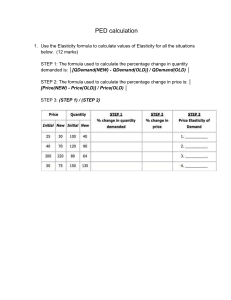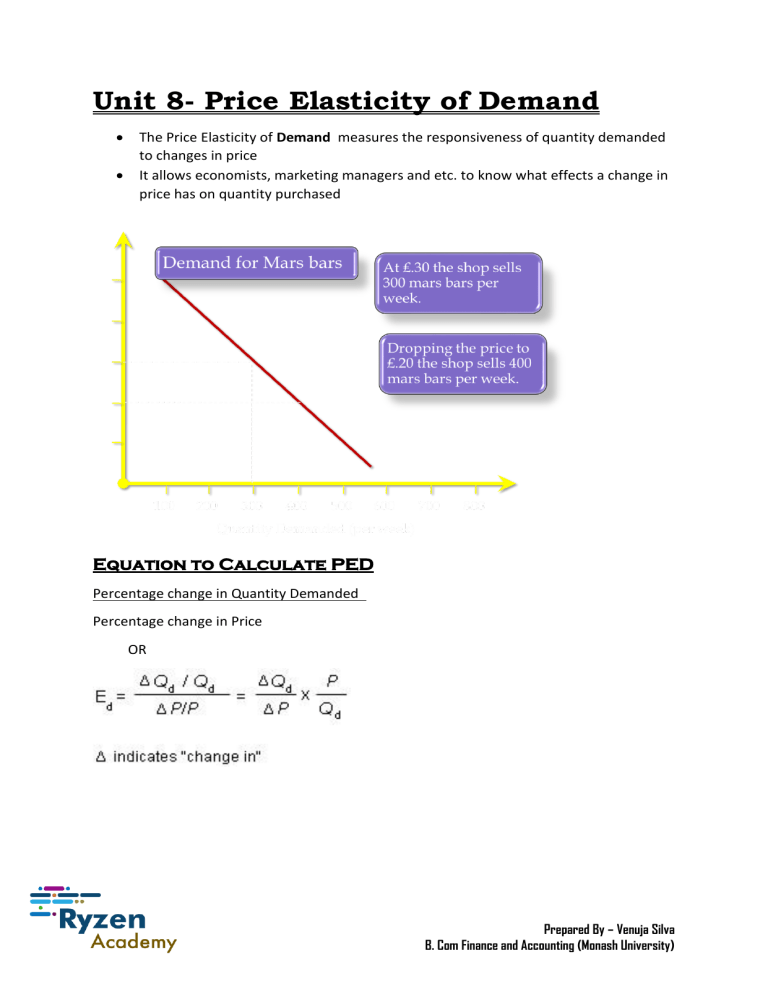
Unit 8- Price Elasticity of Demand • • The Price Elasticity of Demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price It allows economists, marketing managers and etc. to know what effects a change in price has on quantity purchased Equation to Calculate PED Percentage change in Quantity Demanded Percentage change in Price OR Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University) Worked Example • The price of a chocolate bar increased from $10 to $15 and accordingly quantity demanded changed from 100 to 80. Calculate the PED Percentage change in Quantity Demanded Percentage change in Price 20% / 50% ⁼ 0.4 • Types of Price Elasticity of Demand • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Accordingly, there are many types of price elasticity of demand according to the PED values Perfectly Inelastic Demand Inelastic Demand Unitary Elastic Demand Elastic Demand Perfectly Elastic Demand Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University) Perfectly Inelastic Demand This occurs when quantity demanded is not responsive to changes in price. In other words even though the price of the product changes the quantity demanded remains unchanged The PED value is 0 Price QD 10 100 20 100 Inelastic Demand • • • This occurs when quantity demanded is less responsive to changes in price In other words even if the price changes the quantity demanded changed only by a small amount The PED VALUE IS LESS THAN 1 (PED<1) Price Quantity Demanded 10 110 20 100 Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University) Unitary Elastic Demand • • • This occurs when quantity demanded is equally responsive to changes is price This means that the quantity demanded will change in the same proportion to Price THE PED VALUE IS 1 (PED – 1) Price QD 10 200 20 100 Elastic Demand • This occurs when quantity demanded is more responsive to changes in price • In other words it is when there is a price change the change in quantity demanded is highly proportionate to the change in price THE PED VALUE IS GREATER THAN 1 (PED>1) Price Quantity Demanded • 10 100 15 30 Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University) Perfectly Elastic Demand • • This is when quantity demanded is changing even without a change in price In other words the quantity of the commodity which the consumers are demanding are changing even without a price change • PED VALUE IS INFINITE (PED - ∞) Price Quantity Demanded 10 200 10 100 Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand • There exist many factors which determines the PED of a certain commodity 1. Availability of Substitute goods – Substitute goods are the goods which gives the same satisfaction as the other. If there are a large number of substitute goods, then PED is most likely to be elastic. If the product has a smaller number of substitutes, then the product would have an inelastic demand. 2. Proportion of Income Spent – If an individual spends a higher proportion of the total income, then the good is most likely to be elastic. Lower proportion of income spent, then good is likely to have an inelastic demand 3. Degree of Necessity – If the product is a necessity, then the product has an inelastic PED. If it’s a luxury it has an elastic demand. 4. Habit Forming Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University) Advantages of Knowledge Price Elasticity of Demand (Uses of PED) – Businesses 1. Pricing Policy - The knowledge of PED can help a firm to set the price of the product in a way that they can maximize their revenue. For example, if a product has an inelastic demand, then its suitable to set a high price to maximize revenue 2. It also helps to identify how costs of the firm would change over time 3. Distribution of Tax Burden – According to the PED a firm can identify how to transfer the tax burden. If the product has an inelastic demand, then most of the tax can be passed onto the customer by an increase in price 4. Allows a firm to predict the change in revenue with the change in price Uses of PED – Governments 1. Ability to reduce consumption of certain goods, government can identify the change in the quantity demanded after a tax is charged. Goods which have an elastic demand will see a drop in consumption when taxes are charged however, products with an inelastic demand will see a smaller drop in consumption 2. Raising Tax Revenue – government can charge taxes on products that have an inelastic demand and earn higher revenue as consumers are more likely to consume even when taxes are charged. Limitations 1. PED may change from time to time 2. PED of goods may vary from one country to another Prepared By – Venuja Silva B. Com Finance and Accounting (Monash University)