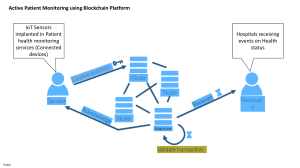
Introduction The traditional education system faces various challenges that affect both students and educators. These challenges include academic fraud, credential verification, and student data privacy. Academic fraud and plagiarism are rampant in higher education and threaten academic integrity. Credential verification and degree authentication are also significant concerns for students and employers, given the lack of transparency and trust in traditional academic systems. Furthermore, student data privacy is increasingly becoming a critical concern, particularly with the widespread use of online learning platforms and student information systems. Blockchain technology has the potential to address these issues by providing a secure and decentralized system for recording and sharing academic information. Background Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger technology that allows secure and transparent record-keeping. Although it is popularly known for its application in cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications beyond financial transactions. In a blockchain system, data is stored in blocks that are linked together in a chain. Each block contains a unique code called a hash that links it to the previous block in the chain, creating a tamper-proof system. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology ensures that there is no single point of failure or control, making it a secure and reliable system for recording and sharing data. Literature Review Several studies have explored the potential application of blockchain technology in higher education. For instance, Wang et al. (2019) proposed a blockchain-based credentialing system that provides a secure and transparent way to verify academic qualifications. The system allows for the creation and management of tamper-proof digital credentials that can be shared and verified easily. Similarly, Kim et al. (2020) proposed a blockchain-based degree verification system that ensures the authenticity and security of academic degrees. The system uses blockchain technology to create an immutable record of degrees that can be easily accessed and verified by employers and other stakeholders. Table 1: Examples of Blockchain Applications in Higher Education Blockchain technology has the potential to address several student issues in higher education. One potential solution is the use of blockchain-based credentialing systems that can provide a secure and transparent way to verify academic qualifications. These systems can create and manage tamper-proof digital credentials that can be easily shared and verified. Another solution is the use of blockchain-based record-keeping systems that can prevent academic fraud and ensure data privacy. These systems can use smart contracts to automate the recording and verification of academic data, creating an efficient and secure system. Challenges and Limitations Despite the potential benefits of blockchain technology in higher education, there are several challenges and limitations that must be addressed. One significant challenge is the lack of awareness and understanding of blockchain technology among educators and students. Additionally, the cost and technical complexity of implementing blockchain systems pose a significant challenge. Moreover, there are concerns around the security and privacy of blockchain systems, particularly in terms of protecting student data from malicious attacks. Another limitation of blockchain technology in higher education is the potential for creating new inequalities. For example, implementing blockchain-based credentialing systems may require significant investment in technology and infrastructure, which may be a barrier for smaller institutions or students from disadvantaged backgrounds. Furthermore, the use of blockchain systems may require specialized skills and knowledge, creating a digital divide among students and educators.