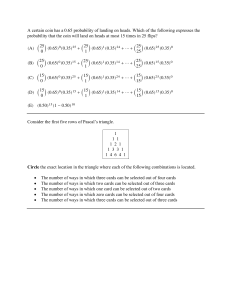
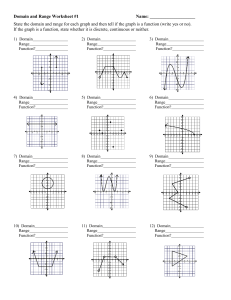
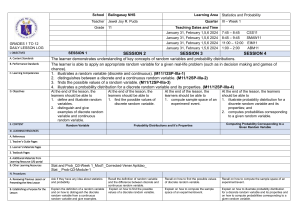
Random Variable - a variable that assigns a numerical value to each outcome of a random event. - It can be classified as discrete or continuous -depending on whether the value is obtained by counting or by measurement. Discrete Variable – a quantitative variable whose value can only be attained through counting. It is measured as whole numbers of units. Example: The number of children in a family Flipping a coin When you flip a coin several times and count the number of heads. The number of heads could be any whole number value. We could get the numbers 0,1,2,3, and so on. Therefore, the number of heads when flipping a coin is a discrete variable Discrete Random Variable – if the experiment has only countable infinite number of outcomes. Continuous Variable – a quantitative variable that can assume an infinitely many, uncountable number of real number values. Example: distance traveled by a vehicle exact age of a person height of a person Continuous Random Variable – an outcome of an experiment that take an uncountably infinite number of possible outcomes within a specified real number interval. Example: height of an employee