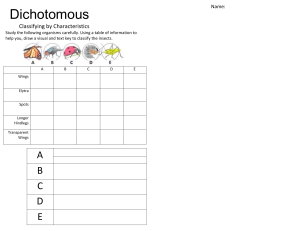
Early classification Early classification was based on ________ features. Species with _______ characteristics were grouped together under ___ kingdoms: animalia and _______. Evidence New Microscopes ________ so scientists could see inside _____. ___ was discovered and scientists began to _______ DNA from different species. Modern classification Today we classify species based on shared ________ which is determined by a range of evidence including ___ analysis, comparison of bio -chemical processes, and more. In Biology, classification is the _______ of species into ______. The Swedish biologist, Carl ________ devised a hierarchical system of classification. He also came up with the system of naming _______. This is known as ________. A worldwide taxonomic system ensures scientistics do not ___-__ species. MNEMONIC Classification hierarchy EXAMPLE D Eukarya K Animalia P Chordata C Mammalia O Carnivora F Canidae G Canis S Canis lupus As we move down the ____, they become increasingly ________, i.e. they are less _________. Which family does the gray wolf belong to? Binomial nomenclature Annotate this to show how species names are written: Canis lupus © Emmatheteachie 2021 Name & describe the 3 domains. This is the most recent and _______ level of classification. Work by the American scientist Carl Woese and his team led to this taxon being added in 1990. There are _____ domains. B Unicellular with no _______ or membrane-bound organelles. Has a ____ ____. Some are harmful and some are ______. A Unicellular with no _______ or membrane-bound organelles. Has a different type of cell ____. Some of them live under _______ conditions, e.g. hydrothermal vents. E A mix of unicellular and multi -cellular organisms. They always have a _______. Doodle some seaweed in the space! There is no clear consensus on the number of kingdoms but 5-6 kingdom systems are currently popular! This taxon falls below the level of ______. It was the first taxon to be described. Name the six kingdoms & describe the four eukaryotic kingdoms (the prokaryotic ones have already been covered on the left boxes) B A A P _____cellular ______trophic No ____ ____ Multicellular ____trophic Cell wall made of _________ Always have Most are multicellular a _______. Most are ___cellular ______trophic ______trophic or ____trophic Cell wall made Some have a of ______ cell wall, some don’t F P Create & use a key for the box outline of each kingdom to show if it is... = Eukaryotic = Prokaryotic © Emmatheteachie 2021 Use the insect dichotomous key to identify these organisms: Dichotomous keys are used to ________ species. They usually focus on one group, e.g. pond insects, coniferous trees, etc. They consist of ___ part questions / statements to ______ down the species. They focus mainly on ________ characteristics so that they are easy to use in the field. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Visible wings Go to step 2 Hidden wings or no wings present Go to step 5 Stripes on body Go to step 3 No stripes on body Go to step 4 Thin waist, stinger, two sets of wings Honey bee No stinger, one set of wings, large eyes Hoverfly Straight proboscis, narrow wings Mosquito Curling proboscis, large colorful wings Butterfly Long and narrow abdomen Go to step 6 Wide abdomen Go to step 7 Pincher at the end of abdomen Earwig Three "tails" at end of abdomen Silverfish Large antler-like mandible on head Stag beetle Small mandible, not visible from top view Scarab beetle © Emmatheteachie 2021 Let’s put your observational skills to the test - create your own dichotomous key for these monsters! Doodle and name your own monster first! Tip: start by labeling the physical features of each monster - you will start to notice features that groups of monsters have and features that are unique to each monster! 1 2 Fang Iggy Bu m b le S ha d o w 3 4 5 6 7 S c ru f f Doodle & name your own monster! © Emmatheteachie 2021