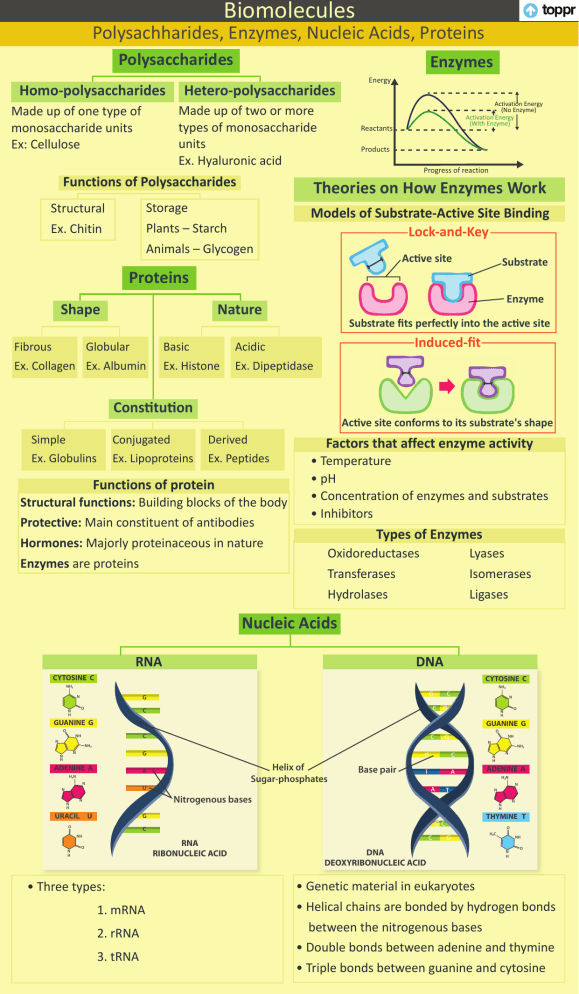
Biomacromolecules Biomolecules Polysachharides, Acids, Proteins Materials-Enzymes, MetalsNucleic &Non-metals Polysaccharides Homo-polysaccharides Enzymes Hetero-polysaccharides Made up of two or more types of monosaccharide units Ex. Hyaluronic acid Made up of one type of monosaccharide units Ex: Cellulose Functions of Polysaccharides Storage Plants – Starch Animals – Glycogen Structural Ex. Chitin Energy Reactants Products Progress of reaction Theories on How Enzymes Work Models of Substrate-Active Site Binding Lock-and-Key Ac�ve site Proteins Fibrous Globular Ex. Collagen Ex. Albumin Basic Ex. Histone Substrate fits perfectly into the ac�ve site Induced-fit Acidic Ex. Dipeptidase Cons�tu�on Simple Ex. Globulins Conjugated Ex. Lipoproteins Substrate Enzyme Nature Shape Activation Energy (No Enzyme) Activation Energy (With Enzyme) Ac�ve site conforms to its substrate's shape Derived Ex. Peptides Functions of protein Structural functions: Building blocks of the body Protective: Main constituent of antibodies Hormones: Majorly proteinaceous in nature Enzymes are proteins Factors that affect enzyme activity • Temperature • pH • Concentration of enzymes and substrates • Inhibitors Types of Enzymes Oxidoreductases Transferases Hydrolases Lyases Isomerases Ligases Nucleic Acids RNA DNA CYTOSINE C CYTOSINE C NH2 NH2 G N O N H N C GUANINE G GUANINE G O O C NH N NH N NH2 G N N H ADENINE A N U N U Base pair ADENINE A H2N N N THYMINE T O C NH H3C RNA RIBONUCLEIC ACID O • Three types: 1. mRNA 2. rRNA 3. tRNA N N H G O N H NH2 N N H Nitrogenous bases N URACIL Helix of Sugar-phosphates A H2N N H O N H DNA DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID NH N H O • Genetic material in eukaryotes • Helical chains are bonded by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases • Double bonds between adenine and thymine • Triple bonds between guanine and cytosine