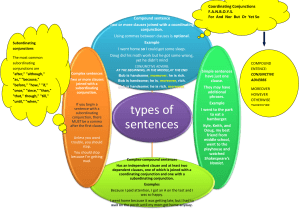
DETAILED DAILY LESSON PLAN In ENGLISH for GRADE 8 School Grade Level Grade 8 Teacher Teaching Dates & Time I. Objectives Learning Area English Quarter Second Week 2 Day 1 A. Content Standard: The learner demonstrates understanding of: East Asian literature as an art form inspired and influenced by nature; relationship of visual, sensory, and verbal signals in both literary and expository texts; strategies in listening to long descriptive and narrative texts; value of literal and figurative language; and appropriate grammatical signals or expressions suitable to patterns of idea development. B. Performance Standard: The learner transfers learning by composing and delivering a brief and creative entertainment speech featuring a variety of effective paragraphs, appropriate grammatical signals or expressions in topic development, and appropriate prosodic features, stance, and behavior. C. Learning Competencies/Objectives: Use appropriate grammatical signals or expressions suitable to each pattern of idea development: EN8G-IIa-9: General to particular Claim and counterclaim Problem-solution Cause-effect And others Recognize the subordinating conjunctions in sentences Write sentences using appropriate subordinating conjunction/s. II. Content: Subordinating Conjunction III. Learning Resources A. References 1. Teacher’s/ Curriculum Guide Pages:180 2. Learner’s Material’s Pages: English Expressways II 2007, pages 106-109 3. Textbook Pages: 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) Portal: B. Other Learning Resources https://www.teach-this.com/parts-of-speech-activities-worksheets/conjunctions https://blog.abaenglish.com/english-grammar-subordinating-conjunctions/ https://www.englishgrammar.org/subordinating-conjunctions-worksheet/ IV. Procedures Preliminaries Prayer Orderliness Checking of Attendance A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting the New Lesson B. Establishing a Purpose for the Lesson C. Presenting Examples/Instances of the Lesson Teacher’s Activity Recall (2 minutes) The teacher will ask the students: What is conjunction? What are the coordinating conjunctions? Agree or Agree (2 minutes) The teacher will say: Learning the subordinating conjunction and its proper uses will equip learners with confidence in speaking and writing grammatically correct sentences. Have you tried confidently speaking/talking to your friends in English? (Knowing that you are grammatically correct). How did you feel? A WHITE BUS (5 minutes) The teacher will introduce the concept: Subordinate conjunction will connect a main clause and a subordinate one. If the main clause comes first in the sentence it won’t be separated from the Student’s Activity The students will answer: Conjunctions are those little words that connect two parts of a sentence together. The students will share their opinions of the idea presented The students will attentively familiarize the concept introduced subordinate clause by a comma. If the subordinate clause comes first, then we will separate the clauses with a comma. D. Discussing New Concepts and Practicing New Skills #1 Subordinating Conjunction (10 minutes) The teacher will show the following usage of the different subordinating conjunctions for reference (for students who will later on give their own examples) The students will study the following sample sentences in using the different subordinating conjunctions. After – later than the time that : later than when. https://blog.abaenglish.com/e Example: “Call me after nglish-grammar-subordinating- you arrive at work” conjunctions/ Although – despite the fact that : used to introduce a fact that makes another fact unusual or surprising. Example: “Although she was tired, she couldn’t sleep” As – used to introduce a statement which indicates that something being mentioned was known, expected, etc. Example: “As we explained last class, coordinating conjunctions are sentence connectors” Because – for the reason that. Example: “I painted the house because it was a horrible colour” Before – earlier than the time that : earlier than when. Example: “Come and visit me before you leave” How – in what manner or way. Example: “Let me show you how to knit” If -used to talk about the result or effect of something that may happen or be true. Example: “It would be fantastic if you could come to the party” Once – at the moment when : as soon as. Example: “Once you’ve learnt how to cycle, it’s very easy” Since – used to introduce a statement that explains the reason for another statement. Example: “Since you’ve studied so well, you can go outside and play” Than – used to introduce the second or last of two or more things or people that are being compared — used with the comparative form of an adjective or adverb. Example: “My sister is older than I am” That – used to introduce a clause that states a reason or purpose. Example: “Olivia is so happy that it’s summer again” When – at or during the time that something happened. Example: “A teacher is good when he inspires his students” Where – at or in the place that something happened. Example: “We went to the bar where there most shade” Whether -used to indicate choices or possibilities. Example: “Bruno wasn’t sure whether to go to India or Thailand” While – during the time that something happened” Example: “While we were in Paris, it snowed” Until – up to the time or point that something happened” Example: “We stayed up talking until the sun came up” E. Discussing New Concepts and Practicing New Skills #2 Choose the Best (5 minutes) F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) Bingo! (20 minutes) The teacher will facilitate this game: Subordinating Conjunctions Bingo The teacher will ask students to identify the subordinating conjunction in the following sentences: 1. The children were happy when the show began. 2. This is the place where the accident occurred. 3. Though he worked hard, he couldn’t win the first prize. 4. I will go even if he forbids me. 5. She will not come unless you invite her. 6. Though she is pretty, I don’t like her. 7. It is surprising that she didn’t invite you. 8. Will you wait here until I come? 9. I couldn’t go because it was raining. 10. Since the sky is overcast we will cancel the picnic. The students will give the following correct answers: 1. The children were happy when the show began. 2. This is the place where the accident occurred. 3. Though he worked hard, he couldn’t win the first prize. 4. I will go even if he forbids me. 5. She will not come unless you invite her. 6. Though she is pretty, I don’t like her. 7. It is surprising that she didn’t invite you. 8. Will you wait here until I come? 9. I couldn’t go because it was raining. 10. Since the sky is overcast we will cancel the picnic. In this rewarding teaching activity, students play games of bingo by completing sentences on a bingo card with subordinating conjunctions. Each https://www.teachthis.com/parts-of-speechactivitiesworksheets/conjunctions G. Finding Practical Applications of Concepts and Skills in Daily Living Imagine… (2 minutes) The teacher will ask: Which conjunctions are used most often? What would happen student is given a bingo card. Each bingo card consists of five sentences with each sentence missing a different subordinating conjunction. The teacher calls out subordinating conjunctions from the caller's sheet in a random order. If a student thinks a conjunction goes in one of their sentences, they write it in the corresponding gap in the sentence. When a student has completed all five sentences with a different conjunction, they shout 'Bingo'. When a student shouts 'Bingo', they read out all five sentences. If the sentences are correct, the student wins the round. If the student has made a mistake, the game continues. Several rounds are played with students receiving a different bingo card each time. As an alternative or extension, the students are divided into groups of five. The students then play the game in their groups with students taking it in turns to be the bingo caller. This continues until all the bingo cards have been used. Students will share their thoughts H. Making Generalizations and Abstractions about the Lesson I. Evaluating Learning if we will not conjunctions in sentences? Know the Difference (2-4 minutes) The teacher will ask: How is subordinating conjunction different from coordinating conjunction? More Practice (10 minutes) The teacher will ask the students to answer the following exercises. A. Identify the subordinating conjunction in each of the sentences below: 1. We were happy when we received the first prize. 2. The people were listening eagerly while the leader was speaking. 3. This is the place where we were attacked. 4. Although he worked hard, he failed. 5. Though she is beautiful, she is not intelligent. B. Write 5 sentences using the following subordinating conjunctions: After If In case However Unless C. Combine the short sentences by using the subordinating conjunction provided in the box. Because Until When After Since 1. Finish eating your The students will answer: Subordinating conjunction connects an independent clause and dependent clause while coordinating conjunction connects two independent clauses. The students will answer the exercises. A. Answers: 1. when 2. while 3. where 4. although 5. though B. Students will write grammatically correct sentences using subordinating conjunctions C. 1. After you finish eating your breakfast, brush your teeth. 2. I have to stay for tutoring because I failed the quiz in math. 3. We won’t have practice today since it is J. Additional Activities for Application or Remediation breakfast. Brush your teeth. 2. I have to stay for tutoring. I failed the quiz in math. 3. We won’t have practice today. It is raining. 4. I woke up. I saw that it was snowing! 5. You eat your vegetables. You cannot have dessert. Your Turn! The teacher will ask the students to write short narrative using the different subordinating conjunctions about any of the following topics. Personal hobby Favorite food Memorable experiences Etc. V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies work well? Why did these work F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovations or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers raining. 4. When I woke up, I saw that it was snowing! 5. Until you eat your vegetables, you cannot have dessert. The students will compose short narrative about topic of choice.