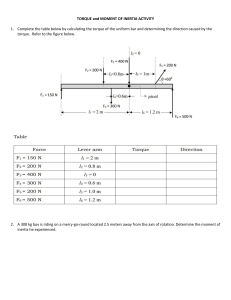
With No Bending Materials Present Definition - Single Cell Torque Box with No Bending Materials Present is no more than a Wing Torque Box with one enclosed area within the wall’s centerline. With One Spar Wing with Flanges or D-Section Introduction - To illustrate the application of the method of shear distribution, the equations of equilibrium will be set up for a typical D-section wing nose torque box. - A section of the torque box is shown in Fig. (a) while a view of the portion of the structure outboard of the section being investigated is shown in Fig. (b). Introduction Introduction - The load P is the sum of the vertical components of all the loads on the wing outboard of the section & is applied at the center of pressure of those load. - It is obvious that P is equal to the shear on the wing section. Introduction - The load P is held in equilibrium by load due to shear stresses in the skins & the spar web. - In calculating moment for the equation of equilibrium which fulfills the condition that the sum of the moments about any axis is equal to zero, any convenient reference axis may be chosen. Introduction - Since it is convenient to take the axis in such a position that the moment due to one of the unknown forces is zero. an axis through point O in the figure is chosen as the reference axis. Introduction - Referring to figure (a), the equations of equilibrium are: - (∑FV = 0) P - qnh - qwh = 0 - (∑M = 0) T - 2Aqn = 0 Sample Problems Problem No. 1 - Find the stresses in the section of a stabilizer shown in the figure. - The shear is 5,000 lb & the torque about the spar web axis is 25,000 in-lb. - (Shear acts downward & the torque in a counter-clockwise direction.) - The shape of the nose section is that of half an ellipse w/ semi-major length of 15 in & minor length of 10 in. Problem No. 1 - Thicknesses: Nose skin = 0.04 in; Spar web = 0.064 in - If the section is constant & is 50 inches long, find the angle of twist. - Material is aluminum alloy, G = 3.8 x 106 psi. Problem No. 1 Problem No. 2 - Determine the shear stresses & the angle of twist of the D-section torque box described in problem no.1 if the shear load (5,000 lb) is applied at the centroidal point of the torque box w/ a different resulting torque load. Problem No. 3 - Find the stresses in the section of a stabilizer w/ configuration as described: - DEFA is a rectangular section w/ spar web EF equal to 3R & LDE = 8R. - AB is a quarter elliptical section w/ center at O1, semi-major length BO1 equal to 4R & semi-minor length AO1 equal to 2R. Problem No. 3 - BC is a quarter circular section w/ center at O2 & radius R = 10 inches. - CDO1O2 is another rectangular section. - The shear is 6000 lbs acting upward at the centroidal position from the spar web axis. Problem No. 3 - If the section is constant & is 5 ft long, find the angle of twist. - Material is an aluminum alloy w/ modulus of rigidity of 4 x 106 psi. - Thicknesses: - Nose-skin = 0.080 in. - Spar web = 0.10 in.