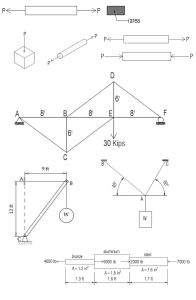
INTRODUCTION: Mechanics – is a physical science that deals with the behavior of bodies under the influence of forces Categories: * Mechanics of Rigid Bodies * Mechanics of Deformable Bodies * Mechanics of Fluids Mechanics of Deformable - deals with how forces with the deformations distributions - these internal forces which could result in Bodies are distributed inside bodies and caused by these internal forces produces “stresses” in the body, the failure of the material itself Simple Stresses: - is an expression as the ratio of the applied force divided by the resisting area; or the expression, force per unit area Categories: * Normal Stresses * Shear Stresses * Bearing Stresses NORMAL STRESSES: - is developed when a force is applied perpendicular to cross-sectional area of the material - it is the strength of material per unit area or unit strength Two Types of Normal Stresses * Tensile Stress – tends to pull the material * Compressive Stress – tends to compress the material Illustrative Problem: For the truss as shown in the figure, determine the stresses in members DE and DF. The cross-sectional area of each member is 1.8 sq.inches. Indicate whether tension (T) or compression (C). Illustrative Problem: Determine the largest weight W that can be supported safely by the structure as shown in the figure. The working stresses are 16000 𝑝𝑠𝑖 for the steel cable AB and 720 𝑝𝑠𝑖 for the wood strut BC. Neglect the weight of the structure. The area of steel cable AB is 0.5 𝑖𝑛2 and the area of the strut BC is 16 𝑖𝑛2 Illustrative Problem: A two-member truss supports a block of weight W as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional areas for the members are 800 𝑚𝑚2 for AB and 400 𝑚𝑚2 for AC. Determine the safe value of W if the working stress are 110 𝑀𝑃𝑎 for AB and 120 𝑀𝑃𝑎 for AC. Illustrative Problem: A composite bar consists of aluminum section rigidly fastened between a bronze section and a steel section as shown in the figure. Axial loads are applied at the positions indicated. Determine the stresses in each section and indicate whether tension (T) or compression (C).