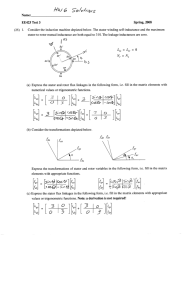
Discussion of Theory. AC MACHINE AC (alternating current) machines are electric machines that operate on AC electrical power. AC machines can be classified into two major types: synchronous machines and induction machines. Synchronous machines operate at a constant speed that is synchronized with the frequency of the AC power source. Synchronous machines are used for applications where precise speed control is required, such as in power plants and large industrial facilities. The operation of synchronous machines is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and the interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields. Induction machines, also known as asynchronous machines, operate at a speed slightly lower than the synchronous speed. Induction machines are the most commonly used type of AC machine and are used in a wide range of applications, including pumps, fans, and compressors. The operation of induction machines is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, and the interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields. There are several key principles and concepts that are important to understand when studying AC machines. These include: Electromagnetic induction: This principle states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor. In AC machines, electromagnetic induction is the fundamental principle that allows the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. Magnetic fields: In AC machines, magnetic fields are created by the interaction of the stator and rotor. The stator contains a set of stationary coils that generate a rotating magnetic field, while the rotor contains a set of conductors that interact with the magnetic field to produce torque. Slip: Slip is the difference between the synchronous speed and the actual speed of the rotor in an induction machine. Slip is a critical parameter in determining the operating characteristics of an induction machine, including efficiency, power factor, and torque. Power factor: Power factor is the ratio of real power to apparent power in an AC machine. A high power factor is desirable because it indicates that the machine is using the electrical power efficiently. Rotor and stator design: The design of the rotor and stator in AC machines is critical to their performance. The geometry, material properties, and winding configurations all play a significant role in determining the efficiency, power factor, and torque of the machine. Control methods: AC machines can be controlled using a variety of methods, including variable frequency drives, soft starters, and static starters. These control methods allow for precise speed control, reduced energy consumption, and improved operating efficiency. Overall, the principles and concepts of AC machines are fundamental to the operation and design of these important electrical devices. Understanding these principles is critical for engineers and technicians working in fields such as power generation, industrial automation, and transportation. AC Motor as Portable Thersher. Introduction: Threshing is the process of removing grain or seeds from the chaff or straw. Traditionally, threshing was done manually using tools like flails or by using animals like bullocks or horses to trample over the crops. With the advent of technology, threshing machines were developed to automate this process. However, many farmers in developing countries still use traditional methods, as threshing machines are expensive and require a reliable source of power. In this paper, we will discuss the design and working principle of a portable thresher made of an AC motor. Design: The portable thresher is designed to be lightweight and easy to transport. It consists of a wooden frame that supports the threshing drum, which is made of metal. The drum has a series of teeth or beaters attached to it, which rotate when the motor is switched on. The motor is mounted on the frame and is connected to the drum using a belt or chain. The AC motor used in the thresher is a single-phase induction motor. This type of motor is simple and reliable, making it suitable for use in agricultural machinery. The motor is connected to a power source using a plug and socket, which allows it to be easily removed and replaced. Working Principle: The portable thresher works by separating the grain or seeds from the chaff or straw. The crop is fed into the threshing drum through a hopper at the top of the machine. The drum rotates at high speed, causing the teeth or beaters to strike the crop, separating the grain from the chaff. The separated grain falls through the drum and onto a tray or container placed below the machine. The chaff and straw are blown out of the machine by a fan or blower attached to the motor. The fan creates a suction that pulls the chaff and straw through a pipe or chute and deposits them onto the ground. The speed of the threshing drum can be adjusted by changing the pulleys or gears used to connect it to the motor. This allows the machine to be used with different types of crops and at different stages of ripeness. Conclusion: The portable thresher made of an AC motor is a simple and effective machine for threshing crops. Its lightweight design makes it easy to transport, and the single-phase induction motor provides a reliable source of power. By separating the grain from the chaff, the thresher improves the efficiency of crop harvesting and reduces the labor required. The machine can be used in a variety of settings, making it a valuable tool for farmers in developing countries.