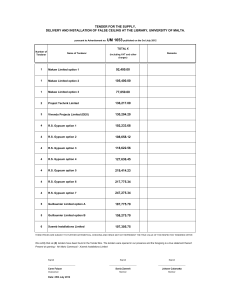
Gypsum Mining Tel:+8617367842747 Gary Gypsum Mining Production Process and Equipment Zhengzhou Hengyang Industry Co., Ltd Mail: sell@chinadjks.com Add: 500 West, cross road of Rizhao and Industrial road, Zhengzhou city, China Hengyang Gypsum Mining Instruction: Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) is a met stable substance derived from the hydration of anhydrite, which is a primary mineral. The essential ingredient in all the rock types is CaSO4. Hardness of gypsum is 2, specific gravity 2.32 and porosity more than 20%. The solubility of gypsum is slow. Various grades of gypsum and their uses as raw materials are as under: High Quality Gypsum: Gypsum (CaSo4.2H2o) containing more than85% is an essential raw material for gypsum and alpha gypsum plaster. Gypsum plaster can only be manufactured from high grade gypsum. Low Quality Gypsum: 50% – 85% gypsum with anhydrite and other impurities, making up the rest, is suitable for cement and agro gypsum. Anhydrite: Less than 50% gypsum content but essentially CaSo4. This material is suitable for cement but its suitability has to be established for use as agro-gypsum and canal and distributaries lining as its solubility is low. Alabaster: An essentially CaSo4 rock that can be either gypsum or anhydrite. Gypsum Current Usage Gypsum / anhydrite obtained from various mines / quarries have been and / or are being used for the following industries. AGRO-GYPSUM In agriculture, gypsum is used as soil amender with a view to improving its chemical and physical characteristics. Application of gypsum helps breakup hard soil, allows better aeration and water penetration and retention. The processing of gypsum for use in the amendment of saline-sodic soils involves crushing and Grinding rock gypsum to 30 – 40 mesh size and loose or bagged product is transported. TREATMENT OF LOW QUALITY TUBE-WELL WATER Many tube-wells are pumping high sodium waters that make productive land unproductive. This low quality tube-well water retards seed germination and plant growth. In this context, gypsum boulders may be used for the patching of distributaries and /or these sodic waters are used after passing through gypsum stored in a haudi (water tank) for the correction of tube-well water. CEMENT INDUSTRY About 3% to 4% gypsum / anhydrite is used in the processing of cement for retarding its setting time. The present installed capacity of cement plants is about20 million tons in the country. The cement production is likely to increase to 30million tons in the next 3-5 years and subsequently gypsum consumption would increase to 3.2 million tons per annum. PLASTER OF PARIS Plaster of Paris is hemi-hydrated calcium sulphate (CaSo4.1/2 H2O) produced by heating of gypsum to a temperature of between 120℃to 160℃. Plants of varying capacities (2-10 t/day installed capacities) are being used for its production. Plaster of Paris so produced is of mediocre quality used in ceramics, paints, ornamental ceiling tiles etc. Gypsum Mining Process: Gypsum is extracted from open air or underground mines, using specific drilling machinery and non-polluting explosives. Rock size may reach up to 50 cm in diameter. Crushing Primary crushing aimed at reducing rocks to a size of less than 10cm, subsequently easier to handle, is carried out in the quarry or at the entrance to the plaster manufacturing station. Mainly Use Crusher for crushing into small sizes and sieves for separating. Storage Rock that has undergone primary crushing is stored to ensure production continuity, and optimal homogeneity between rock extraction batches. Sitering It is necessary to separate and control gypsum particle size in order to obtain the exact product properties required for the plaster being manufactured. Calcination Calcium sulphate hemihydrates (CaSO4.½H2O) or plaster is obtained through the partial or total dehydration of gypsum at a temperature ranging from 120° to 400°C The structure and properties of the final product are directly dependent on the chosen calcination conditions (temperature, pressure, rapidity).Several types of calcinations processes exist: Alpha Process Alpha type plaster is used mainly in industrial plaster formulations for its high mechanical strength. This plaster type is a compact crystal with a low specific surface and low water demands to produce hard, low porosity casts. Alpha plaster can be formed through 2 different production procedures: DRY PROCESS that involves injection of steam vapor during calcinations. The plaster is dried and then treated in the regular manner. WET PROCESS that involves calcinations of gypsum slurry under pressure. The plaster is then spun and dried. BETA PROCESS During the calcinations process, under regular environmental pressure, dehydration water evaporates and a micro-porous structure is formed. Beta plaster crystals have a high specific surface and high water demands. Beta plaster casts have high porosity, but low mechanical properties and are therefore, used in lightweight building applications or moulds in ceramic applications for their absorbent properties. Often a mixture of both Alpha & Beta type plasters will be used to combine the properties of both and optimize product solutions to suit market requirements. Grinding Following the calcinations process, the plaster is ground to obtain a powder. Particle size distribution is an important factor in the product properties. Mixing With the plaster now in finely ground form, the final mixing stage is possible. A choice of additives will finely tune the products properties to match the customer’s needs, in terms of setting time, viscosity, porosity, color, and mechanical strength. Testing Laboratory testing is carried out at several production phases, to ensure allproducts meet the strict product specifications before being bagged and shipped. Packing Feasibility studies are carried out to ensure the packaging item chosen for eachproduct gives optimal protection and guarantees the product quality all the way tothe end-user. Gypsum Machinery Ball Mill Classifications: Overflow Type The overflow type of Ball Mill is designed to overflow and discharge materials from the trunnion on the outlet side. By combining it with a mechanical classifier or wet-processing cyclone, you are able to extensively use this type for grinding in closed circuit or for special applications such as re-grinding in open circuit. Generally, it is best suited to fine-grind materials up to the particle sizes ranging from 150 to 200 mesh. Grate-discharge Type The grate-discharge type of Ball Mill has a grate at the outlet of the shell and causes less excessive grinding, compared to the overflow type. Therefore, generally, it is best suited to grind materials up to the particle sizes ranging from 60 to 100 mesh. Compartment type The compartment type of Ball Mill has a longer shell, inside of which is comparted into 2 to 3 chambers with grates and is best suited to produce products grinding from coarse particles of some 25 mm to fine particles of some 200 mesh. Ultra Fine-Powder Ball Mill Similar with horizontal ball mill, continuous production, but grinding chamber and grinding time is longer. Batch Ball Mill Batch ball mill mainly for grinding raw material into ultra fine powder but production shaft by shaft. Ball Mill Application: Mining Industry : Used to grind various kinds of ores. Ceramic Industry : Used to finish and grind various kinds of raw materials and cement. Smelting Industry : Used to grind various kinds of slag. Power generation : Used to grind coal for combustion use. Chemical Industry : Used to grind coke, ilmenite, and others. Food Industry: used for grinding additive materials. Ball Mill Technical Details: Overflow Type, Grate-discharge Type and Compartment type Inside dia. Length of shell (mm) Ball charging amount (tons) Mill revolution (min-1) Power consumption (kW) Motor output (kW) A B 1212 1515 1200×1200 1500×1500 2.05 4.15 32.0 29.0 16.5 35.8 18.5 37 1.5 3.5 1.3 3.1 1818 2121 1800×1800 2100×2100 7.4 11.7 25.3 23.0 65.3 106 75 110 6.6 11.0 5.8 9.6 2424 2430 2400×2400 2400×3000 17.6 22.0 21.4 21.4 167 209 190 220 18.0 22.4 15.8 19.6 2727 2733 2700×2700 2700×3300 25.4 31.0 20.1 20.1 250 306 260 340 27.5 33.7 24.1 29.6 3030 3036 3000×3000 3000×3600 35.0 42.0 18.8 18.8 350 420 375 450 39.5 47.3 34.6 41.5 3236 3242 3200×3600 3200×4200 48.0 56.0 18.0 18.0 484 565 510 600 55.5 65.0 48.7 57.0 3442 3648 3400×4200 3600×4800 63.5 81.5 17.5 16.6 655 845 700 900 75.5 99.0 66.0 86.0 3848 4051 3800×4800 4000×5100 91.5 108.0 16.2 15.8 960 1160 1000 1200 113.0 139.0 99.0 122.0 Size Capacity (t/h) Ultra Fine-Powder Ball Mill (Super-fine Powder Industry) Model Ø2.4*16m Untra-fine Ball Mill Ø2.6*16m Untra-fine Ball Mill Ø3.2*16m Untra-fine Ball Mill Capacity 25t/h 35t/h 55t/h Rotary Speed 21.3r/min 19.46r/min 17.83r/min Feeding size less them 1mm less them 1mm less them 1mm Volume 64m3 76m3 115m3 Grinding Media Load 105t 120t 190t Drive Model Edge-transmission Edge-transmission Edge-transmission Motor Power YR1250-8-1430/1250 YR1400-8-1430/1400 YR2240-8-1730/2240 Gearbox JDX900 MYB1000 MYB1100 Weight 120T 205T 330T Jaw Crusher PE/PEX Series Jaw Crusher has the features of high crushing and even product size ratio. It can be used to crush material, whose compression strength is not more than 320Mpa. This jaw crusher is mainly used in various industries, such as mining, smelting, road and railway construction, water conservation and chemical industry etc. PE Series is used in primary crushing, while PEX series is used in secondary crushing and fine crushing. Working principle of PE/PEX Series Jaw Crusher: This crusher adopts the electric motor as the power. The eccentric shaft is revolved by an electric motor through v-belts. It causes the swing jaw following the preconcerted path to crush the feeding material. Thus the material will be crushed in the crushing chamber which is composed of the stationary jaw plate, swing jaw plate and the liner plate. The material is discharged from the lower part of machine that is what you want. Technical Details: Model Size of Feed Opening(mm) Max Feed Size (mm) Discharge Range Opening (mm) Capacity (m3/h ) PE-250×400 250×400 210 20-60 3-13 15 2.8 PE-400×600 400×600 340 40-100 10-40 30 6.5 PE-500×750 500×750 425 50-100 28.5-62.5 55 10.8 PE-600×900 600×900 500 65-160 30-75 55- 75 15 PE-750×1060 750×1060 630 80-200 80-160 90-110 28.9 PE-870×1060 870×1060 750 170-270 145-235 90-110 29.5 PE-900×1200 900×1200 750 100-200 100-240 110-132 49 PE-1000×1200 1000×1200 850 200-280 190-275 110-132 51 PE-1200×1500 1200×1500 1020 150-300 250-500 200 88.5 PEX-150×750 150×750 120 10-40 5-16 15 2.5 PEX-250×1000 250×1000 210 25-60 10-30 30-37 6.6 PEX-250×1200 250×1200 210 25-60 10-31.5 37 7 PEX-300×1300 300×1300 250 20-90 12.5-53 75 12 Impact Crusher Motor Power Weight(t) (kw) Impact stone crushing machine which can also be called impact crusher or impact breaker or impactor crusher is a new type highly efficient crushing machine with the advantages of small size, simple structure, high crushing ratio, low energy consumption, high production capacity, even product granularity and selective rock crushing, so that vertical shaft rock impact stone crusher is a promising crushing equipment. The biggest disadvantages of rock impactor crusher lies in that the hammer plate and the impacting plate are very easy to be abraded, especially when crushing hard rocks, so that they should be regularly changed. At present due to the research and development of some anti-abrasion materials, this kind of crushing equipment has been used in some metal dressing plants. Performance: 1) Multiple crushing chambers for even crushing, thus suitable for crushing hard rocks; 2) Big and low material feeding mouth is convenient for arranging the production line and increasing the size of the material feeding; 3) New anti-abrasion material prolongs the service life of the plate hammer, impacting plate and the lining board; 4) The vertical shaft impact crusher adopts high chromium plate hammer and unique impacting lining board, so that is very suitable for crushing hard rocks with high efficiency and saves energy; 5) The unique structure of the machine makes the discharged materials in smaller granularity diameter and cube shape and without internal lines; 6) The final product is in the shape of cube and the discharged granularity can be adjusted; 7) The whole crushing process is simplified; 8) The machine is started in a comprehensive hydraulic way, so it is more convenient for maintenance and changing the easy-wearing parts; Technical details: Model Specification Feed opening The Maximum Capacity Power Total Overall dimension (mm) (mm) Feeding Size(mm) (t/h) (kw) weight(t) (L×W×H) (mm) PF-1007 Φ1000×700 400×730 300 30-70 37-45 12 2330×1660×2300 PF-1010 Φ1000×1050 400×1080 350 50-90 45-55 15 2370×1700×2390 PF-1210 Φ1250×1050 400×1080 350 70-130 110 17.7 2680×2160×2800 PF-1214 Φ1250×1400 400×1430 350 100-180 132 22.4 2650×2460×2800 PF-1315 Φ1320×1500 860×1520 500 130-250 220 27 3180×2720×2620 PF-1520 Φ1500×2000 830×2040 700 300-550 315-400 50.6 3959×3564×3330 PF-1820 Φ1800×2000 1260×2040 800 600-800 630-710 83.21 4400×3866×4009 Fine Impact Crusher The PCX fine impact crusher is digests home and abroad vanguard technology, unifies newest generation of highly effective small aggregate crusher which the domestic correlation profession concrete operating mode condition develops. Uses in each kind of medium degree of hardness solid material, in cement industry, limestone in broken bits, paste, chamotte, and so on mix material. Also can crush may the calcium phosphide in broken bits, the dolomite, and so on pearl ore. It is widely used in the building materials, the chemical fertilizer industry sector and so on mining and fire-proof material. Application of Fine Impact Crusher: It is applicable for granite, basalt, cement clinker, quartz, emery, ore, iron ore and bauxite with large production capacity, long service life hammerhead and environmental protection and energy conservation features. Additionally, the pebbles fine crushing prevent the traditional sand stone making equipments feature which is only applicable for the soft rock(under 150MPa). Working Principle: When the fine impact crusher works, with the help of the motor, the fine impact crusher’s rotor rotates fast, the material is crushed by the shock of rotor’s hammer in the first crushing zone, and being crushed in the second fine crushing zone, then discharged from the output. Technical details: Model Feeding size(mm) Discharging size(mm) Capacity(t/h) Power(kw) Weight(t) PCX800×400 ≤60 ≤5(96%) 20-25 37 2.5 PCX800×600 ≤60 ≤5(94%) 35-50 45 4.7 PCX800×800 ≤70 ≤5(92%) 40-60 75 6.5 PCX1000×1000 ≤80 ≤5(91%) 60-90 90 8.8 PCX1000×1200 ≤90 ≤5(88%) 75-110 110 13.6 PCX1200×1200 ≤100 ≤5(86%) 120-145 160 19.5 PCX1300×1400 ≤120 ≤5(85%) 145-180 180 26 VSI Crusher The working principle of VSI Crusher (sand making machine) has mainly stone hit the stone (material against material) andstone hit iron (material against iron). Stone hit the stone (material against material): through the hopper, the material enters into the crusher, and is divided into two parts by bulk cone. A portion of materials falls into the high-speed rotation swing wheel, and is rapidly accelerated. Then it is thrown away from the swinging wheel. This parts material hit another part material, which falls down from all round of the bulk cone. Stone hit iron (material against iron): The basic work principle is similar with “stone hit the stone”. The difference is that the crushing cavity of "stone hit stone" installs the impact board, and the material forms material lining. But “stone hit iron” use the around guard plate replaced the lower guard board, and the material directly impact on the around guard plate and broken. Technical details: Model Max Feed Size(mm) Speed of Rotor(r/min) Capacity(t/h) Motor Power(Kw) Overall Dimensions(L×W×H)(mm) Weight(Kg) VI-01 30 ( 50 ) 2300-3200 3-20 7.5-22 2200×1300×1880 ≤2800 VI-02 40 ( 60 ) 2000-2500 10-40 30-45 2200×1500×1580 ≤3350 VI-03 45 ( 70 ) 1700-2000 30-60 75-90 3600×1600×1810 ≤4900 VI-04 55 ( 70 ) 1400-1620 50-90 110-150 3700×1800×1900 ≤6900 VI-05 65 ( 80 ) 1330-1530 80-150 180-264 4000×2160×2230 ≤11640 VI-06 80 ( 100 ) 1200-1400 120-250 264-320 5200×2660×2560 ≤15170 VI-07 80 ( 100 ) 1000-1200 180-350 320-400 5300×2660×2830 ≤16280 VI-08 100 ( 150 ) 1000-1100 250-500 440-500 6000×3000×3420 ≤23450 VI-08(II) 100 ( 150 ) 1000-1100 400-650 500-630 6000×3000×3590 ≤25050 VI-09 110 ( 150 ) 900-1000 550-1200 630-740 6200×3300×3890 ≤33100 Rotary Dryer Despite the introduction of new technology, the long established Rotary Rotary Dryer is still widely regarded as the workhorse of many process industries. The robust yet simple construction combines flexibility with reliability, enabling this type of dryer to handle a vast range of materials and to operate continuously under the most arduous conditions. The design also permits the use of the highest possible drying temperatures and in contrast to other dryers is not sensitive to wide variations in material size, moisture content or throughput. Specifications Diameter: 600mm to 3500mm Length: 8000mm to 65 000mm Methods of heating: Direct or indirect Capacity: 500kg/h to 175t/h Fuel: coal, natural gas, heavy oil, etc Temp range: 200-700°C Material: Carbon steel, Stainless steel, etc Thickness: 8mm to 70mm Principles of Operation In its simplest form, the Rotary Dryer consists of a slightly inclined rotating cylinder, fitted with a series of peripheral flights arranged to lift, distribute and transport the material. The flights are designed to suit the particular handling characteristics of the material, which may vary with increasing dryness. The principle of operation is based on showering, or cascading the wet material through a hot gas stream, flowing either co-current or counter-current to the solids. The hot gas induces the evaporation of the moisture. The heat lost to the material and evaporation of water vapor reduces the gas temperature rapidly, such that it leaves the dryer at a comparatively low temperature. The efficiency of the dryer is largely dependent on the differential between the inlet and exhaust gas temperatures, although the heat transfer rate is also influenced by the relationship between the design of flights and the speed of rotation. However, irrespective of the gas and material temperatures the drying (or residence) time may be critical, as this is governed by the rate of diffusion of water from the core to the surface of the material. For special applications, the rotary cascade design is adapted to provide a shortfall, or ‘Cruciform’, lifter configuration. Rotary Kiln Application Rotary kiln is a rotating cylindrical vessel which is used for drying, calcination and sintering in a continuous process with the use of hot gases. The hot gases may be generated in an external furnace or by a flame inside the kiln. Hengyangrotary kiln and sponge iron rotary kiln has been developed for performing drying, calcination and sintering work in a continuous process. Widely used for cement, pet coke calcination, dolomite, bauxite, sponge iron and other materials, it uses hot gases for the operation. Integrated with variable speed drive, process automation and instrumentation, this kiln ensures optimum operational control. In addition to technology, its design features better inlet and outlet sealing to ensure minimum false air entry. Specifications Diameter: 1000mm to 4500mm Length: 12000mm to 130 000mm Methods of heating: Direct or indirect Capacity: 200kg/h to 210t/h Fuel: coal, natural gas, heavy oil, etc Temp range: 900- 1400°C Material: Carbon steel, Stainless steel, etc Thickness: 12mm to 100mm