G76) command was
input although it was undefined in the
specification.
• Check the specification.
P220
No spec: Special fixed cycle
No special fixed cycle specifications are
available.
• Check the specifications.
P221
No. of special fixed holes = 0
A 0 has been specified for the number of
holes in special fixed cycle mode.
• Reconsider the program.
P222
G36 angle error
A G36 command specifies 0 for angle
intervals.
• Reconsider the program.
P223
• Reconsider the program.
G12/G13 radius error
The radius value specified with a G12 or G13
command is below the compensation
amount.
P224
No spec: Circular (G12/G13)
There are no circular cutting specifications.
P230
• Check the number of subprogram calls and
Subprogram nesting over
correct the program so that it does not exceed
• A subprogram has been called 8 or more
8 times.
times in succession from the subprogram.
• The program in the data server contains the
M198 command.
II - 69
• Check the specifications.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P231
No sequence No.
At subprogram call time‚ the sequence No.
set at return from the subprogram or specified
by GOTO‚ was not set.
P232
No program No.
The subprogram has not been found when
the subprogram is called.
• Enter the subprogram.
P235
Program editing
Operation was attempted for the file under
program editing.
• Execute the program again after completion
of program editing.
P241
No variable No.
The variable No. commanded is higher than
the Nos. in the specifications.
• Check the specifications.
• Check the program variable No.
P242
• Designate the "=" sign in the variable
= not defined at vrble set
definition of the program.
The "=" sign has not been commanded when
a variable is defined.
• Correct the program.
Can't use variables
An invalid variable has been specified in the
left or right side of an operation expression.
P243
Remedy
• Specify the sequence Nos. in the call block of
the subprogram.
P252
• Reconsider the program.
Coord rotate in fig. rotation
A coordinate rotation related command (G68,
G69) was issued during figure rotation.
P260
No spec: Coordinates rotation
Even though there were no coordinate
rotation specifications, a coordinate rotation
command was issued.
• Check the specifications.
P270
No spec: User macro
A macro specification was commanded
though there are no such command
specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P271
No spec: Macro interrupt
A macro interruption command has been
issued though it is not included in the
specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P272
NC and macro texts in a block
A statement and a macro statement exist
together in the same block.
• Reconsider the program and place the
executable statement and macro statement in
separate blocks.
P273
• Reconsider the program and correct it so that
Macro call nesting over
The number of macro call nests exceeded the the macro calls do not exceed the limit
imposed by the specification.
specifications.
P275
Macro argument over
The number of macro call argument type II
sets has exceeded the limit.
• Reconsider the program.
P276
Illegal G67 command
A G67 command was issued though it was
not during the G66 command modal.
P277
Macro alarm message
An alarm command has been issued in
#3000.
• Reconsider the program.
• The G67 command is the call cancel
command and so the G66 command must be
designated first before it is issued.
• Refer to the operator messages on the DIAG
screen.
• Refer to the instruction manual issued by the
machine tool builder.
II - 70
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Reconsider the program and correct it so the
number of "[" or "]" does not exceed five.
P280
Brackets [ ] nesting over
The number of parentheses "[" or "]" which
can be commanded in a single block has
exceeded five.
P281
• Reconsider the program and correct it so that
Brackets [ ] not paired
"[" and "]" parentheses are paired up properly.
The number of "[" and "]" parentheses
commanded in a single block does not match.
P282
Calculation impossible
The arithmetic formula is incorrect.
• Reconsider the program and correct the
formula.
P283
Divided by zero
The denominator of the division is zero.
• Reconsider the program and correct it so that
the denominator for division in the formula is
not zero.
P290
IF sentence error
There is an error in the IF conditional
GOTO statement.
• Reconsider the program.
P291
WHILE sentence error
There is an error in the WHILE conditional
DO -END statement.
• Reconsider the program.
P292
SETVN sentence error
There is an error in the SETVN statement
when the variable name setting was made.
• Reconsider the program.
• The number of characters in the variable
name of the SETVN statement must be 7 or
less.
P293
DO-END nesting over
The number of DO-END nesting levels in
WHILE conditional DO -END statement
has exceeded 27.
• Reconsider the program and correct it so that
the nesting levels of the DO - END statement
does not exceed 27.
P294
DO and END not paired
The DO's and END's are not paired off
properly.
• Reconsider the program and correct it so that
the DO's and END's are paired off properly.
P295
• During tape operation‚ a program which
WHILE/GOTO in tape
includes a WHILE or GOTO statement cannot
There is a WHILE or GOTO statement on the
be executed and so the memory operation
tape during tape operation.
mode is established instead.
P296
No address (macro)
A required address has not been specified in
the user macro.
P297
• Review the program.
Address-A error
The user macro does not use address A as a
variable.
P298
G200-G202 cmnd in tape
User macro G200‚ G201‚ or G202 was
specified during tape or MDI mode.
• Review the program.
P300
Variable name illegal
The variable names have not been
commanded properly.
• Reconsider the variable names in the
program and correct them.
P301
Variable name duplicated
The name of the variable has been
duplicated.
• Correct the program so that the name is not
duplicated.
P310
Not use GMSTB macro code
G, M, S, T, or B macro code was called
during fixed cycle.
• Review the program.
• Review the parameter.
II - 71
• Review the program.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P350
No spec: Scaling command
The scaling command (G50, G51) was
issued when the scaling specifications were
not available.
P360
No spec: Program mirror
A mirror image (G50.1 or G51.1) command
has been issued though the programmable
mirror image specifications are not provided.
• Check the specifications.
P370
No spec: Facing t-post MR
The facing turret mirror image specifications
are not provided.
• Check the specifications.
P371
No spec: Facing t-post MR
The mirror image for facing tool posts
specifications are not provided.
• Check the program.
• Check the parameters.
P380
Facing t-post MR illegal
Mirror image for facing tool posts was
commanded to an axis for which external
mirror image or parameter mirror image is
valid.
Mirror image for facing tool posts validating
mirror image for a rotary axis was
commanded.
• Check the specifications.
• Remove the corner chamfering/corner
rounding command from the program.
P381
•
No spec: Arc R/C
Corner chamfering II /corner rounding II was
specified in the arc interpolation block
although corner chamfering/corner rounding II
is unsupported.
•
No corner movement
The block next to corner chamfering/
corner rounding is not a movement
command.
P382
Remedy
• Check the specifications.
Check the specifications.
Replace the block succeeding the corner
chamfering/corner rounding command by
G01 command.
• Make the corner chamfering/corner rounding
less than the movement distance since this
distance is shorter than the corner chamfering/
corner rounding.
P383
Corner movement short
In the corner chamfering/corner rounding
command‚ the movement distance was
shorter than the value in the corner
chamfering/corner rounding command.
P384
• Make the corner chamfering/corner rounding
Corner next movement short
less than the movement distance since this
When the corner chamfering/corner rounding
distance in the following block is shorter than
command was input‚ the movement distance
the corner chamfering/corner rounding.
in the following block was shorter than the
length of the corner chamfering/corner
rounding.
P385
Corner during G00/G33
A block with corner chamfering/corner
rounding was given during G00 or G33
modal.
• Recheck the program.
P390
No spec: Geometric
A geometric command was issued though
there are no geometric specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P391
No spec: Geometric arc
There are no geometric IB specifications.
• Check the specifications.
II - 72
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Correct the geometric angle.
P392
Angle < 1 degree (GEOMT)
The angular difference between the
geometric line and line is 1° or less.
P393
• Specify this block by an absolute value.
Inc value in 2nd block (GEOMT)
The second geometric block was specified by
an incremental value.
• Specify the G01 command.
No linear move command (GEOMT)
The second geometric block contains no
linear command.
P394
P395
Illegal address (GEOMT)
The geometric format is invalid.
• Recheck the program.
P396
Plane selected in GEOMT ctrl
A plane switching command was executed
during geometric command processing.
• Execute the plane switching command before
geometric command processing.
P397
• Recheck the geometric circular arc command
Arc error (GEOMT)
and the preceding and following commands.
In geometric IB‚ the circular arc end point
does not contact or cross the next block start
point.
• Check the specifications.
No spec: Geometric1B
Although the geometric IB specifications are
not included‚ a geometric command is given.
P398
P421
• Check the program.
Parameter input error
• The specified parameter No. or set data is
illegal.
• An illegal G command address was input in
parameter input mode.
• A parameter input command was input
during fixed cycle modal or nose R
compensation.
P430
• Execute reference position return manually.
R-pnt return incomplete
• The command was issued to an axis for
• A command was issued to move an axis‚
which axis removal is validated so invalidate
which has not returned to the reference
axis removal.
position‚ away from that reference position.
• A command was issued to an axis removal
axis.
P431
No spec: 2,3,4th R-point ret
A command for second‚ third or fourth
reference position return was issued though
there are no such command specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P434
Compare error
One of the axes did not return to the start
position when the reference position check
command (G27) was executed.
• Check the program.
P435
• An M code command cannot be issued in a
G27 and M commands in a block
An M command was issued simultaneously in G27 command block and so the G27
command and M code command must be
the G27 command block.
placed in separate blocks.
P436
• An M code command cannot be issued in a
G29 and M commands in a block
An M command was issued simultaneously in G29 command block and so the G29
command and M code command must be
the G29 command block.
placed in separate blocks.
II - 73
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Review the program.
P438
G52 invalid during G54.1
A local coordinate system command was
issued during execution of the G54.1
command.
P450
No spec: Chuck barrier
The chuck barrier on command (G22) was
specified although the chuck barrier was
undefined in the specification.
• Check the specification.
P460
Tape I/O error
An error has arisen in the tape reader or‚
alternatively‚ in the printer during macro
printing.
• Check the power and cable of the connected
devices.
• Check the I/O device parameters.
P461
File I/O error
A file of the machining program cannot be
read.
• In memory mode, the programs stored in
memory may have been destroyed. Output
all of the programs and tool data once and
format them.
• Ensure that the external device (including a
floppy disk drive and IC card) that contains
the file is mounted.
P462
Computer link commu error
A communication error occurred during the
BTR operation.
• "L01 Computer link error" is displayed
simultaneously, so remedy the problem
according to the error No.
P480
No spec: Milling
• Milling was commanded when the milling
specifications were not provided.
• Polar coordinate interpolation was
commanded when the polar coordinate
interpolation specifications were not
provided.
• Check the specification.
P481
• Check the program.
Illegal G code (mill)
• An illegal G code was used during the
milling mode.
• An illegal G code was used during
cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation.
• The G07.1 command was issued during the
tool radius compensation.
P482
• Check the machining program, parameters
Illegal axis (mill)
and PLC I/F signal.
• A rotary axis was commanded during the
milling mode.
• Milling was executed even though an illegal
value was set for the milling axis No.
• Cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation was commanded during mirror
image.
• Cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation was commanded before the
tool compensation was completed after the
T command.
• G07.1 was commanded when cylindrical
interpolation was not possible (there is no
rotary axis, or external mirror image is ON).
• An axis other than a cylindrical coordinate
system axis was commanded during
cylindrical interpolation.
II - 74
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P484
R-pnt ret incomplete (mill)
• Movement was commanded to an axis that
had not completed reference position return
during the milling mode.
• Movement was commanded to an axis that
had not completed reference position return
during cylindrical interpolation or polar
coordinate interpolation.
P485
Illegal modal (mill)
• The milling mode was turned ON during
nose R compensation or constant surface
speed control.
• A T command was issued during the milling
mode.
• The mode was switched from milling to
cutting during tool compensation.
• Cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation was commanded during the
constant surface speed control mode
(G96).
• The command unacceptable in the
cylindrical interpolation was issued.
• A T command was issued during the
cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation mode.
• A movement command was issued when
the plane was not selected just before or
after the G07.1 command.
• A plane selection command was issued
during the polar coordinate interpolation
mode.
• Cylindrical interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation was commanded during tool
radius compensation.
• The G16 plane in which the radius value of
a cylinder is 0 was specified.
• A cylindrical interpolation or polar
coordinate interpolation command was
issued during coordinate rotation by
program (G68).
P486
• Check the program.
Milling error
• The milling command was issued during the
mirror image (when parameter or external
input is turned ON).
• Polar coordinate interpolation, cylindrical
interpolation or milling interpolation was
commanded during mirror image for facing
tool posts.
• The start command of the cylindrical
interpolation or polar coordinate
interpolation was issued during the normal
line control.
P511
• Check the program.
Synchronization M code error
• Two or more synchronization M codes were
commanded in the same block.
• The synchronization M code and "!" code
were commanded in the same block.
II - 75
Remedy
• Carry out manual reference point return.
•
•
•
•
•
Check the program.
Before issuing G12.1, issue G40 or G97.
Before issuing G12.1, issue a T command.
Before issuing G13.1, issue G40.
Specify the radius value of a cylinder other
than 0, or specify the X axis's current value
other than 0 before issuing G12.1/G16.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Check the specifications.
P550
No spec: G06.2(NURBS)
There is no NURBS interpolation option.
P551
G06.2 knot error
The knot (k) command value is smaller than
the value for the previous block.
• Reconsider the program.
• Specify the knot by monotone increment.
P552
Start point of 1st G06.2 err
The block end point immediately before the
G06.2 command and the G06.2 first block
command value do not match.
• Match the G06.2 first block coordinate
command value with the previous block end
point.
P554
Invld manual interrupt in G6.2
Manual interruption using a block was
performed while in G06.2 mode.
• Perform for blocks other than G06.2 mode
when manually interrupting.
P600
No spec: Auto TLM
An automatic tool length measurement
command (G37) was execute though there
are no such command specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P601
No spec: Skip
A skip command (G31) was issued though
there are no such command specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P602
No spec: Multi skip
A multiple skip command (G31.1‚ G31.2 or
G31.3) was issued though there are no such
command specifications.
• Check the specifications.
P603
Skip speed 0
The skip speed is 0.
• Specify the skip speed.
P604
TLM illegal axis
No axis or more than one axis was specified
in the automatic tool length measurement
block.
• Specify only one axis.
P605
T & TLM command in a block
The T code is in the same block as the
automatic tool length measurement block.
• Specify this T code before the block.
P606
• Specify this T code before the block.
T cmnd not found before TLM
The T code was not yet specified in automatic
tool length measurement.
P607
• Check the program.
TLM illegal signal
Before the area specified by the D command
or decelerating area parameter d‚ the
measurement position arrival signal went ON.
The signal remains OFF to the end.
P608
Skip during radius compen
A skip command was specified during radius
compensation processing.
• Specify a radius compensation cancel (G40)
command or remove the skip command.
P610
Illegal parameter
• The parameter setting is not correct.
• G114.1 was commanded when the spindle
synchronization with PLC I/F command was
selected.
• G113 was commanded when the
spindle-spindle polygon machining option
was OFF and the spindle synchronization
with PLC I/F command was selected.
• Check whether "#1549 Iv0vR1" to "#1553
Iv0vR5" are set in descending order (in order
of large values).
• Check whether "#1554 Iv0rd2" to "#1557
Iv0rd5" are set in descending order.
• Check and correct "#1514 expLinax" and
"#1515 expRotax".
• Check the program.
• Check the parameter.
II - 76
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
Remedy
• Check the specification.
P611
No spec: Exponential function
Specification for exponential interpolation is
not available.
P612
Exponential function error
A movement command for exponential
interpolation was issued during mirror image
for facing tool posts.
P700
• Check the program.
Illegal command value
Spindle synchronization was commanded to a • Check the parameter.
spindle that is not connected serially.
P900
No spec: Normal line control
A normal line control command (G40.1,
G41.1, G42.1) was issued when the normal
line control specifications were not provided.
• Check the specifications.
P901
Normal line control axis G92
A coordinate system preset command (G92)
was issued to a normal line control axis
during normal line control.
• Check the program.
P902
Normal line control axis error
• The normal line control axis was set to a
linear axis.
• The normal line control axis was set to the
linear type rotary axis II axis.
• The normal line control axis has not been
set.
• The normal line control axis was the same
as the plane selection axis.
• Correct the normal line control axis.
P903
Plane chg in Normal line ctrl
The plane selection command (G17, G18,
G19) was issued during normal line control.
• Delete the plane selection command (G17,
G18, G19) from the program for normal line
control.
P920
No spec: 3D coord conv
There is no specification for 3-dimensional
coordinate conversion.
• Check the specifications.
P921
• Refer to the "Programming Instruction Manual
Illegal G code at 3D coord
A G code command that cannot be performed (Machining Center Series)" for further details
of usable G commands.
was made during 3-dimensional coordinate
• When the basic specification parameter
conversion modal.
"#1229 set01/bit3" is ON, turn the parameter
OFF or specify the constant surface speed
control cancel (G97).
P922
Illegal mode at 3D coord
A 3-dimensional coordinate conversion
command was issude during a modal for
which 3-dimensional coordinate conversion
cannot be performed.
P923
• Refer to the "Programming Instruction Manual
Illegal addr in 3D coord blk
(Machining Center Series)" for further details
A G code for which G68 to combination could
of usable G commands.
not be performed was specified for the same
block.
II - 77
• Check the program.
• Refer to the "Programming Instruction Manual
(Machining Center Series)" for further details
of usable G commands.
3. Program Error
Error No.
Details
P930
No spec: Tool axis compen
A tool length compensation along the tool axis
command was issued even although there is
no tool length compensation along the tool
axis specification.
P931
Executing tool axis compen
A G code that cannot be commanded exists
during tool length compensation along the
tool axis.
• Reconsider the program.
P932
Rot axis parameter error
There is a mistake in the orthogonal axis
name and rotary axis name in the rotary axis
configuration parameters.
• Set the correct value and reboot.
P940
No spec: Tool tip control
There is no tool tip center control
specification.
• Check the specifications.
P941
• Reconsider the program.
Invalid T tip control command
A tool tip center control command was issued
during a modal for which a tool tip center
control command cannot be issued.
P942
Invalid cmnd during T tip ctrl
A G code that cannot be commanded was
issued during tool tip center control.
P943
• Reconsider the program.
Tool posture command illegal
In the case of tool tip center control type 1, if
the signs at the tool-side rotary axis or table
base-side rotary axis start and finish points
differ, a tool base-side rotary axis or table
workpiece-side rotary axis rotation exists for
the same block, and does not pass a singular
point.
In the case of tool tip center control type 2,
the posture vector command is incorrect.
P990
• Reduce the number of commands that
PREPRO error
require pre-reading or delete such
Combining commands that required
commands.
pre-reading (nose R offset‚ corner
chamfering/corner rounding‚ geometric I‚
geometric IB‚ and compound type fixed cycle
for turning machining) resulted in eight or
more pre-read blocks.
II - 78
Remedy
• Check the specifications.
• Reconsider the program.
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Follow this section to troubleshoot the alarms that occur during start up or while the machine is operating. If
the state is not improved with the following investigations, the drive unit may be faulty. Exchange the unit with
another unit of the same capacity, and check whether the state is improved.
4.1.1 Troubleshooting at Power ON
If the NC system does not start up correctly and a system error occurs when the NC power is turned ON, the
drive unit may not have been started up properly. Check the LED display on the drive unit, and take
measures according to this section.
LED
display
AA
Symptom
Initial communication
with the CNC was not
completed correctly.
Cause of occurrence
Investigation method
The drive unit axis No.
setting is incorrect.
Is there any other drive unit that has the Set correctly.
same axis No. set?
The CNC setting is
incorrect.
Is the No. of CNC controlled axes
correct?
Communication with CNC is Is the connector (CN1A, CN1B)
disconnected?
incorrect.
Ab
12
Initial communication
with the CNC was not
carried out.
Remedy
The axis is not used, the
setting is for use inhibiting.
Connect correctly.
Is the cable broken?
Check the conductivity with a tester.
Replace the cable.
Is the axis setting rotary switch set to
"7" to "F"?
Set correctly.
Communication with CNC is Is the connector (CN1A, CN1B)
disconnected?
incorrect.
An error was detected in The CPU peripheral circuit
the unit's memory and IC is abnormal.
during the self-diagnosis
at power ON.
Set correctly.
Connect correctly.
Is the cable broken?
Check the conductivity with a tester
Replace the cable.
Check the repeatability.
Replace the unit.
Check whether there is any abnormality Improve the
with the unit's surrounding
surrounding
environment, etc.
environment.
The drive unit has started up normally if the following type of emergency stop (E7) is displayed on the display
unit's LED display.
F1
F+axis No.
E7
Emergency stop
F1
F+axis No.
E7
Emergency stop
Not lit
Normal drive unit LED display at NC power ON (for 1st axis)
II - 79
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
4.1.2 Troubleshooting for Each Alarm No.
Alarm No.
11
1
Investigation details
Investigation results
Check the setting of the axis
The same axis No. is set for the L
selection switch on the top of the unit. and M axes.
Alarm No.
12
1
2
3
1
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
{
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Investigation results
The version was changed.
Remedies
Try replacing with the drive unit
containing the original software
version.
The version was not changed.
Investigate item 2.
The error is always repeated.
Replace the drive unit.
The state returns to normal once, but Investigate item 3.
occurs sometimes thereafter.
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
Software processing error 2
The software process was not completed within the specified time. (CPU2)
Investigation details
Carry out the items for alarm No. 13.
Alarm No.
16
SV SP
Software processing error 1
The software process was not completed within the specified time. (CPU1)
Investigation details
Check whether the servo software
version was changed recently.
Alarm No.
14
Remedies
Correctly set the axis No.
0 = No. 1 axis, 1 = No. 2 axis, ...
Memory error 1
A CPU or internal memory error was detected during the self-check at power ON.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Refer to "4.1.1 Troubleshooting at power ON".
Alarm No.
13
1
Axis selection error
The axis No. selection switch setting is incorrect.
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Magnetic pole position detection error
Creation of the initial magnetic pole, required for motor control, was not completed.
1
Investigation details
Was the spindle drive unit replaced?
Investigation results
It was replaced.
2
Check the spindle parameters.
It was not replaced.
SP205 = 0
SP205 = 1
II - 80
Remedies
SV SP
Carry out automatic adjustment of the
PLG Z-phase.
{
Investigate item 2.
Carry out automatic adjustment of the
PLG Z-phase.
Set SP205 to 0, and turn the NC
{
power ON again. Then, carry out
automatic adjustment of the PLG
Z-phase.
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
17
1
2
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Alarm No.
18
1
2
3
4
5
A/D converter error
An error was detected in the A/D converter for current FB detection.
Investigation results
The error is always repeated.
The state returns to normal once, but
occurs sometimes thereafter.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
2
SV SP
{
{
Replace the drive unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
{
Motor side detector, initial communication error
Initial communication with the motor end detector was not possible.
Investigation details
Check the servo parameter (SV025)
setting value.
OSE104: 0, OSA104: 1
Are all other set to 2?
(Excluding slave axis for
synchronous control)
Check whether the drive unit
connectors (CN2) or detector
connectors are disconnected.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
detector cable connection with a
tester.
Connect to another normal axis drive
unit, and check whether the fault is
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The value is not set correctly.
The value is set correctly.
Remedies
Correctly set SV025.
Investigate item 2.
SV SP
{
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
There is a connection fault.
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 3.
Replace the detector cable.
Investigate item 4.
{
The alarm is on the drive unit side.
The alarm is on the detector side.
Replace the drive unit.
Investigate item 5.
{
No abnormality is found in particular.
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Correctly install.
{
Synchronous control/detector communication error
Initial communication with the master axis motor end detector was not possible when the closed current
command synchronous control was set. Or, the communication was cut off.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the MDS-B-SD unit
The connector is disconnected.
Correctly connect.
{
CN2B connector is disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Check the continuity of the cable
The cable is disconnected or
Replace the cable.
between the MDS-B-SD unit CN2B
incorrectly connected.
{
and the slave side drive unit CN3.
There is no abnormality in particular. Try replacing the drive unit or
MDS-B-SD unit.
Alarm No.
19
1
Remedies
Replace the drive unit.
Investigate item 2.
II - 81
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
1A
1
2
3
4
5
Investigation details
Check the servo parameter
(SV025.pen) setting value.
Are the serial communication
parameters set for the pulse-type
detector?
Check whether the drive unit
connectors (CN3) or detector
connectors are disconnected.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
detector cable connection with a
tester.
Connect to another normal axis drive
unit, and check whether the fault is
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Alarm No.
1B
1
2
Machine side detector, initial communication error
Initial communication with the linear scale or ball screw end detector was not possible.
Investigation results
The value is not set correctly.
The value is set correctly.
Remedies
Correctly set SV025.
Investigate item 2.
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
There is a connection fault.
The connection is normal.
Correctly install.
Investigate item 3.
Replace the detector cable.
Investigate item 4.
{
The alarm is on the drive unit side.
The alarm is on the detector side.
Replace the drive unit.
Investigate item 5.
{
No abnormality is found in particular.
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
SV SP
{
{
Machine side detector, CPU error 1
A CPU initial error was detected with the linear scale or ball screw end detector.
Investigation details
Connect to another normal axis drive
unit, and check whether the fault is
on the drive unit side or scale side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The alarm is on the drive unit side.
The alarm is on the detector side.
Remedies
Replace the drive unit.
Investigate item 2.
No abnormality is found in particular.
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
SV SP
{
{
Machine side detector, EEPROM/LED abnormality
An error was detected in the data stored in the memory by the linear scale. Or, LED deterioration was
detected with the linear scale.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Alarm No.
1C
1
Alarm No.
1D
1
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Alarm No.
1E
1
Machine side detector, data error
A data error was detected with the linear scale or ball screw end detector.
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Remedies
SV SP
{
Machine side detector, memory error
An internal memory error was detected with the linear scale.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Investigation results
II - 82
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Machine side detector, communication error
An error was detected in the communication data with the linear scale or ball screw end detector. Or,
the communication was cut off.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors (CN3) or detector
loose).
{
connectors are disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Is the detector cable wired in the
The cables are wired near each
Improve the cable wiring.
same conduit as the motor's power
other. (Noise is entering from the
{
cable or are the two cables laid in
power cable.)
parallel near each other?
The wires are sufficiently separated. Investigate item 3.
Is the motor FG wire connected only The motor FG wire is grounded on
Ground the motor to one point,
to the drive unit which drives it?
the motor side.
connecting the wires together on the
{
(Is the motor grounded to one point?)
drive unit side.
The motor is grounded to one point. Investigate item 4.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 5.
tester. (Is the cable shielded?)
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
Replace the drive unit.
{
unit, and check whether the fault is
The alarm is on the detector side.
Investigate item 6.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detector.
the detector's ambient environment.
(With the absolute position system,
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
the zero point must be established.)
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
{
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
1F
1
2
3
4
5
6
Motor side detector, No signal 1
A PLG Z-phase no signal was detected.
An error was detected in the A/B phase output waveform during PLG automatic adjustment.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors (CN5) or detector
loose).
{
connectors are disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 3.
tester.
Check whether the alarm occurred
The alarm occurred during PLG
Investigate item 4.
during PLG automatic adjustment.
automatic adjustment.
{
The alarm occurred during normal
Investigate item 5.
operation.
Check the PLG output waveform (A/B There is a problem. (The A/B phase Adjust the PLG output waveform.
phase).
input voltage is 0.8V or less or 2.2V
{
or higher.)
Normal
Investigate item 6.
Check the PLG output waveform
There is a problem. (The output
Investigate item 7.
(Z-phase).
waveform is 0V even after the gears'
{
Z-phase is passed.)
Normal
Investigate item 6.
Check the occurrence frequency.
Occurs each time.
Replace the drive unit.
Occurs occasionally.
Check whether the cable is
{
disconnected, whether there is a
contact fault, or a detector fault.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the PLG detector.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take measures according to the error
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
cause.
grounding)
Cable disconnection, contact fault.
{
The sensor is hot during high-load
operation.
Review the operation, and adjust the
Z-phase again.
Alarm No.
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
II - 83
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Machine side detector, No signal 2
The pulse-type linear scale or ball screw end detector's ABZ-phase no signal was detected with the
servo, or the encoder no-signal was detected with the spindle.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the servo parameter (SV025. The value is not set correctly.
Correctly set SV025.
pen) setting value.
The value is set correctly.
Investigate item 3.
{
Are the pulse-type detector
parameters set for a serial
communication type detector?
Check the spindle parameter (SP037, Encoder orientation is not used.
Set SP037, bit0 to 0.
{
bit0) settings.
Encoder orientation is used.
Investigate item 3.
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors (servo: CN3, spindle:
loose).
{ {
CN6) or detector connectors are
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 4.
disconnected.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{ {
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 5.
tester.
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
Replace the drive unit.
{ {
unit, and check whether the fault is
The alarm is on the detector side.
Investigate item 6.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detector.
the detector's ambient environment.
(With the absolute position system,
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
the zero point must be established.)
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
{ {
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
21
1
2
3
4
5
6
Excessive speed deflection 1
A difference of 50r/min or more between the speed command and speed feedback continued for longer
than the set time.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the U, V and W wiring
The wires are not correctly
Correctly connect.
between the spindle drive unit and
connected.
{
spindle motor.
The wires are correctly connected.
Investigate item 2.
Check the settings for SP034,
The correct values are not set.
Correctly set.
{
SP040, SP055, and SP257 to
The correct values are set.
Investigate item 3.
SP384.
Measure the acceleration/
12sec or more.
Increase the SP055 setting value.
deceleration time constants.
Less than 12sec.
Investigate item 4.
{
Measure the time required to reach
the reverse run maximum speed from
the forward run maximum speed.
Measure the load during cutting.
120% or more.
Reduce the load.
{
Less than 120%.
Investigate item 5.
Check the PLG output waveform.
There is a problem.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
{
Normal.
Replace the drive unit.
Alarm No.
23
1
2
3
4
5
II - 84
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
25
1
2
3
4
5
Absolute position lost
The backup voltage in the absolute position detector dropped causing the absolute position to be lost.
Investigation details
Is warning 9F occurring at the same
time?
Measure the battery voltage with a
tester.
Did alarm 18 occur when the power
was turned ON the last time?
Investigation results
The warning is occurring.
The warning is not occurring.
3V or less.
3V or more.
Alarm 18 occurred.
Alarm 18 did not occur.
Was the detector cable or battery
The unit was left for a long time.
cable disconnected from the unit for a Guide at delivery : 20 hours or more
long time?
After 5 years
: 10 hours or more
The cables were not disconnected.
Check the detector cable or battery
The connection is faulty.
cable connection with a tester.
The connection is normal.
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
Investigate item 3.
Replace the battery, and establish
the zero point.
Check the NC bus cable connection.
Turn the drive unit control power ON
again, and establish the zero point.
Investigate item 4.
Turn the drive unit control power ON
again, and establish the zero point.
Investigate item 5.
Replace the cable.
Replace the drive unit.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
Unusable axis error
A power module error is occurring with the axis for which the axis No. selection switch is set to "F" (not
used axis).
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
26
1
Alarm No.
27
1
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Alarm No.
28
1
2
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
1
Remedies
SV SP
{
Investigation results
The rapid traverse rate is higher than
the specified value.
The rapid traverse rate is less than
the specified value.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Remedies
Use within the specified range.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the linear scale.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
{
Machine side detector, absolute position data error
An error was detected in the absolute position data detection circuit with the linear scale.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Alarm No.
2A
Investigation results
Machine side detector, overspeed
A speed exceeding the specified maximum speed was detected with the linear scale.
Investigation details
Check the linear scale's maximum
speed.
Alarm No.
29
1
Machine side detector, CPU error 2
A CPU error was detected with the linear scale.
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Machine side detector, incremental position data error
An error was detected in the relative position data detection circuit with the linear scale.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "1B" items.
Investigation results
II - 85
Remedies
SV SP
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
2B
1
Investigation details
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Alarm No.
2C
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Remedies
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Remedies
SV SP
{
Motor side detector, data error
A data error was detected with the motor end detector.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "2B" items.
Alarm No.
2F
Investigation results
No abnormality is found in particular.
Motor side detector, EEPROM/LED error
Deterioration of the LEDs was detected with the motor end detector.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "2B" items.
Alarm No.
2D
1
Motor side detector, CPU error 1
A CPU initial error was detected with the motor end detector.
Investigation results
Motor side detector, communication error
A communication data error was detected with the motor end detector. Or, communication was cut off.
Investigation details
Check whether the drive unit
connectors (CN2) or detector
connectors are disconnected.
Investigation results
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
Is the detector cable wired in the
The cables are wired near each
same conduit as the motor's power
other. (Noise is entering from the
cable or are the two cables laid in
power cable.)
parallel near each other?
The wires are sufficiently separated.
Is the motor FG wire connected only The motor FG wire is grounded on
to the drive unit which drives it?
the motor side.
(Is the motor grounded to one point?) The motor is grounded to one point.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
tester. (Is the cable shielded?)
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
unit, and check whether the fault is
The alarm is on the detector side.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular.
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
II - 86
Remedies
Correctly install.
SV SP
{
Investigate item 2.
Improve the cable wiring.
{
Investigate item 3.
Connect together on the drive unit
side.
Investigate item 4.
Replace the detector cable.
Investigate item 5.
{
{
Replace the drive unit.
Investigate item 6.
{
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
31
1
2
3
Overspeed
A rotation speed exceeding the motor's tolerable rotation speed was detected.
Investigation details
Check the rapid traverse rate (rapid)
and motor maximum rotation speed.
Check the settings for the servo
parameters SV001 (PC1), SV002
(PC2), SV018 (PIT) and SV025
(MTYP).
Confirm the spindle parameter
SP017 (TSP) setting.
4
Confirm the PLG output waveform.
5
Check whether the speed waveform
is overshooting.
Investigation results
The rapid traverse rate is too fast.
The speed is within the motor's
maximum rotation speed.
The settings are incorrect.
Correctly set.
The setting is incorrect.
The alarm is detected at 115% of
SP017.
Correctly set.
There is a problem.
Normal.
The waveform is overshooting.
The waveform is not overshooting.
Alarm No.
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Remedies
Set within the motor's maximum
rotation speed.
Investigate item 2.
Correctly set.
Investigate item 5.
SV SP
{
{
Correctly set.
{
Investigate item 4.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
Investigate item 5.
Increase the acceleration/
deceleration time constant.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex.: Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
{
{
{
Power module overcurrent
The power module's overcurrent protection function activated.
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check the parameter setting.
• Motor type
Check the parameter settings.
• Current loop gain
• Speed loop gain
Disconnect the UVW phase wiring
from the terminal block, and the
cannon plug from the motor. Check
the insulation with a tester.
Check the insulation between the
motor power cable and FG.
Connect the cannon plug, and check
the insulation between the power
cable and FG.
Check for any abnormalities in the
motor's ambient environment.
(Ex.: Ambient temperature, cutting
water)
Investigation results
Remedies
The alarm occurs before READY ON. Check investigation item 2 and
(The drive unit is faulty.)
following, and remove the cause of
the fault. Then replace the drive unit.
The alarm occurs after READY ON.
Investigate item 2.
The setting is incorrect.
Correctly set.
Servo : SV025
Spindle : SP034, SP040, SP257 to
SP384
The setting is correct.
Investigate item 3.
The setting is large compared to the Set the standard value.
standard value.
The standard value is set.
Investigate item 4.
The power cable is short-circuited.
Replace the motor's power cable.
There is no problem.
Investigate item 5.
SV SP
The power cable is short-circuited.
There is no problem.
The motor is short-circuited.
There is no problem.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
II - 87
Replace the motor's power cable.
Investigate item 6.
Replace the motor.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Investigate item 7.
Replace the drive unit.
Replace the motor and improve the
motor installation environment.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
34
1
2
3
4
Investigation details
Try replacing the terminator or
battery unit.
Check the NC bus communication
cable connection.
• Is the cable disconnected?
• Is the communication pair cable
connected in reverse?
Change the order of the connected
drive units.
(The rotary switch does not need to
be changed.)
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Alarm No.
35
1
2
3
4
Investigation results
The state is improved.
The state is not improved.
The connection is incorrect.
There is no problem.
Remedies
Replace the cause of the fault.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the cable.
Investigate item 3.
The alarm is on the cable
Replace the cable.
connections.
The alarm is on the unit connections. Investigate item 4.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
NC command error
The movement command data received from the NC was excessive.
Investigation details
Is the rapid traverse rate large for
using a sub-micron system or rotary
axis?
Alarm No.
36
1
Communication or CRC error between NC and drive unit
An error was detected in the data received from the NC.
Investigation results
The rapid traverse rate is large.
The rate is not especially large.
Remedies
Check the rapid traverse rate limit.
Look for problems on the NC side,
such as not being able to follow up
the position FB.
SV SP
{
{
Communication or transmission error between NC and drive unit
Communication from the NC was cut off.
Investigation details
Check whether the NC bus
communication cable connectors
(CN1A, CN1B) are disconnected.
Check the NC bus communication
cable connection.
• Is the cable disconnected?
• Is the communication pair cable
connected in reverse?
Change the order of the connected
drive units.
(The rotary switch does not need to
be changed.)
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The state is not improved.
The connection is incorrect.
There is no problem.
Remedies
Connect correctly.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the cable.
Investigate item 3.
The alarm is on the cable
Replace the cable.
connections.
The alarm is on the unit connections. Investigate item 4.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
II - 88
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Initial parameter error
An illegal parameter was detected in the parameters received from the NC at NC power ON.
"S02 initial parameter error ####" is displayed on the NC screen. #### indicates the incorrect
parameter No.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the error parameter No.
SV001 to SV065 (M60S Series: 2201 Set the value within the designated
to 2265)
setting range.
SP001 to SP384 (M60S Series: 3201
{ {
to 3584)
SV101 (M60S Series: 2301)
Check SV001, SV002 and SV018.
The electronic gears are overflowing.
SV102 (M60S Series: 2302)
Absolute position control cannot be
The absolute position detection
used. To use, change to an absolute
parameter is valid when OSE104 and position detector.
OSE105 are connected.
{
SV104 (M60S Series: 2304)
SHG control cannot be used.
No SHG control operation is
provided.
SV105 (M60S Series: 2305)
The adaptive filter cannot be used.
{
No adaptive filter option is provided.
Alarm No.
37
1
(Note) Refer to "4.1.4 Parameter numbers at initial parameter error".
Alarm No.
38
1
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "34" items.
Alarm No.
39
1
2
The speed loop gain (SV005) setting
is larger than the standard value.
4
Disconnect the UVW phase wiring
from the terminal block, and the
cannon plug from the motor. Check
the insulation with a tester.
Check the insulation between the
motor power cable and FG.
7
Investigation results
Investigation details
Investigation results
Check whether vibration is occurring. Vibration is occurring.
Check the current loop gain.
(SV009, SV010, SV011, SV012)
6
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Overcurrent
An excessive current was detected in the motor drive current.
3
5
Investigation results
Communication or protocol error 2 between NC and drive unit
An error was detected in the axis information data received from the NC.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "34" items.
Alarm No.
3A
1
Communication or protocol error 1 between NC and drive unit
An error was detected in the communication frame received from the NC.
Connect the cannon plug, and check
the insulation between the power
cable and FG.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the motor's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, cutting
water)
There is no vibration.
The setting is too large.
The setting is approximately the
same as the standard value.
The setting is incorrect.
The standard value is set.
The power cable is short-circuited.
There is no problem.
There is a ground fault at the power
cable.
There is no problem.
There is a ground fault in the motor.
There is no problem.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
II - 89
Remedies
• Set a filter.
• Lower the speed loop gain
(SV005).
Investigate item 2.
Set an appropriate value.
Investigate item 3.
SV SP
Set the standard value.
Investigate item 4.
Replace the motor power cable.
Investigate item 5.
{
{
{
{
Replace the motor power cable.
{
Investigate item 6.
Replace the motor.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Investigate item 7.
Replace the drive unit.
Improve the installation environment.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
3B
1
2
3
4
Power module overheat
The power module's temperature protection function activated.
Investigation details
Confirm that the fan is rotating
correctly.
Check whether the heat dissipating
fins are dirty.
Measure the drive unit's ambient
temperature.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
Large amounts of cutting oil or cutting
chips, etc., are adhered, or the
rotation is slow.
The fan is rotating properly.
Cutting oil or cutting chips, etc., are
adhered, and the fins are clogged.
The fins are normal.
55°C or more
Less than 55°C.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
2
3
4
5
6
7
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
Investigate item 2.
Clean the fins.
Investigate item 3.
Improve the ventilation and cooling
for the power distribution panel.
Investigate item 4.
If the alarm occurs even after the unit
temperature has dropped, replace
the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Spindle speed lock
Even when the maximum torque was commanded, the motor speed does not increase to 45r/min or
more.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Does the alarm occur immediately
Occurs immediately after power is
Investigate item 2.
after the power is turned ON?
turned ON.
{
Occurs after normal operation.
Investigate item 5.
Is there any abnormal noise when
There is abnormal noise.
Investigate item 4.
starting?
(The initial pole estimate may be
{
incorrect.)
There is no abnormal noise.
Investigate item 3.
Check that the PN voltage is supplied The voltage is not supplied.
Correctly supply the PN voltage.
{
to the drive unit.
Approx. 300V is correctly supplied.
Investigate item 3.
• Is the CHARGE lamp ON?
Check the motor power cable (U, V, The connections are incorrect.
Connect correctly.
W phases). (Also check the operation
immediately after emergency stop is
cancelled.)
• The power cable is not connected.
{
• Is the cable connected to the motor
The connections are correct.
Investigate item 5.
for another axis?
• Is the contactor between the drive
unit and motor OFF?
(When using coil changeover
specifications.)
Check the load value with the spindle The cutting load is large.
Lower the cutting load.
{
monitor, and investigate the
The cutting load is not large.
Investigate item 6.
machine's load state.
Check whether the spindle rotary
Locked with a mechanical lock.
Remove the cause of the lock.
{
section is locked with a mechanical
Not locked with a mechanical lock.
Investigate item 7.
lock (C-axis clamp, etc.).
Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Replace the drive unit.
Not improved.
Investigate the motor.
{
(Check the motor type and
parameters.)
Alarm No.
3D
1
Remedies
Clean or replace the fan.
II - 90
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Spindle speed overrun
1. A state in which the motor's speed feedback exceeded the speed command and accelerated was
detected.
2. Even though the speed command is 0 (including when stopped during position control), motor
rotation exceeding the parameter setting value was detected.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Does the alarm occur immediately
Occurs immediately after power is
Investigate item 2.
after the power is turned ON?
turned ON.
{
Occurs after normal operation.
Investigate item 3.
Check the motor power cable (U, V, The connections are incorrect.
Connect correctly.
W phases). (Also check the operation
immediately after emergency stop is
cancelled.)
• The power cable is not connected.
{
• Is the cable connected to the motor
The connections are correct.
Investigate item 3.
for another axis?
• Is the contactor between the drive
unit and motor OFF?
(When using coil changeover
specifications.)
Check whether the spindle rotary
Locked with a mechanical lock.
Remove the cause of the lock.
{
section is locked with a mechanical
Not locked with a mechanical lock.
Investigate item 4.
lock (C-axis clamp, etc.).
Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Replace the drive unit.
Not improved.
Investigate the motor.
{
(Check the motor type and
parameters.)
Alarm No.
3E
1
2
3
4
Speed excessive deflection 2
During constant speed operation, the difference between the speed command and speed feedback
exceeded the set amount and set time.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV
Check the load value with the spindle The cutting load is large.
Lower the cutting load.
monitor, and investigate the
The cutting load is not large.
Investigate item 2.
machine's load state.
Check whether the spindle rotary
Locked with a mechanical lock.
Remove the cause of the lock.
section is locked with a mechanical
Not locked with a mechanical lock.
Investigate item 3.
lock (C-axis clamp, etc.).
Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Replace the drive unit.
Not improved.
Investigate the motor.
(Check the motor type and
parameters.)
Alarm No.
3F
1
2
3
SP
{
{
{
Detector changeover unit, changeover error
During 1-drive unit 2-motor control, an error was detected in the motor changeover signal received form
the detector changeover unit.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Wiggle the FR-TK unit connector by The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
hand to check whether it is
loose).
{
disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Check whether the cable connected The cable is broken.
Replace the cable.
{
between the spindle drive unit and
The cable is not broken.
Investigate item 3.
FR-TK unit is broken.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
40
1
2
3
Detector changeover unit, communication error
During 1-drive unit 2-motor control, an error was detected in the communication with the detector
changeover unit.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Check the alarm No. "40" items.
Alarm No.
41
1
II - 91
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Feedback error 1
With the servo, pulse-type position detector feedback signal error was detected. With the spindle, a
PLG feedback signal error was detected.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors (servo: CN3, spindle:
loose).
{
CN6) or detector connectors are
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
disconnected.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 3.
tester.
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
Replace the drive unit.
unit, and check whether the fault is
{
The alarm is on the detector side.
Servo :
Investigate item 5.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Spindle :
Investigate item 4.
Check the PLG output waveform.
There is a problem.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
Normal
Investigate item 5.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detector.
the detector's ambient environment.
(With the absolute position system,
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
the zero point must be established.)
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
{
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
42
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
6
{
{
{
{
{
Feedback error 2
With the servo, an excessive error was detected in the position data for the motor side detector and
machine side detector. With the spindle, an error was detected in the encoder feedback signal.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors or detector connectors
loose).
{
are disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Is the detector cable wired in the
The cables are wired near each
Improve the cable wiring.
same conduit as the motor's power
other. (Noise is entering from the
{
cable or are the two cables laid in
power cable.)
parallel near each other?
The wires are sufficiently separated. Investigate item 3.
Is the motor FG wire connected only The motor FG wire is grounded on
Connect together on the drive unit
to the drive unit which drives it?
the motor side.
side.
{
(Is the motor grounded to one point?) The motor is grounded to one point. Investigate item 4.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 5.
tester. (Is the cable shielded?)
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
Replace the drive unit.
{
unit, and check whether the fault is
The alarm is on the detector side.
Investigate item 6.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detector.
the detector's ambient environment.
(With the absolute position system,
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
the zero point must be established.)
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
{
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
43
1
SP
II - 92
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
C-axis changeover alarm
When using the coil changeover control motor, the mode was changed to C-axis control while the
high-speed coil was selected.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the coil selected with the
High-speed coil is selected (bitD = 0) Correct the sequence.
{
spindle control input 3, bitD for the
Low-speed coil is selected (bitD= 1) Investigate item 2.
C-axis control command.
Is coil changeover validated for the
Coil changeover valid (SP034, bit2 = Correctly set the parameter.
special motor specifications?
1)
{
Coil changeover invalid (SP034, bit2 Replace the drive unit.
= 0)
Alarm No.
44
1
2
Alarm No.
46
1
2
3
Motor overheat
The temperature protection function in the motor or detector activated.
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check whether the drive unit
connectors (servo: CN3, spindle:
CN6) or detector connectors are
disconnected.
Using a tester, check whether the
detector cable is broken.
Investigation results
The alarm occurs before operation.
The alarm occurs occasionally after
operation is started.
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
The cable is broken.
The cable is not broken.
4
When using MDS-B-HR, is the motor SV034, bit2 = 0
thermal validated even when it is not SV034, bit2 = 1
provided?
5 Check the overload % (servo) or load The load is large.
meter (spindle).
The load is not large.
6 Is the unbalance torque high?
The constant load torque (friction +
unbalance) is 60% or more.
The constant load torque is less than
60%.
7 Was the overload alarm (50) forcibly The alarm was forcibly reset.
reset by turning the drive unit power
OFF?
The alarm was not forcibly reset.
8 Check the parameter settings.
There was an incorrect setting.
The settings are correct.
9 Measure the motor temperature
Hot.
when the alarm occurs.
Not hot.
10 When using a motor with fan, check The fan motor was stopped.
whether the fan is stopped, or
The motor fan wind flow is poor.
whether it is clogged with dust, etc.
There is no problem.
11 Check the fan wiring.
The cable is broken.
The cable is not broken.
12 Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Not improved.
Alarm No.
4E
1
2
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
Investigate item 5.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
Correctly install.
Investigate item 3.
Replace the cable.
Servo :
Investigate item 4.
Spindle :
Investigate item 12.
Set SP034, bit2 to 1.
Investigate item 12.
Servo :
Investigate item 6.
Spindle :
Investigate item 8.
Investigate item 9.
Select the motor so that the constant
load torque is 60% or less.
Investigate item 7.
Do not turn the drive unit's power
OFF when an overload alarm occurs.
(The NC power can be turned OFF.)
Investigate item 9.
Correctly set.
Investigate item 9.
Investigate item 10.
Investigate item 12.
Investigate item 11.
Clean.
Investigate item 12.
Replace the cable.
Replace the fan.
Replace the drive unit.
Replace the motor.
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
NC command mode error
A spindle control mode selection outside the specifications was input.
Investigation details
Pinpoint where the alarm occurs in
the PLC program.
Does the alarm occur when position
control (C-axis, spindle
synchronization, synchronous tap) is
started?
Investigation results
The alarm always occurs at the same
position.
The alarm occurs irregularly.
The alarm occurs during position
control.
The alarm occurs during speed
control.
II - 93
Remedies
Check the NC and PLC program
process.
Investigate item 2.
Check the NC and PLC program
process.
Check the NC and PLC program
process.
(If the cause cannot be pinpointed,
replace the drive unit, and confirm.)
SV SP
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
50
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Overload 1
The overload detection level reached 100% or more. The motor or drive unit is in the overload state.
Investigation details
Check the overload parameters.
Servo :
SV021, SV022
Spindle :
SP063, SP064
Investigation results
The standard values (below) are not
set.
Servo : SV021 = 60, SV022 = 150
Spindle : SV063 = 60, SP064 = 110
The standard values are set.
Check the overload % (servo) or load The load is large.
meter (spindle).
The load is not large.
Check whether machine resonance is Resonance is occurring.
occurring.
Remedies
Set the standard values.
Investigate item 2.
Servo :
Investigate item 3.
Spindle :
Investigate item 7.
Investigate item 9.
Adjust the parameters.
• Set the notch filter.
• Lower VGN1 (SV005).
Resonance is not occurring.
Investigate item 4.
Check whether the shaft sways when The motor is hunting.
Adjust the parameters.
the motor is stopped. (Hunting)
• Increase VGN1 (SV005).
• Lower VIA (SV008).
The motor is not hunting.
Investigate item 5.
Check the brake operation
The motor brakes are not released.
Correct the faulty section.
• Check the brake relay.
The motor brake operation is normal. Investigate item 6.
• Check the connector (CN20)
connection.
Check the load current with the NC
The cutting load is large.
Lower the cutting load.
Servo Monitor, and investigate the
There is interference with the
When using the positioning pin, turn
machine load.
positioning pin.
the servo OFF when stopped.
An excessive force is applied from
Check whether the ball screw is bent,
the machine.
or whether there is a fault in the
guide.
The machine load is not large.
Investigate item 8.
Check the PLG output waveform.
There is a problem.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
Normal
Investigate item 8.
Confirm the motor capacity selection The motor performance is
Lower the acceleration/deceleration
again.
insufficient.
rate or cutting load.
The motor performance is sufficient. Investigate item 9.
Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Replace the drive unit.
Not improved.
Replace the motor.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
(Note) NR and PR resetting are not possible when the overload level is 50% or more. Do not forcibly reset (AR) by turning the unit
power OFF. If AR resetting is used at 50% or higher, the level is set to 80% when the power is turned ON next. (Servo)
II - 94
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Overload 2
With the servo, a current command exceeding 95% of the unit's maximum current continued for one
second or more. With the spindle, a load exceeding the continuous rating continued for 30 minutes or
more.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Did the alarm occur immediately after The alarm occurred after ready ON
Investigate item 2.
READY ON?
before operation starts.
{
The alarm occurred after normal
Investigate item 5.
operation.
Check that the PN voltage is supplied The voltage is not supplied.
Correctly supply the PN voltage.
{
to the drive unit.
Approx. 300V is correctly supplied.
Investigate item 3.
• Is the CHARGE lamp ON?
Check the motor power cable (U, V, The connections are incorrect.
Connect correctly.
W phases).
{
• The power cable is not connected.
The connections are correct.
Investigate item 4.
• Is the cable connected to the motor
for another axis?
Check the detector cable connection. The connections are incorrect.
Connect correctly.
{
• Is the cable connected to the motor The connections are correct.
Investigate item 5.
for another axis?
Check whether the machine has
The machine has collided.
Check the machining program and
collided.
soft limit settings.
{
The machine has not collided.
Investigate item 6.
Check whether the current value on
The current is saturated during
Increase the acceleration/
the NC Servo Monitor screen is
acceleration/deceleration.
deceleration time constant.
saturated during
{
The current value during
Investigate item 7.
acceleration/deceleration.
acceleration/deceleration is
appropriate.
Check the detector FB.
The FB signal is abnormal.
Replace the detector.
(With the absolute position system,
{
the zero point must be established.)
The FB signal is normal.
Replace the drive unit.
Check the load meter value.
The load is large.
Lower the load.
{
The load is not large.
Investigate item 9.
Check the PLG output waveform.
There is a problem.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
{
Normal
Replace the drive unit.
Alarm No.
51
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Excessive error 1
The difference between the motor's actual position at servo ON and the theoretical position exceeded
the setting value.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Set appropriate values.
Check the excessive error detection The excessive error detection width
width.
is too small.
SV023 (Servo)
Servo standard value:
RAPID
SP102 (Orientation control)
SV023 = 60 × PGN1 ÷ 2
SP154, SP155 (C-axis control)
For the spindle, a value larger than
{ {
SP177, bitD, SP186 (Spindle
the droop amount:
synchronous control)
Droop amount =
SP193, bitD, SP218 (Synchronous
Spindle rotation speed × No. of pulses
tap)
Alarm No.
52
1
60 × position loop gain
2
3
Check the position detector polarity.
SV017, bit4 (Servo)
SP097, bit5 (Orientation control)
SP129, bit5 (C-axis control)
SP177, bit5 (Spindle synchronous
control)
SP193, bit5 (Synchronous tap
control)
Check the alarm No. "51" items.
Appropriate values are set.
The polarity is reversed.
Normal.
II - 95
Investigate item 2.
Correctly set the parameters.
Investigate item 3.
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Excessive error 2
The difference between the motor's actual position at servo OFF and the theoretical position exceeded
the setting value.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the follow-up function while
NC parameter (M60S Series) #1064 Investigate item 2.
the NC is in the servo OFF state.
svof = 0
{
NC parameter (M60S Series) #1064 Investigate item 3.
svof = 1
Check whether the axis has moved
The axis moved.
Adjust the brakes, etc., so that the
during servo OFF, and check the
axis does not move.
{
motor brake operation.
The axis has not moved.
Investigate item 3.
Set an appropriate value.
Check the excessive error detection The excessive error detection width
width.
is too small.
RAPID
SV026 (Servo)
SV026 = 60 × PGN1 ÷ 2
{
An appropriate value is set.
Check for problems on the NC side,
such as the position FB follow-up
control.
Alarm No.
53
1
2
3
Alarm No.
54
1
2
Excessive error 3
The motor current was not detected when the excessive error 1 alarm occurred.
Investigation details
Check that the PN voltage is supplied
to the drive unit.
• Is the CHARGE lamp ON?
Check the motor power cable (U, V,
W phases).
• The power cable is not connected.
• Is the cable connected to the motor
for another axis?
Investigation results
The voltage is not supplied.
Approx. 300V is correctly supplied.
Remedies
Correctly supply the PN voltage.
Investigate item 2.
The connections are incorrect.
Connect correctly.
The connections are correct.
Replace the drive unit.
SV SP
{
{
Supplement (servo)
Depending on the ideal machine position in respect to the command position, the actual machine
position could enter the actual shaded section shown below, which is separated more than the distance
set in OD1.
Position
Command position
OD1
Ideal machine position
OD2
OD2
OD1
Time
Servo OFF
Servo ON
II - 96
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Collision detection 1 G0
When the collision detection function is valid, the disturbance torque exceeded the collision detection
value during rapid traverse (G0).
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the machine has
The machine has collided.
Check the machining program and
collided.
soft limit settings.
The machine has not collided.
Increase the detection level (SV060).
{
(The detection level should have an
allowance and be set as approx.
1.5-times the maximum disturbance
torque.)
Alarm No.
58
1
Collision detection 1 G1
When the collision detection function is valid, the disturbance torque exceeded the collision detection
level during cutting feed (G1).
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the machine has
The machine has collided.
Check the machining program and
collided.
soft limit settings.
The machine has not collided.
Increase the detection level (SV035. {
clG1).
(Set the detection level larger than
the maximum cutting load.)
Alarm No.
59
1
Collision detection 2
When the collision detection function is valid, the command torque reached the motor's maximum
torque.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the machine has
The machine has collided.
Check the machining program and
collided.
soft limit settings.
{
The machine has not collided.
Investigate item 2.
Check whether the current value on
The current is saturated during
Investigate item 3.
the NC Servo Monitor screen is
acceleration/deceleration.
saturated during
{
The current value during
Investigate the cause of the load
acceleration/deceleration.
acceleration/deceleration is
fluctuation.
appropriate.
Can the acceleration/deceleration
The constant can be changed.
Increase the acceleration/
time constant be changed?
deceleration time constant.
{
The constant cannot be changed.
Set to ignore collision detection
method 2.
Alarm No.
5A
1
2
3
Alarm No.
5C
Orientation feedback error
After orientation was completed, the command and feedback error exceeded the parameter setting.
1
Investigation details
Check the PLG cable shield.
2
Check the PLG cable connection.
3
Check the PLG output waveform.
Investigation results
The cable is not correctly shielded.
The cable is correctly shielded.
The cable is incorrectly connected or
broken.
Normal
There is a problem.
Normal
II - 97
Remedies
Shield the cable.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the cable.
SV SP
{
{
Investigate item 3.
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
Replace the drive unit
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Speed monitor/ input mismatch
In respect to the door status signal for speed monitor control, a mismatch of the external input signal
and control signal received from the NC was detected.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the occurrence frequency.
The alarm occurs each time.
Investigate item 2.
{
The alarm occurs occasionally.
Investigate item 3.
Check the external input signal
No particular abnormalities are
Investigate item 3.
waveform and NC reception control
apparent.
signal.
{
A waveform error (external input
Remedy according to the cause.
signal does not change, etc.), or a
signal error was found.
Wiggle the drive unit connector (CN9) The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly connect.
by hand to check whether it is
loose).
{
disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 4.
Check whether the cable is broken.
The cable is broken.
Replace the cable.
{
The cable is not broken.
Investigate item 5.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
5D
1
2
3
4
5
Alarm No.
5E
1
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "5D" items.
Alarm No.
60
1
Speed monitor/ feedback error
During speed monitor control, the spindle speed exceeded the set speed while the door was open.
Remedies
SV SP
{
Instantaneous power failure
A drop in the 24VDC power was detected.
Investigation details
Is 24VDC applied on the CN22
connector?
Is the voltage low, or does it drop
sometimes?
2
Are the LEDs on the CR unit ON?
3
Check the wiring and power voltage.
4
Investigation results
Check whether the voltage is
dropping because of another load.
Investigation results
The voltage is not applied.
The voltage is 20.4VDC or less.
The voltage drops below 20.4VDC
sometimes.
The voltage is correctly applied.
The LEDs are not ON.
The LEDs are ON.
The power is abnormal.
The wiring or connectors are
abnormal.
A voltage drop is not observed.
A voltage drop is observed.
II - 98
Remedies
Investigate item 3.
Increase the power voltage.
Investigate item 4.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the unit.
Investigate item 4.
Replace the power.
Replace the cable.
Check the wiring.
Increase the power capacity.
CV CR
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
61
1
2
3
4
5
6
Investigation details
Check the state of the operation
when the alarm occurs, and check
the repeatability.
Check the load state of all motors,
and the starting/stopping frequency.
Check the power capacity.
Measure the voltage across wires.
•
Is the voltage 170V or
more even when the motor is
accelerating?
Measure the power voltage with a
synchroscope, and check whether
there is any distortion.
•
Are there any other
devices causing the power distortion?
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Alarm No.
62
1
2
3
4
Power module overcurrent
The power module's overcurrent protection function activated.
Investigation results
The alarm occurs immediately after
200VAC is supplied and after READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs frequently during
READY ON.
The alarm occurs after continuous
operation for a long time.
The unit is hot.
The total load of all motors exceeds
the rated capacity of the power
supply unit.
The total does not exceed the
capacity.
The power capacity is insufficient.
The specified power capacity is
secured.
The voltage drops to 170V or less
occasionally.
The difference of the voltage across
wires is 10V or more.
The difference of the voltage across
wires is less than 10V.
The power voltage is distorted.
The power voltage waveform is not
abnormal.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
Remedies
Replace the unit.
CV CR
Investigate item 3.
{
Investigate item 2.
Lower the motor load and operation
frequency.
{
Investigate item 3.
Increase the power capacity.
Investigate item 4.
{
Increase the power capacity.
Improve the power phase balance.
{
Investigate item 5.
Improve the source of the distortion.
Install an AC reactor.
Investigate item 6.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
{
{
Frequency error
The input power frequency exceeded the specified range.
Investigation details
Check the state of the operation
when the alarm occurs, and check
the repeatability.
Investigation results
The alarm occurs each time
immediately after the power is turned
ON. Or, the alarm occurs
occasionally regardless of the
operation state.
The alarm occurs only while the
motor is accelerating/decelerating.
Measure the power voltage waveform The frequency is deviated from
during normal operation.
50Hz±3% or 60Hz±3%.
The voltage waveform dips at some
sections.
There is no problem.
Measure the power voltage when the The frequency greatly fluctuates
motor is accelerating/decelerating.
during acceleration/deceleration.
The voltage waveform during
deceleration dips in some sections.
There is no problem.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular.
the unit's ambient environment.
The grounding is incomplete.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
II - 99
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
CV CR
{
Investigate item 3.
Review the power facilities.
Improve the source of the distortion.
Install an AC reactor.
Investigate item 4.
Review the power facilities.
{
Improve the source of the distortion.
Install an AC reactor.
Investigate item 4.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
63
1
2
Investigation details
Check whether the regenerative
resistor on the back of the unit is
dirty.
2
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Investigation details
Check the voltage for each input
phase.
2
Check the alarm No. "71" items.
2
CV CR
{
{
Investigation results
The alarm occurs each time READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs occasionally.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
Remedies
Replace the unit.
CV CR
{
Investigate item 2.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
{
Phase failure
There is a phase failure in the input power.
1
Alarm No.
68
Remedies
Take measure to prevent cutting oil
and dust from getting on the fins at
the back of the unit, and then carry
out investigation details 2.
Replace the unit.
Replace the unit.
Clean the resistor or fins.
Rush relay error
The rush resistance short-circuit relay does not turn ON.
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Alarm No.
67
1
Investigation results
Cutting oil or oil mist is adhered on
the regenerative resistor.
The resistor is not dirty.
Using a tester, check the continuity of There is continuity.
the terminal block and resistor
The resistance value is ∞.
surface.
Alarm No.
65
1
Auxiliary regeneration error
The auxiliary regenerative transistor is still ON.
Investigation results
There are phases with no voltage.
There is no problem.
Remedies
Correct the power supply.
Investigate item 2.
CV CR
{
{
Watch dog
The system is not operating normally.
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Investigation results
The alarm occurs each time READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs occasionally.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
II - 100
Remedies
Replace the unit.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
CV CR
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
69
1
2
3
4
Investigation details
Investigation results
Measure the insulation across the U, 100kΩ or less.
V, W phase cables for all motors and
the ground. (Carry out a megger
100kΩ or more.
test.)
Has oil come in contact with the
Oil has come in contact.
motor or power cable?
Oil has not come in contact.
1MΩ or less.
1MΩ or more.
Measure the resistance across the U, 100kΩ or less.
V, W phase terminals of the
100kΩ or more.
servo/spindle drive unit and the
ground.
(Do not measure the insulation, as
the unit could be damaged.)
Measure the insulation again.
Alarm No.
6A
1
2
3
2
3
Remedies
The motor or power cable may be
ground faulted.
Investigate item 2.
Take measures so that oil does not
come in contact. Check the motor's
cannon connector and the inside of
the terminal box, and clean as
necessary.
Investigate item 3.
Replace the motor or cable.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the drive unit.
Replace the power supply unit.
CV CR
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
External contactor melting
The external contactor's contact has melted.
Investigation details
Check whether any alarm has
occurred on the drive unit side.
Investigation results
An alarm has occurred.
An alarm has not occurred.
The contactor has melted.
The contactor has not melted.
Check that the contactor excitation
The connection is correct.
wiring is correctly connected from the The connection is incorrect.
power supply unit's MC1 terminal.
Check whether the contactor's
contact has melted.
Alarm No.
6B
1
Ground fault
The motor power cable is contacting FG (ground).
Remedies
Remove the cause of the alarm on
the drive side, and then carry out the
investigation details 2.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the contactor.
Investigate item 3.
Correctly connect.
Replace the power supply unit.
CV CR
{
{
{
Rush relay melted
The rush resistance short-circuit relay does not turn OFF.
Investigation details
Check whether any alarm has
occurred on the drive unit side.
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Investigation results
An alarm has occurred.
An alarm has not occurred.
The alarm occurs each time READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs occasionally.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
II - 101
Remedies
Remove the cause of the alarm on
the drive side, and then carry out the
investigation details 2.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the unit.
CV CR
{
{
Investigate item 3.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
6C
1
2
Main circuit error
An abnormality was detected in the main circuit capacitor's charging operation.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Check the CHARGE lamp state when The CHARGE lamp remains ON for
the alarm occurs.
some time.
The lamp turns ON instantly, but
when the alarm occurs and the
contactor turns OFF, the lamp turns
OFF immediately.
The lamp never turns ON.
Disconnect the power supply unit's
PN terminal block wiring, and
measure the resistance value at 1)
and 2) shown below.
Drive unit
Power supply
unit
2)
1)
P
N
Remedies
Replace the power supply unit.
Investigate item 2.
{
{
{
{
Investigate item 2.
Then replace the unit.
Replace the power supply unit.
1) The power supply unit side is
abnormal.
2) The drive unit side is abnormal.
Disconnect the PN wiring, and then
check the drive unit side.
Replace the power supply unit.
1) and 2) are both normal.
Tester
Polarity
Normal
measurement point +
P
N Several 100Ω
1)
N
P
∞Ω
P
N Several 100Ω
2)
N
P
∞Ω
CV CR
Abnormal
Short-circuit/∞Ω
Several 100Ω
Short-circuit/∞Ω
Several 100Ω
Parameter error
The power supply unit's capacity is not appropriate for the regenerative resistor type set with the
parameters.
CV CR
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
Check the parameters (regenerative SV036 and SP041 setting
resistor type) of the drive unit to
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
which the power supply unit's control
amp
rtyp
ptyp
wire (CN4) is connected.
Servo: SV036, Spindle: SP041
Alarm No.
6D
1
rtyp
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A~F
Alarm No.
6E
1
2
Regenerative resistor type
For MDS-C1-CV
GZG200W260HMJ
GZG300W130HMJ×2
MR-RB30
MR-RB50
GZG200W200HMJ×3
GZG300W200HMJ×3
R-UNIT-1
R-UNIT-2
R-UNIT-3
No setting
ptyp setting
CR-10
×
{
{
×
×
×
×
{
×
×
×
81
CR-15
×
{
{
×
×
×
×
{
×
×
×
82
CR-22
×
{
{
×
×
×
×
{
×
×
×
83
CR-37
×
{
{
{
{
×
×
{
{
{
×
84
CR-55
×
{
{
{
{
×
×
{
{
{
×
86
CR-75
×
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
×
88
CR-90
×
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
×
89
{
Memory error
An error was detected in the internal memory.
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Investigation results
The alarm occurs each time READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs occasionally.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
II - 102
Remedies
Replace the unit.
Investigate item 2.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
CV CR
{
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Power supply error
The power supply is not connected. An error was detected in the power supply's A/D converter.
This is detected simultaneously if another power supply alarm occurs.
CV
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
Check the LED display on the power "F" is flickering.
An A/D converter error has occurred.
supply unit.
Carry out the items for alarm No. 6E.
Another alarm code is flickering.
Refer to the section for each alarm.
"0" is displayed.
Investigate item 2.
{
"F" is displayed.
Investigate item 2.
"8" is displayed.
Refer to the section for alarm No.68.
"b", "C", "d" is displayed.
Investigate item 3.
Something else is displayed.
Refer to the section for alarm No.68.
Check the rotary switch setting.
0 or 4 is set.
Investigate item 3.
{
A value other than the above is set.
Correctly set the rotary switch.
Check the communication cable
There is a problem with the wiring or Replace the cable.
(CN4) connected with the drive unit. shield.
{
There is no problem.
Replace the unit.
Alarm No.
6F
1
2
3
CR
{
{
{
(Note) Alarm 6F is detected at the same time other power supply alarms occur.
Alarm No.
71
1
2
Instantaneous power failure/ external emergency stop
An instantaneous power failure occurred.
Investigation details
Investigate the sequence to check
whether the contactor has been
turned OFF with an emergency stop
button, etc.
Check the repeatability.
3
Check whether the power input wire
and contactor are correctly wired.
4
Check the power voltage waveform
with a synchroscope.
Investigation results
The contactor has been turned OFF
externally.
The contactor has not been turned
OFF.
The alarm occurs each time READY
is turned ON.
The alarm occurs at a certain
operation.
CV CR
Remedies
Review the machine sequence.
When turning the contactor OFF with
external means, such as an
emergency stop button, this alarm
{
can be avoided by inputting NC
emergency stop at the same time.
Investigate item 2.
Investigate item 3.
Investigate item 1.
If there is no problem, carry out
investigation item 3.
The alarm occurs occasionally during Investigate item 4.
operation.
The wiring is incorrect.
Correctly connect.
There is no problem.
Investigate item 4.
An instantaneous power failure or
Correct the power facility.
voltage drop occurs frequently.
There is no problem.
Replace the unit.
II - 103
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Over-regeneration
The over-regeneration detection level exceeded 100%. The regenerative resistor is in the overload
state.
CV
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
Check the alarm occurrence state
The regenerative load display
Check whether the state is affected
and regenerative load displayed on
increases when the power is turned
by power fluctuation, grounding or
the NC Monitor screen while
ON and the motor is not rotated.
noise. If there is no problem, replace
changing the operation mode.
the unit.
The regenerative load display
A-CR : Investigate item 2.
increases each time the motor
C1-CV : Investigate item 4.
{
decelerates, and the alarm occurs.
The regenerative load display
A-CR : Investigate item 2.
increases each time the motor
C1-CV : Ease the operation mode.
decelerates, but the alarm does not
occur when the operation mode is
eased.
Check whether the parameter
The setting is incorrect.
Correctly set. (Refer to the section for
(regenerative resistor type) of the
alarm No. 6D.)
drive unit controlling the power
The setting is correct.
Investigate item 3.
supply unit is correct.
Check the regenerative resistor's
The regenerative resistor is
Replace the regenerative resistor.
state.
abnormal.
• Is oil adhered?
There is no problem.
Investigate item 4.
• Measure the resistance value.
{
Check the alarm No. "75" items.
Alarm No.
73
1
2
3
4
Alarm No.
74
{
{
{
{
Regenerative resistor overheat
The temperature protection function in the regenerative resistor activated.
1
Investigation details
Check whether the regenerative
resistor is overheated.
2
Check the alarm history.
3
CR
Check the connections of the CN22
(B) connector pins 1 and 2.
• Check whether the pins are
short-circuited with the resistor's
thermal terminal or wire.
Investigation results
The resistor is overheated.
The resistor is not overheated.
Check whether over-regeneration
occurred before.
Over-regeneration has not occurred
before.
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
Investigate item 3.
Refer to the section for alarm No.73.
Take measures to dissipate the
regenerative resistor's heat.
• Improve the ventilation.
• Install a fan.
The wire is about to break.
Replace the wire.
There is no continuity at the resistor's Replace the resistor unit.
thermal terminal.
There is no problem.
Replace the power supply unit.
II - 104
CV CR
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
75
1
2
3
4
5
6
Investigation details
Check the repeatability.
Check the power supply's alarm
history.
Check the power capacity.
Measure the voltage across wires.
• Is the voltage 170V or more even
when the motor is accelerating?
Measure the power voltage with a
synchroscope, and check whether
there is any distortion.
• Are there any other devices
causing the power distortion?
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Noise, grounding)
Alarm No.
76
1
2
3
4
Investigation results
The alarm occurs each time the
motor decelerates.
The alarm occurs occasionally.
Auxiliary regeneration frequency over
(E8) occurs just before the
overvoltage occurs.
Others.
The power capacity is insufficient.
The specified power capacity is
secured.
The voltage drops to 170V or less
occasionally.
The difference of the voltage across
wires is 10V or more.
The difference of the voltage across
wires is less than 10V.
The power voltage is distorted.
The power voltage waveform is not
abnormal.
No abnormality is found in particular.
The grounding is incomplete.
An alarm will occur easily if another
device operates.
Remedies
Investigate item 3.
Investigate item 2.
Limit the occurrence of the excessive
instantaneous regeneration by not
decelerating multiple axes at the
same time.
Investigate item 3.
Increase the power capacity.
Investigate item 4.
CV CR
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
{
Increase the power capacity.
Improve the power phase balance.
Investigate item 5.
Improve the source of the distortion.
Install an AC reactor.
Investigate item 6.
Replace the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Noise: Noise measures for
other devices.
External emergency stop setting error
The rotary switch setting for the external emergency stop does not match the parameter setting.
Investigation details
Check the rotary switch settings and
parameter settings.
Alarm No.
77
1
Overvoltage
The main circuit PN bus voltage exceeded the tolerable value.
Investigation results
Remedies
When using external emergency stop:
• Add 0040h to the normal setting for SV036 or SP041, and set the power
supply's rotary switch to "4".
CV CR
{
Power module overheat
The power module's temperature protection function activated.
Investigation details
Confirm that the fan is rotating
correctly.
Check whether the heat dissipating
fins are dirty.
Measure the drive unit's ambient
temperature.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
Large amounts of cutting oil or cutting
chips, etc., are adhered, or the
rotation is slow.
The fan is rotating properly.
Cutting oil or cutting chips, etc., are
adhered, and the fins are clogged.
The fins are normal.
55°C or more
Less than 55°C.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
II - 105
Remedies
Clean or replace the fan.
CV CR
{
Investigate item 2.
Clean the fins.
{
Investigate item 3.
Improve the ventilation and cooling
for the power distribution panel.
Investigate item 4.
If the alarm occurs even after the unit
temperature has dropped, replace
the unit.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
7F
1
Investigation details
Were the parameter settings
changed?
SV009, SV010, SV011, SV012
SV033, bit8, 9
Alarm No.
88
1
2
3
Power reboot request
A mismatch in the program mode selection was detected. Turn the drive unit power ON again.
Investigation results
Remedies
This alarm is detected if the high-gain Turn the drive unit's control power
specification parameters are set
ON again.
when the drive unit is started up with
the standard specification software
mode, or if the standard specification
parameters are set when started up
with the high-gain specifications.
SV SP
{
Watch dog
The system is not operating normally.
Investigation details
Check whether the servo software
version was changed recently.
Check the repeatability.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The version was changed.
Remedies
Replace with a drive unit containing
the original software version.
The version was not changed.
Investigate item 2.
The alarm is always repeated.
Replace the drive unit.
The state is returned to normal once, Investigate item 3.
but then the alarm occurs
occasionally.
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
Encoder converter unit 2, connection error
With the servo, an error was detected in the connection with the analog output linear scale for the
MDS-B-HR unit. With the spindle, initial communication with the MDS-B-PJEX was not possible.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV
Wiggle the MDS-B-HR/MDS-B-PJEX The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
unit connector (CON3) by hand to
loose).
{
check whether it is disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Servo : Investigate item 2.
Spindle : Investigate item 4.
Check whether the cable between
The cable is broken.
Replace the cable.
{
the linear scale and MDS-B-HR is
The cable is not broken.
Investigate item 3.
broken.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the MDS-B-HR unit.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Check whether the cable between
The cable is broken.
Replace the cable.
the spindle drive unit and
The cable is not broken.
Investigate item 5.
MDS-B-PJEX is broken.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the drive unit.
the unit's ambient environment.
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
89
1
2
3
4
5
{
{
{
Detection converter unit 2, communication error
With the servo, an error was detected in the communication with the serial output linear scale for the
MDS-B-HR unit. With the spindle, an error was detected in the communication with the MDS-B-PJEX.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Check the alarm No. "89" items.
Alarm No.
8A
1
SP
II - 106
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Alarm No.
8B
1
2
3
4
Investigation details
Check whether the MDS-B-PJEX
connectors (CN5) or detector
connectors are disconnected.
2
Investigation results
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
There is a connection fault.
The connection is normal.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
detector cable connection with a
tester.
Check the PLG output waveform (A/B There is a problem. (The A/B phase
phase).
input voltage is 0.8V or less or 2.2V
or higher.)
Normal
Check the occurrence frequency.
Occurs each time.
Occurs occasionally.
Alarm No.
8C
1
Encoder converter unit 2, automatic adjustment error
An abnormal signal from the PLG was detected during automatic adjustment of the PLG.
Remedies
Correctly install.
SV SP
{
Investigate item 2.
Replace the detector cable.
Investigate item 3.
{
Adjust the PLG output waveform.
{
Investigate item 4.
Replace the MDS-B-PJEX unit.
Check whether the cable is
disconnected, whether there is a
contact fault, or a detector fault.
{
Encoder converter unit 2, judgment error
A detector type outside the specifications was detected with the MDS-B-PJEX.
Investigation details
Check the spindle parameter SP042.
SP042: C-axis control detector range.
(Spindle end PLG No. of pulse
setting)
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The setting was incorrect.
"4" : 128 pulses
"5" : 256 pulses
"6" : 512 pulses
"8" : 180 pulses
The setting is correct.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Remedies
Set correctly according to the No. of
PLG gear teeth.
SV SP
{
Investigate item 2.
Replace the MDS-B-PJEX.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
Detection converter unit 2, CPU error
With the servo, a CPU error was detected with the MDS-B-HR unit. With the spindle, a CPU error was
detected with the MDS-B-PJEX unit.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detection converter unit.
the detector's ambient environment. An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{ {
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Alarm No.
8D
1
Alarm No.
8E
1
2
3
Detection converter unit 2, data error
A data error was detected with the MDS-B-HR unit.
Investigation details
Check whether the cable between
the linear scale and MDS-B-HR is
broken.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the unit's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The cable is broken.
The cable is not broken.
Remedies
Replace the cable.
Investigate item 2.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Try replacing the MDS-B-HR unit.
The state is improved.
The state is not improved.
Investigate item 3.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Replace the MDS-B-HR unit.
Replace the linear scale.
II - 107
SV SP
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
4.1.3 Troubleshooting for Each Warning No.
Warning No.
90
1
2
3
4
Detector, initial communication error
Initial communication with the absolute position linear scale was not possible.
Investigation details
Check the servo parameter
(SV025.pen) setting.
Check whether the drive unit
connector (CN3) and detector
connector are disconnected.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
detector cable connection with a
tester.
Check if there is any abnormality in
the tool end detector's ambient
environment.
(Ex.: Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
The setting is incorrect.
The setting is correct.
The connector is disconnected
(loose).
The connector is not disconnected.
The connection is faulty.
The connection is normal.
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Remedies
Correctly set SV025.
Investigate item 2.
Correctly install.
SV SP
{
{
Investigate item 3.
Replace the detector cable (CN3
side).
Investigate item 4.
Replace the tool end detector.
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
{
{
Detector, communication error
An error was detected in the communication with the detector for the absolute position detection
system.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check whether the drive unit
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly install.
connectors (CN3) or detector
loose).
{
connectors are disconnected.
The connector is not disconnected.
Investigate item 2.
Is the detector cable wired in the
The cables are wired near each
Improve the cable wiring.
same conduit as the motor's power
other. (Noise is entering from the
{
cable or are the two cables laid in
power cable.)
parallel near each other?
The wires are sufficiently separated. Investigate item 3.
Is the motor FG wire connected only The motor FG wire is grounded on
Ground the motor to one point,
to the drive unit which drives it?
the motor side.
connecting the wires together on the
{
(Is the motor grounded to one point?)
drive unit side.
The motor is grounded to one point. Investigate item 4.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
There is a connection fault.
Replace the detector cable.
{
detector cable connection with a
The connection is normal.
Investigate item 5.
tester. (Is the cable shielded?)
Connect to another normal axis drive The alarm is on the drive unit side.
Replace the drive unit.
{
unit, and check whether the fault is
The alarm is on the detector side.
Investigate item 6.
on the drive unit side or detector side.
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Replace the detector.
the detector's ambient environment.
(With the absolute position system,
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
the zero point must be established.)
grounding)
An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
{
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Warning No.
91
1
2
3
4
5
6
Warning No.
92
1
2
Detector, protocol error
An error was detected in the data for the absolute position detection system.
Investigation details
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Check the repeatability.
Occurs frequently.
Is not repeated.
II - 108
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Replace the detector.
Investigate item 1.
SV SP
{
{
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Warning No.
93
1
Initial absolute position fluctuation
The position data fluctuated when creating the initial absolute position.
Investigation details
Check the state of the axis when the
NC power is turned ON.
Investigation results
The vertical axis or slant axis drops
when the NC power is turned ON.
The axis moves with an external
force when the NC power is turned
ON.
Remedies
Check the brake operation.
SV SP
Make sure that the axis does not
move when the power is turned ON.
{
MP scale feedback error
An excessive deviation was detected between the motor end detector and MP scale feedback data for
the MP scale absolute position detection system.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Check the alarm No. "43" items.
Warning No.
96
1
MP scale offset error
An error was detected in the offset data received from the MP scale for the MP scale absolute position
detection system.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Investigate item 2.
the detector's ambient environment. An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Check the repeatability.
Occurs frequently.
Replace the detector.
{ {
Is not repeated.
Investigate item 1.
Warning No.
97
1
2
Absolute position detector, multi-rotation counter error
An error was detected in the multi-rotation counter for the absolute position detector. The absolute
position cannot be compensated.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check if there is any abnormality in
No abnormality is found in particular. Investigate item 2.
the detector's ambient environment. An abnormality was found in the
Take remedies according to the
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
ambient environment.
causes of the abnormality.
grounding)
{
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Check the repeatability.
Occurs frequently.
Replace the detector.
{ {
Is not repeated.
Investigate item 1.
Warning No.
9E
1
2
(Note) When this alarm occurs, the absolute position system's zero point must be established.
Battery voltage drop
The voltage of the battery supplying to the absolute position detector has dropped. The absolute
position data is held.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Measure the battery (MDS-A-BT)
Less than 3V.
Replace the battery unit.
{
voltage.
3V or more.
Investigate item 2.
Check whether the NC bus cable is
The cable is disconnected.
Connect correctly.
{
disconnected.
There is no problem.
Investigate item 3.
Check whether the battery wire in the The cable is broken.
Replace the cable.
{
detector cable is broken.
The cable is not broken.
Investigate item 4.
Try replacing the drive unit.
Improved.
Replace the drive unit.
Not improved.
Replace the detector.
{
(With the absolute position system,
the zero point must be established.)
Warning No.
9F
1
2
3
4
(Note) When warning 9F occurs, do not turn the drive unit power OFF to ensure that the absolute position data is held.
II - 109
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Warning No.
A8
1
2
Investigation details
Check the parameters.
SP097, bitB = 0 command angle 1°
unit
SP097, bitB = 1 command angle 0.1°
unit
Pinpoint where the alarm occurs in
the PLC program.
Warning No.
A9
1
1
2
Remedies
Correctly set SP097.
Investigate item 2.
The position can be pinpointed.
The position cannot be pinpointed.
Check the PLC program process.
Investigate the details of the NC and
PLC program process.
SV SP
{
{
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
{
Remedies
SV SP
{ {
Overload warning
The overload detection level is 80% or more.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "50" items.
Warning No.
E3
Investigation results
The setting is incorrect.
The setting is correct.
Orientation feedback error warning
Retrying during an orientation feedback error.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "5C" items.
Warning No.
E1
1
Turret indexing error warning
The commanded turret indexing position shift amount is outside the specified range.
Investigation results
Absolute position counter warning
A deviation was detected in the absolute position data and relative position data.
Investigation details
Check if there is any abnormality in
the detector's ambient environment.
(Ex. Ambient temperature, noise,
grounding)
Investigation results
No abnormality is found in particular.
An abnormality was found in the
ambient environment.
Check the repeatability.
Occurs frequently.
Is not repeated.
Remedies
Investigate item 2.
Take remedies according to the
causes of the abnormality.
Ex. High temperature:
Check the cooling fan.
Incomplete grounding:
Additionally ground.
Replace the detector.
Investigate item 1.
SV SP
{
{
(Note) When this alarm occurs, the absolute position system's zero point must be established.
Parameter error warning
A parameter exceeding the setting range was set.
"S51 parameter error ####" is displayed on the NC screen. #### indicates the incorrect parameter No.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
SV SP
Check the error parameter No.
SV001 to SV065
Set the value within the designated
{ {
SP001 to SP384
setting range.
Warning No.
E4
1
Warning No.
E6
1
Control axis removal warning
Control axis removal was commanded.
Investigation details
Investigation results
Remedies
The status in which removal of the control axis was commanded from the NC is indicated.
II - 110
SV SP
{
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
Warning No.
E7
1
2
3
Investigation details
Check whether NC emergency stop
was input.
Check whether an alarm is occurring
in another drive unit.
Check the NC communication bus
line.
Warning No.
E8
1
1
2
1
SV SP
{
{
{
{
{
{
Investigation results
Remedies
CV CR
{
Investigation results
Remedies
CV CR
{
External emergency stop
The external emergency stop signal was input.
Investigation details
Check whether the specifications
allow use of the external emergency
stop.
Measure the input voltage of the
CN23 connector. (While emergency
stop is cancelled.)
Warning No.
EB
Remedies
The NC is in the emergency stop
state. (Normal)
Emergency stop was not input.
Investigate item 2.
An alarm is occurring in another drive Reset the alarm in the other drive
unit.
unit.
An alarm is not occurring.
Investigate item 3.
The terminator or battery unit's cable Correctly connect.
is disconnected.
The NC communication bus
Correctly connect the cable.
connector (CN1A, CN1B) is loose, or
the cable is broken.
Instantaneous power failure warning
An instantaneous power failure occurred.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "71" items.
Warning No.
EA
Investigation results
Emergency stop was input.
Auxiliary regeneration frequency over
Regeneration at the power supply performance limit is occurring frequently.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "75" items.
Warning No.
E9
1
NC emergency stop
Emergency stop was input from the NC.
Investigation results
Use not allowed.
Use is allowed.
24V is input.
24V is not input.
CV CR
Remedies
Invalidate the external emergency
stop.
{
Investigate item 2.
Replace the power supply unit.
Check whether the external
{
emergency stop cable is broken, or
check the external contact operation.
Over-regeneration warning
The over-regeneration level is 80% or more.
Investigation details
Check the alarm No. "73" items.
Investigation results
Remedies
CV CR
{
II - 111
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
4.1.4 Parameter Numbers during Initial Parameter Error
If an initial parameter error (alarm 37) occurs, the alarm and the number of the parameter that may have been
set exceeding the setting range will appear on the CNC Diagnosis screen.
S02 Initial parameter error {{{{
{{{{ :
:
Error parameter number
Axis name
If an error number larger than the servo parameter number is displayed for the servo drive unit
(MDS-C1-V1/V2), the alarm is occurring for several related parameters. Refer to the following table, and
correctly set the parameters.
Error parameter No.
2301
Details
The following settings are overflowing.
• Electronic gears
• Position loop gain
• Speed feedback
Related parameters
SV001, SV002
SV003, SV018
SV019, SV020
SV049
2302
The absolute position parameter is valid when
OSE104 and OSE105 are connected.
SV017, SV025
2304
The servo option is not available. The SHG control
function is set.
SV057, SV058
2305
The servo option is not available. The adaptive filter SV027
function is set.
II - 112
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
4.1.5 Troubleshooting the Spindle System when There Is No Alarm or Warning
If an abnormality is observed in the spindle system but no alarm or warning has occurred, refer to the
following table and check the state.
(1) No abnormality is displayed, but the motor does not rotate.
1
Investigation item
Check the wiring around the spindle
drive unit.
Also check for loosening in the
terminal screws and disconnections, etc.
2
Check the input voltage.
3
Check all of the spindle parameters.
4
Check the input signals.
• Are the READY, forward run and
reverse run signals input?
• In particular, the forward run and
reverse run signals must be input
at least one second after READY
is turned ON.
• Check whether the forward run
and reverse run signals are turned
ON simultaneously.
5
Check the speed command.
Investigation results
The wiring is incorrect, the screws
are loose, or the cables are
disconnected.
No particular problems found.
The voltage is exceeding the
specification value.
The voltage is within the
specification value.
The correct values are not set.
The correct values are set.
Remedies
Correctly wire. Correctly tighten
the screws. Replace the cables.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Restore the power to the correct
state.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
Set the correct values.
Investigate investigation item 4
and remedy.
The signals are not input or the
sequence is incorrect.
The orientation command is input.
Correct the input signals.
No particular problems found.
Investigate investigation item 5
and remedy.
The speed command is not input
correctly.
The speed command is input
correctly.
Input the correct speed
command.
Replace the unit.
(2) No fault is displayed, but the motor only rotates slowly, or a large noise is heard from the motor.
Investigation item
Check the U, V and W wiring
1 between the spindle drive unit and
motor.
2 Check the input voltage.
Investigation results
The wires are not connected
correctly.
The wires are connected correctly.
One of the three phases is not
within the specification value.
No particular problems found.
The speed command is not input
correctly.
3 Check the speed command.
The speed command is input
correctly.
The connector is disconnected (or
Tug on the connector by hand to
check whether the speed detector
loose).
4
connector (drive unit side and speed The connector is not disconnected
detector side) is loose.
(or loose).
Turn the power OFF, and check the The connection is faulty or
5 connection of the speed detector
disconnected.
cable with a tester.
The connection is normal.
II - 113
Remedies
Correctly connect.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Restore the power to the correct
state.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
Check the NC and PLC sequence.
Investigate investigation item 4
and remedy.
Correctly connect the connector.
Investigate investigation item 5
and remedy.
Replace the detector cable.
Correct the connection.
Replace the drive unit.
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
(3) The rotation speed command and actual rotation speed do not match.
Investigation item
1
Check the speed command.
Investigation results
The speed command is not input
correctly.
The speed command is correct.
2
3
Check whether there is slipping
between the motor and spindle.
(When connected with a belt or
clutch.)
Check the spindle parameters
(SP017, SP034, SP040, SP257 and
following).
There is slipping.
Remedies
Input the correct speed
command.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Repair the machine side.
No particular problems found.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
The correct values are not set.
Set the correct values.
The correct values are set.
Replace the drive unit.
(4) The starting time is long or has increased in length.
Investigation item
1
Check whether the friction torque
has increased.
2
Manually rotate the motor bearings
and check the movement.
3
Check whether the torque limit
signal has been input.
Investigation results
The friction torque has increased.
No particular problems found.
The bearings do not rotate
smoothly.
The bearings rotate smoothly.
The signal has been input.
The signal is not input.
Remedies
Repair the machine side.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Replace the spindle motor.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
Do not input this signal.
Replace the drive unit.
(5) The motor stops during cutting.
Investigation item
1
Check the load rate during cutting.
Investigation results
The load meter sways past 120%
during cutting.
No particular problems found.
Remedies
Reduce the load.
Investigate the same matters as
item (4), and remedy.
(6) The vibration and noise (gear noise), etc., are large.
Investigation item
1
Check the machine's dynamic
balance. (Coast from the maximum
speed.)
Investigation results
The same noise is heard during
coasting.
No particular problems found.
2
Vibration and noise increase at a
Check whether there is a resonance
set rotation speed during coasting.
point in the machine. (Coast from
the maximum speed.)
No particular problems found.
3
Check the machine's backlash.
4
Check the spindle parameter
settings.
(SP022, SP023, SP056)
5
6
Tug on the connector by hand to
check whether the speed detector
connector (spindle drive unit side
and speed detector side) is loose.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
connection of the speed detector
cable with a tester.
Remedies
Repair the machine side.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Repair the machine side.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
The backlash is great.
Repair the machine side.
Investigate investigation item 4
No particular problems found.
and remedy.
Change the setting value.
Symptoms decrease when setting
Note that the impact response will
value is set to approx. half.
drop.
Return the setting values to the
The symptoms do not change even original values.
when the above value is set.
Investigate investigation item 5
and remedy.
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly connect the connector.
loose).
The connector is not disconnected Investigate investigation item 6
(or loose).
and remedy.
The connection is faulty or
Replace the detector cable.
disconnected.
Correct the connection.
The connection is normal.
Replace the drive unit.
II - 114
4. Troubleshooting
4.1 Drive System Troubleshooting
(7) The spindle coasts during deceleration.
1
Investigation item
Check whether there is slipping
between the motor and spindle.
(When connected with a belt or
clutch.)
Investigation results
There is slipping.
Remedies
Repair the machine side.
No particular problems found.
Replace the drive unit.
(8) The rotation does not stabilize.
Investigation item
1
2
3
4
Investigation results
The rotation stabilizes when the
settings values are both set to
approx. double.
Remedies
Change the setting value.
Note that the gear noise may
increase.
Check the spindle parameter
Return the setting values to the
settings. (SP022, SP023)
The symptoms do not change even original values.
when the above value is set.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Tug on the connector by hand to
The connector is disconnected (or
Correctly connect the connector.
check whether the speed detector
loose).
connector (spindle drive unit side
The connector is not disconnected Investigate investigation item 3
and speed detector side) is loose.
(or loose).
and remedy.
Turn the power OFF, and check the The connection is faulty or
Replace the detector cable.
connection of the speed detector
disconnected.
Correct the connection.
cable with a tester.
Investigate investigation item 4
(Especially check the shield wiring.) The connection is normal.
and remedy.
Investigate the wiring and
The grounding is incomplete.
Correctly ground.
installation environment.
The alarm occurs easily when a
Use noise measures on the
• Is the ground correctly connected? specific device operates.
device described on the left.
• Are there any noise-generating
No particular problems found.
Replace the drive unit.
devices near the drive unit?
(9) The speed does not rise above a set level.
1
Investigation item
Check the speed command.
Check whether the override input is
input from the machine operation
panel.
2
Check whether the load has
suddenly become heavier.
3
Manually rotate the motor bearings
and check the movement.
4
5
Tug on the connector by hand to
check whether the speed detector
connector (spindle drive unit side
and speed detector side) is loose.
Turn the power OFF, and check the
connection of the speed detector
cable with a tester.
(Especially check the shield wiring.)
Investigation results
The speed command is not input
correctly.
The speed command is input
correctly.
The load has become heavier.
No particular problems found.
Remedies
Input the correct speed
command.
Investigate investigation item 2
and remedy.
Repair the machine side.
Investigate investigation item 3
and remedy.
The bearings do not rotate
smoothly.
Replace the spindle motor.
The bearings rotate smoothly.
Investigate investigation item 4
and remedy.
The connector is disconnected (or
loose).
The connector is not disconnected
(or loose).
The connection is faulty or
disconnected.
The waveform is normal.
II - 115
Correctly connect the connector.
Investigate investigation item 5
and remedy.
Replace the detector cable.
Correct the connection.
Replace the spindle drive unit.
III
Explanation of Parameters
1. Outline
1.1 Screen Transition Chart
1. Outline
1.1 Screen Transition Chart
The menus for screens related to maintenance appear when the function key Mainte is pressed.
The parameter menu appears when the menu key Param is pressed.
Process
parameters
Control
parameters
Axis
parameters
Operation
parameters
I/O
parameters
Ethernet
parameters
Computer
link
parameters
Subprogram
storage
destination
parameters
Base
system
parameters
Base axis
specification
parameters
Base
common
parameters
Axis
specifications
parameters
Absolute
position
parameters
Servo
parameters
Spindle
specification
parameters
Spindle
parameters
Rotary axis
configuration
parameters
PLC timer
PLC
integrated
timer
PLC
counter
PLC
constants
Selecting
the PLC bit
Error
compensation
parameters
Error data
Macro list
Position
switches
Barrier data
User parameters
Zero point
return
parameters
Machine parameters
Auxiliary
axis
parameters
(Note) There are user parameter dedicated menus in the screens related to setup. The menu configuration
differs slightly from the above configuration. Refer to the Instruction Manual for details.
1.2 Unit
(1) Input setting unit and number of decimal digits
The number of digits in the decimal section of the parameters related to length is determined by the input
setting unit.
The input setting unit is set with parameter "#1003 iunit".
Input setting
unit
No. of digits in
decimal section
B
3
0 to 999.999 (mm)
C
4
0 to 999.9999 (mm)
D
5
0 to 999.99999 (mm)
E
6
0 to 999.999999 (mm)
Example of setting range
The setting ranges indicated in this manual use the input setting unit "B".
III - 1
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<WRK COUNT> (No. of workpieces machined)
#
Item
8001 WRK COUNT M
8002 WRK COUNT
8003 WRK COUNT LIMIT
Contents
Set the M code that counts the No. of workpiece
repeated machining.
The No. will not be counted when set to 0.
The current machining No. is displayed. Set the
initial value.
Set the maximum No. of workpieces machined.
A signal is output to PLC when the No. of
machining times is counted to this limit.
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99
0 to 999999
0 to 999999
<AUTO TLM> (Automatic tool length measurement)
#
Item
8004 SPEED
8005 ZONE r
8006 ZONE d
Contents
Setting range (unit)
Set the feedrate during automatic tool length
1 to 1000000 (mm/min)
measurement.
Set the distance between the measurement point
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
and deceleration start point.
Set the tolerable zone of the measurement point.
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
If the sensor signal turns ON in front of d before the
measurement point‚ or if the signal does not turn
ON after d is passed‚ an alarm will occur.
<AUTO CORNER OVR.> (Automatic corner override)
#
Item
OVERRIDE
8007
8008 MAX ANGLE
8009 DSC. ZONE
Contents
Set the override value for automatic corner
override.
Set the max. corner opening angle where
deceleration should start automatically.
If the angle is larger than this value‚ deceleration
will not start.
Set the position where deceleration starts at the
corner.
Designate at which length point before the corner
deceleration should start.
Setting range (unit)
0 to 100 (%)
0 to 180 (°)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
<T-TIP OFFSET> (Wear data input)
#
Item
ABS.
MAX.
8010
(For L system only)
8011 INC. MAX.
(For L system only)
Contents
Set the max. value when inputting the tool wear
compensation amount.
A value exceeding this setting value cannot be set.
Set the max. value for when inputting the tool wear
compensation amount in the incremental mode.
III - 2
Setting range (unit)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
(Input setting
increment applies)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
(Input setting
increment applies)
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<FIXED C.> (Fixed cycle)
#
Item
8012 G73 n
(For M system only)
8013 G83 n
8014 CDZ-VALE
(For L system only)
8015 CDZ-ANGLE
(For L system only)
8016 G71 MINIMUM
(For L system only)
8017 G71 DELTA-D
(For L system only)
8018 G84/G74 n
(For M system only)
Contents
Set the return amount for G73 (step cycle).
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
Set the return amount for G83 (deep hole drilling
cycle).
Set the screw cut up amount for G76‚ G78 (thread
cutting cycle).
Set the screw cut up angle for G76‚ G78 (thread
cutting cycle).
The end of cutting in the rough cutting cycle (G71,
G72) is the remainder cutting amount. If the amount
is smaller than the value set with this parameter,
the last cycle will not be executed.
The rough cutting cycle (G71, G72) cutting amount
repeats d+ d, d, d- d using the value (d)
commanded with D as a reference. Set the change
amount d.
This is not used. Set it to "0".
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
0 to 127 (0.1 lead)
0 to 89 (°)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
0
<PRECISION> (High-accuracy control)
#
Item
8019 R COMP
8020 DCC. ANGLE
Contents
Set up a compensation coefficient for reducing a
control error in the reduction of a corner roundness
and arch radius.
Indicates a maximum control error (mm) in
parentheses.
The larger the setup value, the smaller the
theoretical error will be. However, since the speed
at the corner goes down, the cycle time is
extended.
Coefficient = 100 - setting value
(Note) This is valid when "#8021 COMP CHANGE"
is set to "0".
Set up the minimum value of an angle (external
angle) that should be assumed to be a corner.
When an inter-block angle (external angle) in highaccuracy mode is larger than the set value, it is
determined as a corner and the speed goes down
to sharpen the edge.
θ
If the set value is smaller than
θ, the speed goes down to
optimize the corner.
(Note) If "0" is set, it will be handled as 5 degrees.
III - 3
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99 (%)
0 to 89 (degrees)
0: The angle will be
5°.
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<PRECISION> (High-accuracy control)
#
Item
8021 COMP_CHANGE
8022 CORNER COMP
8023 CURVE COMP
Contents
Select whether to share or separate the
compensation coefficient at the corner/curve during
the high-accuracy control mode.
0: Share (#8019 R COMP)
1: Separate
• Corner (#8022 CORNER COMP)
• Curve (#8023 CURVE COMP)
(Note) Set "1" when using SSS control.
Set the compensation coefficient to further reduce
or increase the roundness at the corner during the
high-accuracy control mode.
Coefficient = 100 - setting value
(Note) This is valid when "#8021 COMP CHANGE"
is set to "1".
Set the compensation coefficient to further reduce
or increase the radius reduction amount at the
curve (arc, involute, spline) during the
high-accuracy control mode.
Coefficient = 100 - setting value
(Note) This is valid when "#8021 COMP CHANGE"
is set to "1".
Setting range (unit)
0/1
-1000 to 99 (%)
-1000 to 99 (%)
<SPILINE> (High-accuracy spline)
#
Item
8025 SPLINE ON
(for M system only)
8026 CANCEL ANG.
(for M system only)
8027 Toler-1
(for M system only)
8028 Toler-2
(for M system only)
8029 FairingL
(for M system only)
8030 MINUTE LENGS
(for M system only)
Contents
Specify whether to enable the spline function.
0: Disable the spline function.
1: Enable the spline function.
When the angle made by blocks exceeds the set
value, spline interpolation is canceled temporarily.
In consideration of the pick feed, set a value a little
smaller than the pick feed angle.
Specify the maximum chord error (tolerance) in a
block that includes an inflection point. Set the
tolerance applicable when the applicable block is
developed to fine segments by CAM. (normally
about 10 µm)
When 0.000 is set, the applicable block is linear.
Specify the maximum chord error (tolerance) in a
block that includes no inflection point. Set the
tolerance applicable when the applicable block is
developed to fine segments by CAM. (normally
about 10 µm)
When 0.000 is set, the applicable block is linear.
Set the length of the block subject to fairing.
(Valid when "#8033 Fairing ON" is set to 1.)
When the length of one block exceeds the set
value, spline interpolation is canceled temporarily
and linear interpolation is performed. Set a value
a little smaller than linear block length of the
workpiece to be machined.
If - 1 is set, spline interpolation is performed
regardless of block length.
III - 4
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0 to 180 (°)
0: 180 (°)
0.000 to 100.000 (mm)
0.000 to 100.000 (mm)
0 to 100.000 (mm)
-1 to 127 (mm)
0: 1 (mm)
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<Fairing>
#
Item
8033 Fairing ON
(for M system only)
8034 AccClamp ON
(for M system only)
8035
8036 CordecJudge
(for M system only)
8037 CorJudgeL
(for M system only)
Contents
Set whether to use the fairing function.
0: Fairing invalid
1: Fairing valid
Set the method for clamping the cutting speed.
0: Clamp with parameter "#2002 clamp" or the
corner deceleration function.
1: Clamp the cutting speed with acceleration
judgment.
(Valid when "#8033 Fairing ON" is set to 1.)
This is not used. Set it to "0".
Change the conditions for judging a corner.
0: Judge the corner from the angle of the
neighboring block.
1: Judge the corner from the angle of the
neighboring block, excluding minute blocks.
(Valid when "#8033 Fairing ON" is set to 1.)
Set the length of the block to be excluded.
(Valid when "#8036 CordecJudge" is set to 1.)
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
0
0/1
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
<C-MODAL> (C axis normal line)
#
Item
8041 C-rot.R
8042 C-ins.R
8043 Tool HDL FD OFS
8044 UNIT*10
Contents
This is valid with normal line control type II.
Set the length from the center of the normal line
control axis to the end of the tool. This is used to
calculate the turning speed at the block joint.
This is valid with normal line control type I.
Set the radius of the arc to be automatically
inserted into the corner during normal line control.
Set the length from the tool holder to the tool tip.
Set the command increment scale.
An arbitrary scale can be designated by inputting
an arbitrary value in the setting value.
• The scale is 1 when 0 is designated.
•
III - 5
Setting range (unit)
0.000 to 99999.999
(mm)
0.000 to 99999.999
(mm)
0.000 to 99999.999
(mm)
0 to 10000 (fold)
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<FIXED C.> (Fixed cycle)
#
8051 G71
Item
THICK
8052 G71
PULL UP
8053 G73
U
8054 G73
W
8055 G73
R
8056 G74
RETRACT
8057 G76
LAST-D
8058 G76
TIMES
8059 G76
ANGLE
Contents
Set the amount of cut-in by the rough cutting cycle
(G71, G72)
Set the amount of pull-up when returning to the
cutting start point for the rough cutting cycle (G71.
G72).
Set the X-axis cutting margin of the forming rough
cutting cycle (G73).
Set the Z-axis cutting margin of the forming rough
cutting cycle (G73).
Set the number of times cutting is performed by the
forming rough cutting cycle (G73).
Set the amount of retract (amount of cut-up) of the
push-cut cycle (G74, G75).
Set the amount of final cut-in by the compound type
thread cutting (G76).
Set the number of times the amount of final cut-in
cycle (G76 finish margin) is divided in the
compound type thread cutting (G76).
Set the angle (thread angle) of the tool nose in the
compound type thread cutting (G76).
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
-99999.999 to
99999.999 (mm)
-99999.999 to
99999.999 (mm)
0 to 99999 (times)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
0 to 999.999 (mm)
0 to 99 (times)
0 to 99 (°)
<3-dimensional tool radius compensation>
#
Item
8071 3-D CMP
(for M system only)
Contents
Value of p in the following denominator constants
for 3-dimensional tool radius compensation
Vx = i x r/p, Vy = j x r/p, Vz = k x r/p
Vx, Vy, Vz: X, Y, and Z axes or vectors of
horizontal axes
i, j, k: Program command value
r: Offset
p=
i2 + j2 + k 2
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99999.999
when the set value is 0.
<Scaling>
#
Item
8072 SCALING P
(for M system only)
Contents
Set the scale factor for reduction or magnification
for the machining program for which the G50 or
G51 command is issued.
This parameter is effective when the program
specifies no scale factor.
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99.999999
#
Item
8075 SpiralEndErr
(for M system only)
Contents
Designate the tolerable error range (absolute value)
when the end point position commanded with the
command format type 2 spiral interpolation or
conical interpolation command differs from the end
point position obtained from the speed and
increment/decrement amount.
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
#
Item
8078 Screen Saver Timer
Contents
When not using, set to "0".
Setting range (unit)
0
<Spiral interpolation>
III - 6
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<Deep hole drilling cycle>
#
Item
8083 G83S modeM
(for M system only)
8084 G83S Clearanse
(for M system only)
8085 G83S Forward F
(for M system only)
8086 G83S Back F
(for M system only)
Contents
Set the M command code for changing to the small
diameter deep hole drilling cycle mode.
Set the clearance amount for the G83 small
diameter deep hole drilling cycle.
Set the feedrate from the R point to the cutting start
position in the G83 small diameter deep hole drilling
cycle.
Set the speed for returning from the hole base
during the G83 small diameter deep hole drilling
cycle.
Setting range (unit)
1 to 99999999
Contents
Set whether to validate SSS control with G05
P10000.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
Adjust the maximum value of the range for
recognizing the shape.
To eliminate the effect of steps or errors, etc., set a
large value. To enable sufficient deceleration, set a
small value.
If "0.000" is set, the standard value (1.000mm) will
be applied.
Adjust the clamp speed at the curved section
configured of fine segments.
setting value
Coefficient =
Set the width of the step at which the speed is not
to be decelerated. (Approximately the same as the
CAM path difference [Tolerance].)
If 0 is set, the standard value (5µm) will be applied.
If a minus value is set, the speed will decelerate at
all minute steps.
Set the time to wait for deceleration when the
speed FB does not drop to the clamp speed.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0 to 999.999 (mm)
0 to 99999 (mm/min)
0 to 99999 (mm/min)
<SSS control>
#
Item
8090 SSS ON
(for M system only)
8091 StdLength
(for M system only)
8092 ClampCoeff
(for M system only)
8093 StepLeng
(for M system only)
8094 DccWaitAdd
(for M system only)
III - 7
0 to 100.000 (mm)
1 to 100
-1000 to 0.100 (mm)
0 to 100 (ms)
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<Coord rotation>
#
Item
8621 Coord rot plane (H)
8622 Coord rot plane (V)
8623 Coord rot centr (H)
8624 Coord rot centr (V)
8625 Coord rot vctr (H)
8626 Coord rot vctr (V)
8627 Coord rot angle
Contents
Setting range (unit)
Axis name
This sets the plane, center coordinates, vector
components and angle.
Plane (horizontal axis):
This sets the name of the 1st axis when measuring
the rotation.
When not set, the name will be the X axis.
-999999.999 to
Plane (vertical axis):
999999.999 (mm)
This sets the name of the 2nd axis when
measuring the rotation.
When not set, the name will be the Y axis.
Plane (vertical)
Center coordinates (vertical)
Center
coordinates
Vector (vertical)
Angle
Vector (horizontal)
Plane (horizontal)
M
Center coordinates
(horizontal)
(Note) The angle is automatically calculated and
enumerated at vector component setting,
but direct setting of the angle is possible.
When directly setting the angle, "0" appears
in both the horizontal axis and vertical axis
of the vector components.
III - 8
-360.000 to 360.000
(°)
2. User Parameters
2.1 Process Parameters
<TLM>
#
Item
8701 Tool length
8702 Tool Dia
8703 OFFSET X
8704 OFFSET Y
8705 RETURN
8706 FEED
8707 Skip past amout (H)
8708 Skip past amout (V)
8709 EXT work sign rvs
8710 EXT work ofs invld
8711 TLM L meas axis
8712 TLM D meas axis
Contents
This sets the length to the touch tool tip.
This sets the diameter of the sphere at the touch
tool tip.
This sets the X direction for the spindle center
deviation amount from the touch tool center.
This sets the Y direction for the spindle center
deviation amount from the touch tool center.
This sets the one-time return distance for contafting
again.
This sets the feedrate when contacting again.
This sets the difference (horizontal axis direction) of
the skip read value and actual skip position.
This sets the difference (vertical axis direction) of
the skip read value and actual skip position.
This is set when using the external workpiece
coordinate system with Z shift.
0: External workpiece offset (Z shift) no sign
reversal (Conventional)
1: External workpiece offset (Z shift) sign reversal
This sets whether external workpiece offset
subtraction is valid when setting the workpiece
coordinate offset.
0: Do not subtract external workpiece offset.
(Conventional)
1: Subtract the external workpiece offset.
This sets the #1022 axname2 axis name.
This sets the #1022 axname2 axis name.
Setting range (unit)
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
1 to 60000 (mm/min)
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
0/1
0/1
Axis name (Note 1)
Axis name (Note 2)
(Note 1) If the axis name is illegal or not set, the 3rd axis name will be set as a default.
(Note 2) If the axis name is illegal or not set, the 1st axis name will be set as a default.
<Surface speed control>
#
Item
19425 ManualB Std R1
19426 ManualB Std F1
19427 ManualB Std R2
19428 ManualB Std F2
Contents
This sets a radius used as standard for the rotary
axis speed.
This sets the rotary axis speed for surface speed
control standard radius 1.
This sets a radius used as standard for the rotary
axis speed.
If the same value is set as "#19425 ManualB Std
R1", the rotary axis speed will be the surface speed
control standard speed 1 if the radius is less than
that value, and the surface speed control standard
speed 2 if larger than the set value.
This sets the rotary axis speed for surface speed
control standard radius 2.
III - 9
Setting range (unit)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
1 to 1000000 (°/min)
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
1 to 1000000 (°/min)
2. User Parameters
2.2 Control Parameters
2.2 Control Parameters
#
Item
8101 MACRO SINGLE
8102 COLL. ALM OFF
8103 COLL. CHK OFF
8105 EDIT LOCK B
8106 G46 NO REV-ERR
(For L system only)
8107 R COMPENSATION
8108 R COMP Select
8109 HOST LINK
8110 G71/G72 POCKET
Contents
Select the control of the blocks where the user
macro command continues.
0: Do not stop while macro block continues.
1: Stop every block during signal block
operation.
Select the interference (bite) control to the
workpiece from the tool diameter during tool radius
compensation and nose R compensation.
0: An alarm is output and operation stops when
an interference is judged.
1: Changes the path to avoid interference.
Select the interference (bite) control to the
workpiece from the tool diameter during tool radius
compensation and nose R compensation.
0: Performs interference check.
1: Does not perform interference check.
Select the edit lock for program Nos. 8000 to 9999.
0: Program can be edited.
1: Editing of above program is prohibited.
Select the control for the compensation direction
reversal in G46 (nose R compensation).
0: An alarm is output and operation stops when
the compensation direction is reversed (G41
→ G42‚ G42 → G41).
1: An alarm does not occur when the
compensation direction is reversed‚ and the
current compensation direction is maintained.
0: In arc cutting mode, the machine moves to
the inside because of a delay in servo
response to a command, making the arc
smaller than the command value.
1: In arc cutting mode, the machine
compensates the movement to the inside
because of a delay in servo response to a
command
Select whether to perform arc radius error
compensation over all axes or axis by axis.
0: Perform compensation over all axes.
1: Perform compensation over axis by axis.
(Note) This parameter is effective only when
"#8107 R COMPENSATION" is "1".
Select whether to enable computer link B instead of
the RS-232C port.
0: Disable computer link B to enable normal
RS-232C communication.
1: Enable computer link B to disable normal
RS-232C communication.
Set the pocket machining if there is a dimple
(pocket) in the rough cutting cycle (G71, G72)
finishing program.
0: Pocket machining OFF
1: Pocket machining ON
III - 10
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
2. User Parameters
2.2 Control Parameters
#
Item
8111 Milling Radius
8112 DECIMAL PNT-P
8113 Milling Init G16
8114 Milling Init G19
Contents
Select the diameter and radius of the linear axis for
milling (cylindrical/pole coordinate) interpolation.
0: All axes radius command
1: Each axis setting (follows "#1019 dia")
(Note) This parameter is valid only in the milling
(cylindrical/pole coordinate) interpolation
mode.
0: The decimal point command for G04 address
P is invalidated.
1: The decimal point command for G04 address
P is validated.
Designate which plane to use for milling machining
after the power is turned ON or reset.
#8113
#8114
Plane
0
0
G17 plane
0
1
G19 plane
1
0
G16 plane
1
1
(Note) This parameter is valid for the G code
system 2, 3 ("#1037 cmdtyp"=3, 4).
8116 Coord rot para invd
Select the validity of coordinate rotation by the
parameters.
0: Valid
1: Invalid
III - 11
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
0: Plane other than
G16
1: Select G16 plane
0: Plane other than
G19
1: Select G19 plane
0/1
2. User Parameters
2.3 Axis Parameters
2.3 Axis Parameters
Set up the parameter required for each axis.
#
Item
8201 AX. RELEASE
8202 OT-CHECK OFF
8203 OT-CHECK-CANCEL
8204 OT-CHECK-N
8205 OT-CHECK-P
8206 TOOL CHG. P
8207 G76/87 IGNR
(For M system only)
8208 G76/87 (-)
(For M system only)
8209 G60 SHIFT
(For M system only)
8210 OT INSIDE
Contents
Select the function to remove the control axis from
the control target.
0: Control as normal.
1: Remove from control target.
Select the stored stroke limit II function set in #8204
and #8205.
0: Valid
1: Invalid
When the simple absolute position method ("#2049
type" is 9) is selected‚ the stored stroke limits I, II
(or IIB) and IB will be invalid until the first zero point
return is executed after the power is turned ON.
0: Valid (according to #8202)
1: Temporary cancel
(Note) "#8203 OT-CHECK-CANCEL" affects all the
stored stroke limits.
This sets the coordinates of the (-) direction in the
moveable range of the stored stroke limit II or the
lower limit coordinates of the prohibited range of
stored stroke limit IIB.
If the sign and value are the same as #8205, the
stored stroke limit II (or IIB) will be invalid.
If the stored stroke limit IIB function is selected, the
prohibited range will be between two points even
when #8204 and #8205 are set in reverse.
When II is selected, the entire range will be
prohibited.
This sets the coordinates of the (+) direction in the
moveable range of the stored stroke limit II or the
upper limit coordinates of the prohibited range of
stored stroke limit IIB.
Set the coordinates of the tool change position for
G30. n (tool change position return).
Set with coordinates in the basic machine
coordinate system.
Select the shift operation at G76 (fine boring) and
G87 (back boring).
Specifies the shift direction at G76 and G87.
Set the last positioning direction and distance for a
G60 (unidirectional positioning) command.
The stored stoke limit function to be set in #8204
and #8205 prevents the machine from moving to
the inside or outside of the specified range.
0: Inhibits outside area
(Select stored stroke limit II.)
1: Inhibits inside area
(Select stored stroke limit II B.)
III - 12
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
0/1
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
0: Shift effective
1: No shift
0: Shift to (+) direction
1: Shift to (-) direction
±99999.999 (mm)
0/1
2. User Parameters
2.3 Axis Parameters
#
Item
8211 MIRR. IMAGE
8213 Rotation axis type
Contents
Enable or disable the parameter mirror image
function.
0: Disable
1: Enable
This designates the rotation type (short-cut
valid/invalid) or linear type (workpiece coordinate
value linear type/all coordinate value linear type).
This parameter is valid only when "#1017 rot" is set
to 1.
III - 13
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0: Short-cut invalid
1: Short-cut valid
2: Workpiece
coordinate value
linear type
3: All coordinate value
linear type
2. User Parameters
2.4 Operation Parameters
2.4 Operation Parameters
#
Item
8901 Counter type 1
8902 Counter type 2
8903 Counter type 3
8904 Counter type 4
8905 Counter type 5
Contents
Setting range (unit)
This sets the type of counter displayed at the upper 0 to 255
left of the AUTO/MDI display on the Monitor screen. 1: Curnt posn
2: Wk co posn
3: Mach posn
4: Prog posn
This sets the type of counter displayed at the lower
left of the AUTO/MDI display on the Monitor screen. 5: Prog 0 pnt
6: Err compen
7: (No name;
TLM value)
This sets the type of counter displayed at the upper 8: Remain cmd
right of the AUTO/MDI display on the Monitor
9: Man int amt
screen.
10: Next cmd
11: Restart pos
This sets the type of counter displayed at the lower 12: Remain dist
13: Meas posn
right of the AUTO/MDI display on the Monitor
screen.
14: Meas posn
15: Meas posn
16: Tip Gxx
This sets the type of counter displayed at the left of
17: Distance
the Manual display on the Monitor screen.
18: Pulse
(Note) The counter displayed at the right of the
Manual display is fixed to the machine
19: Tip Mach posn
position.
20: Relat posn
8910 Edit undo
This sets whether to validate the Undo function
during program edit on the Monitor screen or Edit
screen.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
8920 3D tool ofs select
This designates the method to calculate the drawing 0/1
position when drawing a solid.
With 3D drawing, the drawing position (tool tip
position) is calculated with the method designated
with this parameter, and the image is drawn.
0: Drawing position = Tool center path information
(machine position) - Tool length offset + wear
1: Drawing position = Tool center path information
(machine position) - tool length set on 3D Tool
Setting screen.
III - 14
0/1
2. User Parameters
2.5 Barrier Data
2.5 Barrier Data (For L system only)
#
8300 P0
8301
8302
8303
8304
8305
8306
8311
Item
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
8312 P8
8313 P9
8314 P10
8310 Barrier ON
8315 Barrier Type (L)
8316 Barrier Type (R)
8317 ELIV. AX. Name
8318 Stock Angle (L)
8319 Stock Angle (R)
Contents
Set the reference X-coordinates of the chuck and
the tail stock barrier.
Set the center coordinate (radius value) of
workpiece by the basic machine coordinate
system.
Set the area of the chuck and tail stock barrier.
(radius value)
Set the coordinate value from the center of
workpiece for X-axis. Set the coordinate value by
basic machine coordinate system for Z-axis.
Setting range (unit)
±99999.999 (mm)
Set the area of the left spindle section.
• X axis: Set the coordinate value from the
workpiece center (P0). (radius value)
• Z axis: Set the coordinates in the basic
machine coordinate system.
Set the area of the right spindle section.
• X axis: Set the coordinate value from the
workpiece center (P0). (radius value)
• Z axis: Set the coordinates in the basic
machine coordinate system.
Select the validity of the chuck and tailstock barrier.
0: Invalid (Setting from special display unit valid)
1: Valid
Set the shape of the left chuck and tailstock barrier.
0: No area
1: Chuck
2: Tailstock
Set the shape of the right chuck and tailstock
barrier.
0: No area
1: Chuck
2: Tailstock
When the right chuck and tailstock barrier is
movable, set the name of the delivery axis.
When using the multi-part system method and the
delivery axis is an axis in the other part system,
designate the system as 1A, 1B or 2A, 2B. If the
part system is not designated as A and B, the set
part system will be used.
Set the angle for the left tailstock end section.
The angle will be interpreted as 90° if there is no
setting (when 0 is set).
Set the angle for the right tailstock end section.
The angle will be interpreted as 90° if there is no
setting (when 0 is set).
±99999.999 (mm)
III - 15
±99999.999 (mm)
±99999.999 (mm)
0/1
0/1/2
0/1/2
A/B/..
: (axis
address)
1A/1B/..
2A/2B/.. : (part system
designation)
0
: cancel
0 to 180 (°)
0: 90° default
0 to 180 (°)
2. User Parameters
2.6 I/O Parameters
2.6 I/O Parameters
There are basically two types of input/output parameters which must be set when inputting‚ outputting or
referring to data‚ or when performing tape operation.
9001 to 9014 parameters:
Set which channel to connect which device to for each I/O application.
9101 to 9528 parameters:
Set the transmission speed, etc., for each input/output device.
Up to five types of input/output device parameters can be set in device 0 to 4.
<I/O>
#
<PORT No.>
Specify the board No. to which the serial
input/output device is connected.
• Set "1" to use ch1.
• Set "2" to use ch2.
9001 Specify the port for inputting the data
such as machine program and
parameters.
9003 Specify the port for outputting the data
DATA OUT
such as machine program and
parameters.
9005
Specify
the input port for running with
TAPE MODE
the tape mode.
MACRO PRINT 9007 Specify the output port for the user
macro DPRINT command.
9009
Specify
the port for inputting/outputting
PLC IN/OUT
various data with PLC.
REMOTE PRG 9011 Specify the port for inputting remote
programs.
IN
9013
Specify
the port for communication with
EXT UNIT
an external unit.
DATA IN
III - 16
#
<DEV. No.> <DEV. NAME>
Set the input/output device No. for
each application.
The device Nos. are 0 to 4 and
correspond to the input/output
device parameters.
The device name set in the
input/output device parameter is
also displayed for identification.
9002 Specify the No. of the device that
inputs the data.
9004 Specify the No. of the device that
outputs the data.
9006 Specify the No. of the device to be
run with the tape mode.
9008 Specify the No. of the device for
the DPRINT command.
9010 Specify the No. of the device for
the PLC input/output.
9012 Specify the number of the device
used to input remote programs.
9014 Specify the number of the unit
used for communication with an
external unit
2. User Parameters
2.6 I/O Parameters
#
Item
9101 DEVICE NAME
Contents
Set the device name corresponding to the device
No.
Set a simple name for quick identification.
9102 BAUD RATE
Set the serial communication speed.
9103 STOP BIT
Set the stop bit length used in the start-stop
system.
9104 PARITY CHECK
Specify whether to add the parity check bit to the
data during communication.
Specify the odd or even parity when it is added to
the data.
9105 EVEN PARITY
9106 CHR. LENGTH
Set the length of the data bit.
9107 TERMINATR TYP
The code to terminate data reading can be
selected.
Specify the transmission control method.
The method will be no procedure if a value except 1
to 3 is set.
9108 HAND SHAKE
Setting range (unit)
Use alphabet
characters‚ numerals
and symbols to set a
name within 3
characters.
0: 19200 (bps)
1: 9600
2: 4800
3: 2400
4: 1200
5: 600
6: 300
7: 110
1: 1 (bit)
2: 1.5
3: 2
0: Parity bit not added
1: Parity bit added
0: Odd parity
1: Even parity
0: 5 (bit)
1: 6
2: 7
3: 8
0 and 3: EOR
1 and 2: EOB or EOR
1: RTS/CTS method
2: No procedure (No
handshaking)
3: DC code method
0: No parity to DC
code (DC3 = 13H)
1: DC code with parity
(DC3 = 93H)
DC2 / DC4
0: None / None
1: Yes / None
2: None / Yes
3: Yes / Yes
0: Do not add
1: Add
0: ISO code output
1: EIA code output
9109 DC CODE PRTY
Specify the DC code when the DC code method is
selected.
9111 DC2/4 OUTPUT
Specify the DC code handling when outputting data
to the output device.
9112 CR OUTPUT
Specify whether to insert the (CR) code just before
the EOB (L/F) code during output.
In data output mode, select the ISO or EIA code for
data output.
In data input mode, the ISO and EIA codes are
identified automatically.
Specify the length of the tape feed to be output at
0 to 999 (characters)
the start and end of the data during tape output.
9113 EIA OUTPUT
9114 FEED CHR.
III - 17
2. User Parameters
2.6 I/O Parameters
#
Item
9115 PARITY V
9116 TIME-OUT (sec)
9117 DR OFF
9118 DATA ASCII
9119 INPUT TYPE
9121 EIA CODE
9122
9123
9124
9125
9126
9127
9128
9201 to
9301 to
9401 to
9501 to
[
]
#
∗
=
:
$
!
Contents
Specify whether to check the parity of the No. of
characters in block during data input.
The No. of characters is factory-set so that the
check is valid at all times.
Set the time out time to detect an interruption in
communication.
Time out check will not be executed when set to 0
to 30 seconds.
Specify whether to check the DR data at the data
input/output.
0: Output in ISO/EIA code (Depends on whether
#9113, #9213, #9313, #9413, or #9513 EIA
output parameter is set up)
1: Output in ASC II code
Specify the mode for input (collation).
0: Standard input (Data from the very first EOB is
handled as significant information.)
1: EOBs following the first EOB of the input data
are skipped until data other than EOB is input.
When output with EIA code‚ data can be output
using the alternate code in which the special ISO
code not included in EIA is specified.
Specify the codes which do not duplicate the
existing EIA codes by hexadecimal for respective
special codes.
Set the same settings for device 1.
Set the same settings for device 2.
Set the same settings for device 3.
Set the same settings for device 4.
III - 18
Setting range (unit)
0: Do not perform
parity V check
1: Perform parity V
check
0 to 30 (s)
0: DR valid
1: DR invalid
0/1
0/1
0 to FF (hexadecimal)
2. User Parameters
2.7 Ethernet Parameters
2.7 Ethernet Parameters
Set the parameters related to Ethernet input/output.
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter, turn
ON the power again.
9701 to 9706 parameters:
When several TCP/IP drivers are installed and the IP address is set manually ("#9701 IP address
automatic setting" is set to 0), the same setting will be made for all parameters.
9711 to 9781 parameters:
Set the server information required for using the Ethernet function.
Server information for up to four units can be set.
#
Item
9701 IP addr auto set
(PR)
9702 IP address
(PR)
Contents
The IP address is automatically assigned from the
DHCP server.
(Note) When this setting is validated, the following
parameters "#9702 IP address", "#9703
Sub-net address" and "#9704 Gateway
setting" will be invalid.
Set the IP address.
This sets the IP address of the TCP/IP assigned to
the NC (Windows) computer. Contact the network
controller for the address to be set.
Setting range (unit)
0: Manual setting
1: Automatic setting
15 characters or less
Dot notation numeric
value train
9703 Subnet mask
(PR)
This sets the subnet mask of the TCP/IP assigned
to the NC (Windows) computer. Contact the
network controller for the subnet mask to be set.
9704 Gateway
(PR)
This sets the gateway of the TCP/IP assigned to the 15 characters or less
NC (Windows) computer.
Dot notation numeric
value train
This sets the timeout time (s) for when the
10 to 99 (s)
communication is not completed correctly, or when (Standard: 30)
there is no communication response.
9705 Timeout
15 characters or less
Dot notation numeric
value train
9706 Host No.
This selects the number of the host to be used from 1 to 4 : Host No.
host 1 to host 4.
9711 Host1 host name
This sets the host computer name.
This parameter allows the NC to easily recognize
the host computer on the network. Set the host
computer's name (name registered in
C:\windows\hosts) or the IP address.
<Setting example>
For host name : Mspc160
For IP address : 150.40.0.111
(Note) Set the host computer's TCP/IP address if
communication is not carried out correctly.
9712 Host1 user name
This sets the user name when logging into the host 15 characters
computer.
(alphanumeric) or less
9713 Host1 password
This sets the password when logging into the host
computer.
15 characters
(alphanumeric) or less
9714 Host1 directory
This sets the directory name of the host computer.
Refer to (Note 4) for details.
31 characters
(alphanumeric) or less
III - 19
15 characters
(alphanumeric) or less
2. User Parameters
2.7 Ethernet Parameters
#
Item
9715 Host1 host type
Contents
This sets the type of host computer.
(Note) When "0" is set, the settings for the
following parameters #9716 to #9720 will
be invalid.
Setting range (unit)
0: UNIX/PC automatic
judgment
1: UNIX
2: PC (DOS)
9716 Host 1
Wrd pos: name
This sets the file name display position (nth word
from left) of the list displayed when the ftp
command "dir" is executed.
(Note) One word designates a character string
divided by one or more spaces.
0 to 100
0: Default value
9717 Host 1
Wrd pos: size
This sets the size display position (nth word from
left) of the list displayed when the ftp command "dir"
is executed.
(Note) One word designates a character string
divided by one or more spaces.
This sets the <DIR> display position (nth word from
left) of the list displayed when the ftp command "dir"
is executed.
(Note) One word designates a character string
divided by one or more spaces.
0 to 100
0: Default value
9719 Host 1
Wrd pos: cmnt
This sets the comment (date, time, etc.) display
position (nth word from left) of the list displayed
when the ftp command "dir" is executed.
(Note) One word designates a character string
divided by one or more spaces.
0 to 100
0: Default value
9720 Host 1
Wrd num: cmnt
This sets the number of words to be displayed as a 0 to 100
comment.
0: Default value
(Note) One word designates a character string
divided by one or more spaces.
9721 Host 1
no total siz
This sets whether to display the total number of
0: Display
characters registered in the machining programs of 1: Do not display
host1 when displaying the file list.
If there are many files in the directory to be referred
to, the list can be updated quickly by setting "1".
9731 to
9751 to
Set the same settings for host 2.
Set the same settings for host 3.
9771 to
Set the same settings for host 4.
9718 Host 1
Wrd pos: Dir
0 to 100
0: Default value
(Note 1) The user name and password are required when logging in.
(Note 2) It is necessary to enable reading/writing when exchanging files.
(Note 3) With the Personal WEB Server and Windows NT 4.0 fpt Server, the file list format can be selected
from DOS or UNIX.
(Note 4) The directory released to the client (NC unit) with the host computer's server is handled as the root
directory by the NC unit.
III - 20
2. User Parameters
2.8 Computer Link Parameters
2.8 Computer Link Parameters
#
Item
BAUD
RATE
9601
9602 STOP BIT
9603 PARITY EFFECTIVE
Contents
Specify the rate at which data is transferred.
Setting range (unit)
0: 19200 (bps)
1: 9600
2: 4800
3: 2400
4: 1200
5: 600
6: 300
7: 110
8: 38400
Specify stop bit length used in start-stop mode.
1: 1
See "PARITY EFFECTIVE" in #9603. The
2: 1.5
number of characters is adjusted in output mode so 3: 2
that no problems occur if the parity check is
enabled.
This parameter is set when using a parity bit
separately from the data bit.
1 character
ON
OFF
Start bit
9604 EVEN PARITY
9605 CHR. LENGTH
9606 HAND SHAKE
9607 TIME-OUT SET
9608 DATA CODE
9609 LINK PARAM. 1
b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6
bn
Data bit
Parity bit
Stop bit
Set this to match the input/output device
specifications.
Specify whether even or odd parity is used when
parity is used. This parameter is ignored when no
parity is used.
Specify data bit length.
See "PARITY EFFECTIVE" in #9603.
RS-232C transmission control mode
DC control mode should be set for computer line B.
Specify time-out time at which an interruption of
data transfer during data input/output should be
detected.
If 0 is set, time infinity is specified.
Specify the code to be used.
See "PARITY EFFECTIVE" in #9603.
Bit 1: DC1 output after NAK or SYN
Specify whether to output the DC1 code after
the NAK or SYN code is output.
Bit 7: Enable/disable resetting
Specify whether to enable resetting in the
computer link.
III - 21
0: No parity bit used in
I/O mode
1: Parity bit used in I/O
mode
0: Odd parity
1: Even parity
2: 7
3: 8
0: No control
1: RTS/CTS method
2: No handshaking
3: DC control mode
0 to 999 (1/10s)
0: ASCII code
1: ISO code
0: Don't output the
DC1 code.
1: Output the DC1
code.
0: Enable resetting.
1: Disable resetting.
2. User Parameters
2.8 Computer Link Parameters
#
Item
9610 LINK PARAM. 2
9611
9612
9613
9614
LINK PARAM. 3
LINK PARAM. 4
LINK PARAM. 5
START CODE
9615 CTRL. CODE OUT
9616
9617
9618
9619
9620
9621
9622
9623
9624
CTRL. INTERVAL
WAIT TIME
PACKET LENGTH
BUFFER SIZE
START SIZE
DC1 OUT SIZE
POLLING TIMER
TRANS. WAIT TMR
RETRY COUNTER
Contents
Bit 2: Specify the control code parity (even parity
for the control code).
Set the parity in accordance with the I/O device
specifications.
Setting range (unit)
0: No control code
parity added
1: Control code parity
added
Bit 3: Parity V
0: Disable
Specify whether to enable checking of parity 1: Enable
V in one block in data input mode.
Not used
Not used
Not used
Specify the code by which file data transfer begins 0: DC1 (11H)
at first.
1: BEL (07H)
This parameter is used for a specific user, and set 0
in this parameter for normal operation.
0: Do not output the
Bit 0: NAK output
Specify whether to send the NAK code to the
NAK code.
host if a communication error occurs in
1: Output the NAK
computer link B.
code.
Bit 1: SYN output
0: Do not output the
Specify whether to send the SYN code to the
SYN code.
host if NC resetting or an emergency stop
1: Output the SYN
occurs in computer link B.
code.
Bit 3: DC3 output
0: Do not output the
Specify whether to send the DC3 code to the
DC3 code.
host when communication ends in computer link 1: Output the DC3
B.
code.
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
III - 22
2. User Parameters
2.9 Subprogram Storage Designation Parameters
2.9 Subprogram Storage Designation Parameters
#
Item
8880 Subpro stor D0: dev
8881 Subpro stor D0: dir
8882 Subpro stor D1: dev
8883 Subpro stor D1: dir
8884 Subpro stor D2: dev
8885 Subpro stor D2: dir
8886 Subpro stor D3: dev
8887 Subpro stor D3: dir
8888 Subpro stor D4: dev
Contents
If D1 to D4 is designated when calling the
subprogram, the subprogram to be called will be
searched from the storage destination (device and
directory) designated with this parameter.
Setting range (unit)
Device name (Note 3)
(Note 1) If the called subprogram is not found in
the designated storage destination, a
program error will occur.
(Note 2) If D0 to D4 is not designated when the
subprogram is called, the subprogram
will be searched from the memory.
(Note 3) The following values are set in the device
name.
Directory 48
characters
Directory 48
characters
(Example)
The following will be searched:
M98 P (program No.), D0
Device name (Note 3)
Device : "8880 Subpro stor D0:dev" device
Directory : "8881 Subpro stor D0:dir" directory
Setting value
M
G
F
R
D
E
8889 Subpro stor D4: dir
Display name
Memory
HD
FLD
Memory card
Data server
Ethernet
Device name (Note 3)
Directory 48
characters
Device name (Note 3)
Directory 48
characters
Device name (Note 3)
Directory 48
characters
III - 23
3. Setting the Machine Parameters
3. Setting the Machine Parameters
A password must be set before the machine parameters can be set.
Machine parameter password setting method
(1) Press the function key Mainte.
The menu for the maintenance related
screen will appear.
(2) Press the menu Param.
The parameter menu will appear.
(3) Press the machine parameter selection
menu.
(Example) Menu Basesys param
A message prompting input of the password
will appear.
If the password has been input once after
the power was turned ON, the cursor will
appear at the Machine Parameter screen.
(4) Set the password and press the INPUT
key.
MPARA INPUT
The cursor will appear at the Machine
Parameter screen, and the machine
parameters can be set.
(Note 1) Refer to the section "4. Base Specification Parameters" and following for details on the
machine parameters.
(Note 2) Always turn the power OFF after setting the machine parameters.
III - 24
4. Base Specifications Parameters
4. Base Specifications Parameters
Base specification parameter is the generic term for the following three parameters.
In this Manual, the parameters are explained in order of number.
Base system parameters
#1001-#1012, #1025-#1037
#1073-#1076, #1085-#1086
#1109-#1111, #1151-#1152
#1169-#1216, #1501-#1574
#1590-#1593, #12001-#12004
Base axis specification parameters
#1013-#1024, #1061-#1072
Base common parameters
#1038-#1059, #1077-#1084
#1087-#1108, #1112-#1150
#1153-#1168, #1217-#1348
#1801-#1827, #1901-#1936
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter, turn
ON the power again.
#
Items
1001 SYS_ON System
(PR)
validation
setup
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify the existence of the 1st system‚ 2nd system 0: Not used
and PLC axis with 1 or 0.
1: Used
1002 axisno
(PR)
Number of Set No. of axes in each system and the No. of PLC 0 to 16
axes
axes.
A total of 16 axes can be set.
Part system 1
: 1 to 8
Part system 2 to 4 : 0 to 8
PLC axis
: 0 to 2
1003 iunit
(PR)
Input setup Specify the input setting value for each system and B : 1
µm
unit
the PLC axis. The parameter units will follow this
C : 0.1 µm
specification.
D : 0.01 µm (10nm)
E : 0.001 µm (1nm)
1004 ctrl_unit
(PR)
Control
unit
Specify the control unit for each part system and
PLC axis.
Set the unit for the NC internal position data, data
communciated between the NC and drive unit, and
the servo movement data. Some parameter units,
such as the pitch error and backlash, follow this
specification.
B: 1
µm
C : 0.1 µm
D : 0.01 µm (10nm)
E : 0.001 µm (1nm)
1005 plcunit
(PR)
PLC unit
Specify the PLC interface setting and display unit.
The PLC interface setting and display unit, follow
this specification. Note that the PLC axis follows
#1003 iunit.
B: 1
µm
C : 0.1 µm
D : 0.01 µm (10nm)
E : 0.001 µm (1nm)
Specify the machine error compensation setting and
display unit.
The parameters related to machine error
compensation (backlash, pitch error compensation,
etc.) and PLC interface (external machine
coordinate system compensation) follow this
specification.
B: 1
µm
C : 0.1 µm
D : 0.01 µm (10nm)
E : 0.001 µm (1nm)
1006 mcmpunit Machine
(PR)
error
compensation unit
1010 srvunit
(PR)
Output unit Specify the unit for data communicated with the
(servo)
drive unit.
The data communicated between the NC and drive
unit, and the servo movement data unit follow this
specification. (The standard value when using an
optical cable is E.)
III - 25
B: 1
µm
C : 0.1 µm
D : 0.01 µm (10nm)
E : 0.001 µm (1nm)
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
1013 axname
Axis name Specify each axis’ name address with an alphabetic Axis addresses such as
character.
X, Y, Z, U, V, W, A, B,
Use the characters X‚ Y‚ Z‚ U‚ V‚ W‚ A‚ B or C.
and C
Do not specify the same address in one part
system.
The same address as one used in another part
system can be specified.
The PLC address does not need to be set. (The
axis name is displayed as 1 and 2.)
1014 incax
Increment
command
axis name
1015 cunit
(PR)
Program
command
unit
When specifying the program movement rate’s
absolute or incremental method with an address‚
specify the incremental command axis name
address with an alphabetic character.
The address that can be used is the same as #1013
axname.
Specify an address that is different from that #1013.
Setting is not required if absolute/incremental
specification with addresses is not performed
(#1076 Abslnc = 0).
Specify the minimum unit of the program movement
amount.
cunit Movement amount for movement
command 1
0: Follow #1003 iunit
1: 0.0001 mm (0.1µm)
10: 0.001 mm (1µm)
100: 0.01 mm (10µm)
1000: 0.1
mm (100µm)
10000: 1.0
mm
If there is a decimal point in the movement
command‚ the decimal point position will be
handled as 1mm regardless of this setting.
0
#1003 iunit
1
0.1µm
10
1µm
100
10µm
1000
100µm
10000
1mm
1017 rot
(PR)
Rotational
axis
Specify whether the axis is a rotary axis or linear
0: Linear axis
axis.
1: Rotary axis
For the rotary axis‚ the position display will be 360°‚
and the axis will return to 0°.
If the position display is to be continuously
displayed even with the rotary axis‚ set the axis as a
linear axis
1018 ccw
(PR)
Motor
CCW
Specify the direction of the motor rotation to the
command direction.
0: Rotates clockwise (looking from motor shaft)
with the forward rotation command.
1: Rotates counterclockwise (looking from
motor shaft) with the forward rotation
command.
III - 26
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1019 dia
(PR)
Items
Diameter
specification
axis
1020 sp_ax
(PR)
Spindle
Interpolation
1021 mcp_no
(PR)
Drive unit I/F
channel No.
(servo)
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify whether the program movement amount is 0: Command with
to be commanded with the diameter dimension or
movement amount
as movement amount.
1: Command with
When the movement amount is commanded with
diameter dimension
the diameter dimensions‚ 5mm will be moved when
the command is a movement distance of 10mm.
The movement amount per pulse will also be
halved during manual pulse feed.
Among parameters concerning length‚ the tool
length‚ the wear compensation amount and the
workpiece coordinate offset are displayed in
diameter value when diameter is specified‚ but
other parameters are always displayed in radius
value.
Specify 1 when the NC control axis is used as the 0: The NC control axis
spindle.
is used as the servo
axis.
1: The NC control axis
is used as the
spindle.
(Metal drive unit)
When connecting an axis drive unit, use a 4-digit
0101 to 0108
number to set the drive unit interface channel
0201 to 0208
number and which axis that channel is to be.
This is also used to identify an optical
(Optical drive unit)
communication drive unit and metal
1001 to 1008
communication drive unit.
2001 to 2008
High-order two digits : Drive unit interface
channel No.
* Note that this will
High-order one digit : Number of optical drive
change according to
unit channel
the communication
Low-order one digit : Number of metal drive
cycle.
unit channel
Low-order two digits : Axis No.
1022 axname2 2nd axis
(PR)
name
Set the name of the axis displayed on the screen
Two digits between A to
with two characters. (X1, Z2, etc.)
Z and 1 to 9 (Setting is
Always use an alphabetic character (A to Z) for the cleared when 0 is set)
first character.
1023 crsadr
(PR)
Command
address
during cross
machining
Set the address for issuing a command to this axis A to Z
during cross machining control.
(Setting is cleared when
0 is set)
1024 crsinc
(PR)
Incremental
command
address
during cross
machining
Set the address for issuing an incremental
command to this axis during cross machining
control.
1025 l_plane
Initial plane
selection
Specify the plane to be selected when the power is 1: X-Y plane (G17
turned ON or reset.
command state)
When 0 is specified, 1 is assumed (X-Y plane).
2: Z-X plane (G18
command state)
3: Y-Z plane (G19
command state)
III - 27
A to Z
(Setting is cleared when
0 is set)
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1026 base_l
Base axis I
1027 base_J Base axis J
1028 base_K Base axis K
1029 aux_I
Flat axis I
1030 aux_J
Flat axis J
1031 aux_K
Flat axis K
1037 cmdtyp
Command
type
Details
Specify the basic axis address that composes the
plane.
Specify the axis address set in #1013 axname.
If all three items do not need to be specified‚ such
as for 2-axis specifications‚ input "0"‚ and the
parameter will be blank.
Normally‚ when X‚ Y and Z are specified
respectively for base_l‚_J‚_K‚ the following relation
will be established:
G17: X-Y
G18: Z-X
G19: Y-Z
Specify the desired address to set an axis address
other than the above.
If there is an axis parallel to #1026 base_l‚ specify
that axis address.
Control axis addresses
such as X, Y, and Z
If there is an axis parallel to #1027 base_J‚ specify
that axis address.
If there is an axis parallel to #1028 base_K‚ specify
that axis address.
Control axis addresses
such as X, Y, and Z
Control axis addresses
such as X, Y, and Z
Specify the program G code series and
compensation type.
1 to 8
cmdtyp
1
G code series
System 1 (for M)
2
System 1 (for M)
3
System 2 (for L)
4
5
System 3 (for L)
System 4
(for special L)
System 5
(for special L)
System 6
(for special L)
System 7
(for special L)
6
7
8
Setting range (unit)
Control axis addresses
such as X, Y, and Z
Compensation type
Type A (one compensation
amount for one compensation number)
Type B (shape and wear
amounts for one compensation number)
Type C (two kinds of
compensation amount of
shape and wear per
compensation No.)
Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
There are some items in the specifications that can
be used or cannot be used according to the value
set in this parameter.
The file structure may also change depending on
the compensation data type.
1038 plcsel
Ladder
selection
Specify the PLC type.
III - 28
0: User custom PLC
1: Standard PLC
2: Exclusive PLC for
MELSEC bus link
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1039 spinno Number of
spindles
Details
Specify the existence of a spindle.
Setting range (unit)
0: No spindle
1: One spindle
2: Two spindles
3: Three spindles
4: Four spindles
1040 M_inch
(PR)
Constant
input (inch)
Specify the parameter unit system for the position
and length.
0: Metric system
1: Inch system
1041 l_inch
(PR)
Initial state
(inch)
Specify the unit system for the program movement
amount when the power is turned ON or reset and
for position display. Designate an internal unit.
0: Metric system
1: Inch system
(Note) Selection of inch and metric unit
When set value of "#1041 I_inch" is changed‚ the unit of length is changed after reset.
Among parameters concerning length‚ following items are not changed automatically‚ therefore
change the set values to agree with the new unit system when the unit system is changed.
Tool compensation amount (Tool length compensation amount‚ tool wear compensation amount
and tool tip compensation amount)
Workpiece coordinate offset
Machining
parameter
#8004 SPEED
#8027 Toler-1
#8005 ZONE r
#8028 Toler-2
#8057 G76 LAST-D
#8006 ZONE d
#8029 FairingL
#8075 SpiralEndErr
#8009 DSC. ZONE
#8010 ABS. MAX.
#8030 MINUTE LENGS #8084 G83S Clearance
#8037 CorJudgeL
#8085 G83S Forward F
#8011 INC. MAX.
#8041 C-rot. R
#8012 G73n
#8042 C-ins. R
#8013 G83n
#8051 G71 THICK
#8016 G71 MINIMUM
#8017 G71 DELTA-D
#8052 G71 PULL UP
#8053 G73 U
#8018 G84/G74n
#8054 G73 W
#8056 G74 RETRACT
#8086 G83S Back F
#8204 OT-CHECK-N
Axis parameter
Barrier data
#8205 OT-CHECK-P
#8206 TOOL CHG.P
#8209 G60 Shift
#8300 - #8306, #8311 - #8314
Basic specification
#1084 RadErr
parameter
"#8004 SPEED" is 10 inches/min. unit for the inch system.
III - 29
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1042 pcinch
(PR)
1043 lang
Items
PLC axis
command
(inch)
Select
language
displayed
Details
Specify the unit system for the commands to the
PLC axis.
Setting range (unit)
0: Metric system
1: Inch system
Specify the display language.
0/1
11 to 22
0: English display
1: Japanese display
(Standard)
(Standard)
11:Display in German
12:Display in French
13:Display in Italian
14:Display in Spanish
15:Display in Chinese
(traditional Chinese)
16:Display in Korean
17:Display in Portuguese
18:Display in Dutch
19:Display in Swedish
20:Display in Hungarian
22:Display in Chinese
(simplified Chinese)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
(Note) If no character package is available for a
specified language, the screen is
displayed in English.
1044 auxno
(PR)
MR-J2-CT
Connections
Specify the number of MR-J2-CTs connected.
0 to 4
1045 nskno
(PR)
Megatorgue
motor
connections
Specify the number of NSK megatorque motors
0 to 16
connected. When a value other than 0 is specified,
2nd miscellaneous function data is output as signed
binary data.
1050 MemPrg
(PR)
Definition of
program save
area
0 to 7
MemPrg
Machining program
MDI data
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(Machining program)
: Part system common
Machining program save area is shared by
part systems.
: Part system independent
Machining programs can be registered for
each part system.
(MDI data)
: Part system common
MDI data is shared by part systems.
: Part system independent
MDI data can be set for each part system.
When this parameter is changed, the power must
be turned OFF and ON, and the system formatted.
(Note) This parameter is valid when the
multi-part system is valid.
III - 30
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1051 MemTol Tool
(PR)
compensation memory
common for
part systems
1052 MemVal No. of
(PR)
common
variables
shared in part
system
designation
Details
0: Tool compensation memory separate for part
systems ($1: #1 to #40, $2: #1 to #40)
1: Tool compensation memory common for part
systems ($1: #1 to #80)
0: Common variables common for part system
(number fixed)
#100 to : Per part system
#500 to : Common for part systems
1: Common variables common for part system
(number fixed)
#100 to : Designate with V1comN
#500 to : Designate with V0comN
(Note) When this parameter is changed, the
method of reading the file system will
change after the power is turned ON, so
always reformat again.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
Setting order
MemVal
changeover
Format
Mismatch
displays
Format
Turn
power ON
again
1061 intabs
(PR)
Manual ABS
updating
Defines whether to update the absolute value data
during automatic handle interrupt.
This parameter is valid only when "#1145 l_abs" is
set to 1.
1062 T_cmp
Tool
Specify whether the tool length offset and wear
0 to 3
compensation compensation is valid during T command execution.
function
Setting value
0
1
2
3
Tool length offset
Valid
Valid
Invalid
Invalid
0: Do not update
(shift coordinates
the amount of the
interruption)
1: Update (same
coordinates as
when interrupt did
not occur will be
applied.)
Wear compensation
Valid
Invalid
Valid
Invalid
1063 mandog Manual
dog-type
The initial return to the reference position is per0: High speed return
formed with dog-type return after the power is turned 1: Dog-type
ON‚ and the coordinate system is established.
Specify the manual reference position return method
after the coordinate system is established with this
parameter. (This setting is not required when using
absolute position detection.)
1064 svof
(PR)
Specify whether to correct the error when the servo
is OFF.
Error
correction
1065
1066
1067
III - 31
0: Do not correct the
error
1: Correct the error
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1068 slavno
(PR)
Items
Slave axis
number
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify the number of the slave axis for synchronous 0: No slave axis
control. The axis number is an NC number excluding 1 to 8:
the spindle and PLC axis.
First to eighth
Two or more slave axes cannot be set up for one
axes
master axis.
slaveno cannot be set up for a slave axis.
When using the multi-part system, the relation of the
master axis and slave axis cannot extend over part
systems.
1069 no_dsp
(PR)
Axis with no Set up an axis that displays no counter. This option 0: Displays the
counter
is valid on the counter display screen (relative value
counter
display
screen).
1: Does not display
the counter.
1070 axoff
Axis
removal
Define an axis that enables axis removal control.
0: Disables axis
removal.
1: Enables axis
removal
1072 chop_ax
Chopping
axis
Designate the chopping axis.
0: Non-chopping
axis
1: Chopping axis
1073 I_Absm
Initial
absolute
value
Specify the absolute value/incremental value mode
for when the power is turned ON or reset.
0/1
1074 l_Sync
Initial
synchronou
s feed
Specify the feedrate specification mode for when the 0/1
power is turned ON or reset.
0: Asynchronous feed (feed per minute)
1: Synchronous feed (feed per rotation)
1075 I_G00
Initial G00
1076 Abslnc
(For L
system
only)
1077 radius
Specify the linear command mode for when the
power is turned ON or reset.
0: Linear interpolation (G01 command state)
1: Positioning (G00 command state)
ABS/INC
The absolute value/incremental commands can be
address
issued by using the absolute value address and
incremental value address for the same axis.
0: Absolute/incremental with G command
1: Absolute/incremental with address code
(The #1013 axname address will be the
absolute value command‚ and #1014 incax
address will be the incremental value
command)
Incremental Specify if the diameter specification axis’ (#1019 dia
command
is set to 1) incremental value command uses the
for diameter diameter value or radius value
specification
axis
III - 32
0/1
0/1
0: Diameter value
1: Radius value
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1078 Decpt2
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
Decimal point Specify the unit of position commands that do not 0/1
type 2
have a decimal point.
0: The min. input command unit is used
(follows #1015 cunit)
1: 1mm (or 1inch) unit is used
(For the dwell time, 1s unit is used.)
1079 F1digt
Validate F1
digit
Specify whether to execute the F command with a 0/1
1-digit code command or with a direct numerical
command.
0: Direct numerical command (command
feedrate during feed per minute or rotation)
1: 1-digit code command (feedrate specified
with #1185 spd_F1 – #1189 F5)
1080 Dril_Z
(For D
system
only)
Specify boring Specify a fixed cycle hole drilling axis.
0/1
axis
0: Use an axis vertical to the selected plane as
the hole drilling axis.
1: Use the Z axis as the hole drilling axis
regardless of the selected plane.
1081 Gmac_P Give priority
to G code
parameter
Specify the G code priority relationship during the 0/1
macro call with the G command.
0: G code used in system is priority.
1: Registered G code for call out is priority.
1082 Geomet
(For L
system
only)
Geometric
0/1/2
Specify whether to use the geometric I or IB
function.
0: Do not use.
1: Use only geometric I.
2: Use geometric I and IB.
With geometric, specific address codes are used
for exclusive meanings. Thus, if A or C is used for
the axis address or 2nd miscellaneous command
code, the A used for the axis address may
function as the geometric's angle designation.
Take special care when designating the axis
name, etc., when using this function.
1084 RadErr
Arc error
Specify the tolerable error range when a deviation 0 to 1.000 (mm)
occurs in the end point and center coordinate in
the circular command.
1085 G00Drn
G00 dry run
Specify whether to apply dry run (feed with
manual setting speed instead of command
feedrate) to the G00 command.
0: Do not apply to G00. (move at rapid
traverse rate)
1: Apply to G00. (move at manual set
feedrate)
1086 G0lntp
G00
Specify the G00 movement path type
0/1
non-interpolat
0: Move linearly toward the end point.
ion
(interpolation type)
1: Move to the end point of each axis at the rapid
traverse feedrate for each axis.
(non-interpolation)
III - 33
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1087
Items
G96_G0 Constant
surface
speed
control by
rapid
traverse
feed
command
Details
Specify how to handle the cycle speed for the G00
command when using the constant surface speed
control function.
0: Calculate the cycle speed constantly even
during G00 movement.
1: Calculate the cycle speed at the block end
point in the G00 command.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
1090
Lin_RT
Linear
rotary axis
0/1
Specify how to handle a command for the rotary
axis that exceeds 360°.
0: For absolute value commands that exceed
360°‚ the value will be converted into a
remainder of 360° and the axis will move.
Example: If the command is 420°‚ the applied
value will be 60°.
1: For absolute value commands that exceed
360°‚ the axis will move in the same manner
as a linear axis.
Example: If the command is 420°‚ the axis
will pass the 360° position and will
move to the 60° position.
1091
Mpoint
1092
Tchg _A
Ignore
Specify now to handle the middle point during G28 0/1
middle point and G30 reference point return.
0: Move to the reference position after passing
the middle point designated in the program.
1: Ignore the middle point designated in the
program and move straight to the reference
position.
Replace
Specify the movement of the additional axis during 0/1
tools for
tool change position return.
additional
0: The additional axis does not move with the
axis
tool change position return command.
1: After returning the standard axis with the tool
change position return command‚ the
additional axis also returns to the tool change
position.
1093
Wmvfin
Synchronization
between
part
systems
method
1094
Tl_SBK
(for L
system
only)
Select life
Select whether to count the data units to be used
count for
for a single block when using the tool life
single block management II function (L system).
0: Does not count the data units.
1: Count the data units.
0/1
1095
T0tfof
TF output
0/1
1088
1089
Specify the method for synchronization between
part systems when using the multi-part system.
When the movement command is found in the
synchronization command (!, M) block:
0: Synchronize before executing movement
command
1: Synchronize after executing movement
command
Select how to handle TF for T00 command.
0: TF is output.
1: TF is not output
III - 34
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1096 T_Ltyp Tool life
(for L
management
system type
only)
Details
Specify the tool life management type.
1: Life management type l
2: Life management type ll
Setting range (unit)
1/2
1097 T1digt
Tool wear
compensation
number
1-digit
command
Specify the No. of digits in the tool wear
compensation No. in the T command.
0: The 2 high-order digits are the tool No.‚ and
the 2 Iow-order digits are the wear
compensation No.
1: The 3 high-order digits are the tool No.‚ and
the 1 Iow-order digit is the wear
compensation No.
This parameter will be fixed to 0 when tool life
management II is selected.
0/1
1098 Tlno.
Tool length
offset number
Specify the No. of digits in the tool length offset No. 0/1
in the T command.
0: The 2 or 3 high-order digits are the tool No.
The 2 or 1 Iow-order digits are the tool length
offset and wear compensation Nos.
1: The 2 or 3 high-order digits are the tool No.
and tool length offset Nos.
The 2 or 1 Iow-order digits are the wear
compensation No.
1099 Treset
Cancel tool
compensation
amount
0/1
Specify how to handle tool compensation vector
when resetting system.
0: Clear the tool length and wear compensation
vectors when resetting.
1: Save the tool length and wear compensation
vectors when resetting.
When the values are cleared‚ the compensation will
not be applied‚ so the axis will move the
compensation amount in the next compensation
operation.
When the values are saved‚ the compensation will
be applied‚ so the axis will shift the differential
amount of the compensation amount in the next
compensation operation.
1100 Tmove
Tool wear
compensation
Specify the period to perform tool length offset and 0 to 2
wear compensation.
0: Compensate when T command is executed.
1: Superimpose and compensate with the
movement command in the block where the T
command is located. If there is no movement
command in the same block‚ compensation
will be executed after the movement
command is superimposed in the next
movement command block.
2: Compensate when the T command is
executed.
Superimpose and compensate a tool length
offset with the movement command in the
same block. If there is no movement
command in the same block, compensation
will be executed after the movement
command is superimposed in the next
movement command block.
III - 35
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
1101 Tabsmv Tool wear
Specify the type of movement command when
0/1
compen#1100 Tmove is set to 1.
sation method
0: Compensate regardless of the movement
command type.
1: Compensate only at the movement command
in the absolute value command.
1102 tlm
(For L
system
only)
Manual tool
length
measuring
system
Specify the measurement method for manual tool
measurement l.
0: Align tool with reference position
1: Input measurement results
0/1
1103 T_life
Validate life
management
1106 Tcount
(For L
system
only)
Life
management
count
1107 Tllfsc
(For L
system
only)
Split life
Set up the number of groups to be displayed on the 0 to 2
management tool life management II (L system) screen.
display screen
0: Displayed group count 1,
maximum number of registered tools: 16
1: Displayed group count 2,
maximum number of registered tools: 8
2: Displayed group count 4,
maximum number of registered tools: 4
1108 TlrectM
(For L
system
only)
Life
management
re-count M
code
Set up the M code for tool life management II (L
system) re-count.
0 to 99
1109 subs_M
(PR)
Validate
alternate M
code
Select the user macro interrupt with the substitute
M code.
0: Alternate M code
invalid
1: Alternate M code
valid
1110 M96_M
M96 alternate Specify an M code to replace M96 when #1109
M code
subs_M is set to 1.
3 to 97
(excluding 30)
1111 M97_M
M97 alternate Specify an M code to replace M97 when #1109
M code
subs_M is set to 1.
3 to 97
(excluding 30)
Select the usage of the tool life management
0/1
function.
0: Do not manage tool life.
1: Execute tool life management function
control.
1104 T_Com2 Tool
Select the command method for when #1103
0/1
command
T_Life is set to 1.
method 2
0: Handle the program tool command as the
group No.
1: Handle the program tool command as the tool
No.
1105 T_Sel2
Tool selection Select the tool selection method for when #1103
0/1
method 2
T_Life is set to 1.
0: Select in order of registered No. from the
tools used in the same group.
1: Select the tool with the longest remaining life
from tools used in the same group and the
unused tools.
Specify the function when address N is omitted
0: Time specified
when inputting data (G10 L3 command) for tool life
input
management function ll.
1: No. of times
specified input
III - 36
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
1112 S_TRG
Validate
Specify the validity conditions for the user macro
0/1
(PR)
status trigger interrupt signal.
method
0: Valid when interrupt signal (UIT) turns OFF to
ON.
1: Valid when interrupt signal (UIT) is ON.
1113 INT_2
(PR)
Validate
Specify the movement after user macro interrupt
0/1
interrupt
signal (UIT) input.
method type
0: Execute interrupt program without waiting for
2
block being executed to end.
1: Execute interrupt program after completing
block being executed.
1114 mcrint
Macro
argument
initialization
Select whether to clear statements other than
specified arguments by macro call. Also, select
whether to clear local variables by power-ON and
resetting.
0: Delete non-specified arguments by macro
call.
1: Retain non-specified arguments by macro
call.
2: Retain non-specified arguments by macro
call and clear local variables by power-ON
and resetting.
0/1/2
1115 thwait
Waiting for
thread
cutting
Set the queue number during screw thread cutting
when the chamfering is not valid.
0 to 99
(Approx. 4 ms.)
Standard set value: 4
1116 G30SLM
Invalidate
soft limit
(manual
operation)
Enable this function when disabling the soft limit
0: Enable soft limit
check function from the second to fourth reference
function.
position return.
1: Disable soft limit
function.
1117 H_sens
Handle
response
switch
Switch the handle response mode when feeding
the handle.
0: Standard handle response
1: High-speed handle response
1118 mirr_A
(For L
system
only)
0/1
Select how
Select one of the following two methods:
to set up the
• Set up the current length of tools on each
length of
facing turret.
tools on
• Set up a value, assuming that the tools on
cutter tables
each facing turret are in the same direction
(opposed
as that of those on the base turret.
tables)
0: Current length of the tools on each facing
turret
1: Value, assuming that the tools on each facing
turret are in the same direction as that of
those on the base turret.
1119 Tmiron
(For L
system
only)
Select the
Select whether to validate the mirror image of each 0: Invalid
mirror image facing turret with the T command.
1: Valid
of each
facing turret
with T
command
III - 37
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1120 TofVal
(PR)
1121 edlk_c
Items
Change
macro
variable
Edit lock C
1122 pglk_c
(PR)
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify whether to change the macro variable (tool 0/1
offset) numbers for shape compensation and wear
compensation.
0: Do not change. (Conventional
specifications)
1: Change the shape and wear compensation
variable numbers each for X, Z, and R.
Specify whether to prohibit editing of program Nos. 0/1
9000 to 9999.
0: Edit
1: Do not edit
(Note) If #1122 is set to 1 or 2, 1 will be set in
#1121 when the power is turned ON.
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Select whether to use the origin set function.
0: Use
1: Do not use
0/1
1123 origin
Origin set
prohibit
1124 ofsfix
Fix tool wear
Specify whether to automatically increment the
0/1
compensation compensation No. by 1 with the input or to display
No.
the No. as it is in the setting on the tool
compensation screen.
0: Increment the # No. by 1 when the input key
is pressed. (Same as general parameters)
1: # No. does not change even if INPUT key is
pressed.
When making settings in sequence‚ 0 is handier.
When changing and setting repeatedly while
adjusting one compensation value‚ 1 is handier
Actual
Specify the feedrate display on the monitor screen. 0: Command speed
feedrate
1: Real movement
display
feedrate
1125 real_f
1126 PB_G90
Playback G90 Specify whether the playback movement amount
when performing playback editing is to be an
absolute value or incremental value.
0: Incremental value
1: Absolute value
1127 DPRINT
DPRINT
alignment
Specify the alignment for printing out with the
DPRINT function.
0: No alignment‚ data is printed with left
justification.
1: Align the minimum digit and output.
0/1
1128 RstVCI
Clear
variables by
resetting
Specify how to handle the common variables when 0/1
resetting.
0: Common variables do not change after
resetting.
1: The following common variables are cleared
by resetting:
During variable 100 group specifications:
#100 to #149 are cleared.
Variable 200 and more group specifications:
#100 to #199 are cleared.
III - 38
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1129 PwrVCl Clear
variables by
power-ON
1130 set_t
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify how to handle the common variables when
0/1
the power is turned ON.
0: The common variables are in the same state as
before turning the power OFF.
1: The following common variables are cleared
when the power is turned ON.
During variable 100 group specifications:
#100 to #149 are cleared.
Variable 200 and more group specifications:
#100 to #199 are cleared.
Display
Specify the tool command value display on the
selected tool POSITION screen.
number
0: T-modal value of program command is
displayed.
1: Tool number sent from PLC is displayed.
0/1
1131
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1132 CRT
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1133 ofsmem
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1134 LCDneg
1135 unt_nm
Not used. Set to "0".
Set up a unit name.
Set up the unit name with 4 or less characters
consisting of both alphabets and numbers. If 0 is set
up, the unit name is not displayed.
0
4 or less characters
consisting of both
alphabets and
numbers
1136 optype
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1137 Cntsel
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1138 Pnosel
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1139 edtype
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Unit name
1140 Mn100
M code
number
First number of M code that corresponds to setup
number from 100 to 199
0 to 99999999
1141 Mn200
M code
number
M code
number
First number of M code that corresponds to setup
number from 200 to 299
First number of M code that corresponds to setup
number from 300 to 399
0 to 99999999
M code
number
MDI setup
lock
First number of M code that corresponds to setup
number from 400 to 499
Select whether to enable MDI setup in non-MDI
mode.
0 to 99999999
1142 Mn300
1143 Mn400
1144 mdlkof
1145 I_abs
0 to 99999999
0: Disable MDI
setup
1: Enable MDI setup
Manual ABS Specify how to handle the absolute value data during 0/1
parameter
automatic handle interrupt.
0: Absolute value data is renewed if manual ABS
switch is ON.
Data is not renewed if switch is OFF.
1: Follows the intabs state when #1061 intabs is
valid.
III - 39
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1146 Sclamp Spindle
rotation
speed
clamp
function
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify how to handle the spindle rotation speed clamp 0/1
function with the G92S command.
0: G92S command is handled as a clamp command
only in the G96 state (during constant surface
speed control). G92S will be handled as normal
S command in G97 state (constant surface
speed OFF).
1: The S command in the same block as G92 is
constantly handled as a clamp command.
1147 smin_V
Minimum
spindle
rotation
speed
clamp type
Specify the type of spindle min. rotation speed clamp
value.
0: Rotation speed setting
1: Output voltage coefficient setting
Set the #3023 smini parameter according to this type
setting.
1148 I_G611
Initial high
precision
The modal state when the power is turned ON is set to 0/1
the high accuracy control mode.
0: G64 (cutting mode) at power ON
1: G61.1 (high-accuracy control mode) at power ON
1149 cireft
Arc
Specify whether to enable deceleration at the arc
deceleration entrance or exit.
speed
0: Do not decelerate at arc entrance and exit.
change
1: Decelerate at arc entrance and exit.
0/1
Reset initial Specify whether to initialize (power ON state) the
modals by resetting.
0: Do not initialize modal state.
1: Initialize modal state.
Initial
Specify whether the default mode after power-ON or
command
resetting, inch command or metric command mode.
unit
0: Metric command (G21 command state)
1: Inch command (G20 command state)
Valid when reset input is made.
Related parameter: Bit 6 "Select setting and display
unit" of #1226
0/1
0/1
1150
1151 rstint
1152 I_G20
1153 FixbDc
0/1
Hole bottom Specify whether to perform a deceleration check or
0 to 2
deceleration in-position check at the hole bottom in the hole drilling
check
cycle. This parameter is valid only for a hole drilling
cycle in which no dwell command can be issued at the
hole bottom.
0: Perform no deceleration check and in-position
check.
1: Perform a deceleration check.
2: Perform an in-position check.
1154 pdoor
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1155 DOOR_m
1156 DOOR_s
Not used. Set to "100".
Not used. Set to "100".
100 (Hexadecimal)
100 (Hexadecimal)
1157 F0atrn
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1158 F0atno
Not used. Set to "0".
0
III - 40
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
1160 Mpronum Number of
Set the number of registerable machine tool builder
registerable
macro programs (0 to 1000 programs).
machine tool
builder macros
Setting range (unit)
0 to 1000
1161 Mprosiz
Machine tool Set the size of the machine tool builder macro
builder macro program registration area.
registration
area size
0, 32, 128 (KB)
1163 No rio
(PR)
RIO
connection
detection
invalid
Even if an RIO is not connected when the I/O is
configured only of cards such as CC-Link, the RIO
communication cutoff alarm is not detected.
0: Check the RIO connection.
1: Do not check the RIO connection.
0/1
1164 ATS
Automatic
tuning
function
Set this to validate the automatic tuning function.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
0/1
1166 fixpro
Fixed cycle
editing
Select whether to use the edit, program list and data 0 to 99999999
input/output functions for the fixed cycles, machine
tool builder macro programs or general programs.
0: General programs can be edited, etc.
1: The fixed cycles can be edited, etc.
Password No.: The machine tool builder macro
programs can be edited, etc.
1167 e2rom
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1168 test
Simulation
test
Specify the test mode for the control unit.
0: Normal operation
The test mode does not use reference position
mode
return‚ and tests with a hypothetical zero point return 1: Test mode
completed state. This is limited to test operation of
the control unit itself‚ and must not be used when
connected to the machine.
1169 part
system
name
Part system
name
Set the name of each part system.
A max. of four
This must be set only when using multi-part system. alphabetic characters
This name is displayed on the screen only when the or numerals.
part systems must be identified.
Use a max. of four alphabetic characters or
numerals.
1170 M2name Second
miscellaneous code
Set this address code when using the 2nd
miscellaneous command. Set an address with A‚ B
and C that is not used with "#1013 axname" or
"#1014 incax".
1171 taprov
Tap return
override
Set the tap return override value for the synchronous 1 to 100 (%)
tap.
1172 tapovr
Tap return
override
Set the override value when leaving the tap end
1 to 999 (%)
point in the synchronous tap cycle.
The setting range is 1 to 999‚ and the unit is %.
When a value less than 100 is set‚ it will be judged as
100%.
III - 41
A, B, C
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1173 dwlskp
G04 skip
condition
Details
Specify the skip signal for ending the G04 (dwell)
command.
Setting range (unit)
Skip condition 0 to 7
PLC interface input signal
Setting
Skip 3
Skip 2
Skip 1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
End when
input.
1174 skip_F
G31 skip
speed
1175 skip1
1176
1f
1177
2
1178
2f
1179
3
1180
3f
signal is
Specify the feedrate when there is no F command in 1 to 999999 (mm/min)
the program at G31 (skip) command.
Specify the skip signal in the G31.1 to G31.3
(multi-step skip) command‚ and the feedrate when
there is no F command in the program.
G31.1 skip Skip signal specified at G31.1
condition
G31.2 skip Skip feedrate at G31.1
speed
G31.2 skip Skip signal specified at G31.2
condition
G31.2 skip Skip feedrate at G31.2
speed
G31.3 skip Skip signal specified at G31.3
condition
G31.3 skip Skip feedrate at G31.3
speed
Skip condition 0 to 7
PLC interface input signal
Setting
Skip 3
Skip 2
Skip 1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Skip feedrate
1 to 999999 (mm/min)
1181 G96_ax
Constant
surface
speed
control
Specify the axis to be targeted for constant surface
speed control.
0: Program specification will be invalidated‚ and
the axis will always be fixed to the 1st axis.
1: 1st axis specification
2: 2nd axis specification
3: 3rd axis specification
:
:
8: 8th axis specification
The program specification will be the priority for all
settings other than 0.
0 to 8
1182 thr_F
Thread
cutting
speed
Set the screw cut up speed when not using
chamfering in the thread cutting cycle.
0: Cutting feed clamp feedrate
1 to 60000 mm/min: Set feedrate
0 to 60000 (mm/min)
1183 clmp_M
M code for Set the M code for C-axis clamp in the hole drilling
clamp
cycle.
0 to 99999999
1184 clmp_D
Dwelling
Set the dwell time after outputting the M code for
time after
C-axis unclamp in the hole drilling cycle.
outputting
M code for
unclamp
0.000 to 99999.999 (s)
III - 42
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1185
1186
1187
1188
1189
spd_F1
spd_F2
spd_F3
spd_F4
spd_F5
Items
F1 digit
feedrate
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Details
Specify the feedrate for the F command in the
F1-digit command (#1079 F1 digt is set to 1).
Feedrate when F1 is issued (mm/min)
Feedrate when F2 is issued (mm/min)
Feedrate when F3 is issued (mm/min)
Feedrate when F4 is issued (mm/min)
Feedrate when F5 is issued (mm/min)
Setting range (unit)
1 to 1000000
(mm/min)
1190 s_xcnt
(PR) (For L
system
only)
Validate
inclinedaxis control
Specify whether to disable or enable inclined-axis
control.
0: Disable inclined-axis control
1: Enable inclined-axis control
0/1
1191 s_angl
(PR) (For L
system
only)
Inclination
angle
± 80.000 (°)
1192 s_zrmv
(PR) (For L
system
only)
Compensation
at origin return
Specify the inclination angle (θ).
(Note) If "0" is specified for this parameter, the
angle determined by three-side setting is
valid.
Specify whether to perform compensation for the
base axis corresponding to the inclined axis at
original return.
0: Perform compensation.
1: Don't perform compensation.
1193 inpos
The setting is selected with "#1306 InpsTyp Deceleration check
specification type".
0: Deceleration check method 1
1: Validate in-position check
1194 H_acdc
1195 Mmac
1196 Smac
1197 Tmac
1198 M2mac
0/1
Deceleration
check method
1
Specify the deceleration check method for G0.
0: Command deceleration check
1: In-position check
Validate
in-position
check
0/1
Specify the deceleration confirmation method for
the positioning or cutting command.
0: G0, G1+G9 Command deceleration check
1: G0, G1+G9 In-position check
Time constant
0 for handle
feed
Specify the time constant for the manual handle
feed.
0: Use time constant for G01
1: Time constant 0 (step)
0/1
Specify the user macro M‚ S or T command macro
call out.
Macro call out with M command
0: Invalid
1: Valid
Macro call for
M command
Macro call for Macro call out with S command
S command
Macro call for T Macro call out with T command
command
Macro call with Macro call out with 2nd miscellaneous command
2nd
miscellaneous
code
III - 43
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1199 Sselect
Items
Select
initial
spindle
control
Details
Select the initial condition of spindle control after
power is turned ON.
0: 1st spindle control mode (G43.1)
1: Selected spindle control mode (G44.1)
2: All spindle simultaneously control mode
(G47.1)
(Note) Spindle No. when G44.1 is commanded
is selected with #1534 SnG44.1.
Setting range (unit)
0: G43.1
1: G44.1
2: G47.1
1200 G0_acc
(PR)
G0 constant
inclination
Set up acceleration and deceleration types when a 0: Acceleration and
rapid traverse command is issued
deceleration with
0: Acceleration and deceleration (conventional)
time constant
with time constant
1: Acceleration and
1: Acceleration and deceleration with inclination
deceleration with
angle constant
inclination angle
constant
1201 G1_acc
(PR)
Validate
Set up acceleration and deceleration types when a 0: Acceleration and
acceleration
liner interpolation command is issued.
deceleration with
and
0: Acceleration and deceleration (conventional)
time constant
deceleration
with time constant
1: Acceleration and
with inclination
1: Acceleration and deceleration with inclination
deceleration with
angle constant
inclination angle
constant G1
constant
1202 mirofs
(For L
system
only)
Distance
Set up the distance between tools (edges)
between facing (between facing turrets).
turrets
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
1203 TmirS1
(For L
system
only)
1204 TmirS2
(For L
system
only)
Select turrets
as facing
turrets with T
command
Select turrets
as facing
turrets with T
command
Set up turrets as shown in the mirror image of
facing turrets with the T command that
corresponds to tool numbers 1 to 32.
0 to FFFFFFFF
Set up turrets as shown in the mirror image of
facing turrets with the T command that
corresponds to tool numbers 33 to 64.
0 to FFFFFFFF
1205 G0bdcc
Acceleration
and
deceleration
before G0
interpolation
1206 G1bF
Maximum
speed
0: G00 acceleration and deceleration are
0/1
selected as those after interpolation.
1: The G00 acceleration/deceleration is the
acceleration/decelerate before interpolation
regardless of whether the mode is the high
accuracy control mode.
(Note) "1" cannot be set for the 2nd part system
and following.
Set up a cutting feedrate when selecting
1 to 999999 (mm/min)
acceleration and deceleration before interpolation.
III - 44
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1207 G1btL
Items
Time
constant
Details
Set up a cutting feed time constant when selecting
acceleration and deceleration before interpolation.
Setting range (unit)
1 to 5000 (ms)
Speed
G1bF
Time
G1btL
1208 RCK
1209 cirdcc
1210 RstGmd
Arc radius
error
compensation
factor
Arc
deceleration speed
Modal G
code reset
An arc radius error compensation can be increased
and decreased from −60.0 to 20.0%.
-60.0 to +20.0 (%)
Specify the deceleration speed at the arc entrance or
exit.
1 to 999999 (mm/min)
Specify whether to initialize each G code group modal
and the H and D codes when the system is reset.
Specify the initialization items in bit correspondence.
0: Initialize.
1: Don't initialize.
M system
Specify a hexadecimal
number.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
Group 1 Move G modal
Group 2 Flat selection modal
Group 3 Absolute/increment command modal
Group 5 Feed G modal
Group 6 Inch/metric modal
Group 7 Radius compensation modal
Group 8 Length compensation modal
Group 10 Fixed cycle return command modal
Group 12 Workpiece coordinate system modal
Group 13 Cut modal
Grpup 15 Normal line control modal
Group 17 Constant surface speed control command
modal
Group 18 pole coordinate command modal
Group 19 G command mirror modal
Group 20 Spindle 2 control modal
H, D codes
Spindle clamp rotation speed
(To be continued to the next page)
III - 45
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify a hexadecimal
(Continued from the previous page)
The H code indicates the tool length offset number, and number.
the D code indicates the tool radius compensation
number.
When bit 18 is set to ON, the H and D codes and group
8 G modal area retained.
When bit 7 is set to ON, the H code and group 8 G
modal are retained.
L system
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
1211 FHtyp
Group 1 Move G modal
Group 2 Flat selection modal
Group 3 Absolute/increment command modal
Group 4 Barrier check modal
Group 5 Feed G modal
Group 6 Inch/metric modal
Group 7 Nose R compensation modal
Group 10 Fixed cycle return command modal
Group 12 Workpiece coordinate system modal
Group 13 Cut modal
Group 17 Constant surface speed control command
modal
Group 18 Balance cut
Group 20 Spindle 2 control modal
Group 15 Facing turret mirror image
Feed hold
stop type
Specify the type of the external signal used for feed
hold.
0: Disable the external signal.
1: Enable the external signal (contact A)
2: Enable the external signal (contact B)
0 to 2
1213 proaxy
(For L
system
only)
Side 1 of
inclination
angle
Specify the length on the rectangular coordinates of the ±9999.999
inclined axis in the triangle made up of the inclination
angle.
1214 macaxy
(For L
system
only)
Side 2 of
inclination
angle
Specify the length of the actual base axis
corresponding to the inclined axis in the triangle made
up of the inclination angle.
1212
III - 46
±9999.999
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1215 macaxx
(For L
system
only)
1216 extdcc
1217 aux01
1218 aux02
(bit3)
Items
Side 3 of
inclination
angle
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify the length of the actual axis of the inclined axis ±9999.999
in the triangle made up of the inclination angle.
External
Use an upper limit value at the feedrate indicated when 1 to 999999 (mm/min)
deceleration validating external deceleration signals.
level
This parameter is valid when #1239 set11/bit6 is set to
0.
Parameter
input/output
format
Not used. Set to "0".
Specify a parameter input/output format.
0: Type I
1: Type II (related to #1218 aux02/bit5)
0
0/1
aux02
(bit4)
Tool number Specify the R register that contains the tool number
selection
used for automatic calculation when measuring the
coordinate offset of an external workpiece.
0: Conforms to #1130 set_t.
1: Uses the tool number indicated by user PLC
aux02
(bit5)
Parameter
Specify the spindle specification address of parameter 0/1
I/O II spindle I/O type II.
0: C
specification
1: T
address
This parameter also applies to the spindle specification
address for input and collation.
(Note) This parameter is valid only for parameter I/O
type II (bit 3 of aux02 in #1218 is ″1″).
III - 47
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1219 aux03
(bit1)
Stop highspeed PC
monitoring
function
Details
Set "1" to disable the function that stops the system
when the high-speed processing time is extended.
Disable the monitoring function only as a temporary
measure.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
aux03
(bit2)
Improve skip
coordinate
accuracy
0: Skip accuracy (conventional specification)
1: Changes skip accuracy (correct a position in
skip coordinates when entering skip signals).
0/1
aux03
(bit5)
Dog-type
intermediate
point
Select whether to move to the intermediate point
during automatic dog-type reference position return.
0: Do not move to intermediate point during
dog-type reference position return.
1: Move to intermediate point during dog-type
reference point return.
0/1
Tool life check Specify the life check standard applicable when the
timing
use count is incremented in tool life management II.
selection
0: Determine that the tool life is over when the
incremented use count exceeds the life count.
(Use count > life count)
1: Determine that the tool life is over when the
incremented use count has reached the life
count. (Use count ≥ life count)
0/1
1220 aux04
(bit 0)
(For L
system
only)
(Default: 0)
aux04
(bit1)
Validity of
Validate or invalidate the space code described in the 0/1
space code in comment statements in the machining program in edit
comment
operation with the special display.
(Default: 0)
0: Invalidate the space code in the comment
statements of the machining program.
1: Validate the space code in the comment
statements of the machining program.
aux04
(bit4)
Data input/
output unit
selection
aux04
(bit7)
0/1
Host
Set whether Ethernet communication is enabled
communication during automatic operation.
validity during
automatic
0: Ethernet communication disabled during
operation
automatic operation
1: Ethernet communication enabled during
automatic operation
(Note) If Ethernet communication is enabled during
automatic operation, interrupt processes
required for communication will be carried
out, so the machining performance could be
affected.
Specify the input/output data unit for tool data and
user parameter input/output.
0: Internal unit (metric)
1: Follows command mode set with #1152 I_G20
Metric when set to 0
Inch when #1152 I_G20 is set to 1
This parameter is valid when initial metric (#1041
I_inch 0) is set and the setting and display unit is the
command unit (#1226 aux10 bit6 1). In all other
cases, the tool data will be input and output with the
internal units.
III - 48
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1221 aux05
(bit7)
Items
Details
Current value B Select the type of counter to be displayed on the
valid
POSITION screen.
0: Displays a relative value (value that includes
tool length offset amount, tool radius
compensation amount and workpiece
coordinate offset amount)
1: Displays current value B (value that does not
include tool length offset amount, tool radius
compensation amount and workpiece
coordinate offset amount)
Setting range (unit)
0/1
aux05/bit7 = 1
aux05/bit7 = 0
Tool offset
Workpiece offset
(Note 1) When "#1221 aux05/bit7" is set to "1", the
current value B is selected regardless of the
bit type of #1287 ext23.
When the current value B is valid, the
counter zero or origin zero is invalid.
(Note 2) The following limits apply to M720:
• This is compatible only with the lathe
system.
• The relative value counter on the
COORDINATE screen will also display the
current value B.
• When "#1287 ext23/bit3" is set to 0, the
relative value will be displayed instead of
the current value B regardless of this
parameter setting.
1222 aux06
(bit0)
Validity of tool
length
measurement
confirmation
message
0: Display no confirmation message when tool
compensation data is set.
1: Display a confirmation message when tool
compensation data is set.
aux06
(bit1)
Height axis
specification
When "1" is set in this parameter, the axis specified 0/1
by base specification parameter #1028 base_k is
measured and no other axes are measured if they
move.
aux06
(bit2)
Servo
waveform
display
Specify whether to enable the waveform display
function.
0: Disable the waveform display function.
1: Enable the waveform display function.
aux06
(bit3)
Enable/disable Specify whether to enable the setup parameter lock 0/1
setup parameter function.
lock
0: Disable
1: Enable
III - 49
0/1
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
aux06 Minimum cut-in Select the minimum cut-in amount command value for 0/1
(bit4) amount
the compound thread cutting cycle (G76 command).
selection
0: The minimum cut-in amount (Q) is "0".
1: The minimum cut-in amount (Q) is the CNC
internal data.
aux06 Fixed cycle
(bit5) for compound
lath command
format check
selection
aux06 Zero point
(bit7) return
deceleration
check method
1223 aux07 Rapid traverse
(bit0) inclination
constant
multi-stage
acceleration
and
deceleration
Select the operation to be made if the 1st block of the 0/1
fixed cycle for compound lathe is omitted when the
conventional format is selected (#1265 ext01/bit0 "0").
0: Program error (P33) occurs.
1: Parameter setting value is used.
Set the deceleration check method used during
automatic reference position return.
0: In-position check
1: Commanded deceleration check
Specify whether to enable the rapid traverse
inclination constant multi-stage
acceleration/deceleration function.
0: Disable
1: Enable
Related parameters:
#2064 rapid2 Speed 2
#2065 G0tL2 Time constant 2
#2066 rapid3 Speed 3
#2067 G0tL3 Time constant 3
0/1
0/1
aux07 Deceleration
Select the deceleration check method in G1+G9.
0/1
(bit1) check method 2
0: Command deceleration check in G1+G9
1: In-position check in G1+G9
The deceleration check is not performed except
G1+G9.
When #1306 InpsTyp deceleration check specification
type is set to "1" (Deceleration check specification
type 2), this parameter will be invalid.
aux07 Synchronous
0/1
0: Disable the synchronous tap I-point → R-point
(bit2) tap R-point
in-position check.
in-position
1: Enable the synchronous tap I-point → R-point
check
in-position check.
(Note) This parameter is valid only when 1 (in-position
check is valid) is set in bit 3 of #1223 aux07
(synchronous tap in-position check
improvement).
aux07 Synchronous
(bit3) tap in-position
check
improvement
Specify whether to enable the synchronous tap
in-position check improvement function.
0: Disable
1: Enable
Related parameters:
#1223
bit 2 Synchronous tap R-point in-position check
bit 4 Synchronous tap hole bottom in-position
check
bit 5 Synchronous tap R-point in-position check 2
III - 50
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Synchronous
0: Disable the synchronous tap hole bottom
tap hole bottom
in-position check.
in-position
1: Enable the synchronous tap hole bottom
check
in-position check.
(Note) This parameter is valid only when "1"
(in-position check is valid) is set in bit 3 of
#1223 aux07 (synchronous tap in-position
check improvement).
Setting range (unit)
0/1
aux07
(bit5)
Synchronous
tap R-point
in-position
check 2
0: Disable synchronous tape R-point in-position
check.
1: Enable synchronous tape R-point in-position
check.
(Note) This parameter is valid only when 1
(in-position check is valid) is set in bit 3 of
#1223 aux07 (synchronous tap in-position
check improvement).
0/1
aux07
(bit6)
Cancel
synchronous
tap (,S) return
0: Retains a spindle rotation speed (, S) when
performing synchronous tap return.
1: Cancels a spindle rotation speed (, S) by return
with G80.
0/1
aux07
(bit7)
Synchronous
tap method
Specify a synchronous tap method.
0: Synchronous tap (multi-step acceleration and
deceleration and rapid return)
1: Conventional type synchronous tap
0/1
1224 aux08
(bit0)
Sampling data
output
Set the validity of the sampling data output.
0: Sampling output invalid
1: Sampling output valid
0/1
1225 aux09
(bit7)
Enable/disable
spindle
rotation speed
clamp
Specify whether to enable spindle rotation speed
0/1
clamp by the spindle rotation speed clamp command
(G92S, Q) instead of the spindle rotation speed
command (R108) specified by the user ladder.
0: Enable
1: Disable
1226 aux10
(bit0)
Tool compensation data for
external
workpiece
coordinate
offset
measurement
Select the tool compensation data to be used for
external workpiece coordinate offset measurement.
0: Tool length data and tool nose wear data
1: Tool length data
aux10
(bit1)
Optional block
skip type
Specify whether to enable optional block skipping in 0/1
the middle of a block.
0: Enable block skipping only at the beginning of a
block.
1: Enable block skipping at the beginning of the
block and in the middle of a block.
aux07
(bit4)
III - 51
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Single block
stop timing
Details
Specify the time at which the single block signal is
activated.
0: When the signal goes ON while automatic
operation is starting, the block stops after it is
finished.
1: When the signal is ON at the end of the block,
the block stops.
aux10
(bit3)
C-axis
reference
position return
type
0/1
Specify the C-axis reference position return type.
0: Origin return is performed by the G28 reference
position return command or when manual
reference position return is activated.
The origin dog is used.
1: When the first C-axis command is issued after
the C-axis mode is entered in automatic mode,
reference position return is performed before
execution of the block. Also, reference return is
performed by the G28 reference position return
command or when manual reference position
return is activated.
The Z phase of the encoder is used.
aux10
(bit4)
S command
Specify whether to output a strobe signal when the S 0/1
during constant command is issued in constant surface speed mode.
surface speed
0: Output no strobe signal in constant surface
speed mode.
1: Output strobe signals in constant surface speed
mode.
aux10
(bit5)
Arbitrary
allocation of
dog signal
Specify whether to enable the arbitrary allocation
parameter for the origin dog and H/W OT.
0: Disable arbitrary allocation. (Fixed device)
1: Enable arbitrary allocation. (Device specified
by the parameter)
aux10
(bit6)
Setup and
display unit
Specify the unit to be used as the setup/display unit or 0/1
handle feed unit, the command unit or internal unit.
The machining program variables (system variables
for coordinate system) are changed simultaneously.
0: Internal unit
1: Unit specified by command
(Note 1) This parameter is valid only in initial
millimeter mode ("0" is set in 14041 I_inch).
The internal unit is always used in initial inch
mode ("1" is set in 1041 I_inch).
(Note 2) This parameter is validated immediately after
it is set.
(Note 3) If addition setting is performed for tool and
workpiece offset data with the command unit
being inch and internal unit being mm, an
error may be generated.
(Note 4) If "1" is set for this parameter and multi-part
system is used, the operation will follow the
unit commanded for each part system.
(Note 5) The internal data is an internal unit
determined with #1041 I_inch.
(Note 6) This parameter is not related to the PLC axis.
Related parameter: #1152 I_G20
(Initial command unit)
aux10
(bit2)
III - 52
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
aux10
(bit7)
1227 aux11
(bit0)
Items
Details
Shorten JOG Specify whether to shorten the JOG stop time.
stop time
0: Do not shorten the JOG stop time. (Same as
before)
1: Shorten the JOG stop time.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
Select PLC
signal or
spindle
feedrate
attained
Select H or D
code
Set up this option when disabling the cutting start
0/1
interlock by spindle feedrate attained.
0: Cutting start interlock by PLC signal
1: Cutting start interlock by spindle feedrate
attained
Set up this option to validate the data that is set up on 0/1
the tool life management screen when issuing the H99
or D99 command.
0: The H and D codes validate the data that is set
up on the management setup screen.
1: Validates the data that is set up on the
management setup screen when issuing the
H99 or D99 command.
aux11
(bit2)
Measures
against tool
setter
chattering
Select a condition where a relieving operation
0/1
completes after measurement with tools.
0: Sensor signals has stopped for 500ms or longer.
1: 100µs or longer has passed after sensor signals
stopped.
aux11
(bit3)
Absolute
coordinate
switching
(nose R)
[Special
display unit
compatible]
Select whether to display a tool nose position or
0/1
coordinate value with the absolute coordinate counter.
0: Displays the tool nose position.
1: Displays the position specified by program
command.
aux11
(bit5)
Spindle
rotation
speed clamp
Specify whether to clamp the rotation in constant
surface speed mode when the spindle rotation speed
clamp command is issued.
0: Clamp the rotation regardless of the constant
surface speed mode.
1: Clamp the rotation only in constant surface
speed mode.
0/1
aux11
(bit7)
Switch the
set up the range of tool life data to be input or
range of tool compared.
life data to be
0: Inputs or compares all of the data output.
input
1: Inputs or compares part of the data output
(For M
1) Tool life management I data to be input or
system only)
compared tool number (D), lifetime (E), life
count (F), and auxiliary data (B).
2) Tool life management II data to be input or
compared Group number (G), method (M),
life (E/F), tool number (D), and
compensation number (H)
(Note) When the maintenance function data input/
output #(99) ( ) is set, all data will be input and
compared.
0/1
aux11
(bit1)
III - 53
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1228 aux12
(bit1)
Items
Switch "offset
and parameter"
screen
Details
Set up this option to switch the "offset and
parameter" screen to the parameter screen.
0: Displays the "offset and parameter" screen.
1: Displays the "parameter" screen.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
Switch data
protection in
data
transmission
mode
Nose R
specification
Set up the range of data protection in data
transmission mode.
0: Protects both send and receive data.
1: Protects receive data only.
0/1
aux12
(bit5)
Select constant
surface speed
coordinates
Select constant surface speed coordinates.
0: Workpiece coordinate value
1: Absolute coordinate value
aux12
(bit6)
Switch relative
values
displayed
Select whether to preset the relative coordinates
0/1
with workpiece coordinate preset (G92.1) or counter
preset (G92).
0: Preset relative coordinates.
1: Do not preset relative coordinates.
aux12
(bit7)
Protection with
manual value
command
Set up this option to protect a manual value
command.
0: Does not protect the manual value command
(same as before).
1: Protects the manual value command.
0/1
Subprogram
interrupt
0: Specifies the user macro interrupt of macro
type.
1: Specifies the user macro interrupt of
sub-program type.
0/1
aux12
(bit2)
aux12
(bit3)
aux12
(bit4)
1229 set01
(bit0)
Select whether to specify the nose R compensation 0/1
by shape or wear number.
0: Specifies the nose R compensation by shape
number.
1: Specifies the nose R compensation by wear
number.
Select operation Specify both block cutting start interlock and cutting 0/1
error or stop
start interlock as the operation error or stop code.
code
0: Operation error
1: Stop code
0/1
set01
(bit1)
Accurate thread 0: Address E specifies the number of threads per
cutting E
inch for inch screw cutting.
1: Address E specifies precise reading for inch
screw cutting.
set01
(bit2)
0/1
Radius compen- 0: When the start-up and cancel commands are
operated during radius compensation, their
sation type B
blocks are not handled by intersection operation
(For M system
processing; they are handled as offset vectors
only)
in the direction vertical to that of the commands.
1: When the start-up and cancel commands are
operated during radius compensation, the
intersection operation processing of the
command block and the next block is executed.
III - 54
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
set01
(bit2)
Items
Nose R
compensation
type B (For L
system only)
Details
Setting range (unit)
0: When the start-up and cancel commands are
0/1
operated during nose R and radius
compensation, their blocks are not handled by
intersection operation processing; they are
handled as offset vectors in the direction vertical
to that of the commands.
1: When the start-up and cancel commands are
operated during nose R and radius
compensation, the intersection operation
processing of the command block and the next
block is executed.
set01
(bit3)
Initial constant
surface speed
0: The initial state after power-ON is a constant
surface speed control cancel mode.
1: The initial state after power-ON is a constant
surface speed control mode.
set01
(bit4)
Synchronous
tap
set01
(bit5)
0: Handles the G74 and G84 tap cycles as the tap
cycles with a floating tap chuck.
1: Handles the G74 and G84 tap cycles as the tap
cycles without a floating tap chuck.
Start point alarm Select an operation when the operation start point
cannot be found while moving the next block of
G117.
0: Enables an auxiliary function after the block
has been moved.
1: Outputs an program error (P33) when the
operation start point is not found.
set01
(bit6)
Grid display
selection
0/1
0/1
0/1
Select a grid type to be displayed on the servo
0/1
monitor screen during dog type reference position
return.
0: Selects the distance between dog OFF and
zero point (including a grid mask amount).
1: Selects a value given by reducing a grid mask
amount from the distance between dog OFF
and zero point.
0: The macro interface input/output are shared
0/1
by the part systems.
1: The macro interface input/output are used
independently by the part systems.
1230 set02
(bit7)
Macro interface
input/output for
each part
system
1231 set03
(bit0)
Graphic check
compatibility
parameter
When checking a machining program which rewrites 0/1
the common variables, workpiece offsets and tool
offsets, select whether or not to return the data to
the pre-starting data when finished.
0: Return the data.
1: Do not return the data.
set03
(bit1)
Switch graphic
trace
coordinates
Select whether to draw graphics with the machine
coordinate value or the tool position coordinate
value (position being machined, obtained by
subtracting the tool compensation amount from
machine coordinate values) when displaying the
trace function.
0: Machine coordinate value (same as
conventional method)
1: Tool position coordinate value
The counter display and counter name are
sequenced with this.
III - 55
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
set03
(bit2)
Items
Switch graphic
check trace
Details
Setting range (unit)
Select whether to draw both the machine
0/1
coordinate value (tool center path) and tool position
coordinate value (program path) or draw only the
coordinates selected with switch graphic
coordinates (#1231 set03/bit1) when using the
program check function.
0: Both machine coordinates and tool position
coordinates (same as conventional method)
1: Only coordinates designated with switch
graphic coordinates.
Select whether to hold the display range
0/1
information (drawing position and scale value) for
graphic displays.
0: Hold.
1: Do not hold. (Initialize each time ... same as
conventional method)
set03
(bit3)
Hold display
range
information
set03
(bit4)
Switch zero
point mark
display position
Select the position for displaying the zero point
mark in the graphic display.
0: Machine coordinate zero point (same as
conventional method)
1: Workpiece coordinate zero point
set03
(bit5)
Switch graphic
check counter
display
Select the type of counter displayed on the Graphic 0/1
Check screen.
0: Machine position counter
1: Workpiece coordinate position counter
Switch load
monitor
Select whether to detect the load with the load
monitor's load detection, excluding during
acceleration/deceleration.
0: Detect also during acceleration/deceleration.
(Conventional)
1: Do not detect during
acceleration/deceleration.
Select the format of the file output during copying
(NC → IC).
0: Add "%" to the head of the file.
1: The head of the file is No. 0.
1232 set04
(bit0)
set04
(bit1)
Program format
(IC card)
1233 set05
(bit1)
Spindle clamp
selection
1234 set06
(bit7)
Enable/disable
MELDASNET
1235 set07
(bit0)
Helical
interpolation
speed 2
set07
(bit2)
Fixed type
chopping
compensation valid only at
start
Select whether to validate the spindle override for
the spindle speed clamp command (G92 S?).
0: Spindle override invalid
1: Spindle override valid
Enable or disable the MELDASNET function.
0: Enable
1: Disable
0: Select normal speed designation also for 3rd
axis
1: Select arc plane element speed designation
When the fixed type compensation value is
selected, the method is changed to the
compensation value sequential update type after
the first four cycles.
0: Method changeover invalid
1: Method changeover valid
III - 56
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1236 set08
(bit0)
Items
Manual rotary
axis feedrate
unit
Details
Select the unit of manual rotary axis feedrate.
0: Fixed to [°/min]
1: Same speed as before
set08
(bit1)
Spindle speed
detection
Select the pulse input source of actual spindle
0/1
rotation speed output (R6506/R6507) when spindle
encoder serial connection (#3025 enc-on: 2) is
selected.
0: Serial input
1: Encoder input connector
set08
(bit2)
Current limit
droop cancel
invalid
Set whether to cancel the position droop when the
current limit changeover signal is canceled.
0: Cancel droop.
1: Do not cancel droop.
set08
(bit3)
Rotary axis
command
speed scale
1237 set09
(PR) (bit0)
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
The rotary axis command speed is multiplied by 10 0/1
times.
0: Invalid
1: During initial inching, the rotary axis command
speed is multiplied by 10. In other words, if
"F100" is commanded, the speed will be the
same as when 1000 degree/min is
commanded.
The rotary axis speed display unit is 10°/min.
in this case.
External
Set up this function to use the external workpiece
0/1
workpiece offset coordinates by shifting them to the Z axis.
0: Does not reverse the sign of external
workpiece offsets (Z shift) (same as before).
1: Reverses the sign of external workpiece
offsets (Z shift).
(Note) When the sign of external workpiece offsets
(Z shift) has been reversed, do not measure
those external workpiece offsets. However,
the external workpiece offsets can be
measured by tool pre-setter.
set09
(bit1)
Switch PC I/F F
modal
The feedrate display for the special display unit is
changed.
0: Display as feed per minute.
1: Change between feed per minute and feed
per rotation according to the modal state.
0/1
set09
(bit2)
Switch PC I/F T
modal
The T command display for the special display unit
is changed. (Only L system)
0: Display tool No. (excluding low-order two
digits).
1: Display including the compensation No.
0/1
set09
(bit3)
Switch PC I/F
remaining
distance dwell
time display
Switch PC I/F
execution
program
display/
comment
display
The dwell time display for the special display unit is 0/1
changed.
0: Display at feedrate display position.
1: Display at remaining distance display position.
The display of the program being executed for the 0/1
special display unit is displayed.
0: Display as searched state, regardless of
operation mode.
1: If operation mode and searched program
differ, program is not displayed.
Comment is displayed for head block search.
set09
(bit4)
III - 57
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
set09
(bit5)
1238 set10
(PR) (bit0)
set10
(bit7)
1239 set11
(PR) (bit0)
Items
Switch PC I/F
modal S
Switch G36
function
Details
Setting range (unit)
0/1
This parameter is for the special display unit I/F.
0: The S command commanded last is returned.
1: When "#1039 spinno" is 1
The 1st spindle data is returned.
When "#1039 spinno" is 2
If "#1199 Sselect" for 2nd part system is
set to 1 with 2nd part system setting, the
2nd spindle data is returned.
When another command is issued, the 1st
spindle data is returned.
(Note) When using constant surface speed
control (G96 modal), the actual rotation
speed command is returned.
If a G code system containing the G36 (automatic 0/1
tool length measurement X) function is selected,
select whether to use G36 for the automatic tool
length measurement or arc thread cutting (CCW)
function.
0: Automatic tool length measurement
1: Arc thread cutting (CCW)
Switch operation Select whether to validate the NC alarm 5 (AL5)
0/1
alarm
signal output.
(Default: 0)
0: NC alarm 5 (AL5) invalid
All operation alarms are output to NC alarm 4
(AL4).
All operation alarms are recorded in the alarm
history.
1: NC alarm 5 (AL5) valid
The following operation alarms are not output
to NC alarm 4 (AL4). These are output to NC
alarm 5 (AL5).
The operation alarms output to NC alarm 5
(AL5) are not recorded in the alarm history.
• External interlock axis found
• Cutting override zero
• External feedrate zero
• Block start interlock
• Cutting block start interlock
• Cutting interlock for spindle-spindle
polygon (G51.2)
Coil switching
0: Via PLC. (Y189F)
0/1
method
1: NC internal processing. (Y189F is invalid.)
set11
(bit1)
Handle I/F
selection
Specify the handle connection destination.
0: Use the handle connected to the encoder
communication connector.
1: Use the remote I/O unit as a priority.
When HN391/HN392 is mounted, the handle
connected to the operation panel I/O unit will be
used regardless of this parameter setting.
0/1
set11
(bit3)
Polygon
Select whether to cancel the polygon machining
machining mode mode when reset is applied.
at reset
0: Do not cancel.
1: Cancel.
0/1
III - 58
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
set11
(bit4)
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
Invalidate G51.1 Select whether to carry out phase control with the
0/1
phase
spindle-spindle polygon function.
command
0: Always validate phase control.
* When R is not commanded, it is handled as
R0.
1: Validate phase control only at R command
set11
(bit5)
Door interlock
spindle speed
clamp valid
Select whether to validate the spindle clamp speed 0/1
changeover function by the PLC signal.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
set11
(bit6)
External
Designate the method for setting the external
0/1
deceleration
deceleration speed.
axis compliance
0: Set speed common for all axes (#1216 extdcc
valid
external deceleration speed)
1: Set speed for each axis (#2086 exdcax
external deceleration speed)
1240 set12
(PR) (bit0)
Handle input
pulse
Select the handle input pulse.
0: MITSUBISHI standard handle pulse
1: Handle 400 pulse
0/1
set12
(bit1)
Megatorque
motor handle
feed
magnification
Select the magnification of megatorque motor
handle 1 pulse.
0: Double the handle 1 pulse magnification
specified by the handle feed magnification
signal (YC80 to YC82).
1: Use the handle 1 pulse magnification
specified by the handle feed magnification
signal (YC80 to YC82) as is.
0/1
set12
(bit2)
Zero point shift
amount
magnification
If "1" is set, the following magnification will be
0/1
applied on the #2027 G28sft reference position shift
amount, #2057 zero point proximity + and #2058
zero point proximity - settings.
For 0.1µm : 10-fold
For 0.01µm : 100-fold
1265 ext01
(PR) (bit0)
Command
format 1
Select the command format for the fixed cycle for
compound lathe.
0: Conventional format
1: MITSUBISHI CNC special format
(1 block command method)
ext01
(bit1)
Command
format 2
Select the command format for the lathe fixed cycle. 0/1
0: Conventional format
1: MITSUBISHI CNC special format
ext01
(bit2)
Command
format 3
Select the command format for the hole drilling fixed 0/1
cycle.
0: Conventional format
1: MITSUBISHI CNC special format
1266 ext02
(PR)
0/1
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Select the high-speed high-accuracy G code type.
0: Conventional format
1: MITSUBISHI CNC special format
0/1
1268 ext04
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1269 ext05
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1267 ext03
(PR) (bit0)
G code type
III - 59
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1270 ext06
(PR) (bit6)
ext06
(bit7)
1271 ext07
(PR) (bit0)
Items
Switch
continuous
thread cutting Z
phase wait
operation
Details
Set the continuous thread cutting Z phase wait
operation.
0: If there is no movement command (MST
command, etc.) between the thread cutting
locks, the 2nd block thread cutting waits for
the spindle's single rotation synchronization
signal before starting movement.
1: Even if there is no movement command
(MST command, etc.) between the thread
cutting blocks, the 2nd block thread cutting
starts movement without waiting for the
spindle's single rotation synchronization
command.
Handle C axis
Specify whether the rotary axis coordinate before
coordinate
the cylindrical interpolation start command is
during cylindrical issued is kept during the cylindrical interpolation or
interpolation
not.
0: Do not keep
1: keep
Mirror image
Select the type of mirror image operation.
operation
0: Type 1
• The program mirror image, external mirror
image, and parameter mirror image are
exclusive to each other.
• An increment command moves the image to
the position indicated by the move amount with
the sign inverted.
1: Type 2
• Mirror image operation is enabled when the
program mirror image (G51.1) command is
issued or when the external signal or
parameter is ON.
• An increment command moves the image to
the position determined by applying the mirror
image to the absolute program coordinates.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
0/1
0/1
(Default: 0)
ext07
(bit1)
Address
specifying fixed
cycle repetition
count (For M
system only)
ext07
(bit2)
F-command unit Specify the unit to be used if a thread cutting read 0/1
(Default: 0)
command contains on decimal point.
0: Type 1 (conventional specifications)
F1 → 1 mm/rev, 1 inch/rev
1: Type 2
F1 → 0.01 mm/rev, 0.0001 inch/rev
G-code group for Specify the G-code group for unidirectional
0/1
unidirectional
positioning.
positioning (for
0: Unmodal G code (group 00)
M system only)
1: Modal G code (group 01)
Related parameter: #8209 G60 SHIFT (Set the last
positioning direction and distance for each axis
applicable when the unidirectional positioning
command is issued.)
ext07
(bit3)
Specify the address that specifies the fixed cycle
0/1
repetition count.
(Default: 0)
0: Address L only
1: Addresses K and L
If addresses K and L are specified simultaneously,
the data at address K is used for operation.
III - 60
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Operation by
independent
G40 command
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify the mode of canceling radius compensation 0/1
vector by the independent G40 command.
(Default: 0)
0: Type 1 (conventional specifications)
The independent G40 command cancels the
radius compensation vector.
1: Type 2
The radius compensation vector is not
canceled by the independent G40 command
but is canceled by the next move command
for the radius compensation plane.
ext07
(bit5)
Cut start
position (For L
system only)
Specify the position from where cutting begins in a
fixed cycle for compound lathe.
0: Conventional specifications
The cut start position is determined by the
final shaping program.
1: Extended specifications
The cut start position is determined from the
cycle start point.
0/1
(Default: 0)
ext07
(bit6)
Nose R
compensation
(For L system
only)
Specify whether to apply nose R compensation to
shapes in a rough cutting cycle.
0: Conventional specifications
If nose R compensation is enabled for the
final shaping program, the shape obtained
after applying nose R compensation to the
final shaping program is used as the rough
cutting shape.
1: Extended specifications
The shape made by the final shaping
program, without nose R compensation, is
used as the rough cutting shape.
0/1
(Default: 0)
ext07
(bit7)
Cut amount (For Specify the operation to be performed when the
0/1
L system only)
program-specified cut amount exceeds the cut
(Default: 0)
amount of the final shaping program.
0: Conventional specifications
A program error occurs if the
program-specified cut amount exceeds the
cut amount of the final shaping program.
1: Extended specifications
Rough cutting is performed by one cut if the
program-specified cut amount exceeds the
cut amount of the final shaping program.
Switch pocket
0: Conventional specifications
0/1
machining
Pocket machining is selected with the H
operation
designation.
The pull direction when pocket machining is
ON is the Z direction.
1: Extended specifications
If there is an X and Z axis in the first
movement block after the finished shape start
block is started, pocket machining will start.
The pull direction when pocket machining is
ON is the X direction.
ext07
(bit4)
1272 ext08
(PR) (bit0)
III - 61
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
ext08
(bit1)
Items
Details
M function
Specify whether to enable the M function
synchronous tap synchronous tap cycle.
cycle
0: Invalid
1: Valid
Setting range (unit)
0/1
ext08
(bit2)
Spiral/conical
Select the command format for spiral interpolation 0/1
interpolation
and conical interpolation.
command format
0: Type 1 (conventional specifications)
2
1: Type 2 (spiral speed L designation, increment
designation)
ext08
(bit3)
Switch macro
call function
Select whether to shift the argument to the
0/1
subprogram if nests are overlapped when per block
call (G66.1) is commanded.
0: Shift argument even if nests are overlapped.
1: Do not shift arguments if nests differ.
(Conventional specifications)
ext08
(bit4)
Tap cycle
selection
Select the tap cycle.
0: Pecking tap cycle
1: Deep hole tap cycle
0/1
ext08
(bit5)
Deep hole tap
cycle override
selection
Select whether to validate override on the pulling
operation during synchronized tapping with the
deep hole tap cycle.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
0/1
ext08
(bit6)
Switch corner
The corner chamfering/corner R command format is 0/1
chamfering/
extended.
corner R
0: Command format I (conventional format)
command format
Issue a command with comma (,C and ,R).
1: Command format II
In addition to command format I, commands
can be issued with an address that does not
have a comma.
Corner chamfering: I/K or C, corner R: R
ext08
(bit7)
Return position
after macro
interrupt in fixed
cycle selection
Select the destination to return to after a macro
interrupt in the fixed cycle.
0: Return to block in fixed cycle.
1: Return to block after fixed cycle.
0/1
Switch ASIN
calculation
results range
Select the ASIN calculation results range.
0: -90° to 90°
1: 90° to 270°
0/1
Switch system
variable unit
Select the unit for the system variable #3002 (time
during automatic start).
0: 1ms unit
1: 1 hour unit
0/1
1273 ext09
(PR) (bit0)
ext09
(bit1)
III - 62
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
ext09
(bit2)
ext09
(bit3)
ext09
(bit4)
1274 ext10
(PR) (bit7)
Items
Switch G71,
G72, G73
cutting direction
judgment
Details
Setting range (unit)
0/1
Select whether to determine the cutting direction
with the finished shape, or according to the
commanded finishing allowance and cutting
allowance when the longitudinal rough cutting cycle
(G71), face rough cutting cycle (G72) or closed
loop cutting cycle (G73) is commanded.
0: Conventional specifications
Determined according to the finished shape
program.
1: Extended specifications
Determined according to the finishing
allowance and cutting allowance commanded
in the program.
Facing turret
Select the coordinate values of the axis for which
0/1
mirror image
facing turret mirror image is valid.
coordinate value
0: Move axis in same direction as machine
type
value.
1: Move axis in direction opposite machine
value.
Facing turret
Select the axis for which facing turret mirror image 0/1
mirror image
is valid.
valid axis
0: Fixed to 1st axis.
1: Determined according to plane selected
selection
when facing turret mirror image is
commanded.
Word range
check
Select whether to check that the operation
expression of the word date in the program is
enclosed in brackets ( [ ] ) when the machine
program is executed.
This check is also applied to the 08000 to 09999
and the machine tool builder macro program.
0: Check valid
1: Check invalid
0/1
1275 ext11
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1276 ext12
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
0/1
Specify how and when the mount or use count is
(Default: 0)
incremented in tool life management II.
0: Type 1
The count is incremented when the spindle is
used for cutting.
1: Type 2
The count is incremented for the tool used or
mounted for one program. The increment is
enabled by resetting.
1277 ext13
(PR) (bit0)
Tool life
management II
count type 2
1278 ext14
(PR) (bit0)
Program restart Select the program restart method.
method selection
0: Restart type A
1: Restart type B
III - 63
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1279 ext15
(PR) (bit0)
ext15
(bit1)
ext15
(bit2)
1280 ext16
(PR) (bit0)
Items
Part system
synchronization method
Details
Setting range (unit)
Select the part system synchronization method.
0/1
0: If one part system is not in automatic
operation, ignore the synchronization
command and execute the next block.
1: Operate according to the synchronization
ignore signal.
If the synchronization ignore signal is set to
"1", the synchronization command will be
ignored. When set to "0", synchronization will
be applied.
Interrupt amount Select the manner to handle the interruption
0/1
during machine amount during machine lock.
lock
0: Cancel when reset.
1: Do not cancel when reset. Instead cancel
during manual zero point return.
Selection of
cutting start
interlock target
block
Select whether the cutting start interlock is valid for 0/1
successive cutting blocks.
0: Valid for successive cutting blocks.
1: Invalid for successive cutting blocks.
I/F per axis
during cross
machining
control
0/1
Set the handling of the following PLC I/F for axes
interchanged with cross machining control.
• Mirror image
• Manual/automatic interlock
• Manual/automatic machine lock
0: Follows axis configuration before cross
machining control.
1: Follows axis configuration after cross
machining control.
(Example) Set as follows for the automatic
interlock (+) device for X1 when
carrying out cross machining with the
1st axis (X1) in the 1st part system and
1st axis (X2) in the 2nd part system.
Setting value 0: Y820 (I/F for 1st axis in
1st part system)
Setting value 1: Y828 (I/F for 1st axis in
2nd part system)
(Note) If the number of axes in the part system
changes with cross machining, the I/F of the
target axis may change when this parameter
is set to "1".
(Example) When 1st part system's C axis is moved
to 2nd part system with a 1st part
system (X, Z, C, Y) and 2nd part
system (X, Z) configuration:
When setting value is "1":
Y82A, Y7CA and Y8AA, etc., will be
the I/F for the C axis moved to the 2nd
part system. However, Y7C2, Y822
and Y8A2, etc., will change to the I/F
of the Y axis in the 1st part system
because the axes following the
removed C axis (third place) are
shifted up.
III - 64
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1280 ext16
(PR) (bit1)
Items
Cross
machining
control cancel
with reset
Details
Select whether to cancel the cross machining
control when reset is applied.
0: Cancel cross machining control with reset.
1: Do not cancel cross machining control with
reset
Setting range (unit)
0/1
ext16
(bit2)
0/1
Interchange
Set whether to interchange (or move) the
coordinate value coordinate values when displaying.
display
This setting will be followed when the axes are
interchanged and when the axes are moved.
0: Interchange (or move) coordinate values with
cross machining control, and display.
1: Display coordinate values for cross machining
control without interchanging (or moving).
(Example) When 1st part system's C axis is moved
to 2nd part system with a 1st part
system (X, Z, C, Y) and 2nd part system
(X, Z) configuration:
1st part system: X, Z and Y coordinate
values are displayed.
2nd part system: X, Z and C coordinate
values are displayed.
ext16
(bit3)
Reset operation Select whether to cancel synchronization/
for synchroniza- superimposition control with resetting.
0: Cancel.
tion/super1: Do not cancel.
imposition
control
III - 65
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1281 ext17
(PR) (bit0)
ext17
(bit1)
Items
Zero point
return
operation
changeover
parameter
Tool offset
addition axis
selection
Details
Setting range (unit)
0/1
(Zero point setting operation)
The "Operation error 1036" will occur regardless of
this parameter, and regardless of manual or
automatic operation.
(High-speed zero point return)
0: <During manual operation>
The master axis and slave axis will
simultaneously start zero point return. Even if
one of the axes reaches the zero point, the
other axis will continue to move until it
reaches the zero point. Thus, if the difference
of the master axis and slave axis feedback
position before zero point return is larger than
the tolerable synchronization error amount,
the error "Operation error 0051" will occur
during zero point return.
<During automatic operation>
The master axis and slave axis will
simultaneously start zero point return. When
the master axis reaches the zero point, the
slave axis will stop. Thus, the positional
relation of the master axis and slave axis
established before zero point return is
maintained.
1: <During manual operation>
<During automatic operation>
The master axis and slave axis will
simultaneously start zero point return. When
the master axis reaches the zero point, the
slave axis will stop. Thus, the positional
relation of the master axis and slave axis
established before zero point return is
maintained.
0: Follows Tchg34
0/1
1: Plane selection Base J setting name is set as
the 3rd axis compensation axis.
1282 ext18
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1283 ext19
(PR)
1284 ext20
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Not used. Set to "0".
0
III - 66
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1285 ext21
(PR) (bit0)
Items
Multi-part
system program
generation and
operation
Details
Setting range (unit)
0: When a machining program is newly
0/1
registered, it is registered as a program for
the selected part system.
1: When a program is newly registered, a part
system common program No. is generated
unconditionally. If there are no contents in the
subprogram when a subprogram is called
during automatic operation, the program will
be searched for and executed from $1.
ext21
(bit1)
Changeover of
method to select
operation
program
0: Select the program in the selected part
system with operation search.
1: Select a common part system program with
operation search. (A common part system
program No. will be selected.)
1286 ext22
(PR) (bit0)
Program
input/output
method selection
0: Only the programs in the selected part
0/1
system are input/output.
1: The designated programs are output for all
part systems. The part systems are delimited
with the "$" mark. The programs delimited
with the $ mark are assigned and input into
each part system. (If the program does not
have a $ mark, it will be handled as system
1.)
0/1
ext22
(bit2)
0 No. for
program input
No.
Select the action to be taken when the same
0/1
program No. is input during data input.
0: The 0 No. when the same 0 No. is input
successively is handled as a character string
data.
1: The 0 No. is handled as a program No. when
the same 0 No. is input successively.
Whether to overwrite the program or cause
an error is set with #1218 bit 7 "Input by
program overwrite".
ext22
(bit3)
No 0 No. at
machining
program input
This setting enables the machining program input
even if there is no program No. (0 No.).
The program No. is fixed to 01 in this case.
0: Input disabled
1: Input enabled
Select the mode of displaying the workpiece
coordinate counter.
0: Don’t update the display immediately after
workpiece coordinate data is changed.
1: Update the display immediately after
workpiece coordinate data is changed.
0: Display the command value that does not
consider the tool length offset amount or
workpiece coordinate offset amount.
1: The counter display expanded function is
validated. (bit4 to bit7)
1287 ext23
(PR) (bit0)
ext23
(bit3)
Workpiece
coordinate
display
Counter display
expanded
function
selection
III - 67
0/1
0/1
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
ext23
(bit4)
Items
Relative
coordinate
display
Details
(M system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
length offset.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool length
offset.
(L system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
shape compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool shape
compensation.
Setting range (unit)
0/1
ext23
(bit5)
Relative
coordinate
display
(M system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
radius compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool radius
compensation.
(L system)
0: Display the actual position including nose R
compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding nose R
compensation.
0/1
ext23
(bit6)
Absolute
coordinate
display
[Special display
unit compatible]
(M system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
length offset.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool length
offset.
(L system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
shape compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool shape
compensation.
0/1
ext23
(bit7)
Absolute
coordinate
display
[Special display
unit compatible]
0/1
(M system)
0: Display the actual position including tool
radius compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding tool radius
compensation.
(L system)
0: Display the actual position including nose R
compensation.
1: Display the machining position in terms of a
program command excluding nose R
compensation.
With the L system, the effect onto the nose R
compensation's absolute coordinate counter is also
affected by the L system coordinate changeover
parameter (#1227 aux11/bit 3 absolute coordinate
changeover (nose R)). In actual use, if this
parameter is set to 1, or if #1227 aux 11/bit 3 is set
to 1, the position in the program commands will be
displayed with the absolute coordinate counter.
III - 68
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1288 ext24
(PR) (bit0)
Items
MDI program
clear
Details
Setting range (unit)
Select whether to initialize the MDI buffer when MDI 0/1
operation ends, the power is turned ON again, reset
is input, or emergency stop is canceled.
0: Do not clear programs registered with MDI.
1: Clear programs registered with MDI, and save
only % programs.
1289 ext25
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1290 ext26
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1291 ext27
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1292 ext28
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1293 ext29
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1294 ext30
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1295 ext31
(PR)
1296 ext32
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1297 ext33
(PR)
1298 ext34
(PR)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Not used. Set to "0".
0
1299 ext35
(PR)
1300 ext36
(PR) (bit0)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
Select multiple spindle control I or II.
0: Multiple spindle control I (L system only)
1: Multiple spindle control II (select from ladder)
Select the spindle synchronization command
method.
0: Spindle synchronization with PLC I/F
1: Spindle synchronization with G command
0/1
Multiple spindle
control II
ext36
(bit7)
Spindle
synchronization command
method
1301 nrfchk
Origin
neighboring
check method
1302 AutoRP Automatic
return by
program restart
0/1
Select the high-speed check method of the origin
0 to 2
neighboring signal.
0: Do not check positions near the origin at high
speeds. (Conventional specifications)
1: Check positions near the origin at high speeds
using command machine positions.
2: Check positions near the origin at high speeds
using detector feedback positions.
0: Return the system to the restart position
0/1
manually and then restart the program.
1: For program restarting, the first activation
automatically moves the system to the restart
position.
1303 V1comN No. of #100
Set the number of common variables common for
0 to 100
(PR)
address part
the part system starting from address #100.
system common This is valid only when #1052 MemVal is set to "1".
variables
III - 69
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1304 V0comN No. of #500
(PR)
address part
system
common
variables
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set the number of common variables common for 0 to 500
the part system starting from address #500.
This is valid only when #1052 MemVal is set to "1".
1305
1306 InpsTyp
Deceleration
check
specification
type
Select the parameter specification type for the G0 0/1
or G1 deceleration check.
0: Deceleration check specification type 1
G0 is specified with "#1193 inpos", and
G1+G9 with "#1223 aux07/BIT1".
1: Deceleration check specification type 2
G0 or G1+G9 is specified with "#1193 inpos".
1309 GType
Switch
command
format
Select the operation in respect to the command.
0: Command reverse tap with G84.1/G88.1.
1: Command reverse tap with a minus D
command value.
1310 WtMmin
Minimum value Set the minimum value for the M code. When "0" is 0, 100 to 99999999
for
set, the synchronization M code will be invalid.
synchronization M code
1311 WtMmax
Maximum
value for
synchronization M code
Set the maximum value for the M code. When "0" is 0, 100 to 99999999
set, the synchronization M code will be invalid.
1312 T_base
Tool life
management
standard
number
0 to 9999
When the T code command is issued while
specifying a value that exceeds the value set in this
parameter, the value obtained by subtracting the
set value from the command value is used as the
tool group number for tool life management.
The value specified by the T code command is
equal to or less than the value set in this parameter,
the T code is handled as a normal T code and not
subjected to tool life management.
When 0 is set in this parameter, the T code
command always specifies a group number. (This
parameter is valid for M-system tool life
management II.)
1313 TapDw1
Synchronous
tap hole
bottom wait
time
Specify the hole bottom wait time for synchronous
tapping.
When the P address is specified, the greater value
is used as the hole bottom wait time. When an
in-position check is performed at the hole bottom,
dwelling for the specified time is completed after
the in-position check is complete. (Applicable only
to the M64 D version series)
(Note) This parameter is valid only when "1" is set
in #1223 aux07 bit 3 (synchronous tap
in-position check improvement).
0 to 999 (ms)
1314 TapInp
Synchronous
tap in-position
check width
(tap axis)
Specify the hole bottom in-position check width for
synchronous tapping.
(Note) This parameter is valid only when "1" is set
in #1223 aux07 bit 3 (synchronous tap
in-position check improvement).
0.00 to 99.999 (mm)
III - 70
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
1324 Chop_R
Chopping
Head number of the R register used as the
compensacompensation amount save area during fixed
tion value
compensation amount method.
fixing method
Setting range (unit)
8300 to 9782
1327 3D ATC
type
Tool change
method
specification
Specify the tool change method for determining the
tool used to draw solids.
With 3D drawing, the tool is changed by the method
designated with this parameter, and the image is
drawn.
0: One standby tool
1: Two standby tools
2: No standby tools
0 to 2
1328 TLM type
Tool
measurement
standard
positions
election
Rotational
tool axis
number
Select the tool measurement method.
0/1
0: Use the machine position at TLM switch ON as
standard.
1: Use the machine zero point as standard.
1501 polyax
(For L
system
only)
Specify the number of the rotational tool axis (servo 0 to controlled axis
axis) used for polygon machining (G51.2). Set 0
number
when not using polygon machining (spindle-servo
axis), or when using spindle-spindle polygon
machining. A value exceeding the base specification
parameter #1002 axisno cannot be specified.
This parameter is valid when the G code system is 6
or 7 (7 or 8 is set in base specification parameter
#1037 cmdtyp).
0: Do not perform a deceleration check when the 0/1
move direction is changed from G1 to G0.
1: Perform a deceleration check when the move
direction is changed from G1 to G0.
1502 G0Ipfg
G1 → G0
deceleration
check
1503 G1Ipfg
G1 → G1
deceleration
check
1505 ckref2
Second origin Specify the trigger for a check at the specified
return check position in manual second original return mode.
0: Completion of spindle orientation
1: Generation of second origin return interlock
signal
0/1
1506 F1_FM
Upper limit of
F1 digit
feedrate
F1 digit
feedrate
change
constant
0 to 1000000
(mm/min)
1507 F1_K
1510 DOOR_H
0: Do not perform a deceleration check when the
move direction is changed from G1 to G1.
1: Perform a deceleration check when the move
direction is changed from G1 to G1.
Specify the maximum value up to which the F1 digit
feedrate can be changed.
0/1
Specify the constant that determines the speed
0 to 32767
change rate per manual handle graduation in F1 digit
feedrate change mode.
Shorten door Specify whether to shorten the time during which the 0/1
interlock II
axis is stopped when the door is opened.
axis stop time
0: Use the conventional axis stop time.
1: Shorten the axis stop time.
(Note) When the door interlock II signal is input via a
ladder, the conventional axis stop time is
used.
III - 71
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
000 to 2FF
(hexadecimal)
1511 DOORPm
Signal input
device 1 for
door interlock
II: for each
part system
Specify the fixed device number (X??) for door
interlock II signal input for each part system.
A device number from X01 to XFF can be specified.
Device number 000 is invalid.
Specify device number 100 when using no fixed
device number for door interlock II signal input.
Related parameter: #1154 pdoor (Door interlock II for
each part system)
1512 DOORPs
Signal input
device 2 for
door interlock
II: for each
part system
Specify the fixed device number (X??) for door
000 to 2FF
interlock II signal input for each part system.
(hexadecimal)
(Specify the same value as that of #1155.)
Related parameter: #1154 pdoor (Door interlock II for
each part system)
1513 stapM
M code for
synchronous
tap selection
Select the synchronous tap mode using the
0 to 99999999
miscellaneous function code of the value set in this
parameter. The M function command can be issued
immediately before the tap command or in the same
block. This function is valid only when 1 is set in
#1272 ext08/bit 1 (Enable/disable M-function
synchronous tap cycle).
(Note) Do not use M00, 01 02, 30, 98, and 99.
1514 expLinax
Exponential
function
interpolation
linear axis
Exponential
function
interpolation
rotary axis
Set the axis address name for the linear axis used in
exponential function interpolation.
1516 mill_ax
Milling axis
name
Set the name of the rotary axis used in milling
interpolation. Only one rotary axis can be set.
When there is no E command in issuing the G12.1
command, this parameter will be followed.
A to Z
1517 mill_C
Milling
interpolation
hypothetical
axis name
Select the hypothetical axis command name for
milling interpolation.
When there is no D command in issuing the G12.1
command, this parameter will be followed.
0: Y axis command
1: Command rotary axis name.
0/1
1518 polm
Spindlespindle
polygon
Workpiece
spindle No.
Spindlespindle
polygon
Tool spindle
No.
Set the number of the workpiece spindle used in
spindle-spindle polygon machining.
(Note) The 1st spindle will be selected when "0" is
set.
0 to number of
spindles
Set the number of the tool spindle used in spindlespindle polygon machining.
(Note) The 2nd spindle will be selected when "0" is
set.
0 to number of
spindles
1515 expRotax
1519 pols
1520 Tchg34
(PR)
A to Z
Set the axis address name for the rotary axis used in A to Z
exponential function interpolation.
Additional
Select whether to carry out the additional axis' tool
axis tool
compensation function with the 3rd axis or 4th axis.
compensa0: Select 3rd axis.
tion operation
1: Select 4th axis.
III - 72
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1521 C_min
Items
Minimum
turning angle
Details
Set the minimum turning angle of the normal line
control axis at the block joint during normal line
control.
Setting range (unit)
0.000 to 360.000 (°)
(Input setting
increment applies)
1522 C_axis
(PR)
Normal line
control axis
Set the number of the axis for normal line control.
Designate a rotary axis.
1523 C_feed
Normal line
This is valid with normal line control type I.
control axis
Designate the turning speed of the normal line
turning speed control axis at the block joint during normal line
control.
Set a value that does not exceed the normal line
control axis' clamp speed (#2002 clamp).
Normal line
Set the normal line control type.
control type
0: Normal line control
disabled
1 to 6: Axis No.
(number of control
axes)
0 to 1000000
(°/min)
1524 C_type
0: Normal line control
type I
1: Normal line control
type II
1525
1526
1527
1528
1529
1530
1531
1532
1533 millPax
1534 SnG44.1
Pole
coordinate
linear axis
name
Spindle No.
for G44.1
command
Set the linear axis used for pole coordinate
interpolation.
Control axis address
such as X, Y or Z
Set the selected spindle No. for the G44.1
command.
0: 2nd spindle
1: 1st spindle
2: 2nd spindle
3: 3rd spindle
4: 4th spindle
If a spindle that does
not exist is set, the
2nd spindle will be
used. Note that if
there is only one
spindle, the 1st
spindle will be used.
0.000 to 99999.999
(mm)
(Input setting
increment applies)
#1199
0:G43.1
1:G44.1
2:G47.1
#1534
Not used.
0
1
2
3
4
Not used.
Selected spindle
1st spindle
2nd spindle
1st spindle
2nd spindle
3rd spindle
4th spindle
All spindles
1535 C_leng
Minimum
turning
movement
amount
Set the minimum turning movement amount of the
normal line control axis at the block joint during
normal line control.
1537 crsax[1]
to
to
1544 crsax[8]
Cross
machining
control axis
Set the axis to be interchanged during cross
machining control.
Using two digits, set the name of the axis
interchanged with that where the cross machining
control request signal is input, or that moves to the
position where the signal is input.
III - 73
Two digits between A
to Z and 1 to 9
(Setting is cleared
when 0 is set)
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1561 3Dcdc
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
Switch
workpiece
coordinate
display during
3D coordinate
conversion
The workpiece coordinate display during 3D
0/1
coordinate conversion is switched to the workpiece
coordinate system or G68 program coordinate
system.
0: Workpiece coordinate system
1: G68 program coordinate system
(Note) The special display unit's absolute
coordinates also follow this parameter
setting.
1562 3Dremc Switch
remaining
command
display during
3D coordinate
conversion
The remaining command display during 3D
0/1
coordinate conversion is switched to the workpiece
coordinate system or G68 program coordinate
system.
0: Workpiece coordinate system
1: G68 program coordinate system
1563 3Dcdrc
Switch
coordinate
reading during
3D coordinate
conversion
The coordinate system of the workpiece/skip
coordinate read value in the 3D coordinate
conversion modal is switched.
0: G68 program coordinate system
1: Workpiece (local) coordinate system
1564 3Dspd
Hole drilling
Set the rapid traverse rate for the hole drilling cycle 0/1
speed during 3D during 3D coordinate conversion.
coordinate
0: The cutting feed clamp speed is used.
conversion
Other than 0: The set speed is used.
Note that if the rapid traverse rate
is exceeded, the speed will be
clamped at the rapid traverse rate.
1568 SfiltG1
G01 soft
acceleration/
deceleration
filter
This is the filter time constant for smoothly changing 0 to 200 (ms)
the acceleration rate for the cutting feed
acceleration/deceleration in pre-interpolation
acceleration/deceleration.
1569 SfiltG0
G00 soft
acceleration/
deceleration
filter
This is the filter time constant for smoothly changing 0 to 200 (ms)
the acceleration rate for the rapid traverse
acceleration/deceleration in pre-interpolation
acceleration/deceleration.
1570 Sfilt2
Soft
acceleration/
deceleration
filter 2
This is the filter time constant for smoothly changing 0 to 50 (ms)
the acceleration rate during pre-interpolation
acceleration/deceleration.
1571 SSSdis SSS control
adjustment
coefficient
fixed value
selection
The shape recognition range for SSS control is
fixed.
III - 74
0/1
0/1
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1572 Cirorp
Items
Arc command
overlap
Details
Setting range (unit)
This eliminates speed fluctuations at the joint of the 0 to F (HEX)
arc and straight line and arc and arc.
Set as a bit unit.
0: Do not overlap the arc command blocks
1: Overlap the arc command blocks
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Arc command during high-speed
high-accuracy control II
Arc command during high-speed machining
mode II
Arc command during high-accuracy control
(G61.1)
Arc command during cutting mode (G64)
(Note) This parameter is invalid during SSS
control.
1573 Ret1
Return type 1
Specify the axis to be moved later after tool return.
This is referred to with the movement path (transit
point #1 → interrupt point).
Up to eight axes can be specified by expressing
one axis with one bit.
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
00000000 to
11111111 (Binary)
0
Transit point #1 1st axis
Transit point #1 2nd axis
Transit point #1 3rd axis
Transit point #1 4th axis
Transit point #1 5th axis
Transit point #1 6th axis
Transit point #1 7th axis
Transit point #1 8th axis
1574 Ret2
Return type 2
Specify the axis to be moved later after tool return.
This is referred to with the movement path (return
start point → transit point #2).
Up to eight axes can be specified by expressing
one axis with one bit.
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Transit point #2 1st axis
Transit point #2 2nd axis
Transit point #2 3rd axis
Transit point #2 4th axis
Transit point #2 5th axis
Transit point #2 6th axis
Transit point #2 7th axis
Transit point #2 8th axis
III - 75
00000000 to
11111111 (Binary)
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1590 Animate Machine status
ax direct animated
display axis ±
direction
Details
Setting range (unit)
bit0 0: 1st axis + direction is set to the right
direction.
1: 1st axis + direction is set to the left
direction.
0 to F (HEX)
bit1 0: 2nd axis + direction is set to the rear
direction.
1: 2nd axis + direction is set to the front
direction.
1591 Animate Machine status
ax-1
animated
display axis
name (1st axis)
bit2 0: 3rd axis + direction is set to the top
direction.
1: 3rd axis + direction is set to the bottom
direction.
Set the name of the 1st axis displayed with the
machine status animation. If the axis name is not
specified, the current 1st axis name (#1013
axname) is used.
Address for control
axis such as X, Y, Z
3rd axis
1st axis
2nd axis
1592 Animate Machine status
ax-2
animated
display axis
name (2nd axis)
1593 Animate Machine status
ax-3
animated
display axis
name (3rd axis)
Set the name of the 2nd axis displayed with the
machine status animation. If the axis name is not
specified, the current 2nd axis name (#1013
axname) is used.
Set the name of the 3rd axis displayed with the
machine status animation. If the axis name is not
specified, the current 3rd axis name (#1013
axname) is used.
III - 76
Address for control
axis such as X, Y, Z
Address for control
axis such as X, Y, Z
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
1801 Hacc_c
Items
Details
Arc radius clamp acceleration
Setting range (unit)
-99999999 to
+99999999
1802 Macc_c
Acceleration check at middle speed
-99999999 to
+99999999
1803 Lacc_c
Acceleration check at low speed
-99999999 to
+99999999
1811 Hcof_A
X-axis high acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
1812 Hcof_B
X-axis high acceleration coefficient α
-99999999 to
+99999999
1813 Mcof_A
X-axis middle acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
1814 Mcof_B
X-axis middle acceleration coefficient α
-99999999 to
+99999999
1815 Lcof_A
X-axis low acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
1816 Lcof_B
X-axis low acceleration coefficient α
-99999999 to
+99999999
1817 mag_C
X-axis change magnification θ [%]
Set "0" when no compensation or change is
executed.
-99999999 to
+99999999
1821 Hcof_A
Y-axis high acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
1822 Hcof_B
Y-axis high acceleration coefficient α
1823 Mcof_A
Y-axis middle acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
-99999999 to
+99999999
1824 Mcof_B
Y-axis middle acceleration coefficient α
-99999999 to
+99999999
1825 Lcof_A
Y-axis low acceleration coefficient β
-99999999 to
+99999999
1826 Lcof_B
Y-axis low acceleration coefficient α
-99999999 to
+99999999
1827 mag_C
Y-axis change magnification θ [%]
Set "0" when no compensation or change is
executed.
-99999999 to
+99999999
III - 77
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
1901 station addr
(PR)
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set up a station address number (the NC is the nth 1 to 7
slave station).
1902 Din size
(PR)
Set up the size of the data to be transferred from
the PC to the NC (from the master station to the
slave station) in bytes (8 points).
Set up the size of the data to be transferred from
the NC to the PC (from the slave station to the
master station) in bytes (8 points).
Set up the data length of a character.
1903 Dout size
(PR)
1904 data length
(PR)
0 to 32
(bytes (8 bits))
0 to 32
(bytes (8 bits))
0 to 2 : 7 bits
3
: 8 bits
1905 baud rate
(PR)
Set up a data transfer rate. The transfer rate
differs according to operation clock rates
Clock: 6 MHz/
10 MHz
0: 38400 / 57600
1: 19200 / 28800
2: 9600 / 14400
3: 4800 / 7200
4: 2400 / 3600
5: 1200 / 1800
6:
600 /
900
(bps)
1906 stop bit
(PR)
Set up the stop bit length.
0 and 1: 1 bit
2 and 3: 2 bits
1907 parity check
(PR)
Select whether to make a parity check.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
1908 even parity
(PR)
Select the odd or even parity bit. If no parity check 0: Odd parity
is specified, this parameter is ignored.
1: Even parity
1909 Tout (ini)
(PR)
(ini) specifies a time-out from when the connection
check sequence finishes to when the first usual
sequence (input) finishes.
1910 Tout (run)
(PR)
(run) specifies a time-out from when the NC (slave
station) outputs usual sequence data to when the
next usual sequence data is input.
0 to 999
(0.1 s)
If the time-out is exceeded, an emergency stop
occurs and the system waits for the preparation
sequence to start.
If the set value is 0, no time-out occurs or no
communication stop can be detected.
1911 clock select
(PR)
Select an operation cycle.
III - 78
0: 6 MHz
1: 10 MHz
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
1925 EtherNet Start of service Start or stop the Ethernet communication function. 0/1
0: Stop
1: Start
1926 IP
address
IP address
Set the main CPU's IP address.
Set the NC IP address looking from an external
source.
1927 Subnet
mask
1928 Gateway
address
Subnet mask
Set the subnet mask for the global IP address.
Gateway
Set the IP address for the global gateway.
1929 Port
number
Port No.
Set the port No. for the service function.
1 to 9999
(Set 2000 when not
connected to the
Ethernet.)
1930 Host
address
Host address
Set the host's IP address.
1 to 255
1931 Host
number
Host No.
Set the host's port No.
1 to 9999
1934 Local IP
address
HMI side CPU IP address
1935 Local
Subnet
mask
HMI side CPU subnet mask
Set these parameters
in accordance with the
network rules in the
connection
environment.
III - 79
Set these parameters
in accordance with the
network rules in the
connection
environment.
4. Base Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set the part system axis name (#1013 axname)
Axis addresses such
12001 ManualB Manual feed
RectanA rate B constant for the two axes that intersect with the rotary axis as X, Y, Z, U, V, W, A,
B, and C
xH
surface control direction. If one of the two axes is blank, a
constant speed will be applied without using
intersecting
constant surface speed control.
part system
axis name
(horizontal)
12002 ManualB
RectanA
xV
Manual feed
rate B constant
surface control
intersecting
part system
axis name
(vertical)
12003 ManualB
RotCent
erH
Manual feed
Set the machine coordinate position (horizontal
rate B constant axis) at the center of the rotary axis.
surface control
rotation center
machine
position
(horizontal)
12004 ManualB
RotCent
erV
Manual feed
Set the machine coordinate position (vertical axis) -99999.999 to
rate B constant at the center of the rotary axis.
99999.999 (mm)
surface control
rotation center
machine
position
(vertical)
21007 Sfig
(PR)
Number of S
21008 Sbin
(PR)
S binary
Number of S: Set the number of spindles.
S binary: Refer to the following table.
Data type
0
1
-1
Output data
BCD
Unsigned binary
Singed binary
For unsigned binary:
The absolute value 1 is output for -1.
For singed binary:
-1 is output as "0xFFFFFFFF".
(Note 1) Sfig is set in the range of 1 to 4.
However, the number of outputs by Sfig
cannot be controlled. Thus, only one S
command is output regardless of the
Sfig setting value.
(Note 2) Sbin can be set with -1, 0 and 1, but the
S command cannot be BCD output.
If BCD (0) is selected for Sbin, it will be
handled as a singed binary (-1).
III - 80
-99999.999 to
99999.999 (mm)
1 to 4
Data type
(-1,0,1)
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter,
turn ON the power again.
#
2001 rapid
Items
Rapid traverse
rate
Details
Set up the rapid traverse feedrate for each axis.
The maximum value to be set differs with
mechanical systems.
2002 clamp
Cutting feedrate
for clamp
function
Define the maximum cutting feedrate for each axis. 1 to 1000000
Even if the feedrate in G01 exceeds this value‚ the (mm/min)
clamp will be applied at this feedrate.
2003 smgst
(PR)
Acceleration and Specify acceleration and deceleration control
deceleration
modes.
modes
F E D C B A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
OT3 OT2 OT1 C3
C1
LC
R3
R1
Setting range (unit)
1 to 1000000
(mm/min)
LR
(Note) Set 0 in null bits.
Rapid traverse feed acceleration and deceleration
types
LR: Linear acceleration/deceleration
R1: Primary delay
R3: Exponential acceleration and linear
deceleration
(Note) Designate "F" with bits 0 to 3 for rapid
traverse with acceleration/deceleration by
software.
Cutting feed acceleration and deceleration types
LC: Linear acceleration/deceleration
C1: Primary delay
C3: Exponential acceleration and linear
deceleration
(Note) Designate "F" with bits 4 to 7 for cutting
feed with acceleration/deceleration by
software.
(To be continued to the next page)
III - 81
Specify the modes in
hexadecimal notation.
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
(Continued from the previous page)
<Combination of acceleration and deceleration
patterns>
Primary delay
R1=1 (C1=1)
Command
speed
Linear to linear
LR=1 (LC=1)
Step
LR=0 (LC=0)
Exponential to linear
R3=1 (C3=1)
Step
R1-R3=0
(C1-C3=0)
Values in parentheses indicate the
cutting feed.
R1 > R3 when both R1 and R3 contain 1.
<Stroke end stop types>
Type
OT2
OT3
Linear deceleration
0
0
Position loop step stop
1
0
Speed loop step stop
0
1
Position loop step stop
1
1
OT1
0 Deceleration by G0t1
1 Deceleration by 2 × G0t1
Stroke end signal
Speed
Time
G0t1
2×G0t1 (OT1=1, OT2=OT3=0)
G0t1 (OT1=OT2=OT3=0)
OT1 is valid under the following conditions (valid for
dog type zero point return):
Stop type: Linear deceleration
Acceleration mode: Exponential
Deceleration mode: Linear
III - 82
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
2004 G0tL
Items
Details
G0 time constant Set up a linear control time constant for rapid
(linear)
traverse acceleration and deceleration.
The time constant is validated when LR (rapid
traverse feed with linear acceleration or
deceleration) or F (acceleration or deceleration by
software) is selected in acceleration or deceleration
mode "#2003 smgst".
Setting range (unit)
1 to 4000 (ms)
Speed
Time
G0tL
2005 G0t1
G0tL
G0 time constant Set up a primary-delay time constant for rapid
1 to 5000 (ms)
(primary delay)
traverse acceleration and deceleration.
The time constant is validated when R1 (rapid
traverse feed with primary delay) or R3 (exponential
acceleration and linear deceleration) is selected in
acceleration or deceleration mode "#2003 smgst".
Second-step
When acceleration or deceleration by software is
time constant for selected, the second-step time constant is used.
acceleration and
deceleration by
<Rapid traverse feed with primary delay>
software
Speed
Time
G0t1
G0t1
<Rapid traverse feed with exponential
acceleration and linear deceleration>
Speed
Time
G0t1
2×G0t1
<Soft acceleration/deceleration>
Speed
Time
G0t1
G0t1
G0t1
G0tL
G0tL
2006 G0t2
G0t1
Not used. Set to "0".
III - 83
0
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
2007 G1tL
Items
G1 time
constant
(linear)
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set up a linear control time constant for cutting
1 to 4000 (ms)
acceleration and deceleration.
The time constant is validated when LC (cutting feed
with linear acceleration and deceleration) or F
(acceleration and deceleration by software) is
selected in acceleration or deceleration mode
"#2003 smgst".
Speed
Time
G1tL
2008 G1t1
G1tL
Set up the primary delay time constant for cutting
G1 time
1 to 5000 (ms)
acceleration and deceleration.
constant
(primary delay) The time constant is validated when C1 (cutting feed
with the primary delay) or C3 (cutting feed with
exponential acceleration and linear deceleration) is
selected in acceleration or deceleration mode
"#2003 smgst".
Second stage When acceleration or deceleration by software is
selected, the second stage time constant is used.
time constant
for
acceleration
<Cutting feed with primary time constant>
and
deceleration by
Speed
software
Time
G1t1
G1t1
<Cutting feed with exponential acceleration
and linear deceleration>
Speed
Time
G1t1
2×G1t1
<Soft acceleration/deceleration>
Speed
Time
G1t1
G1t1
G1t1
G1tL
G1tL
2009 G1t2
G1t1
Not used. Set to "0".
III - 84
0
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
2010 fwd_g
Items
Feed
forward
gain
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set up a feed forward gain for pre-interpolation
0 to 200 (%)
acceleration and deceleration.
The larger the set value, the smaller the theoretical
control error will be. However, if a mechanical vibration
occurs, the set value must be reduced.
2011 G0back
G0
backlash
Set up the backlash compensation amount when the
direction is reversed with the movement command in
rapid traverse feed mode or in manual mode.
-9999999 to 9999999
(mm)
2012 G1back
G1
backlash
Set up the backlash compensation amount when the
direction is reversed with the movement command in
cutting mode.
-9999999 to 9999999
(mm)
III - 85
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
2013 0T 2014 0T +
Items
Soft limit I soft limit I +
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set up a soft limit area with reference to the zero
point of the basic mechanical coordinates.
For the movable area of stored stroke limit 1, set the
coordinate in the negative direction in #2013 and the
coordinate in the positive direction in #2014.
To narrow the available range in actual use, use the
parameters #8204 OT- and #8205 OT+.
When the same value (other than 0) is set in #2013
and #2014, this function is disabled.
OT+ (Z)
Basic mechanical coordinates
OT- (X)
M
OT+ (X)
Movable area
±99999.999 (mm)
OT- (Z)
2015 t1m1-
Negative
direction
sensor of tool
setter or TLM
standard
length
2016 t1m1+
Positive
Set up the sensor position in the positive direction
direction
when using the tool setter.
sensor of tool
setter
Axis servo gain Set the position loop gain for special operations
(synchronized tapping, interpolation with spindle C
axis, etc.)
Set the value in 0.25 increments.
The standard setting is 10.
±99999.999 (mm)
Operation with
no servo
control
0/1
2017 tap_g
2018 no_srv
Set up a sensor position in the negative direction
when using the tool setter. When the TLM is used,
set up the distance of a tool replacement point
(reference position) for measuring the tool length
from the zero point to the measurement standard
point (surface).
Set when performing test operation without
connecting the drive unit and motor.
0: Specify normal operation.
1: Operation is possible even if units are not
connected as the drive system alarm will be
ignored.
This is for test operation during start up and is not
used normally.
If 1 is set during normal operation‚ errors will not be
detected even if they occur.
III - 86
±99999.999 (mm)
0.25 to 200.00 (rad/s)
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.1 Axis Specifications Parameters
#
Items
2019 revnum Return steps
Details
Set up the steps required for reference position
return for each axis.
0: Does not execute reference position return.
1 to max. number of NC axes:
Sets up the steps required for reference
position return.
Setting range (unit)
0 to max. number of
NC axes
2020 o_chkp
Spindle
orientation
completion
check during
second
reference
position return
Set up the distance from the second reference
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
position to the position for checking that the spindle
orientation has completed during second reference
position return. If the set value is 0, the above check
is omitted.
2021 out_f
Maximum
Set up the maximum speed outside the soft limit
speed outside range.
soft limit range
0 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2022 G30SLX Validate soft
Set up this function to disable a soft limit check
limit (automatic during the second to the fourth zero point return in
and manual)
both automatic and manual operation modes.
0: Enables soft limit check.
1: Disables soft limit check.
0/1
2023 ozfmin
Set up ATC
speed lower
limit
0 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2024 synerr
Allowable error Set up the following for the master axis: the
maximum synchronization error that is allowed to
check for synchronization errors
When 0 is set up, the error check is not carried out.
Set up the minimum speed outside the soft limit
range during the second to the fourth reference
position return in both automatic and manual
operation modes.
III - 87
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.2 Zero Point Return Parameters
5.2 Zero Point Return Parameters
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter,
turn ON the power again.
#
Items
2025 G28rap G28 rapid
traverse rate
Details
Set up a rapid traverse rate for dog type reference
position return command.
Setting range (unit)
1 to 999999
(mm/min)
2026 G28crp
G28
approach
speed
Set up the speed of approach to the reference
position in the reference position return command.
This speed is attained after the system stops with
deceleration by dog detection.
(Note) The G28 approach speed unit is (10°/min)
only when using the Z-phase type encoder
(#1226 aux10 bit3=1) for the spindle/C-axis
reference position return type. The same unit
is used for both the micrometric and submicrometric specifications.
1 to 60000 (mm/min)
2027 G28sft
Reference
position shift
distance
Set up the distance from the electrical zero-point
detection position to the actual machine reference
position during reference position return control.
(Note) When #1240 set12 (bit2) is ON, a
magnification (C: 10-fold, D: 100-fold)
corresponding to the input setting unit (#1003
iunit) will be applied on the setting value.
0.000 to 99.999
(mm)
2028 grmask
Grip mask
amount
Set up a distance where the grid point is ignored
when near-point dog OFF signals are close to that
grid point during reference position return.
0.000 to 99.999
(mm)
Near-point dog
Grid mask setup distance
The grid mask is valid by one grid.
2029 grspc
Grid interval
Set up a detector grid interval.
0.000 to 999.999
Generally, set up the value equal to the ball screw
(mm)
pitch. However, if the detector grid interval is not
equal to the screw pitch when measured with a linear
scale, set up the detector grid interval.
To reduce the grid interval, use its divisors.
III - 88
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.2 Zero Point Return Parameters
#
2030 dir (-)
(PR)
Items
Reference
position
direction (-)
Details
Set which side of the near-point dog the reference
position is at during reference point return.
<For dog type reference position return>
Setting range (unit)
0: Positive direction
1: Negative direction
Direction in which zero point is established
as viewed from the near-point dog
Negative
direction
Near-point dog
Positive
direction
dir (-)=0
dir (-)=1
2031 noref
Axis without
reference
position
2032 nochk
Whether
reference
position return
is completed
not checked
2033 zp_no
Z phase pulse
system
reference
position return
spindle
encoder No.
The reference position return is performed with the Z 0: Dog type
phase pulse of the spindle encoder. Set the
1 to 4: Spindle No.
spindle encoder No. to be used.
2037
2038
2039
2040
Reference
position #1 to
#4
Set up the position of the first, second, third, and
fourth reference positions from the zero point of the
basic mechanical coordinates.
G53ofs
#2_rfp
#3_rfp
#4_rfp
Specify the axis that does not have a reference
position. Before automatic operation starts,
reference position return is not required.
0: Normal controlled
axis
1: Axis without
reference position
The absolute and incremental commands can be
0: Reference
executed even if dog type (or Z phase pulse system)
position return
reference position return is not completed.
completion is
Specify whether to check that the reference point
checked.
return is completed.
1: Reference
position return
completion is not
checked.
Basic mechanical coordinates
Reference position #1
M
Reference position #2
Reference position #3
III - 89
Reference position #4
±999999.999 (mm)
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.3 Absolute Position Parameters
5.3 Absolute Position Parameters
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter,
turn ON the power again.
#
2049 type
(PR)
Items
Absolute
position
detection
method
Details
Setting range (unit)
0 to 9
Specify the absolute position zero point alignment
method.
0: Not absolute position detection
1: Stopper method (push with mechanical stopper)
2: Marked point alignment method (align to
alignment point)
3: Dog-type (align with dog and proximity switch)
4: Marked point alignment method II (align to
alignment mark)
(Type that does not return grid after marked
point alignment)
9: Simple absolute position
(Not absolute position detection‚ but the position
when the power is turned off is registered.)
Automatic initial setting is valid only when the stopper
method is selected.
2050 absdir
Basic point
of Z
direction
Set the direction of the absolute position reference
point (grid point immediately before) seen from the
machine basic point for when using marked point
alignment.
2051 check
Check
Set the tolerable range for the movement amount
0 to 99999.999 (mm)
(deviation amount) when the power is turned OFF.
0: Not checked
1 to 99999.999mm: If the difference of the position
when the power is turned OFF
and turned ON again is larger
than this value‚ an alarm will
be output.
2052 absg28
2053 absm02
Not used. Set to "0".
Not used. Set to "0".
2054 clpush
Current
limit (%)
2055 pushf
Push speed Set the feedrate for the automatic initial setting during
stopper method.
2056 aproch
Approach
0: Positive direction
1: Negative
direction
0
0
Set up the current limit value for the initial setting when 0 to 100 (%)
detecting an absolute position with a dog-less system.
The setup value is the ratio of the current limit value to
the rated value.
1 to 999 (mm/min)
Set the approach distance for the automatic initial
0 to 999.999 (mm)
setting in the push method.
Approach distance:
After using stopper once‚ the
tool returns this distance‚ and
then use stopper again.
When set to 0‚ the reference
position coordinates set in
"#2037 G53ofs" will be used as
the approach start position.
III - 90
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.3 Absolute Position Parameters
#
2057 nrefp
Items
Near zero
point +
Details
Setting range (unit)
Set the width where the near reference position signal 0 to 999.999 (mm)
is output. (Positive direction width)
(Input setting
When set to 0‚ the width is equivalent to the grid width increment applies)
setting.
(Note) When #1240 set12 (bit2) is ON, a
magnification (C: 10-fold, D: 100-fold)
corresponding to the input setting unit (#1003
iunit) will be applied on the setting value.
2058 nrefn
Near zero
point -
Set the width where the near reference position signal 0 to 999.999 (mm)
is output. (Negative direction width)
(Input setting
When set to 0‚ the width is equivalent to the grid width increment applies)
setting.
(Note) When #1240 set12 (bit2) is ON, a
magnification (C: 10-fold, D: 100-fold)
corresponding to the input setting unit (#1003
iunit) will be applied on the setting value.
2059 zerbas
Select zero
point
parameter
and basic
point
Specify the position to be the zero point coordinate
during absolute position initial setting.
0: Position that was stopped during stopper
method
Specify the coordinates of the alignment mark
position when using the marked point method.
1: Grid point just before stopper
Specify the coordinates of the grid point just
before the alignment mark.
III - 91
0/1
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
After setting up the parameter (PR) listed in the table, turn OFF the NC power. To validate the parameter,
turn ON the power again.
#
Items
Details
2061 OT_1B- Soft limit IB- Set up the coordinates of the lower limit of the
inhibited area of stored stroke limit IB.
Specify a value in the basic mechanical coordinates
system. If the same value (non-zero) with the same
sign as that of #2062 OT_IB+ is specified, the stored
stroke limit IB function is disabled.
Setting range (unit)
±99999.999 (mm)
2062 OT_1B+ Soft limit IB+ Set up the coordinates of the upper limit of the
±99999.999 (mm)
inhibited area of stored stroke limit IB.
Specify a value in the basic mechanical coordinates
system.
2063 OT_1B Soft limit IB Select OT_IB or OT_IC in which OT_IB+/- is used in
0 to 3
type
stored stroke limit I.
type
0: Soft limit IB valid
1: Invalid
2: Soft limit IC valid
3: When using the inclined axis specifications, the
soft limit is checked with the program coordinate
system.
(Note) This is invalid for axes other than the
inclined axis' base axis and inclined
axis.
2064
2065
2066
2067
2068 G0fwdg G00 feed
Specify the feed forward gain applicable to
forward gain acceleration/deceleration before G00 interpolation.
The greater the set value, the shorter the positioning
time during in-position checking.
If machine vibration occurs, decrease the set value.
0 to 200 (%)
2069 Rcoeff
Axis arc
radius error
correction
efficient
-100.0 to +100.0 (%)
2070 div_RT
(PR)
Rotational
Specify the number of divisions of one turn of the
0 to 999
axis division rotational axis for purpose of control.
count
(Example) When "36" is set, one turn is supposed to
be 36.000.
(Note 1) When "0" is set, the normal rotational axis
(360.000 degrees for one turn) is assumed.
(Note 2) If this parameter is changed when the
absolute position detection specification is
used, absolute position data is lost.
Initialization must be performed again.
The amount of arc radius error correction can be
increased or decreased between -100% to +100% for
each axis.
III - 92
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
Items
2071 s_axis
Inclined
(For L
axis
system
selection
only)
Details
Select the axis subjected to inclined-axis control or the
base axis corresponding to the inclined axis.
0: Axis not subjected to inclined-axis control
1: Inclined axis
2: Base axis corresponding to inclined axis
(Note) Set 1 or 2 for only one axis. If it is set for two
or more axes, inclined-axis control does not
work.
Setting range (unit)
0 to 2
2072 rslimt
Restart
limit
If the machine is positioned on the minus (-) side of the ±9999.999 (mm)
set value in T-command restart mode, restart search in
type 3 is disabled.
2073 zrn_dog
Origin dog
Under the standard specifications, the origin dog signal 0000 to 02FF (HEX)
is assigned to a fixed device. When it is desired to
assign the origin dog signal to a position other than the
fixed device, specify the input device in this parameter.
* This parameter is valid when "1" is set in
#1226 aux10 bit 5.
* When this parameter is valid, do not set the
same device number. If the same device
number exists, an emergency stop occurs.
However, no device number check is
performed for an axis to which a signal that
ignores the near-point dog signal (R157) is
input.
2074 H/W_OT+ H/W OT+
Under the standard specifications, the OT (+) signal is 0000 to 02FF (HEX)
assigned to a fixed device. When it is desired to
assign the OT (+) g signal to a position other than the
fixed device, specify the input device in this parameter.
* This parameter is valid when "1" is set in
#1226 aux10 bit 5.
* When this parameter is valid, do not set the
same device number. If the same device
number exists, an emergency stop occurs.
However, no device number check is
performed for an axis to which a signal that
ignores the OT signal (R156) is input.
2075 H/W_OT- H/W OT-
0000 to 02FF (HEX)
Under the standard specifications, the OT (-) signal is
assigned to a fixed device. When it is desired to
assign the OT (-) g signal to a position other than the
fixed device, specify the input device in this parameter.
* This parameter is valid when "1" is set in
#1226 aux10 bit 5.
* When this parameter is valid, do not set the
same device number. If the same device
number exists, an emergency stop occurs.
However, no device number check is
performed for an axis to which a signal that
ignores the OT signal (R248) is input.
2076 index_x
Index table Specify the index table indexing axis.
indexing
0: Normal axis
axis
1: Index table indexing axis
(Note) This parameter is valid only for the NC axis.
The parameter is invalid if specified for the PLC
axis.
III - 93
0/1
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
Items
2077 G0inps
G0 inposition
width
Details
When an in-position check is performed for G0, this
parameter is valid.
(Comparison of SV024 and this parameter, the
parameter that the in-position width is wider is
applied.)
When 0 is set, this parameter is invalid.
(Applicable only to SV024)
Setting range (unit)
0.000 to 99.999
(mm)
2078 G1inps
G1 inposition
width
When an in-position check is performed for G1, this
parameter is valid.
(Comparison of SV024 and this parameter, the
parameter that the in-position width is wider is
applied.)
When 0 is set, this parameter is invalid.
(Applicable only to SV024)
0.000 to 99.999
(mm)
2079 chcomp
Chopping
compensation
coefficient
Set the coefficient applied on the compensation
amount for the insufficient amount caused by servo
delay during chopping.
0 to 10
(standard value: 8)
2080 chwid
Bottom
dead center
position
width
Set the tolerance between the commanded stroke and 0 to 10.000 (mm)
actual stroke.
During chopping, if the (command width - maximum
stroke of top/bottom dead center position /2) is within
this tolerance, compensation will be applied.
2081 chclsp
Maximum
chopping
speed
Set the chopping axis clamp speed applied during
chopping.
2082 a_rstax
Restart
Designate the order for automatically returning to the
position
restart position.
return order
0: Do not return.
When 0 is designated for all axes, all of the axes
will return simultaneously.
0 to 60000 (mm/min)
0 to 6
2083
2084 G60_ax
Unidirectional
positioning
operation
selection
0/1
Select the unidirectional positioning with G00.
Select the axis for carrying out the positioning per time
operation when the positioning command is issued
regardless of the unidirectional positioning command
and modal.
0: Carry out unidirectional positioning according to
the command and modal.
1: When the positioning command (G00) is issued,
carry out unidirectional positioning regardless of
the command and modal.
<Related parameters>
#8209 G60 SHIFT:
The final positioning direction and distance for
the unidirectional positioning command is set
for each axis.
#2076 Index table indexing axis:
Set the indexing axis for each axis.
2086
III - 94
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
2087 syncnt
Items
Synchronization/superimposition
control setting
for each axis
Details
BIT0: Polarity of synchronous axis in respect to
reference axis
0: Polarity with reference axis is positive
1: Polarity with reference axis is negative
Setting range (unit)
0 to FF
(hexadecimal)
2088 bsax_sy
Reference axis Set the reference axis for synchronous control with
for
the 2nd axis name (axname2).
synchronous
control
1st character:
A to Z
2nd character:
A to Z, 1 to 9
2089 bsax_pl
Reference axis Set the reference axis for superimposition control
for
with the 2nd axis name (axname2).
superimposition control
1st character:
A to Z
2nd character:
A to Z, 1 to 9
2090 plrapid
Rapid traverse Set the rapid traverse rate for superimposition
rate for super- control.
imposition
(Equivalent to #2001 rapid (rapid traverse rate).)
control
1 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2091 plclamp
Cutting feed
clamp speed
for superimposition
control
Set the cutting feed clamp speed for
superimposition control.
(Equivalent to #2002 clamp (cutting feed clamp
speed).)
1 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2092 plG0tL
G0 time
constant for
superimposition control
(linear)
Set the G0 time constant (linear) for
superimposition control.
(Equivalent to #2004 G0tL (G0 time constant
(linear).)
1 to 4000 (ms)
2093 plG0t1
G0 time
constant for
superimposition control
(primary delay)
Set the G0 time constant (primary delay) for
superimposition control.
(Equivalent to #2005 G0t1 (G0 time constant
(primary delay).)
1 to 5000 (ms)
2094 plG1tL
G1 time
constant for
superimposition control
(linear)
Set the G1 time constant (linear) for
superimposition control.
(Equivalent to #2007 G1tL (G1 time constant
(linear).)
1 to 4000 (ms)
2095 plG1t1
G1 time
constant for
superimposition control
(primary delay)
Set the G1 time constant (primary delay) for
superimposition control.
(Equivalent to #2008 G1t1 (G1 time constant
(primary delay).)
1 to 5000 (ms)
2096 crncsp
Minimum
corner
deceleration
speed
Set the minimum clamp speed for corner
0 to 1000000
deceleration during the high-accuracy control mode. (mm/min)
Normally set "0".
(Note) This parameter is invalid during SSS control.
2097 tlml2-
Sub side tool
setter
- direction
sensor
Set the - direction sensor position (sub side) when
using the tool setter on the sub spindle side.
±99999.999 (mm)
2098 tlml2+
Sub side tool
setter
+ direction
sensor
Set the + direction sensor position (sub side) when
using the tool setter on the sub spindle side.
±99999.999 (mm)
III - 95
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
2099
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
2102 skip_tL
Skip time
constant
linear
Set up a linear control time constant for variable
1 to 4000 (ms)
speed skip acceleration and deceleration.
The time constant is validated when LC (cutting feed
with linear acceleration and deceleration) or "F"
(acceleration and deceleration by software) is
selected in acceleration or deceleration mode "#2003
smgst".
2103 skip_t1
Skip time
constant
primary delay
acceleration
and
deceleration
by software
second stage
Set up a primary-delay time constant for variable
speed skip acceleration and deceleration.
The time constant is validated when C1 (cutting feed
with primary delay) or C3 (exponential acceleration
and linear deceleration) is selected in acceleration or
deceleration mode "#2003 smgst".
When acceleration or deceleration by software is
selected, the second-step time constant is used.
1 to 5000 (ms)
2106 Index
unit
Indexing unit
Set the indexing unit to which the rotary axis can be
positioned.
0 to 360 (°)
2109 Rapid (H- Rapid
precision) traverse rate
for highaccuracy
control mode
Set the rapid traverse rate for each axis in the highaccuracy control mode. "#2001 rapid" is used when
"0" is set.
0 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2110 Clamp (H- Cutting feed
precision) clamp speed
for highaccuracy
control mode
Set the cutting feed maximum speed for each axis in
the high-accuracy control mode. "#2002 clamp" is
used when "0" is set.
0 to 1000000
(mm/min)
2111 Blf valid
Set to this to validate the quadrant protrusion
0/1
compensation.
If "#2112 Blf motor inertia", "#2115 Blf motor stl trq" or
"#2113 Blf visc friction" is set to "0", quadrant
protrusion compensation will not function even if this
parameter is set to "1".
0: Quadrant protrusion compensation invalid
1: Quadrant protrusion compensation valid
Quadrant
protrusion
compensation
valid
2112 Blf motor Motor inertia
inertia
2113 Blf visc
friction
Viscous
friction
Set the motor inertia for quadrant protrusion
compensation.
Refer to the servo manual and input the value
appropriate for the motor.
Set the viscous friction for quadrant protrusion
compensation.
After setting the other parameters to the appropriate
values, monitor the machine end and gradually adjust
the value.
If this parameter setting is small, a recess will form on
the inner side of the circle, and if large, a protrusion
will form on the outer side of the circle. When the
value is appropriate, a pike-shaped quadrant
protrusion will form based on normal step-shaped
backlash.
III - 96
1 to 32000
(10-6kgm2)
1 to 32767
(1/16 Nm/(rad/s))
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
Items
Details
Setting range (unit)
2114 Blf fwdg Compensation Set the feed forward gain for quadrant protrusion
0 to 1000 (%)
FF gain
compensation.
After setting the other parameters to the appropriate
values, monitor the machine end and gradually adjust
the value.
If this parameter setting is small, a large quadrant
protrusion will form, and if large, a recess will form on
the inner side of the circle.
2115 Blf motor Motor stall
stl trq
torque
1 to 16000
(1/256 Nm)
2132 vback
pos1
Set the motor rated current for quadrant protrusion
compensation.
Refer to the servo manual and input the value
appropriate for the motor.
Variable
Set the range of the center of the end point position.
backlash
(The range less than position 1 is the - range, and the
compensation range exceeding position 2 is the + range.)
amount
The end point position range is determined in the
changeover
order of -, + , and center, so take care to the size of
end point
the setting value.
position 1/2
(Note 1) If continuous variable backlash is set with
#2121, position 1 will be set as the position
- point and position 2 will be set as the
position + point.
(Note 2) When the variable backlash compensation
is valid, and the size relation of the
compensation amount changeover speed,
distance 1/2 is not correct, if the backlash
speed and distance are smaller than the
compensation amount changeover speed
and distance 1, the speed and distance will
both be small. If larger than the
compensation amount changeover speed
and distance 2, the speed and distance will
both be large.
-999999.999999 to
999999.999999
(mm)
Variable
Set the arc compensation coefficient.
backlash arc
compensation
coefficient
Variable
Select the speed range to be used as the reference
backlash
position.
reference
0: Low speed
position
1: Medium speed
selection
2: High speed
(speed)
0 to 300 (%)
2133 vback
pos2
2134 vback
arc K
2135 vback
feed
refpt
0 to 2
2136 vback
Variable
Set the end point range to be used as the reference
pos refpt backlash
position.
reference
0: Position + range
position
1: Position center range
selection (end
2: Position - range
point position)
0 to 2
2137 vback dir Variable
refpt
backlash
reference
position
selection
(entry
direction)
0/1
Set the entry direction to be used as the reference
position.
0: Entry direction +
1: Entry direction -
III - 97
5. Axis Specifications Parameters
5.4 Axis Specifications Parameters 2
#
2138 vback
pos
center
Items
Continuous
variable
backlash
position center
point
2139 omrff_off OMR-FF
invalid
Details
Set the position center point. (This is used only when
continuous variable backlash is set with #2121.) Set a
value between "#2132 vback pos1" and "#2133
vbackpos2" for the position center point.
(Note 1) When the variable backlash compensation
is valid, and the size relation of the
compensation amount changeover speed,
distance 1/2 is not correct, if the backlash
speed and distance are smaller than the
compensation amount changeover speed
and distance 1, the speed and distance will
both be small. If larger than the
compensation amount changeover speed
and distance 2, the speed and distance will
both be large.
Setting range (unit)
-999999.999999 to
999999.999999
(mm)
Even when OMR-FF is valid, OMR-FF can be
0/1
temporarily invalidated and conventional feed forward
control applied.
0: If OMR-FF is valid, OMR-FF control is applied.
1: Even if OMR-FF is valid, it is temporarily
invalidated, and conventional feed forward
control is applied.
III - 98
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
(1) Details for servo parameters
For parameters marked with a (PR) in the table, turn the NC power OFF after setting. After the power is
turned ON again, the parameter is validated.
! CAUTION
!
In the explanation on bits, set all bits not used, including blank bits, to "0".
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
Set the motor side and machine side gear ratio.
1 to 32767
For the rotary axis, set the total deceleration
(acceleration) ratio.
1 to 32767
Even if the gear ratio is within the setting range, the
electronic gears may overflow and cause an alarm.
2201 SV001
(PR) PC1
Motor side
gear ratio
2202 SV002
(PR) PC2
Machine side
gear ratio
2203 SV003
PGN1
Position loop
gain 1
Set the position loop gain. The standard setting is 1 to 200
"33".
(rad/s)
The higher the setting value is, the more precisely
the command can be followed and the shorter the
positioning time gets, however, note that a bigger
shock is applied to the machine during
acceleration/deceleration.
When using the SHG control, also set SV004
(PGN2) and SV057 (SHGC).
2204 SV004
PGN2
Position loop
gain 2
When using the SHG control, also set SV003
(PGN1) and SV057 (SHGC).
When not using the SHG control, set to "0".
2205 SV005
VGN1
Speed loop gain Set the speed loop gain.
1 to 9999
Set this according to the load inertia size.
1
The higher the setting value is, the more accurate
the control will be; however, vibration tends to
occur.
If vibration occurs, adjust by lowering by 20 to 30%.
The value should be determined to be 70 to 80% of
the value at the time when the vibration stops.
2206 SV006
Speed loop gain If the noise is bothersome at high speed during
rapid traverse, etc, lower the speed loop gain.
2
As shown below, set the speed loop gain to 1.15fold of the motor's maximum speed, and use this
with SV028 (VSC).
When not using, set to "0".
VGN2
VGN1
VGN2
0
III - 99
VLMT
VCS
(Maximum speed × 1.15)
0 to 999
(rad/s)
-1000 to 9999
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
2207 SV007
VIL
Speed loop
delay
compensation
Details
Setting range
(unit)
Set this when the limit cycle occurs in the full-closed 0 to 32767
loop, or overshooting occurs in positioning.
Select the control method with SV027 (SSF1)/bit1,
0 (vcnt).
Normally, use "Changeover type 2".
When you set this parameter, make sure to set the
torque offset (SV032 (TOF)). When not using, set
to "0".
No changeover
When SV027 (SSF1)/ bit1, 0 (vcnt)=00
The delay compensation control is always valid.
Changeover type 1
When SV027 (SSF1)/ bit1, 0 (vcnt)=01
The delay compensation control works when the
command from the NC is "0".
Overshooting that occurs during pulse feeding can
be suppressed.
Changeover type 2
When SV027 (SSF1)/ bit1, 0 (vcnt)=10
The delay compensation control works when the
command from the NC is "0" and the position droop
is "0". Overshooting or the limit cycle that occurs
during pulse feeding or positioning can be
suppressed.
2208 SV008
VIA
Speed loop
lead
compensation
Set the gain of the speed loop integration control.
The standard setting is "1364". During the SHG
control, the standard setting is "1900". Adjust the
value by increasing/decreasing it by about 100 at a
time.
Raise this value to improve contour tracking
precision in high-speed cutting. Lower this value
when the position droop vibrates (10 to 20Hz).
1 to 9999
2209 SV009
IQA
Current loop q
axis lead
compensation
1 to 20480
2210 SV010
IDA
Current loop d
axis lead
compensation
Set the gain of current loop.
As this setting is determined by the motor’s
electrical characteristics, the setting is fixed for
each type of motor.
Set the standard values for all the parameters
depending on each motor type.
2211 SV011
IQG
Current loop q
axis gain
2212 SV012
IDG
Current loop d
axis gain
2213 SV013
ILMT
Current limit
value
2214 SV014
ILMTsp
Current limit
Set the current (torque) limit value in a special
value in special control (initial absolute position setting, stopper
control, etc). (Limit values for both of the + and control
directions.)
Set to "800" when not using.
1 to 8192
Set the normal current (torque) limit value. (Limit
values for both + and - direction.)
When the value is "800" (a standard setting), the
maximum torque is determined by the specification
of the motor.
III - 100
0 to 999
(Stall current %)
0 to 999
(Stall current %)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
2215 SV015
FFC
Acceleration
rate feed
forward gain
When a relative error in the synchronous control is
large, apply this parameter to the axis that is
delaying. The standard setting value is "0". For
the SHG control, set to "100".
To adjust a relative error in
acceleration/deceleration, increase the value by 50
to 100 at a time.
0 to 999
(%)
2216 SV016
LMC1
Lost motion
compensation
1
Set this when the protrusion (that occurs due to the
non-sensitive band by friction, torsion, backlash,
etc) at quadrant change is too large.
This compensates the torque at quadrant change.
This is valid only when the lost motion
compensation (SV027 (SSF1/lmc)) is selected.
-1 to 200
(Stall current %)
Type 2: When SV027 (SSF1)/ bit9, 8 (lmc)=10
Set the compensation amount based on the stall
(rated) current of the motor.
The standard setting is double of the friction torque.
Setting to "0" means the compensation amount is
zero.
Other than Type 2: When SV027 (SSF1))/bit9, 8
(lmc) ≠ 10
Lost motion compensation (type 2) is not
performed.
When you wish different compensation amount
depending on the direction
When SV041 (LMC2) is "0", compensate with the
value of SV016 (LMC1) in both of the + and directions.
If you wish to change the compensation amount
depending on the command direction, set this and
SV041 (LMC2). (SV016: + direction, SV041: direction. However, the directions may be
opposite depending on other settings.)
When "-1" is set, the compensation won’t be
performed in the direction of the command.
III - 101
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Items
No.
2217
(PR)
SV017 Servo
SPEC1 specification
selection 1
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo specifications.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
spm
7
6
mp
5
abs
4
3
2
1
0
fdir
vfb
seqh
dfbx
fdir2
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Speed feedback forward
0 fdir2
polarity
1 dfbx Dual feedback control stop
2 seqh Normal sequence
3 spwv Speed feedback filter stop
4
fdir
8
Position feedback forward
polarity
Meaning when "1" is set
Speed feedback reverse
polarity
Dual feedback control start
High-speed sequence
Speed feedback filter start
(2250Hz)
Position feedback reverse
polarity
5
6
7 abs Incremental control
Absolute position control
8 mp MPI scale 360 pole (2mm)
MPI scale 180 pole (1mm)
9
A
B
C
Select the motor series.
D
spm 0: HF, HP motor (200V specifications)
E
2: HF-H, HP-H motor (400V specifications)
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
2218
(PR)
SV018
PIT
Ball screw
pitch
Set the ball screw pitch. Set to "360" for the rotary axis.
III - 102
1 to 32767
(mm/rev)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2219 SV019
(PR) RNG1
Items
Position
detector
resolution
Setting range
(unit)
Details
In the case of the semi-closed loop control
Set the same value as SV020 (RNG2). (Refer to the
explanation of SV020.)
0 to 32767
(kp/rev)
In the case of the full-closed loop control
Set the number of pulses per ball screw pitch.
0 to 32767
(kp/pit)
Detector model name
2220 SV020
(PR) RNG2
Speed
detector
resolution
Resolution
SV019 setting
OSA105-ET2
1,000,000 (p/rev)
1000
OSA166-ET2
16,000,000 (p/rev)
16000
RCN723 (Heidenhain)
8,000,000 (p/rev)
8000
RCN223 (Heidenhain)
8,000,000 (p/rev)
8000
Relative position scale
Refer to specification
manual for each detector
SV018 (PIT)/
Rresolution (µm)
AT342 (Mitsutoyo)
0.5 (µm/p)
AT343 (Mitsutoyo)
0.05 (µm/p)
AT345 (Mitsutoyo)
0.05 (µm/p)
LC191M (Heidenhain)
Refer to specification
manual for each detector
LC491M (Heidenhain)
Refer to specification
manual for each detector
Futaba absolute
position scale (Futaba)
Refer to specification
manual for each detector
MPI scale (MHI)
Refer to specification
manual for each detector
MDS-B-HR
Analog cycle/500
Set the number of pulses per one revolution of the motor 1 to 32767
end detector.
(kp/rev)
Detector model name
SV019 setting
OSA105
1000
OSA166
16000
2221 SV021
OLT
Overload
Set the detection time constant of Overload 1 (Alarm 50). 1 to 999
detection
Set to "60" as a standard. (For machine tool builder
(s)
time constant adjustment.)
2222 SV022
OLL
Overload
detection
level
Set the current detection level of Overload 1 (Alarm 50) in 110 to 500
respect to the stall (rated) current. Set to "150" as a
(Stall current %)
standard. (For machine tool builder adjustment.)
2223 SV023
OD1
Excessive
error
detection
width during
servo ON
Set the excessive error detection width when servo ON.
<Standard setting value>
Rapid traverse rate
(mm/min)
OD1=OD2=
60×PGN1
/2 (mm)
When "0" is set, the excessive error detection will not be
performed.
III - 103
0 to 32767
(mm)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting
range (unit)
Details
2224 SV024
INP
In-position
detection
width
Set the in-position detection width.
Set the accuracy required for the machine.
The lower the setting is, the higher the positioning accuracy
gets; however, the cycle time (setting time) becomes longer.
The standard setting value is "50".
2225 SV025
(PR) MTYP
Motor/
Detector
type
Set the position detector type, speed detector type and motor type.
F
E
D
C
B
A
pen
7
6
0 to 32767
(µm)
9
8
1
0
ent
5
4
3
2
mtyp
ent: Set the speed detector type.
pen: Set the position detector type.
Set ent and pen to the same value when using semi-closed droop control.
pen setting
value
ent setting
value
Detector model name
0
0
1
1
2
2
OSA105, OSA166
3
3
-
4
Setting impossible
5
Setting impossible
6
Setting impossible
OSA105-ET2, OSA166-ET2
7
Setting impossible
-
8
Setting impossible
AT342, AT343, AT345 (Mitsutoyo)
LC191M, LC491M, RCN723, RCN223
(Heidenhain)
Futaba absolute position scale (Futaba)
MPI scale (MHI)
MDS-B-HR
9
Setting impossible
-
A
Setting impossible
-
B
Setting impossible
-
C
Setting impossible
-
D
Setting impossible
-
E
Setting impossible
-
F
Setting impossible
(To be continued to the next page)
III - 104
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting
range (unit)
Details
(Continued from the previous page)
mtyp: Set the motor type. Set according to SV017 (SPEC1)/spm.
(1) For SV017/spm = 0 (200V standard motor series)
mtyp
0x
1x
2x
3x
4x
5x
x0
x1
HF75
HP54
x2
HF105 HP104
x3
HF54
HP154
x4
HF104 HP204
x5
HF154 HP354
x6
HP454
x7
HF204 HP704
x8
HF354 HP903
x9
HF453 HP1103
xA
HF703
xB
HF903
xC
xD
xE
xF
(2) For SV017/spm = 2 (400V standard motor series)
mtyp
0x
1x
2x
3x
4x
5x
x0
x1
HF-H75 HP-H54
x2 HF-H105 HP-H104
x3
HF-H54 HP-H154
x4 HF-H104 HP-H204
x5 HF-H154 HP-H354
x6
HP-H454
x7 HF-H204 HP-H704
x8 HF-H354 HP-H903
x9 HF-H453 HP-H1103
xA HF-H703
xB HF-H903
xC
xD
xE
xF
2226 SV026 Excessive error
OD2 detection width
during servo
OFF
Set the excessive error detection width when servo ON.
For the standard setting, refer to the explanation of SV023
(OD1).
When "0" is set, the excessive error detection will not be
performed.
III - 105
6x
7x
6x
7x
0 to 32767
(mm)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Items
No.
2227
SV027 Servo
SSF1 function
selection 1
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
aflt
zrn2
7
6
D
C
afse
5
zrn3
bit
0
1
2
3
4
5
vcnt
vfct
6 zrn3
7
8
9
A
B
C
lmc
ovs
afse
D
E zrn2
F aflt
B
A
9
ovs
4
3
8
lmc
2
1
vfct
0
vcnt
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
Set the execution changeover type of the speed loop delay
compensation.
00: Delay compensation changeover invalid
01: Delay compensation changeover type 1
10: Delay compensation type 2
11: Setting prohibited
When not using, set to "0".
When not using, set to "0".
Set the number of compensation pulses of the jitter
compensation.
00: Jitter compensation invalid
01: Jitter compensation 1 pulse
10: Jitter compensation 2 pulses
11: Jitter compensation 3 pulses
Z phase detection:
Z phase detection:
Rising edge/falling edge
Rising edge
changeover method
When not using, set to "0".
Set the compensation amount with SV016 (LMC1) and
SV041 (LMC2).
10: Lost motion compensation type 2 start
Other than 10: Lost motion compensation type 2 stop
Set the compensation amount with SV031 (OVS1) and
SV042 (OVS2).
11: Overshoot compensation type 3 start
Other than 11: Overshoot compensation type 3 stop
00: Adoptive filter sensitivity standard
11: Adoptive filter sensitivity increase (Set 2bits at a time)
Set to "1".
Adoptive filter stops
Adoptive filter starts
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
2228
SV028
2229
SV029
VCS
Speed at
the change
of speed
loop gain
Not used. Set to "0".
0
If the noise is bothersome at high speed during rapid
traverse, etc, lower the speed loop gain.
Set the speed at which the speed loop gain changes,
and use this with SV006 (VGN2). (Refer to SV006.)
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 9999
(r/min)
III - 106
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
2230 SV030 Voltage nonsensitive band
IVC
compensation
When 100% is set, the voltage equivalent to the logical 0 to 255
non-energized time will be compensated.
(%)
When "0" is set, a 100% compensation will be
performed.
Adjust in increments of 10% from the default value
100%.
If increased too much, vibration or vibration noise may
be generated.
2231 SV031 Overshooting
OVS2 compensation
1
-1 to 100
Set this if overshooting occurs during positioning.
This compensates the motor torque during positioning. (Stall current %)
This is valid only when the overshooting compensation
SV027 (SSF1/ovs) is selected.
Type 3: When SV027 (SSF1)/ bitB, A (ovs)=11
Set the compensation amount based on the motor’s
stall current.
Increase by 1% and determine the amount that
overshooting doesn’t occur.
Other than type 3: When SV027 (SSF1)/ bitB, A (ovs)
≠11
Overshooting compensation (Type 2) is not executed.
When you wish different compensation amount
depending on the direction
When SV042 (OVS2) is "0", compensate with the
value of SV031 (OVS1) in both of the + and directions.
If you wish to change the compensation amount
depending on the command direction, set this and
SV042 (OVS2). (SV031: + direction, SV042: direction. However, the directions may be opposite
depending on other settings.)
When "-1" is set, the compensation won’t be performed
in the direction of the command.
2232 SV032 Torque offset 1 Set the unbalance torque of vertical axis and inclined
TOF
axis.
III - 107
-100 to 100
(Stall current %)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2233 SV033
SSF2
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Servo function Select the servo functions.
selection 2
F
E
D
C
lmc2a
zup
rps
dos
7
6
5
4
nfd2
bit
B
A
9
8
3
2
1
0
nf3
nfd1
Meaning when "0" is set
zck
Meaning when "1" is set
0 zck
Z phase check valid (Alarm 42) Z phase check invalid
1
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 1 (SV038).
2 nfd1
Deep ←
3
→ Shallow
000
Depth
(dB)
-∞
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
-18.1 -12.0 -8.5
-6.0
-4.1
-2.5
-1.2
4 nfd3
Notch filter 3 stop
5
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 1 (SV046).
6 nfd2
Deep ←
7
Notch filter 3 start (1125Hz)
→ Shallow
000
Depth
(dB)
-∞
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
-18.1 -12.0 -8.5
-6.0
-4.1
-2.5
-1.2
8
9
A
B
C dos
Normal use
Specified speed output
D rps
Specified speed output setting Specified speed output setting
unit mm/min
unit 100mm/min
E zup
Vertical axis lift-up function
stop
Vertical axis lift-up function
start
F lmc2a
Lost motion compensation 2
timing normal
Lost motion compensation 2
timing change
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 108
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
2234 SV034 Servo function
SSF3 selection 3
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
5
4
3
2
1
0
ovsn
7
6
zeg
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
mohn
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2 mohn
MDS-B-HR motor thermal
valid
MDS-B-HR motor thermal
invalid
Z phase normal edge
detection
(Setting for normal use)
Z phase reverse edge
detection
(Valid only when
SV027/bit6=1)
3
4
5 zeg
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
ovsn
Set the non-sensitive band of the overshooting compensation
type 3 in increments of 2µm at a time.
In the feed forward control, the non-sensitive band of the model
position droop is set, and overshooting of the model is ignored.
Set 2µm (0001) as a standard.
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 109
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2235
Items
SV035 Servo function
SSF4 selection 4
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
clt
7
bit
C
clG1
6
5
4
Meaning when "0" is set
B
A
cl2n
clet
3
2
9
8
cltq
1
0
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
cltq
9
Set the retracting torque for collision detection in respect to the
maximum torque of the motor.
00:100%
01:90%
Setting for normal use
The disturbance torque peak
of the latest two seconds is
displayed in MPOS of the
servo monitor screen.
Collision detection method 2
valid
Collision detection method 2
invalid
A clet
B cl2n
10:80% (Standard) 11:70%
Collision detection method 1
Set the collision detection level during cutting feed (G1).
D
clG1 The G1 collision detection level=SV060×clG1.
When clG1=0, the collision detection method 1 during cutting
E
feed won’t function.
C
Setting for normal use
F
clt
The guide value of the SV059
setting value is displayed in
MPOS of the servo monitor
screen.
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 110
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
2236 SV036 Power supply
PTYP type
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Set the power supply type.
F
E
D
C
B
A
amp
7
6
9
8
1
0
rtyp
5
4
3
2
ptyp
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0 ptyp When the CN4 connector of the drive unit and the power
supply are connected, setting below is necessary.
1
Always set when using the NC communication terminator unit.
2
3
MDS-D-CV
4
External
External
External
External
emergency emergency emergency emergency
stop invalid stop valid stop invalid stop valid
5
6
7
A
CV-37
04
44
04
44
CV-75
08
48
08
48
CV-110
11
51
11
51
CV-185
19
59
19
59
CV-300
30
70
30
70
CV-370
37
77
37
77
CV-450
45
85
45
85
CV-550
55
95
-
-
CV-750
-
-
75
B5
Set "0".
8
9
MDS-DH-CV
rtyp
B
Set "0".
C
D
E
amp
F
2237
SV037 Load inertia
JL
scale
Set "the motor inertia + motor axis conversion load
inertia" in respect to the motor inertia.
SV037(JL)=
Jm+Jl
×100
Jm
Jm : Motor inertia
Jl : Motor axis conversion load inertia
III - 111
0 to 5000
(%)
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
2238 SV038 Notch filter
FHz1 frequency 1
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine
vibration occurs.
(Valid at 50 or more) When not using, set to "0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
2239 SV039 Lost motion
LMCD compensation
timing
Set this when the lost motion compensation timing
does not match.
Adjust by increasing the value by 10 at a time.
0 to 2000
(ms)
2240 SV040 Lost motion
LMCT compensation
non-sensitive
band
Set the non-sensitive band of the lost motion
compensation in the feed forward control.
When "0" is set, the actual value that is set is 2µm.
Adjust by increasing by 1µm at a time.
0 to 255
(µm)
2241 SV041 Lost motion
Set this with SV016 (LMC1) only when you wish to set -1 to 200
LMC2 compensation 2 the lost motion compensation amount to be different
(Stall current %)
depending on the command directions.
Set to "0" as a standard.
2242 SV042 Overshooting Set this with SV031 (OVS1) only when you wish to set -1 to 100
OVS2 compensation 2 the overshooting compensation amount to be different (Stall current %)
depending on the command directions.
Set to "0" as a standard.
2243 SV043 Disturbance
OBS1 observer filter
frequency
Set the disturbance observer filter band.
Set to "100" as a standard.
To use the disturbance observer, also set SV037 (JL)
and SV044 (OBS2). When not using, set to "0".
0 to 1000
(rad/s)
2244 SV044 Disturbance
OBS2 observer gain
Set the disturbance observer gain. The standard
setting is "100" to "300".
To use the disturbance observer, also set SV037 (JL)
and SV043 (OBS1). When not using, set to "0".
0 to 500
(%)
2245 SV045 Frictional
TRUB torque
(Low
order)
When you use the collision detection function, set the
frictional torque.
0 to 255
(Stall current %)
2246 SV046 Notch filter
FHz2 frequency 2
If the machine vibrates, set the vibration frequency to
be suppressed.
(Valid when set to 50 or more.) When not using, set to
"0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
III - 112
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
2247 SV047
EC
Inductive
voltage
compensation
gain
2248 SV048
EMGrt
Vertical axis
Input a length of time to prevent the vertical axis
drop
from dropping by delaying Ready OFF until the
prevention time brake works when the emergency stop occurs.
Increase the setting by 100ms at a time and set the
value where the axis does not drop.
0 to 20000
(ms)
2249 SV049
PGN1sp
Position loop
gain 1 in
spindle
synchronous
control
Set the position loop gain for synchronous tap
control.
Set the same value as the value of the spindle
parameter, position loop gain in synchronous
control.
When performing the SHG control, set this with
SV050 (PGN2sp) and SV058 (SHGCsp).
1 to 200
(rad/s)
2250 SV050
Position loop
gain 2 in
spindle
synchronous
control
When using SHG control during synchronous tap
control, set both SV049 (PGN1sp) and SV058
(SHGCsp).
When not performing the SHG control, set to "0".
0 to 999
(rad/s)
PGN2sp
Set the inductive voltage compensation gain. Set
to "100" as a standard.
If the current FB peak exceeds the current
command peak, lower the gain.
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 200
(%)
2251 SV051
DFBT
Dual feed back Set the control time constant in dual feed back.
control time
When "0" is set, the actual value that is set is 1ms.
The higher the time constant is, the closer it gets to
constant
the semi-closed control, so the limit of the position
loop gain is raised.
0 to 9999
(ms)
2252 SV052
DFBN
Dual feedback
control nonsensitive band
Set the non-sensitive band in the dual feedback
control.
Set to "0" as a standard.
0 to 9999
(µm)
2253 SV053
OD3
Excessive error
detection width
in special
control
Set the excessive error detection width when servo
ON in a special control (initial absolute position
setting, stopper control, etc.).
If "0" is set, excessive error detection won’t be
performed when servo ON during a special control.
0 to 32767
(mm)
2254 SV054
ORE
Overrun
detection width
in closed loop
control
Set the overrun detection width in the full-closed
loop control.
If the gap between the motor end detector and the
linear scale (machine end detector) exceeds the
value set by this parameter, it is judged to be
overrun and Alarm 43 will be detected.
When "-1" is set, the alarm detection won’t be
performed. When "0" is set, overrun is detected
with a 2mm width.
-1 to 32767
(mm)
2255 SV055
EMGx
Max. gate off
delay time after
emergency
stop
Set a length of time from the point when the
emergency stop is input to the point when READY
OFF is compulsorily executed.
Normally, set the same value as the absolute value
of SV056.
In preventing the vertical axis from dropping, the
gate off is delayed for the length of time set by
SV048 if SV055’s value is smaller than that of
SV048.
0 to 20000
(ms)
III - 113
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
2256 SV056
EMGt
Deceleration
time constant
at emergency
stop
In the vertical axis drop prevention control, set the
-20000 to 20000
time constant used for the deceleration control at
(ms)
emergency stop. Set a length of time that takes
from rapid traverse rate (rapid) to stopping.
Normally, set the same value as the rapid traverse
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
When executing the synchronous operation, put the
minus sign to the settings of both of the master axis
and slave axis.
2257 SV057
SHGC
SHG control
gain
When performing the SHG control, set this with
S003 (PGN1) and SV004 (PGN2).
When not performing the SHG control, set to "0".
0 to 1200
(rad/s)
2258 SV058
SHGCsp
SHG control
gain in
spindle
synchronous
control
When using SHG control during synchronous tap
control, set both SV049 (PGN1sp) and SV050
(PGN2sp).
When not performing the SHG control, set to "0".
0 to 1200
(rad/s)
2259 SV059
TCNV
Collision
detection
torque
estimating
gain
Set the torque estimating gain when using the
-32768 to 32767
collision detection function.
After setting as SV035/bitF(clt)=1 and performing
acceleration/deceleration, set the value displayed in
MPOS of the NC servo monitor screen.
Set to "0" when not using the collision detection
function.
2260 SV060
TLMT
Collision
detection
level
When using the collision detection function, set the
collision detection level during the G0 feeding.
If "0" is set, none of the collision detection function
will work.
2261 SV061
DA1NO
D/A output
channel 1
data No.
2262 SV062
DA2NO
D/A output
channel 2
data No.
Input the data number you wish to output to D/A
-1 to 4
output channel.
When using the 2-axis drive unit, set "-1" for the axis
on the side to which the data will not be output.
2263 SV063
DA1MPY
D/A output
channel 1
output scale
2264 SV064
DA2MPY
D/A output
channel 2
output scale
2265 SV065
Machine end
compensation
spring
constant
TLC
Set the scale with a 1/100 unit.
When "0" is set, output is done with the standard
output unit.
0 to 999
(Stall current %)
-32768 to 32767
(Unit: 1/100)
Set the machine end compensation spring constant. -32768 to 32767
For semi-closed droop control, the machine end
compensation amount can be approximated with
the following expression.
2
Compensation Command speed F(mm/min) ×SV065
(µm)
=
amount
Radius R(mm) × 109
Set to "0" when not using.
III - 114
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
System
setting
parameter
These parameters are set automatically by the NC
system.
Specified
speed output
speed
Set the specified speed as a mm/min unit.
When SV033/bitD (rps) is set to 1, set the speed
with a 100mm/min unit.
0 to 32767
SV074
Not used. Set to "0".
0
2275
SV075
Not used. Set to "0".
0
2276
SV076
Not used. Set to "0".
0
2277
(PR)
SV077
2278
(PR)
SV078
2279
(PR)
SV079
2280
(PR)
SV080
2266
(PR)
SV066
2267
(PR)
SV067
2268
(PR)
SV068
2269
(PR)
SV069
2270
(PR)
SV070
2271
(PR)
SV071
2272
(PR)
SV072
2273
(PR)
SV073
FEED
out
2274
System
setting
parameter
These parameters are set automatically by the NC
system.
III - 115
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2281
(PR)
Items
SV081
SPEC2
Servo
specification
selction 2
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo specifications.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 116
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2282 SV082
SSF5
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Servo function Select the servo functions.
selection 5
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
dis
7
6
8
alcdsp
5
4
3
2
1
0
lmc3
lmct
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0 lmct
Lost motion compensation 3
adjustment time
measurement invalid
Lost motion compensation 3
adjustment time
measurement valid
1 lmc3
Lost motion compensation 3
stop
Lost motion compensation 3
start
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 alcdsp Alarm history display
Alarm counter display
9
A
B
Digital signal input selection
C
D
E
dis
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 117
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
2283 SV083 Servo function Select the servo functions.
SSF6 selection 6
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
nfd5
bit
nfd4
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 4 (SV087).
2
This is valid only when SV119 is set to 0.
3 nfd4
Setting value Deep ←
000
Depth (dB)
-∞
001
→ Shallow
010
011
100
101
110
111
-18.1 -12.0 -8.5
-6.0
-4.1
-2.5
-1.2
4
5
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 5 (SV088).
6
This is valid only when SV120 is set to 0.
7 nfd5
Setting value Deep ←
000
Depth (dB)
-∞
001
→ Shallow
010
011
100
101
110
111
-18.1 -12.0 -8.5
-6.0
-4.1
-2.5
-1.2
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 118
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2284 SV084
SSF7
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Servo function Select the servo functions.
selection 7
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
irms
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
0 irms Normal motor current display
Meaning when "1" is set
Effective motor current display
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
2285 SV085
LMCk
Lost motion
compensation
3 spring
constant
Set the machine system's spring constant when using
lost motion compensation type 3.
When not using, set to "0".
2286 SV086
LMCc
Lost motion
compensation
3 viscous
coefficient
Set the machine system's viscous coefficient when using 0 to 32767
lost motion compensation type 3.
When not using, set to "0".
2287 SV087
FHz4
Notch filter
frequency 4
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine
vibration occurs. (Valid at 50 or more)
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
2288 SV088
FHz5
Notch filter
frequency 5
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine
vibration occurs. (Valid at 50 or more)
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
2289 SV089 Torque
TQMAX maximizing
kq
control Kp
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0 to 32767
2290 SV090 Torque
TQMAX maximizing
kd
control Kd
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0 to 32767
III - 119
0 to 32767
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
2291
:
2300
SV091
:
SV100
2301
SV101
TMA1
2302
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
OMR-FF 1st
movement
average filter
time constant
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 71
(0.1ms)
SV102
TMA2
OMR-FF 2nd
movement
average filter
time constant
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 71
(0.1ms)
2303
SV103
TRES
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control
ResponsiveWhen not using, set to "0".
ness
compensation
time constant
α resp
0 to 32767
(0.1ms)
2304
SV104
FER0
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control
Inward turning When not using, set to "0".
compensation
gain for G0
0 to 200
(%)
2305
SV105
PGM
OMR-FF
IIR filter gain
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 4500
(rad/s)
2306
SV106
FR
OMR-FF
Resonance
frequency
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 100
(Hz)
2307
SV107
FA
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
Antiresonance When not using, set to "0".
frequency
0 to 100
(Hz)
2308
SV108
ZR
OMR-FF
Resonance
attenuation
rate
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 100
(%)
2309
SV109
ZA
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
Antiresonance When not using, set to "0".
attenuation
rate
0 to 100
(%)
2310
SV110
FER1
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control
Inward turning When not using, set to "0".
compensation
gain for G1
0 to 200
(%)
2311
SV111
TDM
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control Set the delay time that occurs with the 0 to 142
Delay
normal model.
(0.1ms)
compensation When not using, set to "0".
time
2312
SV112
RDCN
Number of
Set the number of rippers per motor rotation.
ripple
disturbance
compensations
III - 120
0
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2313
Items
SV113 Servo function
SSF8 selection 8
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
ssc
7
omrffdb omrffoff omrffon
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0 omrffon Normal setting
OMR-FF control valid
1 omrffoff Normal setting
OMR-FF control temporary
invalid
2 omrffdb Normal setting
OMR-FF control debug
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F ssc
Safe speed control function
invalid
Safe speed control function
valid
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 121
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2314
Items
SV114
SSF9
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Servo function Select the servo functions.
selection 9
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 122
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
2315
Items
SV115 Servo function
SSF10 selection 10
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 123
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
2316 SV116 Servo function
SSF11 selection 11
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 124
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting range
(unit)
Details
2317
SV117
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
2318
SV118
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
2319
SV119
FSP4
Notch filter 4
specification
0 to 32767
2320
SV120
FSP5
Notch filter 5
specification
Set the notch filter target attenuation amount and
damping coefficient.
Add a value 10000-fold the damping coefficient to the
target attenuation rate -dB absolute value, and set.
The setting range of each coefficient is as follows.
Damping coefficient: 0.01 to 1.00 (0.01 increments)
When 0 is set, the value is 1.00.
Target attenuation amount:
-80dB to -1dB (1dB increments) When 0 is set, the
value is -80dB.
(Example) To set target attenuation amount to -40dB
and damping coefficient to 1.00
1.00×10000+ABS(-40)=10040
When using nfd4 or ndf5 of SV083, set "0".
2321
:
SV121
:
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
2456
SV256
III - 125
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
(2) List of standard parameters for each servomotor
The standard parameters for each motor are given below.
The standard parameters are set to drive the isolated motor. When setting the parameters with the
actual machine, set the parameters according to the machine specifications and detector being used,
etc.
(a) 200V Standard motor HF Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-D-V1-
HF75
HF105
HF54
HF104
HF154
HF204
HF354
HF453
HF703
HF903
20
20
40
40
80
80
160
160
160W
320
SV001
PC1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV002
PC2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV003
PGN1
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
SV004
PGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV005
VGN1
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
SV006
VGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV007
VIL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV008
VIA
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
SV009
IQA
20480
10240
20480
10240
10240
8192
8192
6144
6144
4096
SV010
IDA
20480
10240
20480
10240
10240
8192
8192
6144
6144
4096
SV011
IQG
768
512
3072
1280
1536
2048
2048
2048
2048
1536
SV012
IDG
768
512
3072
1280
1536
2048
2048
2048
2048
1536
SV013
ILMT
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV014
ILMTsp
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV015
FFC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV016
LMC1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV017
SPEC
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV018
PIT
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV019
RNG1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV020
RNG2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV021
OLT
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
SV022
OLL
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
SV023
OD1
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
SV024
INP
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
SV025
MTYP
xx01
xx02
xx03
xx04
xx05
xx07
xx08
xx09
xx0A
xx0B
SV026
OD2
SV027
SSF1
SV028
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV029
VCS
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV030
IVC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV031
OVS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV032
TOF
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
III - 126
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-D-V1-
HF75
HF105
HF54
HF104
HF154
HF204
HF354
HF453
HF703
HF903
20
20
40
40
80
80
160
160
160W
320
SV033
SSF2
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV034
SSF3
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV035
SSF4
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV036
PTYP
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV037
JL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV038
FHz1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV039
LMCD
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV040
LMCT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV041
LMC2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV042
OVS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV043
OBS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV044
OBS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV045
TRUB
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV046
FHz2
SV047
EC1
SV048
EMGrt
SV049
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PGN1sp
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
SV050
PGN2sp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV051
DFBT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV052
DFBN
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV053
OD3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV054
ORE
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV055
EMGx
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV056
EMGt
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV057
SHGC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV058
SHGCsp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV059
TCNV
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV060
TLMT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV061
DA1NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV062
DA2NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV063
DA1MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV064
DA2MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV065
TLC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
SV066
:
SV256
Note that a value other than "0" may be automatically set by the NC system for the system setting parameters.
III - 127
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
(b) 200V Standard motor HP Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-D-V1-
HP54
HP104
HP154
HP204
HP354
HP454
HP704
40
40
80
80
160
160
160W
HP903 HP1103
320
320W
SV001
PC1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV002
PC2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV003
PGN1
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
SV004
PGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV005
VGN1
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
SV006
VGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV007
VIL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV008
VIA
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
SV009
IQA
8192
4096
6144
3072
4096
3072
3072
2048
2048
SV010
IDA
8192
4096
6144
3072
4096
3072
3072
2048
2048
SV011
IQG
1280
768
1536
1024
1280
1024
1024
1280
1280
SV012
IDG
1280
768
1536
1024
1280
1024
1024
1280
1280
SV013
ILMT
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV014
ILMTsp
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV015
FFC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV016
LMC1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV017
SPEC
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV018
PIT
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV019
RNG1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV020
RNG2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV021
OLT
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
SV022
OLL
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
SV023
OD1
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
SV024
INP
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
SV025
MTYP
xx11
xx12
xx13
xx14
xx15
xx16
xx17
xx18
xx19
SV026
OD2
SV027
SSF1
SV028
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV029
VCS
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV030
IVC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV031
OVS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV032
TOF
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
III - 128
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-D-V1-
HP54
HP104
HP154
HP204
HP354
HP454
HP704
40
40
80
80
160
160
160W
HP903 HP1103
320
320W
SV033
SSF2
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV034
SSF3
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV035
SSF4
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV036
PTYP
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV037
JL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV038
FHz1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV039
LMCD
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV040
LMCT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV041
LMC2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV042
OVS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV043
OBS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV044
OBS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV045
TRUB
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV046
FHz2
SV047
EC1
SV048
EMGrt
SV049
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PGN1sp
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
SV050
PGN2sp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV051
DFBT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV052
DFBN
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV053
OD3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV054
ORE
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV055
EMGx
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV056
EMGt
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV057
SHGC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV058
SHGCsp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV059
TCNV
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV060
TLMT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV061
DA1NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV062
DA2NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV063
DA1MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV064
DA2MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV065
TLC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
SV066
:
SV256
Note that a value other than "0" may be automatically set by the NC system for the system setting parameters.
III - 129
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
(c) 400V Standard motor HF-H Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-DH-V1-
HF-H75 HF-H105 HF-H54 HF-H104 HF-H154 HF-H204 HF-H354 HF-H453 HF-H703 HF-H903
10
10
20
20
40
40
80
80
80W
160
SV001
PC1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV002
PC2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV003
PGN1
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
SV004
PGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV005
VGN1
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
SV006
VGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV007
VIL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV008
VIA
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
SV009
IQA
20480
10240
20480
10240
15360
8192
8192
6144
6144
6144
SV010
IDA
20480
10240
20480
10240
15360
8192
8192
6144
6144
6144
SV011
IQG
768
512
3072
1280
2048
2048
2048
2048
2048
2048
SV012
IDG
768
512
3072
1280
2048
2048
2048
2048
2048
2048
SV013
ILMT
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV014
ILMTsp
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV015
FFC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV016
LMC1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV017
SPEC
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
SV018
PIT
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV019
RNG1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV020
RNG2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV021
OLT
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
SV022
OLL
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
SV023
OD1
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
SV024
INP
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
SV025
MTYP
xx01
xx02
xx03
xx04
xx05
xx07
xx08
xx09
xx0A
xx0B
SV026
OD2
SV027
SSF1
SV028
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV029
VCS
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV030
IVC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV031
OVS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV032
TOF
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
III - 130
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-DH-V1-
HF-H75 HF-H105 HF-H54 HF-H104 HF-H154 HF-H204 HF-H354 HF-H453 HF-H703 HF-H903
10
10
20
20
40
40
80
80
80W
160
SV033
SSF2
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV034
SSF3
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV035
SSF4
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV036
PTYP
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV037
JL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV038
FHz1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV039
LMCD
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV040
LMCT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV041
LMC2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV042
OVS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV043
OBS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV044
OBS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV045
TRUB
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV046
FHz2
SV047
EC1
SV048
EMGrt
SV049
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PGN1sp
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
SV050
PGN2sp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV051
DFBT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV052
DFBN
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV053
OD3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV054
ORE
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV055
EMGx
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV056
EMGt
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV057
SHGC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV058
SHGCsp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV059
TCNV
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV060
TLMT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV061
DA1NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV062
DA2NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV063
DA1MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV064
DA2MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV065
TLC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
SV066
:
SV256
Note that a value other than "0" may be automatically set by the NC system for the system setting parameters.
III - 131
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
(d) 400V Standard motor HP-H Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-DH-V1-
HP-H54 HP-H104 HP-H154 HP-H204 HP-H354 HP-H454 HP-H704 HP-H903 HP-H1103
20
20
40
40
80
80
80W
160
160W
SV001
PC1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV002
PC2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV003
PGN1
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
33
SV004
PGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV005
VGN1
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
SV006
VGN2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV007
VIL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV008
VIA
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
1364
SV009
IQA
8192
4096
6144
3072
4096
3072
3072
2048
2048
SV010
IDA
8192
4096
6144
3072
4096
3072
3072
2048
2048
SV011
IQG
1280
768
1536
1024
1280
1024
1024
1280
1280
SV012
IDG
1280
768
1536
1024
1280
1024
1024
1280
1280
SV013
ILMT
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV014
ILMTsp
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
800
SV015
FFC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV016
LMC1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV017
SPEC
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
SV018
PIT
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV019
RNG1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV020
RNG2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SV021
OLT
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
SV022
OLL
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
SV023
OD1
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
SV024
INP
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
50
SV025
MTYP
xx11
xx12
xx13
xx14
xx15
xx16
xx17
xx18
xx19
SV026
OD2
SV027
SSF1
SV028
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV029
VCS
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV030
IVC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV031
OVS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV032
TOF
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
III - 132
6. Servo Parameters
6.1 MDS-D/DH Series
Motor
Drive unit
MDS-DH-V1-
HP-H54 HP-H104 HP-H154 HP-H204 HP-H354 HP-H454 HP-H704 HP-H903 HP-H1103
20
20
40
40
80
80
80W
160
160W
SV033
SSF2
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV034
SSF3
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV035
SSF4
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV036
PTYP
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
0000
SV037
JL
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV038
FHz1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV039
LMCD
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV040
LMCT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV041
LMC2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV042
OVS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV043
OBS1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV044
OBS2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV045
TRUB
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV046
FHz2
SV047
EC1
SV048
EMGrt
SV049
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
100
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PGN1sp
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
SV050
PGN2sp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV051
DFBT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV052
DFBN
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV053
OD3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV054
ORE
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV055
EMGx
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV056
EMGt
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV057
SHGC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV058
SHGCsp
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV059
TCNV
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV060
TLMT
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV061
DA1NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV062
DA2NO
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV063
DA1MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV064
DA2MPY
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
SV065
TLC
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
0
:
0
SV066
:
SV256
Note that a value other than "0" may be automatically set by the NC system for the system setting parameters.
III - 133
6. Servo Parameters
6.2 Supplement
6.2 Supplement
6.2.1 D/A Output No.
(1) D/A output specifications
Item
Explanation
Number of channels 2ch
Output cycle
888µs (min. value)
Output precision
12bit
Output voltage
range
0V to 2.5V to +5V
-32768 to 32767%
Output scale setting
(1% increments)
CN9 connector
MO1 = pin 9
MO2 = pin 19
GND = pin 1, 11
The D/A output is 2ch even
for the 2-axis drive unit
(MDS-D/DH-V2).
Thus, when using the 2-axis
drive unit, set -1 for the
output data (SV061, 62) of
the axis which is not to be
measured.
Output pins
Others
CN9 connector
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1
LG
11 LG
2
12
3
13
4
14
5
15
6
16
7
17
8
18
9 MO1
19 MO2
10
20
(2) Setting the output data
Input the No. of the data to be output to each D/A output channel.
#
No.
Abbrev.
Parameter name
2261 SV061 DA1NO D/A output channel 1 data No.
2262 SV062 DA2NO D/A output channel 2 data No.
No.
Details
Output unit
-1
D/A output stop
-
0
Motor speed
1000(r/min)/V
1
Current command
100%/V
2
Current feedback
100%/V
3
Position droop
1mm/V
4
Command F∆T
1mm/0.8ms/V
5
6
7
8
9
10
III - 134
6. Servo Parameters
6.2 Supplement
6.2.2 Electronic Gears
The servo drive unit has internal electronic gears. The command value from the NC is converted into a
detector resolution unit to carry out position control. The electronic gears are single gear ratios calculated
from multiple parameters as shown below. However, each value (ELG1, ELG2) must be less than 32767.
If the value overflows, the initial parameter error (alarm 37) or error parameter No.2301 will be output.
If an alarm occurs, the mechanical specifications and electrical specifications must be revised so that the
electronic gears are within the specifications range.
(1) For semi-closed loop control
Reduced fraction of
ELG1
ELG2
PC2 × RNG1
= PC1 × PIT × IUNIT (reduced fraction)
IUNIT = 2/NC (µm) command unit
1µm : IUNIT = 2, 0.1µm : IUNIT = 20
When the above is calculated, the following conditions must be satisfied.
ELG1 ≤ 32767
ELG2 ≤ 32767
(2) For full-closed loop control
Reduced fraction of
PGNX
PGNY
=
PC2 × RNG2 × PGN1
PC1 × RNG1 × 30
(reduced fraction)
When the above is calculated, the following conditions must be satisfied.
PGNX ≤ 32767
PGNY ≤ 32767
And,
PGNXsp
Reduced fraction of PGNYsp =
PC2 × RNG2 × PGN1sp
PC1 × RNG1 × 30
(reduced fraction)
When the above is calculated, the following conditions must be satisfied.
PGNXsp ≤ 32767
PGNYsp ≤ 32767
III - 135
6. Servo Parameters
6.2 Supplement
6.2.3 Lost Motion Compensation
When the motor is to rotate in the clockwise direction (looking from the load side) at the command for the +
direction, the command direction is CW. Conversely, when the motor is to rotate in the counterclockwise
direction, the command direction is CCW.
This rotation direction can be set with the CNC machine parameters. Note that the meaning of the ± will
differ for some servo parameters according to this motor rotation direction. The servo parameters affected by
CW/CCW are shown below.
SV016 (LMC1), SV041 (LMC2) (When different values are set for SV016 and SV041)
<Example> If the lost motion compensation amount is to be changed according to the direction, the
compensation amount at the quadrant changeover point of each arc where the lost motion
compensation is applied will be as shown below according to the command polarity.
CW
CCW
A
X: SV041
X: SV016
B
Y: SV016
Y: SV041
C
X: SV016
X: SV041
D
Y: SV041
Y: SV016
+Y
The Y axis command
direction changes from
the + to - direction.
D
A
-X
C
The X axis command
direction changes from
the + to - direction.
+X
The X axis command
direction changes from
the - to + direction.
-Y
B
The Y axis command
direction changes from
the - to + direction.
(Note) The setting value for the parameter is "0" or "-1", the compensation amount is determined as
shown below.
Setting value
for SV016
Setting value
for SV041
Compensation
amount
in + direction
Compensation
amount
in - direction
0
0
No compensation
No compensation
n
0
n
n
0
m
m
m
n
m
n
m
n
-1
n
No compensation
-1
m
No compensation
m
III - 136
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specification Parameters
For parameters indicated with a (PR) in the table, turn the NC power OFF after setting. The setting is
validated after the power is turned ON again.
No.
Items
3001
3002
3003
3004
slimit
3005
3006
3007
3008
smax
3009
3010
3011
3012
Details
Setting
range (unit)
1
2 Limit rotation
3 speed
4
Set spindle rotation speed for maximum motor rotation speed
with gears 00, 01, 10, 11.
(Set the spindle speed for the S analog output 10V.)
0 to 99999
(r/min)
1
2 Maximum
3 rotation speed
4
Set maximum spindle rotation speed with gears 00, 01, 10, 11.
Set to slimt ≥ smax.
By comparing the S command value and the value of gear 1 to
4, a spindle gear shift command will be output automatically.
0 to 99999
(r/min)
ssift
1
2 Shift rotation
3 speed
4
Set spindle speed for gear shifting with gears 00, 01, 10, 11.
(Note) Setting too large value may cause a gear nicks when
changing gears.
3013
3014
3015
3016
stap
1
2 Tap rotation
3 speed
4
Set maximum spindle rotation speed during tap cycle with
gears 00, 01, 10, 11.
3017
3018
3019
3020
stapt
1
2 Tap time
3 constant
4
Set time constants for constant inclination synchronous tap
cycles for gears 00, 01, 10, 11 (linear acceleration/deceleration
pattern).
III - 137
0 to 32767
(r/min)
0 to 99999
(r/min)
1 to 5000
(ms)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
<Relation of spindle limit rotation speed and spindle maximum rotation speed>
Spindle motor rotation speed
(r/min)
The spindle rotation speed which can be attained at the spindle motor's maximum rotation speed is set
for the limit rotation speed (slimt). This value is obtained by multiplying the gear ratio on the spindle
motor maximum rotation speed (SP017). Set the maximum rotation speed (smax) when the rotation
speed is to be limited according to the machine specifications, such as the spindle gear specifications.
Up to four value can be set for gear changeover.
SP017
0
smax1 slimt1 smax2
slimt2
smax(n)
slimt(n)
Spindle rotation speed (r/min)
<Relation of tap time constant and actual acceleration/deceleration time constant>
(For constant inclination synchronous tap cycle)
Set the acceleration time up to the tap rotation speed (stap) in the tap time constant (stapt).
Acceleration/deceleration is carried out at the same inclination for all speed commands. Up to four
values can be set for gear changeover.
Spindle speed (r/min)
stap(n)
Actual
command
0
Actual time
Time (ms)
III - 138
stapt(n)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
3021 sori
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 32767 (r/min)
Orientation
rotation
speed
Encoder
gear ratio
Set the spindle orientation rotation speed.
Set the rotation speed for when the spindle rotates at
the constant rotation speed.
Set the gear ratio of the spindle to the encoder.
3023 smini
Minimum
rotation
speed
Set the minimum rotation speed of the spindle.
0 to 32767 (r/min)
If an S command instructs the rotation speed below this
setting, the spindle rotates at the minimum rotation
speed set by this parameter.
3024 sout
(PR)
Spindle
connection
Set the type of the spindle to be connected.
0: No connection with the spindle
1: Serial connection (bus)
2 to 5: Analog output
0 to 5
3025 enc-on
Spindle
encoder
0 to 2
3026 cs_ori
Selection of
winding in
orientation
mode
Set connection information of the spindle encoder.
0: No connection
1: Spindle connection (Spindle encoder connection
check function valid.)
2: Serial connection of encoder
0: Perform orientation using the coil selected when the
orientation command is issued.
1: Use winding L whenever the orientation command is
issued.
3027 cs_syn
Selection of 0: The coil H/L is selected by the actual spindle motor
0/1
winding in
rotation speed (calculated from commanded rotation
spindle
speed) when spindle synchronous control starts. (The
synchronous
winding is not switched during synchronous control.
mode
The control is carried out with the winding selected at
start.)
If the actual spindle motor rotation speed is less than
SP020, the winding L is selected, and if more than
the value, the winding H is selected.
1: Use winding H whenever the spindle synchronous
command is issued.
3028 sprcmm
L system tap
cycle spindle
forward run/
reverse run
M command
Set the M code of the spindle forward run/reverse run
command.
High-order three digits: The spindle forward run
command's M code is set.
Low-order three digits: The spindle reverse run
command's M code is set.
0 to 999999
3029 tapusel
Asynchronous tap
gear
selection
Specify whether to use the tap rotation speed or
maximum rotation speed for the gear that is selected
when an asynchronous tap command is issued.
0: Tap rotation speed
1: Maximum rotation speed
This parameter is valid only when the M-function
synchronous tap cycle enable parameter (#1272 ext08
bit1) is ON.
Not used.
Set to "0".
0/1
3022 sgear
3030
III - 139
0: 1/1
1: 1/2
2: 1/4
3: 1/8
0/1
0
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
Items
3031 smcp_no Drive unit I/F
(PR)
channel No.
(spindle)
3032
Setting range
(unit)
Using a 4-digit number, set the drive unit interface
0000
channel No. and which axis in that channel is to be used 0101 to 0107
when connecting a spindle drive.
0201 to 0207
High-order two digits : Drive unit interface channel No.
Low-order two digits : Axis No.
When using the conventional fixed layout, set all axes to
"0000".
Set "0000" when using an analog spindle.
Details
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
Specify the unit for communication data with the spindle
drive unit.
The data communicated between the NC and spindle
drive unit and the spindle movement data unit follow this
specification. Note that this parameter is valid only for
the D drive unit spindle.
The spindle C axis relies on this parameter, and the C
axis output unit (servo) is ignored.
Also set "#1003 ctrl_unit" when using the optical
communication drive unit.
B: 1µm
C: 0.1µm
D: 10nm
E: 1nm
3035 spumit
(PR)
Output unit
3037 taps 21
3038
22
3039
23
3040
24
Synchronous Set the spindle rotation speed at which the step-2
tap switching acceleration/deceleration time constant is to be
spindle speed switched at gear 00, 01, 10, or 11.
2
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3041 tapt 21
3042
22
3043
23
3044
24
Synchronous
tap switching
time constant
2
Set the time constant to reach synchronous tap
switching spindle rotation speed 2 (taps 21 to 24) at
gear 00, 01, 10, or 11.
1 to 5000 (ms)
3045 tapt 31
3046
32
3047
33
3048
34
Synchronous
tap switching
time constant
3
Set the time constant to reach the maximum rotation
speed (smax 1 to smax 4) at gear 00, 01, 10, or 11.
1 to 5000 (ms)
3049 spt
Spindle
synchronization
acceleration/
deceleration
time constant
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant for when 0 to 9999 (ms)
the spindle synchronization command's rotation speed
changes during spindle synchronous control.
3050 sprlv
Spindle
synchronization
rotation speed
attainment
level
The spindle rotation speed synchronization complete
0 to 4095 (pulse)
signal will turn ON when the difference of the reference (1 pulse =
spindle and synchronous spindle actual rotation speeds 0.088°)
is less than the level set for the synchronous spindle
rotation speed command value during spindle
synchronous control.
3051 spplv
Spindle phase
synchronization
attainment
level
Spindle motor
spindle
relative
polarity
The spindle phase synchronization complete signal will
turn ON when the phase difference of the reference
spindle and synchronous spindle is less than the set
level during spindle phase synchronization control.
0 to 4095 (pulse)
(1 pulse =
0.088°)
Set the spindle motor and spindle's relative polarity.
Spindle CW rotation at motor CW rotation: Positive
polarity
Spindle CCW rotation at motor CW rotation: Negative
polarity
0: Positive
polarity
1: Negative
polarity
3052 spplr
III - 140
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 359999
(1/1000°)
3053 sppst
Spindle
encoder
Z -phase
position
Set the deviation amount from the spindle's reference
position to the spindle encoder's Z phase.
The deviation amount is obtained using the clockwise
direction looking from the front of the spindle as the
positive direction.
3054 sptc1
Spindle
synchronization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 1
Set the spindle speed for changing the 1st step's
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3055 sptc2
Spindle
synchronization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 2
Set the spindle speed for changing the 2nd step's
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3056 sptc3
Spindle
synchronization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 3
Set the spindle speed for changing the 3rd step's
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3057 sptc4
Spindle
synchronization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 4
Set the spindle speed for changing the 4th step's
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3058 sptc5
Spindle
synchronization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 5
Set the spindle speed for changing the 5th step's
acceleration/deceleration time constant.
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3059 sptc6
Spindle
Set the spindle speed for changing the 6th step's
synchroacceleration/deceleration time constant.
nization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 6
0 to 99999 (r/min)
III - 141
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
3060 sptc7
Items
Details
Spindle
Set the spindle speed for changing the 7th step's
synchroacceleration/deceleration time constant.
nization multistep
acceleration/
deceleration
changeover
speed 7
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 99999 (r/min)
3061 spdiv1 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 1
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 1 (sptc1) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step acceleration/
deceleration changeover speed 2 (sptc2) as a
magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
3062 spdiv2 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 2
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between 0 to 127
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 2 (sptc2) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 3 (sptc3) as
a magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
3063 spdiv3 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 3
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between 0 to 127
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 3 (sptc3) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 4 (sptc4) as
a magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
3064 spdiv4 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 4
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between 0 to 127
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 4 (sptc4) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 5 (sptc5) as
a magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
3065 spdiv5 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 5
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between 0 to 127
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 5 (sptc5) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 6 (sptc6) as
a magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant between 0 to 127
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 6 (sptc6) to
the spindle synchronization multi-step
acceleration/deceleration changeover speed 7 (sptc7) as
a magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
3066 spdiv6 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 6
3067 spdiv7 Magnification
for time
constant
changeover
speed 7
0 to 127
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant for the
0 to 127
spindle synchronization multi-step acceleration/
deceleration changeover speed 7 (sptc7) and higher as a
magnification in respect to the spindle synchronization
acceleration/deceleration time constant (spt).
III - 142
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 9999 (ms)
3068 symtm1 Phase
synchronization start
confirmation
time
Set the time to confirm that synchronization is attained
before phase synchronization control is started.
When "0" is set, the time will be 2 seconds. When "100"
or less is set, the time will be 100ms.
3069 symtm2 Phase
synchronization end
confirmation
time
Set the time to wait for phase synchronization control to
end as the time for the rotation speed to reach the
attainment range.
When "0" is set, the time will be 2 seconds. When "100"
or less is set, the time will be 100ms.
0 to 9999 (ms)
3070 syprt
Phase
synchronization speed
Set the fluctuation amount to change the synchronous
spindle rotation speed during phase synchronization
control as the command speed and rate.
When "0" is set, the amount will be 100%.
0 to 100 (%)
3071
(Not used.)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
3072
(Not used.)
Not used. Set to "0".
0
3101 sp_t 1
3102
2
3103
3
3104
4
Time constant
for spindle
rotation with S
command
Set the acceleration/deceleration time constant for
spindle rotation using the S command (spindle control
mode = speed operation mode) at the gears (00, 01,
10,11). (Linear acceleration/deceleration pattern.)
1 to 5000 (ms)
3105 sut
Speed reach
range
Set the speed deviation rate with respect to the
commanded speed for output of the speed reach signal.
0 to 100 (%)
3106 zrn_typ Zero point
bit0 : Z phase detection direction
return
bit1, 2 : Orientation direction
specifications
(00: Short-cut, 01: Forward run, 10: Reverse run)
bit 4 : Synchronous tapping zero point
return/deceleration stop designation
(0: Zero point return, 1: Deceleration stop)
0x0000 to 0xffff
(Hex)
bit5, 6 : Synchronous tapping zero point return direction
(00: Short-cut, 01: Forward run, 10: Reverse run)
bit7 : Synchronous tapping command polarity
(0: Forward direction, 1; Reverse direction)
bit8 : Spindle/C axis zero point return/deceleration stop
designation
(0: Zero point return, 1: Deceleration stop)
bit9, A : Spindle C axis zero point return direction
(00: Short-cut, 01: Forward run, 10: Reverse run)
3107 ori_spd Orientation
Spindle speed during orientation command
command
speed
3108 ori_sft In-position
Set the stop position for orientation.
shift amount
for orientation
1 to 99999 (r/min)
3109 zdetspd Z phase
detection
speed
1 to 99999 (r/min)
Spindle rotation speed at initial Z phase detection
III - 143
0.00 to 35999
(0.01°)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.1 Spindle Specifications Parameters
No.
3110 tap_spd
Items
Details
Synchronous Synchronous tapping zero point return speed
tapping zero
point return
speed
3111 tap_sft
Synchronous Synchronous tapping zero point return shift amount
tapping zero
point return
shift amount
3112 cax_spd Spindle C
Spindle C axis zero point return speed
axis zero
point return
speed
3113 cax_sft
Spindle C
Spindle C axis zero point return shift amount
axis zero
point return
shift amount
III - 144
Setting range
(unit)
1 to 99999 (r/min)
0.00 to 35.999
(0.01°)
1 to 99999 (r/min)
0.00 to 359999
(0.001°)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
Parameters indicated as (PR) in the table will be validated when the NC power is turned OFF and ON after
setting.
The spindle parameter setting and display methods differ according to the NC being used. Refer to the
instruction manuals for the NC and each spindle.
Mitsubishi CNC Control Unit MDS-D Series Specifications Manual ・・・・・・・・・IB-1500011
Mitsubishi CNC Control Unit MDS-DH Series Specifications Manual・・・・・・・・IB-1500003
! CAUTION
!
No.
In the explanation on bits, set all bits not used, including blank bits, to "0".
Items
13001 SP001
PGV
Position loop
gain Noninterpolation
mode
13002 SP002
PGN
Position loop
gain
interpolation
mode
13003 SP003
PGS
Position loop
gain spindle
synchronization
Setting range
(unit)
1 to 200
Set the position loop gain. Set to "33" as a standard.
When the setting value is increase, the tracking in respect (1/s)
to the command will increase, and the settling time during
positioning can be reduced. However, the impact applied
on the machine during acceleration/deceleration will
1 to 200
increase.
(1/s)
The position loop gain can be selected according to the
control mode selection command set with control input 4/
bit 2, 1, 0.
1 to 200
(1/s)
Control input 4
Details
Mode
bit2
bit1
bit0
0
0
0
Non-interpolation
0
0
1
Spindle interpolation
0
1
0
Interpolation
When carrying out SHG control, set SP035 (SFNC3)/bitC
(shgn) or SP036 (SFNC4)/bit4 (shgs) to 1.
13004 SP004
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
Set the speed loop gain.
Set this according to the load inertia size.
The higher the setting value is, the more accurate the
control will be, however, vibration tends to occur.
If vibration occurs, adjust by lowering by 20 to 30%.
The value should be determined to be 70 to 80% of the
value at the time when the vibration stops.
1 to 9999
13005 SP005
VGN1
Speed loop
gain 1
13006 SP006
VIA1
Speed loop
Set the gain of the speed loop integration control.
lead
Set to "1900" as a standard. Adjust the value by
compensation 1 increasing/decreasing it by about 100 at a time.
Raise this value to improve contour tracking precision in
high-speed cutting. Lower this value when the position
droop vibrates (10 to 20Hz).
13007 SP007
VIL1
Speed loop
Set this when the limit cycle occurs in the full-closed loop, 0 to 32767
delay
or overshooting occurs in positioning.
compensation 1 Select the control method with SP033 (SFNC1)/bit1, 0
(vcnt).
Normally, use "Changeover type 2".
When you set this parameter, make sure to set the torque
offset (SP050 (TOF)).
When not using, set to "0".
III - 145
1 to 9999
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13008 SP008
VGN2
Speed loop
gain 1
13009 SP009
VIA2
Speed loop
lead
compensation
2
13010 SP010
VIL2
Speed loop
delay
compensation
2
13011 SP011
:
:
13013 SP013
Details
Setting range
(unit)
1 to 9999
Normally, SP005 (VGN1), SP006 (VIA1) and SP007
(VIL1) are used.
By setting SP035 (SFNC3)/bit1 (vgin), SP035
1 to 9999
(SFNC3)/bit9 (vgn) or SP035 (SFNC4)/bit1 (vgs) to 1, gain
2 can be used according to the application.
Gain 2 can also be used by setting the speed gain set 2
changeover request (control input 5/bitC) to 1.
Refer to SP005 (VGN1), SP006 (VIA1) and SP007 (VIL1) 0 to 32767
for the procedures.
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
13014 SP014
PY1
Minimum
excitation rate
1
Set the minimum value for the variable excitation rate. Set 0 to 100
(%)
to "50" as a standard.
Set "0" when using the IPM spindle motor.
If the gear noise, etc., is large, select a small value.
However, a larger value is more effective for impact
response.
• When setting a value "50 or more", check that there is
no gear noise or motor excitation noise, vibration during
low-speed rotation, or vibration when the servo is locked
during orientation stop, etc.
• When setting a value "less than 50", check that there is
no problem with the impact load response or rigidity
during servo lock.
13015 SP015
PY2
Minimum
excitation rate
2
13016 SP016
DDT
Phase
alignment
deceleration
rate
Normally, SP014 (PY1) is used.
Excitation rate 2 can be used according to the application
by setting SP035 (SFNC23)/bit2 (pyin), SP035
(SFNC3)/bitA (pyn) or SP036 (SFNC4)/bit2 (psy) to 1.
Excitation rate 2 can also be used by setting the minimum
excitation rate 2 changeover request (control input 5/bitB)
to 1. Refer to SP014 (PY1) for the procedures.
Set "0" when using the IPM spindle motor.
Set the single rotation position alignment deceleration rate
for orientation stopping, phase alignment during rotation,
and for changing the mode from non-interpolation during
rotation to spindle synchronization.
If the load inertia is large, decrease the setting.
When the setting value is increased, the orient in-position
and single rotation position alignment will end faster, but
the impact applied on the machine will increase.
To change the deceleration rate only during the rotation
/ 0), set this parameter
command (command F∆T =
together with SP070 (KDDT).
III - 146
0 to 100
(%)
1 to 32767
(0.1 (r/mn)/ms)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13017 SP017 Spindle
(PR) SPEC1 specifications
1
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle specifications.
F
E
7
6
D
C
B
A
9
8
5
4
3
2
1
0
fdir
vfb
seqh
dfbx
fdir2
spm
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Speed feedback forward
0 fdir2
polarity
Meaning when "1" is set
Speed feedback reverse
polarity
1 dfbx Dual feedback control stop
High-speed READY ON
2 seqh
sequence valid
3 vfb Speed feedback filter stop
Dual feedback control start
High-speed READY ON
sequence invalid
Speed feedback filter start
Position feedback forward
polarity
Position feedback reverse
polarity
Select the motor series.
0: 200V specification IM
D
spm
spindle motor
E
1: 200V specification IPM
F
spindle motor
2: 400V specification IM
spindle motor
3: 400V specification IPM
spindle motor
4
fdir
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 147
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13018 SP018 Spindle
(PR) SPEC2 specifications
2
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle specifications.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
oplp
close
spsu
mkch
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Semi-closed position control
0 close
system
Meaning when "1" is set
Full closed position control
system
1 oplp Open loop invalid
2
3
4
Open loop valid
5 mkch
Coil changeover function
invalid
Coil changeover function valid
6
7
8 spsu Speed setting unit [r/min]
Speed setting unit [×4r/min]
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
13019 SP019
(PR) RNG1
Position
detector
resolution
Set the same value as SP020 (RNG2).
(Refer to the explanation for SP020.)
13020 SP020
(PR) RNG2
Speed
detector
resolution
Set the number of pulses per one revolution of the motor end 1 to 32767
detector.
(kp/rev)
Detector model name
TS5691
13021 SP021
(PR) OLT
SP020 setting value
128 teeth
2000
256 teeth
4000
384 teeth
6000
512 teeth
8000
Overload
Set the detection time constant of Overload 1 (Alarm 50).
detection time (For machine tool builder adjustment.)
constant
Set to "60" as a standard.
Set "300" when using the IPM spindle motor.
III - 148
0 to 32767
(kp/rev)
1 to 15300
(s)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Setting range
(unit)
1 to 200
(Short-time
rated %)
Details
13022 SP022 Overload
OLL
detection level
Set the overload 1 (alarm 50) current detection level as a
percentage in respect to the motor short-time rated output
current.
(For machine tool builder adjustment.)
Set to "120" as a standard.
Set "100" when using the IPM spindle motor.
13023 SP023 Excessive error
OD1
detection width
(interpolation
mode, spindle
synchronization)
13024 SP024 In-position width
INP
Set the excessive error detection width for the interpolation 0 to 32767
mode and spindle synchronization.
(°)
Set to "120" as a standard.
Excessive error detection is not executed, so do not set "0".
13025 SP025 2nd in-position
INP2
width
Set the in-position detection width.
0 to 32767
Set the accuracy required for the machine.
(1°/1000)
The lower the setting is, the higher the positioning accuracy
gets, however, the cycle time (setting time) becomes
longer. The standard setting is "875".
Use this when detecting a different in-position from the
0 32767
normal in-position detection, such as advancing the in(°/1000)
position signal. The procedure is the same as SP024 (INP).
Set to "875" as a standard.
13026 SP026 Maximum motor Set the maximum motor speed. If the actual motor speed
(PR) TSP
speed
exceeds the set maximum speed, an overspeed alarm will
occur.
1 to 32767
(r/min)
13027 SP027 Motor zero
ZSP
speed
1 to 1000
(r/min)
Set the motor speed for detecting zero speed. If the actual
motor speed is less than the set speed, the zero speed
detection will turn ON. Set to "50" as a standard.
13028 SP028 Speed detection Set the motor speed for detecting the speed. If the actual
10 to 32767
SDTS set value
motor speed is less than the set value, the speed detection (r/min)
will turn ON. Set a value 10% of the maximum motor speed
as a standard.
13029 SP029 Speed detection Set the hysteresis value at which the speed detection
SDTR reset width
changes from ON to OFF. If the setting value is small, the
speed detection will chatter easily. Set to "30" as a
standard.
10 to 1000
(r/min)
30
13030 SP030 2nd speed
SDT2 detection set
value
Use this when detecting the speed with a value different
0
from the normal speed detection set value.
(r/min)
The procedure is the same as SP028 (SDTS). SP029
(SDRT) is also used for the 2nd speed detection hysteresis
width.
13031 SP031 Motor type
(PR) MTYP
Set the position detector type, speed detector type and motor type.
F
E
D
C
B
A
pen
7
6
9
8
1
0
ent
5
4
3
mtyp
ent: Set "2".
pen: Set "2"
mtyp: Set "0".
III - 149
2
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
13032 SP032
(PR) PTYP
Items
Power supply
type
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Set the power supply type.
F
E
7
6
D
C
B
A
5
4
3
2
amp
9
8
1
0
rtyp
ptyp
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0 ptyp When the CN4 connector of the drive unit and the power
supply are connected, setting below is necessary.
1
Always set when using the NC communication terminator unit.
2
3
MDS-D-CV
MDS-DH-CV
4
5
6
7
CV-37
CV-75
CV-110
CV-185
CV-300
CV-370
CV-450
CV-550
CV-750
Set to "0".
8
9
A
B
rtyp
Set to "0".
C
D
E
External
External
External
External
emergency emergency emergency emergency
stop
stop
stop
stop
invalid
valid
invalid
valid
04
44
04
44
08
48
08
48
11
51
11
51
19
59
19
59
30
70
30
70
37
77
37
77
45
85
45
85
55
95
75
B5
amp
F
III - 150
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13033 SP033 Spindle
SFNC1 function 1
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle function.
F
E
D
6
5
aflt
7
C
B
4
3
afse
lmc2a
A
9
2
1
ovs
lmc
vfct
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
00: Delay compensation
0
changeover invalid
vcnt
01: Delay compensation
1
changeover type 1
8
0
vcnt
Meaning when "1" is set
10: Delay compensation
changeover type 2
11: Delay compensation
changeover type 2
2
3
4
5
vfct
00: Jitter compensation
invalid
01: Jitter compensation 1
pulse
10: Jitter compensation 2
pulse
11: Jitter compensation 3
pulse
Lost motion compensation 2
timing normal
Timing changed
6
7 lmc2a
8
9
lmc
ovs
Set the compensation amount with SP043 (OVS1) and SP042
(OVS2).
11: Overshoot compensation type 3 start
Other than 11: Overshoot compensation type 3 stop
afse
00: Adoptive filter sensitivity standard
11: Adoptive filter sensitivity increase
aflt
Adoptive filter stops
A
B
C
D
E
F
Set the compensation amount with SV048 (LMC1) and SP041
(LMC2).
10: Lost motion compensation type 2 start
Other than 10: Lost motion compensation type 2 stop
Adoptive filter starts
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 151
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13034 SP034 Spindle
SFNC2 function 2
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
7
nfd5
6
D
C
5
4
nfd2
B
A
3
nfd4
2
nfd3
Meaning when "0" is set
Z phase check valid (ALM42)
1
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 1.
Depth (dB)
-∞
-18
8
1
pwm
0
nfd1
bit
0 zck
2 nfd1 Setting value Deep ←
3
000 001
9
zck
Meaning when "1" is set
Invalid
010
011
100
101
-12
-9
-6
-4
→ Shallow
110 110
-3
-1
4 nfd3 Notch filter 3 stop
Notch filter 3 start (1125Hz)
5
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 2.
6 nfd2 Setting value Deep ←
→ Shallow
7
Depth (dB)
000
-∞
001
010
011
100
101
110
110
-18
-12
-9
-6
-4
-3
-1
8 pwm Standard current control
9
High frequency current control
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 4.
A nfd4 This is valid only when SP119 is set to 0.
B
Setting value Deep ←
000 001
-∞ -18
Depth (dB)
010
011
100
101
-12
-9
-6
-4
→ Shallow
110 110
-3
-1
C
D
Set the filter depth for Notch filter 5.
E nfd5 This is valid only when SV120 is set to 0.
F
Setting value Deep ←
Depth (dB)
000
-∞
→ Shallow
001
010
011
100
101
110
110
-18
-12
-9
-6
-4
-3
-1
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 152
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13035 SP035 Spindle
(PR) SFNC3 function 3
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
7
6
5
C
B
shgn
4
nopc
bit
3
A
9
pyn
vgn
2
1
pyin
vgin
8
0
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set Mode
Speed loop gain set 1
selection
Speed loop gain set 2
selection
0
1 vgin
2 pyin Excitation rate 1 selection
Excitation rate 2 selection
3
4
Noninterpolation
5
6
7 nopc Phase alignment start
Phase alignment stop
8
9
vgn
A pyn
Speed loop gain set 1
selection
Excitation rate 1 selection
Speed loop gain set 2
selection
Excitation rate 2 selection
B
C shgn SHG control stop
SHG control start
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 153
Interpolation
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13036 SP036 Spindle
(PR) SFNC4 function 4
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
pys
vgs
mksl
bit
shgs
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set Mode
0
1
vgs
Speed loop gain set 1
selection
Speed loop gain set 2
selection
2
pys
Excitation rate 1 selection
Excitation rate 2 selection
3
4 shgs SHG control stop
SHG control start
5
6
7 mksl
Use command coil during
spindle synchronization
Spindle
synchronization
Use high-speed coil
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
13037 SP037
JL
Load inertia
scale
Set "the motor inertia + motor axis conversion load inertia" in 0 to 5000
(%)
respect to the motor inertia.
SV037(JL)=
Jm+Jl
×100
Jm
Jm : Motor inertia
Jl : Motor axis conversion
load inertia
13038 SP038
FHz1
Notch filter
frequency 1
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine vibration
occurs.
(Valid at 50 or more) When not using, set to "0".
13039 SP039
LMCD
Lost motion
compensation
timing
Set this when the lost motion compensation timing doest not 0 to 2000
match.
(ms)
Adjust by increasing the value by 10 at a time.
13040 SP040
LMCT
Lost motion
compensation
non-sensitive
band
Set the non-sensitive band of the lost motion compensation
in the feed forward control.
When "0" is set, the actual value that is set is 2°/1000.
Adjust by increasing by 1°/1000 at a time.
III - 154
0 to 2250
(Hz)
–32768 to
32767
(1°/1000)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
13041 SP041
LMC2
Lost motion
compensation
2
Set this with SP048 (LMC1) only when you wish to set the
lost motion compensation amount to be different depending
on the command directions.
Set to "0" as a standard.
13042 SP042
OVS2
Overshooting
compensation
2
13043 SP043
OVS1
Overshooting
compensation
1
Set this with SP043 (OVS1) only when you wish to set the
overshooting compensation amount to be different
depending on the command directions.
Set to "0" as a standard.
Set this if overshooting occurs during positioning. This
compensates the motor torque during positioning.
This is valid only when the overshooting compensation
SP033 (SFNC1/ovs) is selected.
Setting range
(unit)
-1 to 200
(Short-time
rated %)
-1 to 100
(Short-time
rated %)
-1 to 100
(Short-time
rated %)
Type 3: When SP033 (SFNC1)/bitB, A (ovs) = 11
Set the compensation amount based on the motor shorttime rated current.
Increase in increments of 1%, and find the value where
overshooting does not occur.
Other than Type 3: When SP033 (SFNC1)/bitB, A (ovs) =
/ 11
Overshooting compensation (Type 3) is not executed.
When you wish different compensation amount depending
on the direction
When SP042 (OVS2) is "0", compensate with the value of
SP043 (OVS1) in both of the + and - directions.
If you wish to change the compensation amount
depending on the command direction, set this and SP042
(OVS2).
(SP043: + direction, SV042: - direction. However, the
directions may be opposite depending on other settings.)
When "-1" is set, the compensation won’t be performed in
the direction of the command.
13044 SP044
OBS2
Disturbance
observer gain
Set the disturbance observer gain. The standard setting is
"100" to "300".
To use the disturbance observer, also set SP037 (JL) and
SP045 (OBS1). When not using, set to "0".
III - 155
0
(%)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0
(rad/s)
13045 SP045
OBS1
Disturbance
observer filter
frequency
Set the disturbance observer filter band.
Set to "100" as a standard.
To use the disturbance observer, also set SP037 (JL) and
SP044 (OBS2). When not using, set to "0".
13046 SP046
FHz2
Notch filter
frequency 2
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine vibration
occurs.
(Valid at 50 or more) When not using, set to "0".
13047 SP047
EC
Inductive
voltage
compensation
gain
Set the inductive voltage compensation gain. Set to "100" as 0 to 200
a standard.
(%)
If the current FB peak exceeds the current command peak,
lower the gain.
13048 SP048
LMC1
Lost motion
compensation
1
-1 to 200
Set this when the protrusion (that occurs due to the nonsensitive band by friction, torsion, backlash, etc) at quadrant (Short-time
rated %)
change is too large.
This compensates the torque at quadrant change.
This is valid only when the lost motion compensation
(SP033 (SFNC1/lmc)) is selected.
0 to 2250
(Hz)
Type 2: When SP033 (SFNC1)/bit9, 8 (lmc) = 10
Set the compensation amount based on the motor shorttime rated current.
Set a value double the friction torque as a standard. The
compensation amount will be 0 if "0" is set.
Other than type 2: When SP033 (SFNC1)/bit9, 8 (lmc) =
/ 10
Lost motion compensation (Type 2) is not executed.
When you wish different compensation amount depending
on the direction
When SP041 (LMC2) is "0", compensate with the value of
SP048 (LMC1) in both of the + and - directions.
If you wish to change the compensation amount
depending on the command direction, set this and SP041
(LMC2).
(SP048: + direction, SP041: - direction. However, the
directions may be opposite depending on other settings.)
When "-1" is set, the compensation won’t be performed in
the direction of the command.
13049 SP049
FFC
Acceleration
rate feed
forward gain
13050 SP050
TOF
Torque offset
When a relative error in the synchronous control is large,
0 to 999
apply this parameter to the axis that is delaying.
(%)
The standard setting value is "0". For the SHG control, set to
"100".
To adjust a relative error in acceleration/deceleration,
increase the value by 50 to 100 at a time.
Set the unbalance torque.
-100 to 100
(Short-time
rated %)
III - 156
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0
(ms)
13051 SP051 Dual feed back
DFBT control time
constant
Set the control time constant in dual feed back.
When "0" is set, the actual value that is set is 1ms.
The higher the time constant is, the closer it gets to the
semi-closed control, so the limit of the position loop gain is
raised.
13052 SP052 Dual feedback
DFBN control nonsensitive band
13053 SP053 Excessive error
ODS
detection width
(non-interpolation mode)
Set the non-sensitive band in the dual feedback control.
Set to "0" as a standard.
0
(1°/1000)
Set the excessive error detection width for the noninterpolation mode.
<Standard setting value>
ODS = Maximum motor speed [r/min]×60/PGV/2
0 to 32767
(°)
Excessive error detection is not executed, so do not set "0".
13054 SP054 Overrun
ORE
detection width
in closed loop
control
Set the overrun detection width in the full-closed loop
control.
If the gap between the motor end detector and the linear
scale (machine end detector) exceeds the value set by this
parameter, it is judged to be overrun and Alarm 43 will be
detected.
When "-1" is set, the alarm detection won’t be performed.
When "0" is set, overrun is detected with a 2° width.
-32768 to
32767
(°)
13055 SP055 Max. gate off
Set a length of time from the point when the emergency stop 0 to 20000
EMGx delay time after is input to the point when READY OFF is compulsorily
(ms)
emergency stop executed.
Normally, set the same value as the absolute value of
SP056.
13056 SP056 Deceleration
Set the time constant used for deceleration control during
-20000 to
EMGt time constant at emergency stop. Set the time to stop from the maximum
20000
emergency stop motor speed (TSP).
(ms)
When executing the synchronous operation, put the minus
sign to the settings of both of the master axis and slave axis.
13057 SP057 Spindle side
(PR) GAR1 gear ratio 1
Set the number of teeth on the spindle side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 00.
1 to 32767
13058 SP058 Spindle side
(PR) GAR2 gear ratio 2
Set the number of teeth on the spindle side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 01.
0 to 1
13059 SP059 Spindle side
(PR) GAR3 gear ratio 3
Set the number of teeth on the spindle side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 10.
0 to 1
13060 SP060 Spindle side
(PR) GAR4 gear ratio 4
Set the number of teeth on the spindle side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 11.
0 to 1
13061 SP061 Motor side gear
(PR) GRB1 ratio 1
Set the number of teeth on the motor side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 00.
1 to 32767
13062 SP062 Motor side gear
(PR) GRB2 ratio 2
Set the number of teeth on the motor side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 01.
0 to 1
13063 SP063 Motor side gear
(PR) GRB3 ratio 3
Set the number of teeth on the motor side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 10.
0 to 1
III - 157
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 1
13064 SP064
(PR) GRB4
Motor side
gear ratio 4
Set the number of teeth on the motor side when the gear
selection command (control input 4/bit6, 5) is set to 11.
13065 SP065
TLM1
Torque limit 1
13066 SP066
TLM2
Torque limit 2
Set the torque limit value when the torque limit (control input 0 to 999
1/bitA, 9, 8) is set to 001.
(Short-time
rated %)
Set the torque limit value when the torque limit (control input 0 to 999
1/bitA, 9, 8) is set to 010.
(Short-time
rated %)
13067 SP067
TLM3
Torque limit 3
Set the torque limit value when the torque limit (control input 0 to 999
1/bitA, 9, 8) is set to 011.
(Short-time
rated %)
13068 SP068
TLM4
Torque limit 4
Set the torque limit value when the torque limit (control input 0 to 999
1/bitA, 9, 8) is set to 100.
(Short-time
rated %)
13069 SP069
PCMP
Phase
alignment
completion
width
0 to 32767
(1°/1000)
13070 SP070
KDDT
Phase
alignment
deceleration
rate scale
Set the width for completing phase alignment during
rotation, and for single rotation position alignment when
changing the mode from non-interpolation to spindle
synchronization while rotating.
Set the rotation error required of the machine.
The rotation error will decrease when the setting value is
decreased, but the cycle time (settling time) will increase.
Set to "875" as a standard.
Set the scale for SP016 (DDT) only when the deceleration
rate is to be changed during a rotation command (command
F∆T =
/ 0).
The single rotation position alignment will be completed
faster when the setting value is increased, but the impact
applied on the machine will increase. Set to "0" when not
using this function.
13071 SP071
DIQM
Variable
current limit
during
deceleration,
lower limit
value
The deceleration time can be
adjusted by changing the
current limit value during
deceleration according to the
motor speed.
As shown on the right, set the
lower limit rate of the current
limit in SP071 (DIQM), and
use this with SP072 (DIQN).
0 to 999
(%)
13072 SP072
DIQN
Variable
current limit
during
deceleration,
break point
speed
100%
(TMLR)
DIQM
0
DIQN
Motor speed
When DIQM is set to 100%, the current limit value for
deceleration (TMRL) set in the motor constants will be
applied.
III - 158
0 to 255
(1/16-fold)
1 to 32767
(r/min)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
13073 SP073
VGVN
13074 SP074
VGVS
Items
Details
Variable speed If noise is bothersome during
gain target
high-speed rotation, the state
VGN1
value
can be improved by lowering
(VGN2)
Variable speed the speed loop gain at high
VGVN
speeds.
gain change
As shown on the right, set
start speed
0
VLMT
VGVS
the speed loop gain rate for
(VLMT= Maximum motor speed×1.15)
the overspeed detection
speed in SP073 (VGVN),
and use this with SP074
(VGVS).
Setting range
0 to 100
(%)
0 to 32767
(r/min)
Set to "0" when not using this function.
The overspeed detection speed (VLMT) is 115% of the
maximum motor speed (TSP).
This function can be used when either VGN1 or VGN2 is
selected.
13075 SP075
DWSH
Slip
compensation
scale during
regeneration
High-speed
coil
Adjust the slip frequency scale for deceleration.
Normally, set this to "0".
(For machine tool builder adjustment)
0 to 255
(1/16-fold)
13076 SP076
DWSL
Slip
compensation
scale during
regeneration
Low-speed coil
Adjust the slip frequency scale at deceleration when using
the low-speed coil.
Normally, set this to "0".
(For machine tool builder adjustment)
0 to 255
(1/16-fold)
13077 SP077
IQA
Q axis current
advance
compensation
1 to 20480
13078 SP078
IDA
D axis current
advance
compensation
13079 SP079
IQG
Q axis current
gain
Set the current loop gain.
When changing the coils, set the current loop gain for when
the high-speed coil is selected.
The setting value is determined by the electrical
characteristics, so the setting value is fixed for the motor
being used.
Set the value given in the spindle parameter list.
(For machine tool builder adjustment)
13080 SP080
IDG
D axis current
gain
13081 SP081
IQAL
Q axis current
advance
compensation
Low-speed coil
1 to 20480
13082 SP082
IDAL
D axis current
advance
compensation
Low-speed coil
Set the current loop gain for when the coil is changed and
the low-speed coil is selected.
The setting value is determined by the electrical
characteristics, so the setting value is fixed for the motor
being used.
Set the value given in the axis parameter list.
(For machine tool builder adjustment)
13083 SP083
IQGL
Q axis current
gain
Low-speed coil
13084 SP084
IDGL
D axis current
gain
Low-speed coil
1 to 8192
1 to 8192
III - 159
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 32767
13085 SP085
LMCk
Lost motion
When not using, set to "0".
compensation
3 spring
constant
13086 SP086
LMCc
Lost motion
When not using, set to "0".
compensation
3 viscous
constant
0 to 32767
13087 SP087
FHz4
Notch filter
frequency 4
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine vibration
occurs. (Valid at 50 or more)
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
13088 SP088
FHz5
Notch filter
frequency 5
Set the vibration frequency to suppress if machine vibration
occurs. (Valid at 50 or more)
When not using, set to "0".
0 to 2250
(Hz)
13089 SP089
TMKQ
Maximum
output control
Kq
Maximum
output control
Kd
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0 to 32767
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0 to 32767
Not used.
Set to "0".
0
13090 SP090
TMKD
13091 SP091
:
:
13100 SP100
13101 SP101
TMA1
OMR-FF 1st
movement
average filter
time constant
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0
(0.1ms)
13102 SP102
TMA2
OMR-FF 2nd
movement
average filter
time constant
OMR-FF
Responsiveness
compensation
time constant
α resp
OMR-FF
Inward turning
compensation
gain for G0
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0
(0.1ms)
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0
(0.1ms)
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0
(%)
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
When not using, set to "0".
0
(rad/s)
0
(Hz)
13103 SP103
TRES
13104 SP104
FER0
13105 SP105
PGM
13106 SP106
FR
OMR-FF IIR
filter gain
OMR-FF
Resonance
frequency
13107 SP107
FA
OMR-FF
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
Antiresonance When not using, set to "0".
frequency
III - 160
0
(Hz)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
13108 SP108
ZR
OMR-FF
Resonance
attenuation
rate
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
When not using, set to "0".
Setting range
(unit)
0
(%)
13109 SP109
ZA
OMR-FF
Antiresonance
attenuation
rate
OMR-FF
Inward turning
compensation
gain for G1
OMR-FF control Set "0" for a rigid model.
When not using, set to "0".
0
(%)
OMR-FF control
When not using, set to "0".
0
(%)
OMR-FF Delay
compensation
time
Number of
ripple
disturbance
compensations
OMR-FF control Set the delay time that occurs with the
normal model.
When not using, set to "0".
Set the number of rippers per motor rotation.
0
(0.1ms)
13113 SP113
OPLP
Current
command
value for open
loop
0 to 999
(Short-time
rated %)
13114 SP114
MKT
Coil
changeover
gate cutoff
timer
Set the current command value for when open loop control
is valid.
A "0" setting is the same as a "50" setting.
Set "0" when not using this function.
Open loop control is valid when SP018 (SPEC2)/bit1 (oplp)
is set to 1.
Set the time to cut off the gate when turning the coil
changeover contactor OFF and ON.
Set a value longer than the coil changeover contactor's
OFF/ON time.
Set to "150" as a standard.
13115 SP115
MKT2
Coil
changeover
current limit
timer
Set the time to limit the current immediately after the gate is
turned ON when the coil changeover contactor ON/OFF is
completed.
Set to "25" as a standard.
0 to 3500
(ms)
13116 SP116
MKIL
Coil
changeover
current limit
value
Set the value to limit the current immediately after the gate
0 to 999
is turned ON when the coil changeover contactor ON/OFF is (Short-time
completed.
rated %)
Set to "120" as a standard.
13117 SP117
SETM
Excessive
Set the time to detect the speed excessive error alarm.
speed
Set the time required of the machine.
deviation timer Set to "12" as a standard.
0 to 60
(s)
13118 SP118
MSFT
Magnetic pole
shift amount
0
(°)
No.
13110 SP110
FER1
13111 SP111
TDM
13112 SP112
RDCN
Items
Details
Set the magnetic pole shift amount for the IPM spindle
motor.
III - 161
0
0 to 3500
(ms)
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
13119 SP119
FSP4
13120 SP120
FSP5
Items
Details
Notch filter
Set the notch filter target attenuation amount and damping
specifications coefficient.
4
Add a value 10000-fold the damping coefficient to the target
attenuation rate -dB absolute value, and set.
Notch filter
specifications The setting range of each coefficient is as follows.
Damping coefficient: 0.01 to 1.00 (0.01 increments)
5
When 0 is set, the value is 1.00.
Target attenuation amount: -80dB to -1dB (1dB
incremnets)
When 0 is set, the value is -80dB.
(Example) To set target attenuation amount to -40dB and
damping coefficient to 1.00
1.00 × 10000 + ABS (-40) = 10040
When using nfd4 or ndf5 of SP034, set "0".
Setting range
(unit)
0 to 32767
13121 SP121
MP Kpp
Magnetic pole
detection
position loop
gain
This is used for the initial magnetic pole detection when the
IPM spindle motor is turned ON.
Set the position loop gain in the magnetic pole detection
loop.
Set "0" when using the IM spindle motor.
13122 SP122
MP Kvp
Magnetic pole
detection
speed loop
gain
This is used for the initial magnetic pole detection when the 0 to 32767
IPM spindle motor is turned ON.
Set the speed loop gain in the magnetic pole detection loop.
Set "0" when using the IM spindle motor.
13123 SP123
MP Kvi
Magnetic pole
detection
speed loop
advance
compensation
This is used for the initial magnetic pole detection when the
IPM spindle motor is turned ON.
Set the speed loop advance compensation in the magnetic
pole detection loop.
Set "0" when using the IM spindle motor.
0 to 32767
13124 SP124
ILMTsp
Magnetic pole
detection
current limit
value
This is used for the initial magnetic pole detection when the
IPM spindle motor is turned ON.
Set the current limit value in the magnetic pole detection
loop.
Set "0" when using the IM spindle motor.
0 to 999
(Short-time
rated %)
13125 SP125
DA1NO
D/A output
channel 1
data No.
Input the data number you wish to output to D/A output
channel.
0 to 4
13126 SP126
DA2NO
D/A output
channel 2
data No.
Set the output scale as a 1/100 unit.
The same scale as "100" is applied when "0" is set.
-32768 to
32767
(1/100-fold)
13127 SP127
D/A output
DA1MPY channel 1
output scale
13128 SP128
D/A output
DA2MPY channel 2
output scale
III - 162
0 to 32767
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
Details
13129 SP129
(PR)
:
:
13160 SP160
(PR)
Set the unique constants for the spindle motor. (High-speed
coil)
The setting value is determined by the motor's mechanical
and electrical characteristics and specifications, so normally
set the value given in the spindle parameter list.
13161 SP161
(PR)
:
:
13192 SP192
(PR)
Set the unique constants for the spindle motor. (Low-speed
coil)
The setting value is determined by the motor's mechanical
and electrical characteristics and specifications, so normally
set the value given in the spindle parameter list.
13193 SP193
:
:
13224 SP224
Not used.
Set to "0".
Setting range
(unit)
0
III - 163
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13225 SP225 Spindle
SFNC5 function 5
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
7
6
D
C
B
A
9
8
5
4
3
2
1
0
ovsn
dcd
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
dcd
Direct excitation mode stop
Direct excitation mode start
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
Set the non-sensitive band for overshooting compensation type
3 with a 2µm unit.
D
ovsn When using feed forward control, set the non-sensitive band for
E
the model position loop to ignore the model overshooting. Set
F
to 2µm (0001) as a standard.
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 164
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13226 SP226 Spindle
SFNC6 function 6
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 165
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
13227 SP227
SFNC7
Items
Servo
function 7
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the servo functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
dis
7
bit
0
lmct
1
lmc3
6
8
alcdsp
5
4
Meaning when "0" is set
Lost motion compensation 3
adjustment time
measurement invalid
Lost motion compensation 3
stop
3
2
1
0
lmc3
lmct
Meaning when "1" is set
Lost motion compensation 3
adjustment time
measurement valid
Lost motion compensation 3
start
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 alcdsp Alarm history display
9
A
B
Digital signal input selection
Set to 0001 when using the safe speed control function.
C
D
E
Alarm counter display
dis
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 166
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13228 SP228 Spindle
SFNC8 function 8
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
irms
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
0 irms Normal load meter display
Meaning when "1" is set
Effective motor current display
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 167
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13229 SP229 Spindle
SFNC9 function 9
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
ssc
7
omrffoff omrffon
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
0 omrffon OMR-FF control invalid
Meaning when "1" is set
OMR-FF control valid
1 omrffoff Normal setting
OMR-FF control temporary
stop
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
ssc
Safe speed control function
invalid
Safe speed control function
valid
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 168
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13230 SP230
Spindle
SFNC10 function 10
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 169
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13231 SP231
Spindle
SFNC11 function 11
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
III - 170
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13232 SP232
Spindle
SFNC12 function 12
Setting range
(unit)
Details
Select the spindle functions.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
bit
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(Note) Set to "0" for bits with no particular description.
13233 SP233
IVC
Voltage nonsensitive
band
compensation
When 100% is set, the voltage equivalent to the logical non- 0 to 255
energized time will be compensated.
(%)
When "0" is set, a 100% compensation will be performed.
Adjust in increments of 10% from the default value 100%.
If increased too much, vibration or vibration noise may be
generated.
III - 171
7. Spindle Parameters
7.2 MDS-D/DH Series
No.
Items
13234 SP234
13235 SP235
(PR) R2H
13236 SP236
(PR) WIH
13237 SP237
(PR) TCF
Details
Not used.
Set to "0".
Temperature
compensation
initial value
Temperature
compensation
iron loss
coefficient
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0
(%)
Normally set this to "0". (For machine tool builder
adjustment)
0
(%)
Torque
command
filter
Set the filter for the torque command. Set to "0" when not
using this function.
The standard value is "500" when using the motor end
detector TS5690 or TS5691.
0 to 4500
(Hz)
Set to "0" when not using this function.
Set the safe speed at the spindle end when using the safe
speed control function.
0 to 18000
(°/min)
13238 SP238
Safe speed
SSCFEED control safe
speed
13239 SP239
Safe speed
When not using, set to "0".
SSCRPM control safe
rotation speed
13240 SP240
Not used.
(PR)
Set to "0".
13241 SP241
(PR)
:
:
SP256
13256
(PR)
Setting range
(unit)
0
System
setting
parameter
These parameters are set automatically by the NC system.
III - 172
0 to 32767
(r/min)
0
7. Spindle Parameters
7.3 Supplement
7.3 Supplement
7.3.1 D/A Output Numbers
(1) D/A output specifications
Item
Number of
channels
Output cycle
Explanation
2ch
CN9 connector
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1
LG
11 LG
2
12
3
13
4
14
5
15
6
16
7
17
8
18
9 MO1
19 MO2
10
20
888µs (min. value)
Output precision 12bit
Output voltage
range
0V to 2.5V to +5V
Output scale
setting
-32768 to 32767%
(1% increments)
Output pins
CN9 connector
MO1 = 9 pin
MO2 = 19 pin
GND = 1, 11 pin
(2) Setting the output data
Input the No. of the data to be output to each D/A output channel.
#
No.
Abbrev.
Parameter name
13125 SP125 DA1NO D/A output channel 1 data No.
13126 SP126 DA2NO D/A output channel 2 data No.
No.
Details
Output unit
0
Motor speed
1000(r/min)/V
1
Current command
100%/V
2
Current feedback
100%/V
3
Position droop
1mm/V
4
Command F∆T
1mm/0.8ms/V
5
6
7
8
9
10
III - 173
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters
Parameters indicated as (PR) in the table will be validated when the NC power is turned OFF and ON after
setting.
#
Items
Details
7900 RCDAX_I Orthogonal
Set the name of the horizontal axis in the
(PR)
coordinate
orthogonal coordinate system.
horizontal axis
name
Setting range (unit)
A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
7901 RCDAX_J Orthogonal
(PR)
coordinate
vertical axis
name
Set the name of the vertical axis in the orthogonal
coordinate system.
A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
7902 RCDAX_K Orthogonal
(PR)
coordinate
height axis
name
Set the name of the height axis in the orthogonal
coordinate system.
A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
7903 G92_CRD Origin zero
Select whether the coordinates preset when origin 0 / 1
set coordinate zero (G92_X_Y_Z;) is commanded are the tool
selection
end or the holder end coordinates.
0: Tool nose
1: Holder end
7904 NO_TIP
Tool handle
feed function
selection
7905 NO_ABS
Selection of
tool axis
movement
amount
display at
manual ABS
switch
ON/OFF
Select whether to validate or ignore the tool handle 0 / 1
function.
0: Valid (tool handle feed)
1: Invalid (standard)
Select whether to update the displayed tool axis
0/1
movement amount at manual ABS switch OFF, or
at both manual ABS switch ON and OFF.
0: Only at ABS switch OFF
1: ABS switch ON/OFF
7906 PASSTYP Singular point Select the movement after passing through a
passage type singular point.
0: Type 1
The same direction as when the A axis or B
axis rotation angle sign is the tool nose
control start is selected.
1: Type 2
The direction with less C axis rotation
movement amount on the singular point is
selected.
0/1
7907 CHK_AN
G
0.000 to 5.000 (°)
Near singular
judgment
angle
Set the angle for judging a position near the
singular point.
7908 SLCT_PR Programming Select whether to use the workpiece coordinate
G_COOR coordinate
system or table coordinate system (coordinate
D
system
system that rotates together with workpiece) for
selection
the programming coordinate system.
0: Table coordinate system
1: Workpiece coordinate system
0/1
7909 IJK_VEC_ Posture
MR
vector mirror
image
selection
0/1
Select whether to apply a mirror image on the
posture vector (IJK) for Type 2.
0: Mirror OFF
1: Mirror ON
III - 174
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters
#
Items
7910 SLCT_INT Interpolation
_MODE
method
selection
7911 SLCT_ST Rotary axis
ANDARD_ basic
POS
positions
election
7920 SLCT_T1
(PR)
Rotary axis
selection
Details
Select whether to use single axis rotation
interpolation or joint interpolation.
0: Joint interpolation method
1: Single axis rotation interpolation method
Select whether to use the machine coordinate
system zero point or the position at the end point
command as a reference.
0: Machine coordinate system
1: Position at command
Setting range (unit)
0/1
Set in which axis direction to rotate the tool
rotating type base-side rotary axis.
0: Invalid
(Example) A-B axis
1: I axis rotation Base-side rotary axis
2: J axis rotation
3: K axis rotation
0 to 3
0/1
Tool-side B axis
rotary axis
Z
Y
A axis
X
7922 ROTAXT1 Rotary axis
(PR)
name
Set the name of the tool rotating type base-side
rotary axis.
0,A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
0: Mechanical axis
specifications
7923 DIR_T1
Set the rotation direction of the tool rotating type
base-side rotary axis.
0: CW
1: CCW
Set the distance from the tool-side rotary axis
rotation center in the horizontal axis direction to
the base-side rotary axis rotation center.
0/1
Rotation
direction
7924 COFST1H Horizontal
axis rotation
center offset
-99999.999 to
99999.999 (mm)
7925 COFST1V Vertical axis
Set the distance from the tool-side rotary axis
rotation center rotation center in the vertical axis direction to the
offset
base-side rotary axis rotation center.
7926 COFST1T Height axis
Set the distance from the tool-side rotary axis
rotation center rotation center in the height axis direction to the
offset
base-side rotary axis rotation center.
7930 SLCT_T2
(PR)
Rotary axis
center
0 to 3
Set in which axis direction to rotate the tool
rotating type tool-side rotary axis.
0: Invalid
(Example) A-B axis
1: I axis rotation Base-side rotary axis
2: J axis rotation
3: K axis rotation
Tool-side B axis
rotary axis
Z
A axis
III - 175
Y
X
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters
#
Items
7932 ROTAXT2 Rotary axis
(PR)
name
Details
Set the name of the tool rotating type tool-side
rotary axis.
Setting range (unit)
0,A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
0: Mechanical axis
specifications
7933 DIR_T2
Rotation
direction
Set the rotation direction of the tool rotating type
tool-side rotary rotary axis.
0: CW
1: CCW
0/1
7934 COFST2H
Horizontal
Set the distance from the spindle holder end in the -99999.999 to
axis rotation horizontal axis direction to the tool-side rotary axis 99999.999 (mm)
center offset rotation center.
7935 COFST2V
Vertical axis Set the distance from the spindle holder end in the
rotation
vertical axis direction to the tool-side rotary axis
center offset rotation center.
7936 COFST2T
Height axis
Set the distance from the spindle holder end in the
rotation
height axis direction to the tool-side rotary axis
center offset rotation center.
7940 SLCT_W1
(PR)
Rotary axis
selection
Set in which axis direction to rotate the table
rotating type base-side rotary axis.
0:
1:
2:
3:
0 to 3
(Example) A-C axis
Invalid
I axis rotation
Workpiece-side
rotary axis
J axis rotation
C axis
K axis rotation
Z
A axis
Y
X
Base-side
rotary axis
7942 ROTAXW1 Rotary axis
(PR)
name
Set the name of the table rotating type base-side
rotary axis.
7943 DIR_W1
Set the rotation direction for the table rotating type 0 / 1
base-side rotary axis.
0: CW
1: CCW
Rotation
direction
0,A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
0: Mechanical axis
specifications
7944 COFSW1H Horizontal
Set the distance from the machine zero point in
-99999.999 to
axis rotation the horizontal axis direction to the base-side rotary 99999.999 (mm)
center offset axis rotation center when all axes are at the
machine zero point.
7945 COFSW1V Vertical axis Set the distance from the machine zero point in
rotation
the vertical axis direction to the base-side rotary
center offset axis rotation center when all axes are at the
machine zero point.
7946 COFSW1T Height axis
Set the distance from the machine zero point in
rotation
the height axis direction to the base-side rotary
center offset axis rotation center when all axes are at the
machine zero point.
III - 176
8. Rotary Axis Configuration Parameters
#
Items
7950 SLCT_W2 Rotary axis
(PR)
selection
Details
Set in which direction to rotate the table rotating
type workpiece-side rotary axis.
0:
1:
2:
3:
Setting range (unit)
0 to 3
Invalid
(Example) A-C axis
I axis rotation
Workpiece-side
rotary axis
J axis rotation
C axis
K axis rotation
Z
A axis
Y
X
Base-side
rotary axis
7952 ROTAXW2 Rotary axis
(PR)
name
Set the name of the table rotating type workpieceside rotary axis.
7953 DIR_W2
Set the rotation direction for the table rotating type 0 / 1
workpiece-side rotary axis.
0: CW
1: CCW
Rotation
direction
7954 COFSW2H Horizontal
Set the distance from the base-side rotary axis
axis rotation rotation center in the horizontal axis direction to
center offset the workpiece-side rotary axis rotation center
when all axes are at the machine zero point.
7955 COFSW2V Vertical axis Set the distance from the base-side rotary axis
rotation
rotation center in the vertical axis direction to the
center offset workpiece-side rotary axis rotation center when all
axes are at the machine zero point.
7956 COFSW2T Height axis
Set the distance from the base-side rotary axis
rotation
rotation center in the height axis direction to the
center offset workpiece-side rotary axis rotation center when all
axes are at the machine zero point.
III - 177
0,A,B,C,U,V,W,X,Y,Z
0: Mechanical axis
specifications
-99999.999 to
99999.999 (mm)
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.1 Function Outline
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.1 Function Outline
Machine error compensation includes two independent functions: memorized pitch error compensation and
memorized relative position compensation.
(1) Memorized pitch error compensation
According to the specified parameters‚ this method compensates an axis feed error caused by a ball
screw pitch error‚ etc.
With the reference position defined as the base‚ set the compensation amount in the division points
obtained by equally dividing the machine coordinates. (See Fig. 1. 1)
The compensation amount can be set by either the absolute or incremental system.
Select the desired method with the #4000:Pinc. Machine position is compensated between division
points n and n+1 as much as compensation amount between them by linear approximation.
Real machine
position
Ideal machine
position
Real machine position for
which no compensation
has been made
S
S
S
Command machine
position
Reference position
Compensation
amount
Compensation
amount
between
division points
S: Division point
S
S
S
n
n+1
n+2
Command machine position
Fig. 1.1 Relationship between the compensation amount and machine position
III - 178
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.1 Function Outline
(2) Memorized relative position compensation
This method‚ according to the parameters specified in advance‚ compensates the relative position error
between two orthogonal axes caused by deflection of the moving stand.
For this‚ as shown in Fig. 1. 2‚ specify the compensation amount in the compensation axis direction in
the division points obtained by equally dividing the machine coordinates of the base axis.
The base axis is one of the two orthogonal axes to which relative position compensation applies. This
axis is used as the criterion for relative-error measurement. The compensation axis is the coordinate
axis that is orthogonal to the base axis. The compensation is actually made for this coordinate axis.
The section between division points n and n+1 is compensated smoothly by linear approximation.
Actual machine position
of compensation axis
Actual machine position for
which no compensation
has been made
S: Division point
Reference position
Compensation
amount
S
S
S
n
n+1
n+2
T
T
T
Command machine
position along base axis
Command machine position
Compensation amount
between division points
Fig. 1.2 Relationship between the compensation amount and machine position
#
4000 Pinc
(PR)
Item
Machine error
compensation
increment method
Details
Specify whether to use the incremental
amount method or absolute amount method
when setting the machine error
compensation data.
III - 179
Setting range
0: Absolute volume
method
1: Incremental volume
method
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.1 Function Outline
<1st axis>
#
4001 cmpax
4002 drcax
4003 rdvno
4004 mdvno
4005 pdvno
4006 sc
4007 spcdv
Item
Basic axis
Details
Specify the basic axis address for machine
error compensation.
1) For pitch error compensation‚ set the
name of the axis to be compensated.
2) For relative position compensation‚ set
the name of the axis to be the base axis.
Set as the "system No. + axis name" when
using the multi-system.
(Example) Z axis for 2nd system: 2Z
Compensation axis Set the compensation axis address for
machine error compensation.
1) For pitch error compensation‚ set the
same axis name as #4001 cmpax.
2) For relative position compensation‚ set
the name of the axis to be actually
compensated.
Set as the "system No. + axis name" when
using the multi-system.
(Example) Z axis for 2nd system: 2Z
Division point
Set the compensation data No.
number at
corresponding to the reference position. The
reference position reference position is actually the base‚ so
there is no compensation No. Set the
number that is decremented by 1.
Division point
Set the compensation data No. that is on the
number at the most farthest negative side.
negative side
Division point
Set the compensation data No. that is on the
number at the most farthest positive side.
positive side
Compensation
Set the compensation amount’s scale.
scale factor
Division interval
Set the interval to divide the basic axis.
Each compensation data will be the
compensation amount for each of these
intervals.
Setting range
X, Y, Z, U, V, W, A, B,
or C axis address
X, Y, Z, U, V, W, A, B,
or C axis address
4101 to 5124
4101 to 5124
4101 to 5124
0 to 99
1 to 9999999
(control unit applied)
2nd axis 3rd axis 4th axis 5th axis 6th axis 7th axis 8th axis 9th axis 10th axis
4011
4012
4013
4014
4015
4016
4017
#
4101
y
y
y
5124
4021
4022
4023
4024
4025
4026
4027
4031
4032
4033
4034
4035
4036
4037
Item
4041
4042
4043
4044
4045
4046
4047
4051
4052
4053
4054
4055
4056
4057
4061
4062
4063
4064
4065
4066
4067
4071
4072
4073
4074
4075
4076
4077
4081
4082
4083
4084
4085
4086
4087
4091
4092
4093
4094
4095
4096
4097
Set the parameters
corresponding to the 1st
axis’ parameters 4001 to
4007 for each axis.
A maximum of 6 axes can
be controlled‚ but as the
relative position is
compensated‚ settings for
10 axes can be made.
Details
Setting range
Set the compensation amount for each axis. -32768 to 32767
The actual compensation amount will be the
value obtained by
multiplying the setting
value with the
compensation scale.
III - 180
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.2 Setting Compensation Data
9.2 Setting Compensation Data
Compensation data can be set according to either absolute or incremental system.
"#4000:Pinc" 0: Absolute system
1: Incremental system
(1) Absolute system
Feed from the reference position to each division point is executed as shown in Fig. 2.1. The following is
obtained at this time. Set it as the compensation amount.
(Specified position - Real machine position) × 2 (Unit of output)
For example‚ assume that the feed from the reference position to the +100mm position is executed.
Also‚ assume that the real machine position is 99.990mm. In this case‚ the following value is defined as
the compensation amount used at the +100mm position:
(100000 - 99990) × 2 = 20 pulses
The resultant value is defined as the compensation amount. Assume that the real machine position
resulting when feed to the -100mm position is executed‚ is -99.990mm. In this case‚ the following value
is defined as the compensation amount used at the -100mm position:
(-100000 - (-99990)) × 2 = -20 pulses
-100
+99.990
Compensation
amount:
20 pulses
(10um)
Compensation
amount:
-20 pulses
(-10um)
-99.990
+100
Fig. 2.1
(2) Incremental system
Fig. 2.2 contains a machine position that is placed in the positive direction with respect to the reference
position. Assume that feed from division n-1 to n (division interval) is executed. In this case‚ the
following value is defined as the compensation amount:
(Division interval - Actual movement distance) × 2 (Unit of output)
III - 181
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.2 Setting Compensation Data
(3) Fig. 2.3 contains a machine position that is placed in the negative direction with respect to the reference
position. Assume that feed from division point n+1 to n by the division interval is executed. In this case‚
the following value is defined as the compensation amount:
(Division interval + Actual movement distance) × 2 (Unit of output)
1
n
n+1
n: Division point compensation number
1: Division interval
n-1
n
1
Fig. 2.2
Fig. 2.3
Unit
: Unit of output
Range : -128 to 127
(Note) The unit of output is used as the unit of setting. The actual unit of compensation pulses
depends on the compensation scale factor.
III - 182
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis
(1) When "mdvno" or "pdvno" exists at both ends of "rdvno":
Compensation amount
in incremental system
(1)
(3)
(-3)
(-2)
(0)
(3)
Error
#4101
#4102
3
#4103
#4104
#4105
#4106
2
1
Base axis machine
coordinate
-1
-2
-3
(3)
Compensation amount
in absolute system
Division point number
(-2)
(0)
(-2)
(-1)
rdvno
4103
Specified machine position -300.000 -200.000 -100.000 100.000 200.000 300.000
mdvno
4101
Real machine position
pdvno
4106
Compensa- Incremental
tion amount Absolute
#4101
(1)
#4102
#4103
#4104
#4105
#4106
-299.999 -200.000 -100.003 100.002 200.002 299.999
2
6
-6
-4
0
6
-2
0
6
-4
-4
2
If the setting range ("mdvno" to "pdvno") is exceeded‚ the compensation will be based on compensation
amount at "mdvno" or "pdvno".
III - 183
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis
(2) When the range compensated is only the positive range:
Compensation amount
in incremental system
(-2)
(1)
(0)
(3)
(1)
Error
3
#4113
#4114
#4115
#4116
#4117
2
1
Base axis machine
coordinate
-1
-2
-3
(-2)
(-1)
Compensation amount
in absolute system
(-1)
(2)
(3)
Division point number
Compensa- Incremental
tion amount Absolute
#4113
-4
#4114
2
#4115
0
#4116
6
#4117
2
rdvno
mdvno
4112
4113
-4
-2
-2
4
6
pdvno
4117
If the machine position exceeds "pdvno"‚ the compensation will be based on the compensation amount
at "pdvno". If the machine position is negative in this case‚ no compensation will be executed.
III - 184
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis
(3) When the range compensated is only the negative range:
Compensation amount
in incremental system
(-1)
(1)
(3)
(1)
(0)
(-3)
Error
#4125
#4126
#4127
#4128
#4129
#4130
3
2
1
Base axis
machine
coordinate
-1
-2
-3
(3)
(3)
(2)
(-1)
Compensation amount
in absolute system
Division point number
Compensa- Incremental
tion amount Absolute
(-2)
(-1)
#4125
-2
#4126
2
#4127
6
#4128
2
#4129
0
#4130
-6
rdvno
mdvno
4130
4125
-2
-4
-2
4
6
6
pdvno
4130
If the machine position exceeds "mdvno"‚ the compensation will be based on compensation amount at
"mdvno".
III - 185
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.3 Example in Using a Linear Axis as the Base Axis
(4) When compensation is executed in a range that contains no reference position:
Compensation
amount in
incremental system
Error
3
#4135
#4136
(-1)
(-1)
#4137
(1)
(3)
#4138
#4140
#4139
2
1
Base axis machine
coordinate
-1
-2
-3
Compensation
amount in
absolute system
(-1)
(-2)
(1)
(2)
Division point number
Compensation amount
#4135
#4136
#4137
#4138
#4139
#4140
rdvno
4134
Incremental
-2
-2
6
2
mdvno
4136
Absolute
-2
-4
2
4
pdvno
4140
In this case‚ the compensation is executed in the range from "mdvno" to "pdvno". This setting rule
applies also when the compensation is executed in a range which contains negative machine positions
and no reference position.
III - 186
9. Machine Error Compensation
9.4 Example in Using a Rotary Axis as the Base Axis
9.4 Example in Using a Rotary Axis as the Base Axis
Compensation amount
in incremental system
(-2)
(1)
(0)
(3)
(1)
(-3)
Error
3
#4123
#4125
#4124
#4126
#4128
#4127
2
1
360°
Base axis machine
coordinate
-1
-2
-3
(-2)
(-1)
(-1)
Compensation amount
in absolute system
(2)
(3)
(0)
Division point number
Compensa- Incremental
tion amount Absolute
#4123
-4
#4124
2
#4125
0
#4126
6
#4127
2
#4128
-6
rdvno
mdvno
4122
4123
-4
-2
-2
4
6
0
pdvno
4128
In this case‚ the sum of the compensation amounts set according to the incremental system is always
"0". For the absolute system‚ the compensation amount at the terminal point (360 degrees) is always "0".
III - 187
10. PLC Constants
10.1 PLC Timer
10. PLC Constants
10.1 PLC Timer
#
PLC device
16000
:
:
:
:
16703
T0
:
:
:
:
T703
Item
PLC timer
<10ms/100ms>
Details
Set the time for the timer used in the PLC
program (ladder).
The 10ms timer and 100ms timer are
identified by the command used.
(Note) This setting value is valid when
parameter "#6449 bit0" in the
following "[BIT SELECT]" is set to
"0".
Setting range
0 to 32767
(×10ms or ×100ms)
(Note 1) Setting the timer setting value from the setting and display unit
The timer T setting value can be set with the following two methods.
• Method to validate the setting value (Kn) programmed with the sequence program (fixed timer)
• Method to validate the setting value set from the setting and display unit (variable timer)
(Note 2) The fixed timer and variable timer range can be set with the bit selection parameters (#6454bit0 to
bit3).
No. of
points
Range
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
All points
None
#16000 to #16099
#16000 to #16199
#16000 to #16299
#16000 to #16399
#16000 to #16499
#16000 to #16599
#16000 to #16703
Bit selection parameter (#6454)
bit3
bit2
bit1
bit0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
III - 188
Fixed timer/
variable timer
All fixed timers
Variable timers in
range on left
All variable timers
10. PLC Constants
10.2 PLC Integrated Timer
10.2 PLC Integrated Timer
#
PLC device
17000
:
:
17063
ST0
:
:
ST63
Item
Details
Setting range
PLC integrated Set the time for the integrated timer used with 0 to 32767 (×100ms)
timer
the PLC program (ladder).
<100ms INC.> (Note) This setting value is valid when
parameter "#6449 bit0" in the
following "[BIT SELECT]" is set to "0".
(Note 1) Setting the timer setting value from the setting and display unit
The timer T setting value can be set with the following two methods.
• Method to validate the setting value (Kn) programmed with the sequence program (fixed
integrated timer)
• Method to validate the setting value set from the setting and display unit (variable integrated
timer)
(Note 2) The fixed integrated timer and variable integrated timer range can be set with the bit selection
parameters (#6454bit5 to bit7).
No. of
points
Range
0
None
20
#17000 to #17019
40
#17000 to #17039
All points #17000 to #17063
Bit selection parameter (#6453)
bit7
bit6
bit5
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
Fixed integrated timer/
variable integrated timer
All fixed integrated timers
Variable integrated timers in
range on left
All variable integrated timers
10.3 PLC Counter
#
PLC device
17200
:
:
:
17455
C000
:
:
:
C255
Item
Counter
Details
Setting range
Set the time for the counter used with the PLC 0 to 32767
program (ladder).
(Note) This setting value is valid when
parameter "#6449 bit1" in the
following "[BIT SELECT]" is set to "0".
(Note 1) Setting the counter setting value from the setting and display unit
The counter C setting value can be set with the following two methods.
• Method to validate the setting value (Kn) programmed with the sequence program (fixed
counter)
• Method to validate the setting value set from the setting and display unit (variable counter)
(Note 2) The fixed counter and variable counter range can be set with the bit selection parameters
(#6454bit4 to bit7).
No. of
points
Range
0
40
80
120
160
200
240
All points
None
#17200 to #17239
#17200 to #17279
#17200 to #17319
#17200 to #17359
#17200 to #17399
#17200 to #17439
#17200 to #17455
Bit selection parameter (#6454)
bit7
bit6
bit5
bit4
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
III - 189
Fixed counter/
variable counter
All fixed counters
Variable counter in
range on left
All variable counters
10. PLC Constants
10.4 PLC Constants
10.4 PLC Constants
#
PLC device
Item
PLC
constant
18001 R7500,7501
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
18150 R7798,7799
Details
Set the value to be set in the data type R
register used in the PLC program
(ladder).
Even if the data is set in the R register
that corresponds to the PLC side when
this parameter is displayed‚ the screen
will not change. Enter a different screen
once‚ and then select this screen again.
Setting range
-99999999 to
99999999
Setting range
0: OFF
1: ON
10.5 Selecting the PLC Bit
#
6401
6402
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
6495
6496
PLC device
Item
R7800-Low Bit selection
R7800-High
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
R7847-Low
R7847-High
Details
This is the bit type parameter used in the
PLC program (ladder).
Even if the data is set in the R register
that corresponds to the PLC side when
this parameter is displayed‚ the screen
will not change. Enter a different screen
once‚ and then select this screen again.
Some of the parameters following #6449
may be fixed according to the usage
purpose.
Refer to the PLC Program Development
On-board Instruction Manual.
6497
6498
:
:
:
:
:
6595
6596
R7848-Low Bit selection
R7848-High expansion
:
:
:
:
:
R7897-Low
R7897-High
This is the bit type parameter (expansion) 0: OFF
used in the PLC program (ladder).
1: ON
Even if the data is set in the R register
that corresponds to the PLC side when
this parameter is displayed‚ the screen
will not change. Enter a different screen
once‚ and then select this screen again.
III - 190
10. PLC Constants
10.5 Selecting the PLC Bit
Table: "Contents of bit selection parameters #6449 to #6496"
Symbol
name
0
1
7
6
5
4
Setting
#6449
Control unit
display unit
temperature
R7824 L
thermal
alarm ON
alarm ON
External
#6450
Alarm/
alarm
R7824 H
operator
message
change
display
3
2
Integrating
Counter C
timer T
retention
retention
Full screen
display of
message
-
PLC
GX Developer
development
communienvironment
cation ON
selection
Operator
message
ON
Onboard
editing not
possible
1
0
PLC counter
program ON
1
PLC timer
program ON
0
Alarm
message
R type F type ON
2
#6451
R7825 L
-
3
#6452
R7825 H
-
4
#6453
R7826 L
5
#6454
R7826 H PLC counter number of variable counter points setting
6
#6455
R7827 L
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
7
#6456
R7827 H
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
8
#6457
R7828 L
9
#6458
R7828 H
A
#6459
R7829 L
B
#6460
R7829 H
C
#6461
R7830 L
D
#6462
R7830 H
E
#6463
R7831 L
F
#6464
R7831 H
-
GOT
communication
connection
Counter
(fixed)
retention
PLC integrated timer
Number of variable integrated timer
points setting
-
Integrated
timer
(fixed)
retention
Onboard
ON
-
-
PLC timer number of variable timer points setting
High-speed input specification 1
High-speed input specification 2
High-speed output specification 1
High-speed output specification 2
III - 191
-
10. PLC Constants
10.5 Selecting the PLC Bit
0
Symbol
name
#6465
R7832 L
1
#6466
R7832 H
2
#6467
R7833 L
3
#6468
R7833 H
4
#6469
R7834 L
5
#6470
R7834 H
6
#6471
R7835 L
7
#6472
R7835 H
8
#6473
R7836 L
9
#6474
R7836 H
A
#6475
R7837 L
B
#6476
R7837 H
C
#6477
R7838 L
D
#6478
R7838 H
E
#6479
R7839 L
F
#6480
R7839 H
7
6
5
4
3
2
High-speed input specification 3
High-speed input specification 4
High-speed input specification 5
High-speed input specification 6
High-speed output specification 3
High-speed output specification 4
High-speed output specification 5
High-speed output specification 6
(Note 1) Be sure to set the bits indicated - and blanks to 0.
(Note 2) Parameters #6481 to #6496 are reserved for debugging by Mitsubishi.
III - 192
1
0
11. Macro List
11. Macro List
#
Item
7001 M [01]
to
to
7091 M [10]
7002
to
7092
Details
<Code>
Set the M code used for calling out the macro with
the M command.
This is valid when "#1195 Mmac" is set to 1.
<Type>
Set the macro call out type.
0
M98 P∆∆∆∆; and equivalent value call
1
G65 P∆∆∆∆; and equivalent value call
2
G66 P∆∆∆∆; and equivalent value call
3
G66.1 P∆∆∆∆; and equivalent value call
Setting range (unit)
1 to 9999
0 to 3
others M98 P∆∆∆∆; and equivalent value call
7003
to
7093
<Program No.>
Set the No. of the program to be called out.
M2mac
Program name of file
name
(up to 32 characters)
Set the type and program No. for when calling out the macro with the 2nd
miscellaneous command. The macro will be called out with the "#1170
M2name" address command when "#1198 M2mac" is set to 1.
7102
<Type>
Same as the M call macro.
0 to 3
7103
<Program No.>
Same as the M call macro.
Program name of file
name
(up to 32 characters)
7201 G [01]
to
to
7291 G [10]
<Code>
Set the G code to be used when calling the macro
with a G command. Do not set a G code used in the
system.
1 to 255
7202
to
7292
<Type>
Same as the M call Marco.
0 to 3
7203
to
7293
<Program No.>
Same as the M call Marco.
Smac
Program name of file
name
(up to 32 characters)
Set the type and program No. for when calling the macro with an S
command.
This is valid when "#1196 Smac" is set to 1.
7302
<Type>
Same as the M call Marco.
0 to 3
7303
<Program No.>
Same as the M call Marco.
Program name of file
name
(up to 32 characters)
Tmac
Set the type and program No. for when calling the macro with a T command.
This is valid when "#1197 Tmac" is set to 1.
7312
<Type>
Same as the M call macro.
0 to 3
7313
<Program No.>
Same as the M call macro.
Program name of file
name
(up to 32 characters)
III - 193
11. Macro List
#
Item
7401 ASCII
[01]
Details
The ASCII code macro parameters (#7402 to
7405) are validated.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
Valid
7402
Code
Set the ASCII code used to call macros with the
ASCII code.
L system:
A, B, D, F, H, I, J, K,
M, Q, R, S, T
M system:
A, B, F, H, I, K, M,
Q, R, S, T
7403
Type
Set the macro call type.
0: M98, 1: G65, 2: G66, 3: G66.1
0 to 3
7404
Program
No.
Set the program No. called with macro call.
0 to 99999999
7405
Variable
When the call type is "0", set the variable No. set
after the ASCII code.
100 to 149
7411 ASCII
[02]
Valid
The ASCII code macro parameters (#7412 to
7415) are validated.
0: Invalid
1: Valid
0/1
7412
Code
Set the ASCII code used to call macros with the
ASCII code.
L system:
A, B, D, F, H, I, J, K,
M, Q, R, S, T
M system:
A, B, F, H, I, K, M,
Q, R, S, T
7413
Type
Set the macro call type.
0: M98, 1: G65, 2: G66, 3: G66.1
0 to 3
7414
Program
No.
Set the program No. called with macro call.
0 to 99999999
7415
Variable
When the call type is "0", set the variable No. set
after the ASCII code.
100 to 149
III - 194
Setting range
0/1
12. Position Switch
12. Position Switch
The position switch (PSW) is used as an alternate switch for the dog switch provided on an axis of the
machine. The position switch uses parameters by which the names of axes and their corresponding
coordinates indicating imaginary dog positions are defined in advance. When the machine reaches the
imaginary dog position‚ a signal is output to the PLC interface. The position switch thus works as an
imaginary dog switch.
#
7500
Pcheck
Item
High-speed
switching of
position switch
Details
Setting range (unit)
Specify whether to perform position
0/1
switch area checking at high speeds.
0: Do not perform position switch area
checking at high speed (do it the same
as before).
1: Perform position switch area checking
at high speed.
Specify the name of the axis for which a X, Y, Z, U, V, W, A, B,
position switch is provided.
or C axis address
75 1 <axis>
Axis name
75 2 <dog1>
Imaginary dog
position 1
When the machine enters the range
-99999.999 to
between imaginary dog positions 1 and 2, 99999.999
a signal is output to the PLC.
(mm)
75 3 <dog2>
Imaginary dog
position 2
1st part system device : X1D00
2nd part system device : X1D20
75 4 <check>
Selection of area
check method
0/1
When position switch area checking at
high speed is selected, specify the mode
of area checking, i.e., whether to use the
command type machine position or
detector feedback position, for each
position switch point.
0: Use the command type machine
position as the machine position for
position switch area checking.
1: Use the detector feedback position as
the machine position for position switch
area checking.
(Note) This parameter is valid only when
1 set in "#7500 Pcheck. "
Position switch Nos. of PSW1 to PSW8 and signal devices
<axis>
<dog1>
<dog2>
Part system 1
device
Part system 2
device
PSW1
PSW2
#7501
#7511
#7502
#7512
#7503
#7513
X1D00
X1D01
X1D20
X1D21
PSW3
#7521
#7522
#7523
X1D02
X1D22
PSW4
#7531
#7532
#7533
X1D03
X1D23
:
:
:
:
:
:
PSW24
#7731
#7732
#7733
X1D17
X1D37
Instead of the dog switch provided on the machine axis‚ the coordinate values indicating imaginary dog
positions (dog1 and dog2) on the coordinate axis of the axis name preset with axis are set with the position
switches (PSW1 - PSW24). When the machine reaches the position‚ the signal is output to the device
corresponding to the PLC interface.
III - 195
12. Position Switch
Example of settings of dog1 and dog2 and operation
Setting of dog1 and
dog2
dog1, dog2 position
dog1 < dog2
dog1 > dog2
dog1 = dog2
dog1
dog2
Operation
A signal is output between
dog1 and dog2.
dog2
A signal is output between
dog2 and dog1.
dog1
Basic machine coordinate
system zero point
Imaginary
dog
dog1
PSW
width
dog2
If dog1 equals dog2‚ the
dog1 position triggers a
signal.
dog1 = dog2
Rotary axis
Setting of dog1 and dog2
dog1 < dog2
dog1, dog2 position
dog2
dog1
(Example)
dog1 = 30.000
dog2 = 330.000
dog1
dog2
(Example)
dog1 = -30.000
dog2 = 30.000
dog1 > dog2
dog1
dog2
(Example)
dog1 = 330.000
dog2 = 30.000
|dog1 - dog2| ≥ 360
dog2 dog1
(Example)
dog1 = 30.000
dog2 = 390.000
III - 196
Description
A signal is output
between dog1 and dog2.
A signal is also output
when dog1 is negative.
A signal is output
between dog2 and dog1.
A signal is kept output
when the difference
between dog1 and dog2
exceeds 360 degrees.
12. Position Switch
12.1 Canceling the Position Switch
12.1 Canceling the Position Switch
To cancel the position switch‚ enter the number (#75 1) of the position switch to be canceled in # ( ) of the
setting field‚ enter a slash "/" in DATA ( )‚ then press the INPUT key. This deletes the axis name for the
specified position switch‚ thus invalidating the position switch.
The data specified for <dog1> and <dog2> are still stored in memory. To validate the position switch again‚
therefore‚ it is enough to specify the axis name only.
III - 197
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
Turn the NC power OFF after setting parameters indicated with a (PR) in the table. The setting will be
validated after the power is turned ON again.
No.
Name
50001 MSR
(PR)
Motor series
50002 RTY
(PR)
Regeneration
option type
Details
Setting range
Default
value
0000
Set the motor series. This is automatically judged 0000 to FFFF
by the system when the default value (0000) is
(hexadecimal)
set.
Set the regenerative resistor type. Do not set values without a description.
0 0 0 0 (Default value)
Setting
value
1
Drive unit standard built-in resistor
(10CT has no built-in resistor)
Setting prohibited
2
MR-RB032 (30W)
3
MR-RB12 (100W)
4
MR-RB32 (300W)
5
MR-RB30 (300W)
6
7 to F
MR-RB50 (500W)
Setting prohibited
0
50003 PC1
(PR)
Details
Set the number of gear teeth on the motor side
and the number of gear teeth on the machine
side as an integer reduced to its lowest terms.
Set the total gear ratio if there are multiple gear
Machine side levels.
For rotary axes, set the motor rotation speed per
gear ratio
(motor rotation machine rotation.
ratio)
1 to 32767
1
1 to 32767
1
50005 PIT
(PR)
Feed pitch
360
50006 INP
In-position
In-position is detected when the position droop
detection width becomes this setting value or less.
1 to 32767
(° or mm)
1 to 32767
(1/1000° or
µm)
50004 PC2
(PR)
Motor side
gear ratio
(machine
rotation ratio)
Set 360 (default value) for rotary axes.
Set the feed lead for linear axes.
III - 198
50
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
50007 ATU
Name
Auto-tuning
Default
value
Set the adjustment of the auto-tuning. Do not set values without a description.
Details
Setting range
0 1 0 2 (Default setting value)
Setting
value
2
Low response (low-rigidity loads, loads
which easily vibrate)
Standard setting value
3
Standard setting value
4
Standard setting value
5
High response (high-rigidity loads, loads
which do not easily vibrate)
1
Setting
value
0
1
Setting
value
0
1
2
50008 PG1
Position loop
gain 1
50009
Details
Details
Standard
Large friction amount (set the position loop
gain slightly lower)
Details
Only auto-tuning PG2, VG2, VIC, and GD2.
Only auto-tuning PG1, PG2, VG1, VG2,
VIC, and GD2 (total gain).
(Standard setting)
No auto-tuning.
Set the position loop gain for the model loop.
Determine the tracking ability regarding the
position commands.
4 to 1000 (1/s)
70
(Not used.)
0
500
50011
Set the deceleration time from the clamp speed
0 to 32768
(Aspeed1). For normal rapid traverse, set the
(ms)
same value as the acceleration/deceleration time
constant.
(Not used.)
50012
(Not used.)
0
50010 EMGt
50013 MBR
Deceleration
control time
constant
Vertical axis
drop
prevention
time
Input the time the servo OFF is delayed during
servo OFF command. Increase the setting by
100ms at a time and set the minimum value
where the axis does not drop.
III - 199
0 to 1000 (ms)
0
100
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
Details
Default
value
Setting range
50014 NCH Notch filter No. Set the frequency of the machine resonance suppression filter.
Do not set values without a description.
50015
50016 JIT
Setting value
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Frequency
(Hz)
No
start
1125
563
375
282
225
188
161
(Not used.)
Jitter
compensation
0
Set the number of ignored jitter compensation pulses. Do not set values
without a description.
Setting value
0
1
2
3
Number of ignore
pulses
No start
1
2
3
50017
(Not used.)
0
50018
(Not used.)
0
50019 PG2 Position loop
gain 2
Set the position loop gain of the actual loop.
Determine the position responsiveness for
external disturbance.
1 to 500 (1/s)
25
50020 VG1 Speed loop
gain 1
Set the speed loop gain of the model loop.
Determine the tracking ability regarding the
speed commands.
20 to 5000
(1/s)
1200
50021 VG2 Speed loop
gain 2
Set the speed loop gain of the actual loop.
Determine the speed responsiveness for
external disturbance.
20 to 8000
(1/s)
600
1 to 1000 (ms)
20
50022 VIC
Speed integral Determine the characteristics of the speed lowcompensation frequency region.
50023 VDC Speed
differential
compensation
PI control normally results from a default value of 0 to 1000
1000.
Adjust the overshoot amount by lowering in
increments of 20.
1000
50024 DG2 Load inertia
ratio
Set the load inertia ratio for the motor inertia.
2.0
50025
(Not used.)
50030 MTY Motor type
(PR)
Set the motor type. This is automatically judged
by the system when the default value (0000) is
set.
0.0 to 50.0
(fold)
0
III - 200
0000 to FFFF
(hexadecimal)
0000
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
50050 MD1
Name
D/A output
channel 1
data No.
Details
Set the Nos. of the data to be output on D/A output channel 1.
0 0 0 0 (Default setting value)
Setting
value
Details
Magnification
0
Speed feedback
(with sign)
Maximum rotation speed = 8V
1
Current feedback
(with sign)
Maximum current (torque) = 8V
2
Speed feedback
(without sign)
Maximum rotation speed = 8V
3
Current feedback
(without sign)
Maximum current (torque) = 8V
Current command
Maximum current (torque) = 8V
Command F∆T
100000 [degrees/min] = 10V
6
Position droop 1
(1/1)
2048 [pulse] = 10V
7
Position droop 2
(1/4)
8192 [pulse] = 10V
8
Position droop 3
(1/16)
32768 [pulse] = 10V
9
Position droop 4
(1/32)
65536 [pulse] = 10V
A
Position droop 5
(1/64)
131072 [pulse] = 10V
4
5
50051 MO1
Default
value
Setting range
D/A output
Set this value when the zero level of D/A output
channel 1
channel 1 is not suitable.
output offset
(Not used.)
-999 to 999
(mV)
50053 MD2
D/A output
channel 2
data No.
0000 to FFFF
(hexadecimal)
0000
50054 MO2
D/A output
Set this value when the zero level of D/A output
channel 2
channel 2 is not suitable.
output offset
-999 to 999
(mV)
0
50052
Set the Nos. of the data to be output on D/A
output channel 2.
The descriptions are the same as "50050 MD1".
50055
(Not used.)
50100 station Number of
(PR)
indexing
stations
Set the number of stations. For linear axes, this
value is expressed by: number of divisions =
number of stations - 1.
0
0
0
III - 201
2 to 360
2
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
50101 Cont Control
(PR) 1
parameter 1
Default
value
This is a HEX setting parameter. Set bits without a description to their default
values.
Details
Setting range
bit
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Default
value
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
bit
0
1
Meaning when "0" is set
Meaning when "1" is set
High-speed zero point return after Dog-type return for each zero
establishment of zero point.
point return operation.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Reference position return
direction (+)
Reference position return
direction (-)
9
Rotation direction determined by
operation control signal (DIR)
Rotation direction in the shortcut
direction
A
Machine basic position becomes
the standard point
Electrical zero point becomes the
standard point
Coordinate zero point creation
valid
Rotation direction in operation
control signal (DIR) or in the
shortcut direction
Zero point established at power
supply ON position
Rotation direction in the arbitrary
position command sign direction
Stopper direction is positioning
direction
Stopper direction is in the sign
direction of the stopper amount
B
C
D
E
F
III - 202
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
50102 Cont2
(PR)
Default
value
Control
This is a HEX setting parameter. Set bits without a description to their default
parameter 2 values.
bit
F E D C B A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
value
Name
Details
bit
0
Meaning when "0" is set
Setting range
Meaning when "1" is set
1
Error not corrected at servo OFF Error corrected at servo OFF
2
Linear axis
Rotary axis
Station assignment direction CW Station assignment direction
CCW
Uniform index
Non-uniform index
DO channel standard assignment DO channel reverse assignment
2-wire detector communication
4-wire detector communication
Incremental detection
Absolute position detection
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
III - 203
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
Default
value
50103 EmgCont Emergency This is a HEX setting parameter. Set bits without a description to their default
(PR)
stop control values.
bit
F E D C B A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
value
No.
Name
Details
bit
0
1
2
3
Meaning when "0" is set
Setting range
Meaning when "1" is set
External
emergency stop
External emergency stop valid invalid (default
value)
Dynamic brake stop at
Deceleration control stop at
emergency stop
emergency stop
NC bus emergency stop input
NC bus emergency stop input
valid
invalid
NC bus emergency stop output NC bus emergency stop output
valid
invalid
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
III - 204
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
50104 tleng
(PR)
Linear axis
stroke
length
50110 ZRNspeed Reference
position
return
speed
Details
Set the movement stroke length for linear axes.
This is meaningless when setting non-uniform
assignments or commanding random positions.
Setting range
0.001 to
99999.999
(mm)
Set the clamp value of the feedrate when a
1 to 100000
reference position return is carried out. The
(°/min or
feedrate becomes the manual operation speed mm/min)
of the parameter group selected at that time, but
it is clamped by this parameter setting value.
Default
value
100.000
1000
50111 ZRNcreep Reference Set the approach speed to the reference
position
position after dog detection during a reference
return creep position return.
speed
1 to 65535
(°/min or
mm/min)
200
50112 grid mask
Grid mask
Set the amount that the dog is artificially
extended. Set 1/2 the grid spacing as a
standard.
0 to 65536
(1/1000° or
µm)
0
50113 grspc
(PR)
Grid
spacing
Divide the grid spacing that is the conventional
motor rotation movement amount into 2, 4, 8, or
16 divisions.
0 to 4
(1/2n division)
0
50114 ZRNshift
Reference
position
shift
amount
Set the shift amount in a dog-type reference
0 to 65536
point return from the electric zero point
(1/1000° or
determined on the grid to the reference position. µm)
0
50115 ST. ofset
Station
offset
Set the distance (offset) from the reference
position to station 1.
0.000
50116 ABS base
(PR)
Absolute
position
zero point
-99999.999 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
When movement of the machine coordinate zero -99999.999 to
point from the standard point is required during 99999.999
absolute position initializing, set that movement (° or mm)
amount.
50117 Limit (+)
Soft limit (+) Commands in the plus direction that exceed this -99999.999 to
setting value are not possible. If the machine is 99999.999
in a position exceeding the setting value,
(mm)
commands in the minus direction are possible.
The soft limit function will not operate if Limit (+)
and Limit (-) are set to the same value.
1.000
50118 Limit (-)
Soft limit (-) Commands in the minus direction that exceed
-99999.999 to
this value are not possible. If the machine is in a 99999.999
position exceeding the setting value, commands (mm)
in the plus direction are possible.
1.000
III - 205
0.000
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
50120 ABS
Type
Name
Absolute
position
detection
parameter
Default
value
This parameter is set as a hexadecimal. Set the default value for bits that
have no description.
Details
Setting range
bit
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Default
value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
bit
0
1
2
3
Meaning when "0" is set
Dogless-type method initializing
Mechanical stopper method
initializing
Meaning when "1" is set
Dog-type method initializing
Marked point alignment method
initializing
Electrical zero point direction (+) Electrical zero point direction (–)
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Set the value for the tolerable amount of
movement for a machine that moved during
power OFF in an absolute position detection
system. The "Absolute position power OFF
movement exceeded (ABS)" signal will turn
ON if the machine moves more than this
setting value during power OFF.
The movement amount is not checked when
this parameter is set to 0.000.
0.000 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
0.000
50130 backlash Backlash
compensation amount
Set the backlash compensation amount.
0 to 9999
(1/1000° or
µm)
0
50132
(Not used.)
0
50133
(Not used.)
0
50134
(Not used.)
0
50135
(Not used.)
0
50123 ABS
(PR) check
Absolute
position
power OFF
tolerable
movement
value
III - 206
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
< Operation parameter group 1 >
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
50150 Aspeed1 Operation
parameter
group 1
Automatic
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during automatic operation
1 to 100000
when operation parameter group 1 is selected. (°/min or
This parameter is regarded as the clamp value mm/min)
for the automatic operation speeds and
manual operation speeds of all operation
groups.
A speed exceeding Aspeed1 cannot be
commanded, even if set in the parameters.
50151 Mspeed1 Operation
parameter
group 1
Manual
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during manual operation or
JOG operation when operation parameter
group 1 is selected.
50152 time1.1
Operation
parameter
group 1
Acceleration/
deceleration
time constant
1
1 to 9999 (ms)
Set the linear acceleration/deceleration time
for Aspeed 1(the operation parameter group 1
automatic operation speed (clamp speed))
when operation parameter group 1 is selected.
When operating at speeds less than the clamp
speed, the axis will linearly accelerate/
decelerate at the inclination determined above.
When this is set together with acceleration/
deceleration time constant 2, S-shape
acceleration/ deceleration is carried out. In this
case, set the acceleration/deceleration time of
the linear part in this parameter.
50153 time1.2
Operation
parameter
group 1
Acceleration/
deceleration
time constant
2
50154 TL1
Operation
parameter
group 1
Torque limit
value
Set this parameter when carrying out S-shape
acceleration/deceleration.
When S-shape acceleration/deceleration is
carried out, set the total time of the non-linear
parts. When "1" is set in this parameter, linear
acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
In the handle feed operation mode, this set
value is regarded as the time constant for the
linear acceleration/deceleration.
Set the motor output torque limit value when
operation parameter group 1 is selected. At
the default value, the torque is limited at the
maximum torque of the motor specification.
Set the default value when torque limit is not
especially required. In the stopper positioning
operation mode, this becomes the torque limit
value when positioning to the stopper starting
coordinates.
50155 OD1
Operation
parameter
group 1
Excessive
error
detection
width
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
2000
100
1 to 999 (ms)
1
1 to 500 (%)
500
Set the excessive error detection width when
0 to 32767
operation parameter group 1 is selected. An
(° or mm)
alarm of excessive error (S03 0052) is
detected when the position droop becomes
larger than this setting value.
In the stopper positioning operation mode, this
becomes the excessive error detection width
when positioning to the stopper starting
coordinates.
III - 207
Default
value
5000
100
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
50156 just1
Operation
parameter
group 1
Set position
output width
The signal indicating that the machine
0.000 to
position is at any one of the stations is the set 99999.999
position reached (JST) signal. During
(° or mm)
automatic operation, the automatic set
position reached (JSTA) signal is also output
under the same conditions.
Set the tolerable values at which these
signals are output when operation parameter
group 1 is selected. These signals turn OFF
when the machine position is separated from
the station by more than this value.
50157 near1
Operation
parameter
group 1
Near set
position output
width
The signal indicating that the machine
position is near any one of the station
positions is the near set position (NEAR)
signal.
Set the tolerable value at which this signal is
output when operation parameter group 1 is
selected. This value is generally set wider
than the set position output width.
During operations, this is related to special
commands when the station selection is "0".
III - 208
0.000 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
Default
value
0.500
1.000
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
< Operation parameter group 2 >
No.
50158 Aspeed2
Name
Details
Setting range
Default
value
5000
Operation
parameter
group 2
Automatic
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during automatic operation
when operation parameter group 2 is
selected.
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
50159 Mspeed2 Operation
parameter
group 2
Manual
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during manual operation or
JOG operation when operation parameter
group 2 is selected.
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
50160 time2.1
Operation
parameter
group 2
Acceleration/
deceleration
time
constant 1
1 to 9999 (ms) 100
Set the linear acceleration/deceleration time
for the operation parameter group 1 automatic
operation speed (clamp speed) when
operation parameter group 2 is selected.
When operating at speeds less than the
clamp speed, the axis will linearly
accelerate/decelerate at the inclination
determined above.
When this is set together with
acceleration/deceleration time constant 2, Sshape acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
In this case, set the acceleration/deceleration
time of the linear part in this parameter.
50161 time2.2
Operation
parameter
group 2
Acceleration/
deceleration
time
constant 2
Set this parameter when carrying out S-shape 1 to 999 (ms)
acceleration/deceleration.
When S-shape acceleration/deceleration is
carried out, set the total time of the non-linear
parts. When 1 is set in this parameter, linear
acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
In the handle feed operation mode, this set
value is regarded as the time constant for the
linear acceleration/deceleration.
III - 209
2000
1
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
Default
value
500
50162 TL2
Operation
parameter
group 2
Torque limit
value
Set the motor output torque limit value when
1 to 500 (%)
operation parameter group 2 is selected. At
the default value, the torque is limited at the
maximum torque of the motor specifications.
Set the default value when torque limit is not
especially required.
In the stopper positioning operation mode, this
becomes the torque limit value during stopper
operation.
50163 OD2
Operation
parameter
group 2
Excessive
error
detection
width
Set the excessive error detection width when
0 to 32767
operation parameter group 2 is selected. An
(° or mm)
excessive error alarm (S03 0052) is detected
when the position droop becomes larger than
this setting value.
In the stopper positioning operation mode, this
becomes the excessive error detection width
during stopper operation.
100
50164 just2
Operation
parameter
group 2
Set position
output width
The signal indicating that the machine position 0.000 to
is at any one of the stations is the set position 99999.999
reached (JST) signal. During automatic
(° or mm)
operation, the automatic set position reached
(JSTA) signal is also output under the same
conditions.
Set the tolerable values at which these signals
are output when operation parameter group 2
is selected. These signals turn OFF when the
machine position is separated from the station
by more than this value.
0.500
50165 near2
Operation
parameter
group 2
Near set
position
output width
The signal indicating that the machine position 0.000 to
is near any one of the station positions is the
99999.999
near set position (NEAR) signal. Set the
(° or mm)
tolerable values at which these signals are
output when operation parameter group 2 is
selected. These values are generally set wider
than the set position output width.
During operations, this is related to special
commands when the station selection is "0".
1.000
III - 210
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
< Operation parameter group 3 >
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
Default
value
5000
50166 Aspeed3 Operation
parameter
group 3
Automatic
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during automatic operation
when operation parameter group 3 is selected.
50167 Mspeed3 Operation
parameter
group 3
Manual
operation
speed
Set the feedrate during manual operation or JOG 1 to 100000
operation when operation parameter group 3 is
(°/min or
selected.
mm/min)
50168 time3.1
Operation
parameter
group 3
Acceleration
/deceleration
time
constant 1
Set the linear acceleration/deceleration time for 1 to 9999 (ms) 100
the operation parameter group 1 automatic
operation speed (clamp speed) when operation
parameter group 3 is selected. When operating
at speeds less than the clamp speed, the axis
will linearly accelerate/decelerate at the
inclination determined above.
When this is set together with
acceleration/deceleration time constant 2, Sshape acceleration/deceleration is carried out. In
this case, set the acceleration/deceleration time
of the linear part in this parameter.
50169 time3.2
Operation
parameter
group 3
Acceleration
/deceleration
time
constant 2
Set this parameter when carrying out S-shape
1 to 9999 (ms) 1
acceleration/deceleration.
When S-shape acceleration/deceleration is
carried out, set the total time of the non-linear
parts. When 1 is set in this parameter, linear
acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
In the handle feed operation mode, this set value
is regarded as the time constant for the linear
acceleration/deceleration.
III - 211
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
2000
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
50170 TL3
Operation
parameter
group 3
Torque
limit value
Set the motor output torque limit value when
operation parameter group 3 is selected. At the
default value, the torque is limited at the
maximum torque of the motor specifications.
Set the default value when torque limit is not
especially required.
In the stopper positioning operation mode, this
becomes the pressing torque limit value after
completion of the positioning.
50171 OD3
Operation
parameter
group 3
Excessive
error
detection
width
Set the excessive error detection width when
0 to 32767
operation parameter group 3 is selected. An
(° or mm)
excessive error alarm (S03 0052) is detected
when the position droop becomes larger than this
setting value.
In the stopper positioning operation mode, this
becomes the excessive error detection width
during pressing after completion of the
positioning.
100
50172 just3
Operation
parameter
group 3
Set
position
output
width
The signal indicating that the machine position is 0.000 to
99999.999
at any one of the stations is the set position
(° or mm)
reached (JST) signal. During automatic
operation, the automatic set position reached
(JSTA) signal is also output under the same
conditions.
Set the tolerable values at which these signals
are output when operation parameter group 3 is
selected. These signals turn OFF when the
machine position is separated from the station by
more than this value.
0.500
50173 near3
Operation
parameter
group 3
Near set
position
output
width
The signal indicating that the machine position is
near any one of the station positions is the near
set position (NEAR) signal. Set the tolerable
values at which these signals are output when
operation parameter group 3 is selected. These
values are generally set wider than the set
position output width.
During operations, this is related to special
commands when the station selection is "0".
0.000 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
1.000
III - 212
1 to 500 (%)
Default
value
500
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
< Operation parameter group 4 >
No.
Name
50174 Aspeed4
Operation
parameter
group 4
Automatic
operation
speed
50175 Mspeed4 Operation
parameter
group 4
Manual
operation
speed
50176 time4.1
Operation
parameter
group 4
Acceleratio
n/decelerati
on time
constant 1
50177 time4.2
Details
Setting range
Set the feedrate during automatic operation
when operation parameter group 4 is selected.
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
Set the feedrate during manual operation or
JOG operation when operation parameter
group 4 is selected.
1 to 100000
(°/min or
mm/min)
Default
value
5000
2000
Set the linear acceleration/deceleration time for 1 to 9999 (ms) 100
the operation parameter group 1 automatic
operation speed (clamp speed) when operation
parameter group 4 is selected. When operating
at speeds less than the clamp speed, the axis
will linearly accelerate/decelerate at the
inclination determined above.
When this is set together with
acceleration/deceleration time constant 2, Sshape acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
In this case, set the acceleration/deceleration
time of the linear part in this parameter.
Operation
Set this parameter when carrying out S-shape 1 to 9999 (ms) 1
parameter acceleration/deceleration.
group 4
When S-shape acceleration/deceleration is
Accelerati- carried out, set the total time of the non-linear
on/decelera parts. When 1 is set in this parameter, linear
tion time
acceleration/deceleration is carried out.
constant 2 In the handle feed operation mode, this set
value is regarded as the time constant for the
linear acceleration/deceleration.
III - 213
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
Details
Setting range
Default
value
500
50178 TL4
Operation
parameter
group 4
Torque
limit value
Set the motor output torque limit value when
operation parameter group 4 is selected. At the
default value, the torque is limited at the
maximum torque of the motor specifications.
Set the default value when torque limit is not
especially required.
In the stopper method initializing mode in
absolute position detection systems, this
becomes the torque limit value during stopper
operation.
1 to 500 (%)
50179 OD4
Operation
parameter
group 4
Excessive
error
detection
width
0 to 32767
(° or mm)
100
50180 just4
Operation
parameter
group 4
Set
position
output
width
Set the excessive error detection width when
operation parameter group 4 is selected. An
excessive error alarm (S03 0052) is detected
when the position droop becomes larger than this
setting value.
In the stopper method initializing mode in
absolute position detection systems, this
becomes the excessive error detection width
during stopper operation.
The signal indicating that the machine position is
at any one of the stations is the set position
reached (JST) signal. During automatic
operation, the automatic set position reached
(JSTA) signal is also output under the same
conditions.
Set the tolerable values at which these signals
are output when operation parameter group 4 is
selected. These signals turn OFF when the
machine position is separated from the station by
more than this value.
0.000 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
0.500
50181 near4
Operation
parameter
group 4
Near set
position
output
width
The signal indicating that the machine position is
near any one of the station positions is the near
set position (NEAR) signal. Set the tolerable
values at which these signals are output when
operation parameter group 4 is selected. These
values are generally set wider than the set
position output width.
During operations, this is related to special
commands when the station selection is "0".
0.000 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
1.000
III - 214
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
50190 stpos2
Station 2
coordinate
value
50191 stpos3
Station 3
coordinate
value
50192 stpos4
Station 4
coordinate
value
50193 stpos5
Station 5
coordinate
value
50194 stpos6
Station 6
coordinate
value
50195 stpos7
Station 7
coordinate
value
Station 8
coordinate
value
50196 stpos8
50197 stpos9
Details
Setting range
Set the coordinate value of each station when
non-uniform assignment is selected.
The station 1 coordinate value is fixed at 0.000
(machine coordinate zero point).
-99999.999 to
99999.999
(° or mm)
Default
value
0.000
Station 9
coordinate
value
50200 PSWcheck PSW
detection
method
This is a HEX setting parameter. Set bits without a description to their default
values.
bit
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Default
value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
bit Position switch Meaning when "0" is set
The position switch
0 PSW1
output is judged by the
1 PSW2
machine position of the
2 PSW3
command system.
PSW4
3
4
PSW5
5
PSW6
6
PSW7
7
PSW8
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
III - 215
Meaning when "1" is set
The position switch
output is judged by the
machine FB position
(actual position).
13. Auxiliary Axis Parameter
No.
Name
50201 PSW1dog1
50202 PSW1dog2
PSW1 area
setting 1
PSW1 area
setting 2
50203 PSW2dog1
50204 PSW2dog2
PSW2 area
setting 1
PSW2 area
setting 2
50205 PSW3dog1
50206 PSW3dog2
PSW3 area
setting 1
PSW3 area
setting 2
50207 PSW4dog1
50208 PSW4dog2
PSW4 area
setting 1
PSW4 area
setting 2
50209 PSW5dog1
50210 PSW5dog2
PSW5 area
setting 1
PSW5 area
setting 2
50211 PSW6dog1
50212 PSW6dog2
PSW6 area
setting 1
PSW6 area
setting 2
PSW7 area
setting 1
PSW7 area
setting 2
50213 PSW7dog1
50214 PSW7dog2
Details
Setting range
When the machine position is in the region
-99999.999 to
between region settings 1 and 2, the position 99999.999
switch of each No. will turn ON.
(° or mm)
Whether the value of setting 1 is larger than
setting 2 (vice versa) does not affect the
position switch operation.
For rotary axes, the output turns ON at the
region without including 0.000 degree.
Default
value
0.000
50215 PSW8dog1
50216 PSW8dog2
PSW8 area
setting 1
PSW8 area
setting 2
50220 push.1
Stopper
amount
50221 push.t1
Stopper
Set the standby time from the stopper
0 to 9999 (ms)
standby time starting coordinate positioning to the stopper
operation start during stopper positioning
operations.
0
50222 push.t2
Stopper
Set the time from the completion of the
0 to 9999 (ms)
torque
stopper operation to the changeover of the
release time stopper torque during stopper positioning
operations.
Set position Set the time from the completion of the
0 to 9999 (ms)
signal output stopper operation to the output of the
delay time
automatic set position reached (JSTA), set
position reached (JST), and near set position
(NEAR) signals during stopper positioning
operations.
0
50223 push.t3
Set the command stroke of the stopper
operation during stopper positioning
operations.
III - 216
0.000 to
359.999
(° or mm)
0.000
0
Revision History
Date of revision
Manual No.
Sept. 2004
IB-1500124-A
Revision details
First edition created.
Notice
Every effort has been made to keep up with software and hardware revisions in the
contents described in this manual. However, please understand that in some
unavoidable cases simultaneous revision is not possible.
Please contact your Mitsubishi Electric dealer with any questions or comments
regarding the use of this product.
Duplication Prohibited
This manual may not be reproduced in any form, in part or in whole, without written
permission from Mitsubishi Electric Corporation.
© 2004 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
MITSUBISHI CNC
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
HEAD OFFICE : MITSUBISHI DENKI BLDG., 2-2-3, MARUNOUCHI, CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO 100-8310, JAPAN
MODEL
700 Series
MODEL
CODE
008-336
Manual No.
IB-1500124 (ENG)
Specifications subject to change without notice.
IB(NA)1500124(ENG)-A(0409)MEE
Printed in Japan on recycled paper.