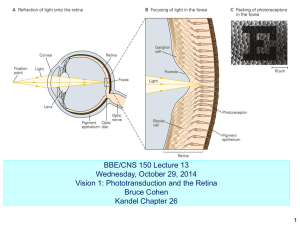
Chapter Opener 15 554-575 Vision: Describe the structural components of the eye Explain the concepts of refraction, image formation, accommodation Describe the principal refraction abnormalities Describe the processing of visual signals in the retina Describe the neural pathway for vision © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Eyebrows • • • • Coarse hairs that overlie the supraorbital margins Functions include: – Shading the eye – Preventing perspiration from reaching the eye Orbicularis muscle – depresses the eyebrows Corrugator muscles – move the eyebrows medially Palpebrae (Eyelids) • • • • Protect the eye anteriorly Palpebral fissure – separates eyelids Tarsal plates of connective tissue support the eyelids internally Levator palpebrae superioris – elevates the upper eyelid not responsible for terms except __ Conjunctiva • Transparent membrane that: – Lines the eyelids as the palpebral conjunctiva – Covers the whites of the eyes as the ocular conjunctiva – Lubricates and protects the eye. What is conjunctivitis? ___ not responsible for terms except Figure 15.2 The lacrimal apparatus. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.3 Extrinsic eye muscles. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.4 Internal structure of the eye (sagittal section). © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.5 Pupil constriction and dilation. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.6 Microscopic anatomy of the retina. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. The Retina: Ganglion Cells and the Optic Disc • • Ganglion cell axons: – Run along the inner surface of the retina – Leave the eye as the optic nerve The optic disc: – Is the site where the optic nerve leaves the eye – Lacks photoreceptors (the blind spot) Figure 15.8 Circulation of aqueous humor. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.10 The electromagnetic spectrum and photoreceptor sensitivities. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.11 Refraction. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.12 Light is focused by a convex lens. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.13 Focusing for distant and close vision. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.14 Problems of refraction. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.15 Photoreceptors of the retina. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.16 The formation and breakdown of rhodopsin. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.17 Events of phototransduction. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.18 Signal transmission in the retina. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell –40 mV –70 mV Bipolar cell Ganglion (a) 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light (b) Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 2 Ca2+ channels closed Ca2+ channels open Bipolar cell Ganglion (a) 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light (b) Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 3 Ca2+ channels open 2 Ca2+ channels closed Neurotransmitter released 3 No neurotransmitter released Bipolar cell Ganglion (a) 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light (b) Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 3 Ca2+ channels open 2 Ca2+ channels closed Neurotransmitter released 3 No neurotransmitter released 4 IPSP in bipolar cell Bipolar cell 4 No IPSP, bipolar cell depolarizes Ganglion (a) 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light (b) Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 3 Ca2+ channels open 2 Ca2+ channels closed Neurotransmitter released 3 No neurotransmitter released 4 IPSP in bipolar cell Bipolar cell 4 No IPSP, bipolar cell depolarizes 5 No neurotransmitter released Ganglion (a) (b) Ca2+ 5 Neurotransmitter released Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 3 Ca2+ channels open 2 Ca2+ channels closed Neurotransmitter released 3 No neurotransmitter released 4 IPSP in bipolar cell Bipolar cell 4 No IPSP, bipolar cell depolarizes 5 No neurotransmitter released 6 No EPSP in ganglion cell 5 Neurotransmitter released 6 EPSP in ganglion cell Ganglion (a) Ca2+ (b) Na+ Ca2+ 1 Photoreceptor depolarized Photoreceptor cell 1 Photoreceptor hyperpolarized Light –40 mV –70 mV 2 Ca2+ 3 Ca2+ channels open 2 Ca2+ channels closed Neurotransmitter released 3 No neurotransmitter released 4 IPSP in bipolar cell Bipolar cell 4 No IPSP, bipolar cell depolarizes 5 No neurotransmitter released Ca2+ 5 Neurotransmitter released 6 No EPSP in ganglion cell 6 EPSP in ganglion cell 7 No action potentials 7 Action potentials Ganglion (a) (b) Figure 15.19 Visual pathway to the brain and visual fields, inferior view. © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Visual Pathways • • Axons of retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve Medial fibers of the optic nerve decussate at the optic chiasm • • Most fibers of the optic tracts continue to the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus Other optic tract fibers end in superior colliculi (initiating visual reflexes) and pretectal nuclei (involved with pupillary reflexes) Optic radiations travel from the thalamus to the visual cortex A small subset of visual fibers contain melanopsin (circadian pigment) which: – Sets daily biorhythms, biological clock • • Table 15.1 Comparison of Rods and Cones © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.