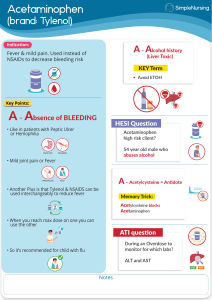
Acetaminophen Medication Review: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions
advertisement
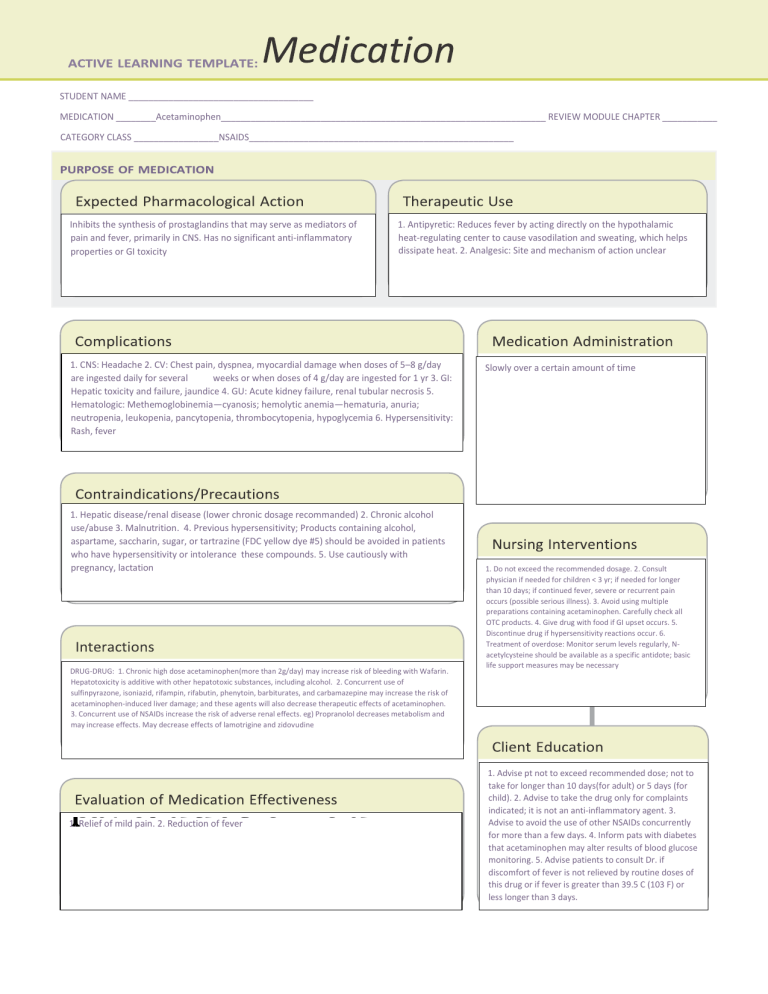
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________ MEDICATION ________Acetaminophen_________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________ CATEGORY CLASS _________________NSAIDS_____________________________________________________ Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain and fever, primarily in CNS. Has no significant anti-inflammatory properties or GI toxicity 1. Antipyretic: Reduces fever by acting directly on the hypothalamic heat-regulating center to cause vasodilation and sweating, which helps dissipate heat. 2. Analgesic: Site and mechanism of action unclear 1. CNS: Headache 2. CV: Chest pain, dyspnea, myocardial damage when doses of 5–8 g/day are ingested daily for several weeks or when doses of 4 g/day are ingested for 1 yr 3. GI: Hepatic toxicity and failure, jaundice 4. GU: Acute kidney failure, renal tubular necrosis 5. Hematologic: Methemoglobinemia—cyanosis; hemolytic anemia—hematuria, anuria; neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypoglycemia 6. Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever 1. Hepatic disease/renal disease (lower chronic dosage recommanded) 2. Chronic alcohol use/abuse 3. Malnutrition. 4. Previous hypersensitivity; Products containing alcohol, aspartame, saccharin, sugar, or tartrazine (FDC yellow dye #5) should be avoided in patients who have hypersensitivity or intolerance these compounds. 5. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation DRUG-DRUG: 1. Chronic high dose acetaminophen(more than 2g/day) may increase risk of bleeding with Wafarin. Hepatotoxicity is additive with other hepatotoxic substances, including alcohol. 2. Concurrent use of sulfinpyrazone, isoniazid, rifampin, rifabutin, phenytoin, barbiturates, and carbamazepine may increase the risk of acetaminophen-induced liver damage; and these agents will also decrease therapeutic effects of acetaminophen. 3. Concurrent use of NSAIDs increase the risk of adverse renal effects. eg) Propranolol decreases metabolism and may increase effects. May decrease effects of lamotrigine and zidovudine 1. Reduction 2. pain. fever Relief of mild of 1. Relief of mild pain. 2. Reduction of fever Slowly over a certain amount of time 1. Do not exceed the recommended dosage. 2. Consult physician if needed for children < 3 yr; if needed for longer than 10 days; if continued fever, severe or recurrent pain occurs (possible serious illness). 3. Avoid using multiple preparations containing acetaminophen. Carefully check all OTC products. 4. Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. 5. Discontinue drug if hypersensitivity reactions occur. 6. Treatment of overdose: Monitor serum levels regularly, Nacetylcysteine should be available as a specific antidote; basic life support measures may be necessary 1. Advise pt not to exceed recommended dose; not to take for longer than 10 days(for adult) or 5 days (for child). 2. Advise to take the drug only for complaints indicated; it is not an anti-inflammatory agent. 3. Advise to avoid the use of other NSAIDs concurrently for more than a few days. 4. Inform pats with diabetes that acetaminophen may alter results of blood glucose monitoring. 5. Advise patients to consult Dr. if discomfort of fever is not relieved by routine doses of this drug or if fever is greater than 39.5 C (103 F) or less longer than 3 days.