
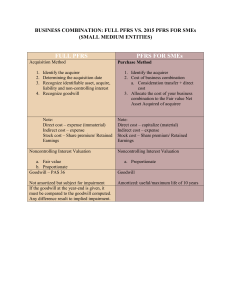
ABC - Final Exam mitchieteocson@gmail.com Switch account Draft saved * Required Email* Surname, Given name, MI* The method required under PFRS 3 to be used in accounting for business combinations is* Buy method Acquisition method Purchase method Combination method Should the following costs be included in the consideration transferred in a business combination, according to PFRS 3 Business Combinations? I. Costs of maintaining an acquisitions department. II. Fees paid to accountants to effect the combination.* No, Yes Yes, Yes Yes, No No, No PFRS 3 requires that the contingent liabilities of the acquired entity should be recognized in the balance sheet at fair value. The existence of contingent liabilities is often reflected in a lower purchase price. Recognition of such contingent liabilities will* Increase the value attributed to goodwill, thus decreasing the risk of impairment of goodwill. Increase the value attributed to goodwill, thus increasing the risk of impairment of goodwill. Decrease the value attributed to goodwill, thus decreasing the risk of impairment of goodwill. Decrease the value attributed to goodwill, thus increasing the risk of impairment of goodwill. Are the following statements about an acquisition true or false, according to PFRS 3 Business combinations? I. The acquirer should recognize the acquiree's contingent liabilities if certain conditions are met. II. The acquirer should recognize the acquiree's contingent assets if certain conditions are met.* True, False True, True False, False False, True 1. Given the following information, how is goodwill from a business combination computed under PFRS 3?A = Consideration transferred; B = Non-controlling interest in net assets of subsidiary; C = Previously held equity interest; D = Fair value of net identifiable assets of subsidiary; % = Percentage of ownership acquired by the parent in the subsidiary* A+B+C-D (A+C) – (D x %) (A+B) – [(D x %) – B] A – (D x %) In a business combination, an acquirer's interest in the fair value of the net assets acquired exceeds the consideration transferred in the combination. Under PFRS 3 Business Combinations, the acquirer should* reassess the recognition and measurement of the net assets acquired and the consideration transferred, then recognize any excess immediately in other comprehensive income reassess the recognition and measurement of the net assets acquired and the consideration transferred, then recognize any excess immediately in profit or loss recognize the excess immediately in other comprehensive income recognize the excess immediately in profit or loss Which one of the following reasons would not contribute to the creation of negative goodwill?* A requirement in an IFRS to measure net assets acquired at a value other than fair value. Errors in measuring the fair value of the acquiree’s net identifiable assets or the cost of the business combination. A bargain purchase. Making acquisitions at the top of a “bull” market for shares The “excess of the acquirer’s interest in the net fair value of acquiree’s identifiable assets, liabilities, and contingent liabilities over cost” (formerly known as negative goodwill) should be* Reassessed as to the accuracy of its measurement and then recognized immediately in profit or loss. Reassessed as to the accuracy of its measurement and then recognized in retained earnings. Amortized over the life of the assets acquired. Carried as a capital reserve indefinitely. This type of business combination occurs when, for example, a private entity decides to have itself “acquired” by a smaller public entity in order to obtain a stock exchange listing.* Step acquisition Stock acquisition Reverse acquisition Rewind acquisition Acquisition accounting requires an acquirer and an acquiree to be identified for every business combination. Where a new entity (H) is created to acquire two preexisting entities, S and A, which of these entities will be designated as the acquirer?* A H A or S S The aggregate cash flows arising from acquisitions and from disposals of subsidiaries or other business units resulting to loss or obtaining of control are presented separately and classified as* Disclosed only Operating activities Financing activities Investing activities Cash flows arising from changes in ownership interests in a subsidiary that do not result in a loss of control are classified as cash flows from* Disclosed only Operating activities Financing activities Investing activities PFRS 3 requires the acquirer in a business combination to measure the acquiree’s identifiable tangible and intangible assets and liabilities at (with some limited exceptions)* some other amount acquisition-date fair value cost fair value less transaction costs Which of the following accounting methods must be applied to all business combinations under PFRS 3 Business Combinations?* Acquisition method. Purchase method. Pooling of interests method. Equity method. PESTER TO ANNOY is involved in a business acquisition on January 1, 20x1. At the date of acquisition the deferred tax assets were ₱300,000. On January 1, 20x1, the directors considered that realization of the deferred tax assets were not probable. What effect would this decision have on the allocation of the purchase price?* Negative goodwill of ₱300,000 would arise. There would be no effect on goodwill. The unrecognized deferred tax would be allocated to goodwill, which would increase by ₱300,000. The value of goodwill would decrease by ₱300,000. A parent entity is acquiring a majority holding in an entity whose shares are dealt in on a recognized market. Under PFRS 3 Business Combinations, which of the following measurement bases may be used in measuring the non-controlling interest at the acquisition date? I. The nominal value of the shares in the acquiree not acquired; II. The fair value of the shares in the acquiree not acquired; III. The non-controlling interest in the acquiree's assets and liabilities at book value; IV. The non-controlling interest in the acquiree's assets and liabilities at fair value* II and III II and IV IV only ASININE STUPID Company acquired a 30% equity interest in OBTUSE TORPID Company many years ago. In the current accounting period it acquired a further 40% equity interest in OBTUSE. Are the following statements true or false, according to PFRS 3 Business Combinations? I. ASININE's pre-existing 30% equity interest in OBTUSE should be remeasured at fair value at the acquisition date. II. II. ASININE's net assets should be remeasured at fair value at the acquisition date.* True, True False, False False, True True, False The SKEWER Company acquired 80% of PIERCE Company for a consideration transferred of ₱100 million. The consideration was estimated to include a control premium of ₱24 million. PIERCE's net assets were ₱85 million at the acquisition date. Are the following statements true or false, according to PFRS 3 Business Combinations? I. Goodwill should be measured at ₱32 million if the non-controlling interest is measured at its share of PIERCE's net assets. II. Goodwill should be measured at ₱34 million if the non-controlling interest is measured at fair value* True, True False, False True, False False, True PFRS 3 requires all identifiable intangible assets of the acquired business to be recorded at their fair values. Many intangible assets that may have been subsumed within goodwill must be now separately valued and identified. Under PFRS 3, when would an intangible asset be “identifiable”?* When it meets the definition of an intangible asset in PAS 38, Intangible Assets, and its fair value can be measured reliably. Where it has been acquired in a business combination When it meets the definition of an asset in the Conceptual Framework document only. If it has been recognized under local generally accepted accounting principles even though it does not meet the definition in PAS 38. Which of the following examples is unlikely to meet the definition of an intangible asset for the purpose of PFRS 3?* Marketing related, such as trademarks and internet domain names. Customer related, such as customer lists and contracts. Technology based, such as computer software and databases. Pure research based, such as general expenditure on research. An intangible asset with an indefinite life is one where* There is no foreseeable limit on the period over which the asset will generate cash flows. There is a contractual or legal arrangement that lasts for a period in excess of five years The length of life is over 20 years. The directors feel that the intangible asset will not lose value in the foreseeable future. An intangible asset with an indefinite life is accounted for as follows:* Amortize and impairment tested if there is a “trigger event.” No amortization but annual impairment test. Amortized and no impairment test. Amortized and impairment tests annually. An acquirer should at the acquisition date recognize goodwill acquired in a business combination as an asset. Goodwill should be accounted for as follows* Write off against retained earnings. Recognize as an intangible asset and impairment test when a trigger event occurs. Recognize as an intangible asset and amortize over its useful life. Recognize as an intangible asset and annually impairment test (or more frequently if impairment is indicated). If the impairment of the value of goodwill is seen to have reversed, then the company may* Reverse the impairment charge and credit retained earnings. Not reverse the impairment charge. Reverse the impairment charge and credit income for the period. Reverse the impairment charge only if the original circumstances that led to the impairment no longer exist and credit retained earnings. An acquirer might obtain control of an acquire in all of the following, except* By transferring cash, cash equivalents and other assets By acquiring interest in a joint venture By contract alone, even without consideration By issuing equity interests A business combination maybe structured in all of the following, except* One entity transfers its net assets to another entity An entity acquires assets that are not a business. A group of former owners of one of the combining entities obtains control of the combined entity One or more businesses become subsidiaries of an acquirer It is a business combination in which all of the combining entities or businesses ultimately are controlled by the same party or parties both before and after the combination and that control is not transitory.* Combination of entities or businesses under common control True merger Consolidation Merger of equals On acquisition, all identifiable assets and liabilities, including goodwill, will be allocated to cash-generating units within the business combination. Goodwill impairment is assessed within the cash-generating units. If the combined organization has cashgenerating units significantly below the level of an operating segment, then the risk of an impairment charge against goodwill as a result of PFRS 3 is* Likely to be unchanged from previous accounting practice. Significantly decreased because goodwill will be spread across many cash-generating units. Likely to be decreased because goodwill will be a smaller amount due to the greater recognition of other intangible assets. Significantly increased because poorly performing units can no longer be supported by those that are performing well. The management of an entity is unsure how to treat a restructuring provision that they wish to set up on the acquisition of another entity. Under PFRS 3, the treatment of this provision will be* To provide for the amount and, if the provision is overstated, to release the excess to the income statement in the post-acquisition period. To include the provision in the allocated cost of acquisition if the acquired entity commits itself to a restructuring within a year of acquisition. To include the provision in the allocated cost of acquisition. A charge in the income statement in the post-acquisition period. MIME TO IMMITATE Co. initially tested its goodwill for impairment on September 30, 20x1. When should MIME perform its second impairment testing on its goodwill?* on or before December 31, 20x2 at any date during 20x2 at any date not earlier than September 30, 20x2 on or before September 30, 20x2 For purposes of impairment testing, PAS 36* requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to cash-generating units 12 months after the date of acquisition. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to corporate assets in the year of business combination. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to cash-generating units in the year of business combination. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to operating segments 3 months after the date of acquisition. each of the acquirer’s each of the acquirer’s each of the acquirer’s each of the acquirer’s On September 1, 20x1, TEPID Co. acquired LUKEWARM Co. in a business combination that resulted to goodwill. By December 31, 20x1, the initial allocation of goodwill is not yet completed. According to PAS 36, TEPID should* complete the initial allocation before complete the initial allocation before complete the initial allocation before complete the initial allocation before the the the the end of December 31, 20x1. end of September 1, 20x2. end of December 31, 20x2. end of November 30, 20x1. Which of the following is incorrect regarding the accounting for business combinations in accordance with PFRSs?* Goodwill is computed as the difference between the consideration transferred and the acquisition-date fair value of net identifiable assets acquired. Any goodwill recognized on acquisition date should be allocated to the acquirer’s CGUs prior to the end of the year of acquisition. If allocation is incomplete prior to the end of the year of acquisition, the allocation should be completed prior to the end of the immediatel y preceding year. PFRS 3 requires the use of the acquisition method in accounting for business combination. In applying the acquisition method, PFRS 3 requires that the acquirer should be identified. For purposes of impairment testing, PAS 36* requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to each of the acquirer’s corporate assets in the year of business combination. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to each of the acquirer’s cash-generating units 12 months after the date of acquisition. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to each of the acquirer’s cash-generating units in the year of business combination. requires goodwill acquired in a business combination to be allocated to each of the acquirer’s operating segments 3 months after the date of acquisition. Goodwill must not be amortized under PFRS 3. The transitional rules do not require restatement of previous balances written off. If an entity is adopting PFRS for the first time, and it wishes to restate all prior acquisitions in accordance with PFRS 3, then it must apply the PFRS to* All acquisitions from the date of the earliest. Only past and present acquisitions of entities that have previously and currently prepared their financial statements using PFRS. Only those acquisitions since the issue of the PFRS 3 and PAS 22, Business Combinations, to the earlier ones. Those acquisitions selected by the entity. On September 1, 20x1, TEPID Co. acquired LUKEWARM Co. in a business combination that resulted to goodwill. By December 31, 20x1, the initial allocation of goodwill is not yet completed. According to PAS 36, TEPID should* complete the initial allocation before the end of December 31, 20x2. complete the initial allocation before the end of November 30, 20x1. complete the initial allocation before the end of September 1, 20x2. complete the initial allocation before the end of December 31, 20x1. Which of the following factors is used as multiplier of super profits in valuation of goodwill of a business?* Normal profits Simple profits Number of years’ purchase Normal rate of return Average capital employed in the business A business combination may be legally structured as a merger, a consolidation, an investment in stock, or a direct acquisition of assets. Which of the following describes a business combination that is legally structured as a merger?* The surviving company is neither of the two combining companies. A parent-subsidiary relationship is established. An investor-investee is established. The surviving company is one of the two combining companies Business combinations are accomplished either through a direct acquisition of assets and liabilities by a surviving corporation or by stock investment in one or more companies. A parent-subsidiary relationship always arise from a* Greater than 50% stock investment in another company. Vertical combination Horizontal combination Tax-free reorganization Should the following costs be included in the consideration transferred in a business combination, according to IFRS 3, Business Combination? 1. Costs of maintaining an acquisitions department. 2. Fees paid to accountants to effect the combination.* Yes No Costs of goodwill from purchase business combination Costs of developing goodwill internally Costs of goodwill from purchase business combination Costs of developing goodwill internally On August 31, 2019, Cheese Co. issued 100,000 shares of its P20 par value common stock for the net assets of Butter , Co, in a business combination accounted for by the purchase method. The market value of Cheese Co.’s common stock on august 31 was P36 per share. Cheese paid a fee of P160,000 to the consultant who arranged this acquisition. Cost of registering and issuing the equity securities amounted to P80,000. No goodwill was involved in the purchase. What amount should cheese capitalize as the cost of acquiring Butter’s net assets?* P3,600,000 P3,680,000 P3,760,000 P3,840,000 100% of the equity share capital of the Moon Co. was acquired by the River Co. on July 30, 2019. River Co. issued 500,000 new P1 ordinary shares which had a fair value of P8 each at the acquisition date. In addition, the acquisition resulted in River incurring fees payable to external advisers of P200,000 and share issue costs of P180,000.In accordance with IFRS 3, Business Combination, goodwill at the acquisition date is measured by subtracting the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed from* P4,000,000 P4,180,000 P4,200,000 P4,380,000 In a business combination, Best Co purchased Foods Co. at a cost that resulted in recognition of goodwill having an expected 10-year benefit period. However, Best plans to make additional expenditures to maintain goodwill for a total of 40 years. What costs should be capitalized* Acquisition costs Maintenance cost Acquisition costs and Maintenance Costs None of the above In a business combination, Best Co purchased Foods Co. at a cost that resulted in recognition of goodwill having an expected 10-year benefit period. However, Best plans to make additional expenditures to maintain goodwill for a total of 40 years. How many years should the costs be amortized?* 0 years 10 years 40 years None the above Philippine Co. acquired 100% of the outstanding common stock of Star Co. in a purchase transaction. The cost of acquisition exceeded the fair value of the identifiable net assets and assumed liabilities. The general guidelines for assigning amounts to the inventories acquired provide for:* Raw materials to be valued at original cost. Work in process to be valued at the estimated selling prices of finished goods, less both costs to complete and costs of disposal. Finished goods to be valued at estimated selling prices, less both costs of disposal and a reasonable profit allowance. Finished goods to be valued at replacement cost. What is the amount of goodwill resulting from the business combination?* P120,000 P 50,000 P150,000 P 20,000 On January 1, 2020, Pine Corp acquired the net assets of Apple Corp. in a business combination. At that date, the property, plant and equipment of Apple had a book value of P21,000,000 and a fair value of P22,500,000. These assets were originally acquired at a cost of P30,000,000, but would presently cost P12,000,000.Using the purchase method, what amount should the combined entity report its property, plant and equipment account?* P 36,000,000 P 21,000,000 P 30,000,000 P 22,500,000 For the next items refer to the image below In the books of Monte Co., this transaction resulted to:* Goodwill recorded at P441,400 Goodwill recorded at P224,800 Current assets increased by P224,800 Current assets decreased by P224,800 The net assets (excluding goodwill, if any) recorded in the books of the acquiring company was:* P 1,309,000 P 958,200 P 1,400,000 P 1,175,200 Compared with the unadjusted values recorded in the books of Dole Co., this transaction resulted to:* P224,800 more than recorded owners’ equity P666,200 more than recorded owners’ equity P441,400 more than recorded owners’ equity P224,800 less than recorded owners’ equity Assuming Monte Co. paid P1,000,000 for the net assets of Dole Co., the excess of fair market value over cost was:* P 175,200 P 157,334 P 162,200 P 152,614 The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Noy Company is contemplating selling the business to new interests. The cumulative earnings for the past 5 years amounted to P800,000. The annual earnings, based on an average rate of return on investment for this industry, would have been P145,000.If excess earnings are to be capitalized at 8%, what would be the implied goodwill in this transaction?* P937,500 P187,500 P800,000 P 52,400 Refer to the image below On the assumption that the “purchase” method is applied, the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity of Mix Co. reflecting the combination is:* P6,000,000 P6,500,000 P6,800,000 P6,200,000 The capital stock reflecting the combination under purchase method is:P3,000,000* P3,300,000 P3,500,000 P4,000,000 P3,000,000 Refer to the image Below Based on the information provided, in Newsprint's 2018 consolidated income statement, what amount should be included as foreign exchange loss in computing net income, if the LCU is the functional currency and the translation method is appropriate?* Php 25,000 Php 8,000 Php 13,000 Php 28,000 Based on the information provided, in Newsprint's 2018 consolidated income statement, what amount should be included as foreign exchange loss in computing net income, if the U.S. dollar is the functional currency and the remeasurement method is appropriate?* Php 28,000 Php 25,000 Php 10,000 Php 15,000 Infinity Corporation acquired 80 percent of the common stock of an Egyptian company on January 1, 2018. The goodwill associated with this acquisition was $18,350. Exchange rates at various dates during 2018 follow: January 1, 2018 "1 E£ = $ 0.1835 "December 31, 2018 "1 E£ = $ 0.1850" ; Average for 2018 "1 E£ = $ 0.1840" Goodwill suffered an impairment of 20 percent during the year. If the functional currency is the Egyptian Pound, how much goodwill impairment loss should be reported on Infinity's consolidated statement of income for 2018?* $3,670 $3,680 $3,690 $3,700 When the local currency of the foreign subsidiary is the functional currency, a foreign subsidiary's inventory carried at cost would be converted to Philippine peso by:* remeasurement using historical exchange rates. remeasurement using the current exchange rate. translation using historical exchange rates. translation using the current exchange rate. When the local currency of the foreign subsidiary is the functional currency, a foreign subsidiary's income statement accounts would be converted to Philippine peso by:* translation using historical exchange rates. remeasurement using the current exchange rate at the time of statement preparation. remeasurement using current exchange rates at the time of statement preparation. translation using average exchange rate for the period. If the restatement method for a foreign subsidiary involves remeasuring from the local currency into the functional currency, then translating from functional currency to Philippine peso, the functional currency of the subsidiary is: I. Philippines peso; II. Local currency unit. III. A third country's currency.* III Either I or II I II If the Philippine peso is the currency in which the foreign affiliate's books and records are maintained, and the Philippines peso is also the functional currency* no restatement is required. the translation method should be used for restatement. either translation or remeasurement could be used for restatement. the remeasurement method should be used for restatement. All of the following stockholders' equity accounts of a foreign subsidiary are translated at historical exchange rates except:* preferred stock. retained earnings. common stock. additional paid-in capital. Dividends of a foreign subsidiary are translated at:* the exchange rate on the date of declaration. the current exchange rate on the date of preparation of the financial statement. the average exchange rate for the year. the exchange rate on the record date If the functional currency is the local currency of a foreign subsidiary, what exchange rates should be used to translate the items below, assuming the foreign subsidiary is in a country which has not experienced hyperinflation over three years?* Current Rate Historical Rate Average Rate Depreciation - Equipment Equipment Inventories Depreciation - Equipment Equipment Inventories If the functional currency is the local currency of a foreign subsidiary, what exchange rates should be used to translate the items below, assuming the foreign subsidiary is in a country which has not experienced hyperinflation over three years?* Current Rate Historical Rate Average Rate Premium Bond Payables Sales Common Stock Premium Bond Payables Sales Common Stock Which combination of accounts and exchange rates is correct for the translation of a foreign entity's financial statements from the functional currency to Philippine peso?* Exchange Rate: Current ----- Accounts: Salary Expense, Sales, Depreciation Expense Exchange Rate: Weighted ----- Accounts: Retained Earnings, Land, Inventories Exchange Rate: Current ----- Accounts: Accounts Payable, Inventories, Investments Exchange Rate: Historical ----- Accounts: Common Stock, Dividends Payable, retained Earning What total amount should appear for these assets on the Philippine company's consolidated balance sheet?* Php 960,000 Php 636,000 Php 648,000 Php 708,000 The gain or loss on the effective portion of a Philippine parent company's hedge of a net investment in a foreign entity should be treated as:* an adjustment to the retained earnings account in the stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet. an adjustment to a valuation account in the asset section of its balance sheet. other comprehensive income. a translation gain or loss in the computation of net income for the reporting period. For each of the items listed below, state whether they increase or decrease the balance in cumulative translation adjustments (assuming a credit balance at the beginning of the year) when the foreign currency strengthened relative to the Philippine peso during the year.* Net Income Dividend Declared Decrease Increase Decrease Increase This question requires one response per row Nichols Company owns 90% of the capital stock of a foreign subsidiary located in Ireland. As a result of translating the subsidiary's accounts, a debit of Php 160,000 was needed in the translation adjustments account so that the foreign subsidiary's debits and credits were equal in Philippine Peso. How should Nichols report its translation adjustments on its consolidated financial statements?* As a Php144,000 increase in the stockholders' equity section of the balance sheet. As a Php144,000 reduction in consolidated comprehensive net income. As a Php160,000 debit in stockholders' equity section of the balance sheet. As a Php160,000 reduction in consolidated comprehensive net income. 2. Under the temporal method, which of the following is usually used to translate monetary amounts to the functional currency? I. The current exchange rate; II The historical exchange rate; III. Average exchange rate* III I II Either I or II Submit Page 1 of 1 Clear form Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This content is neither created nor endorsed by Google. Report Abuse - Terms of Service - Privacy Policy Forms

![[Date] [Name of College] ATTN: [Department]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015675584_1-19c1f2d4f2acfcfa6a51fd36241fad38-300x300.png)

