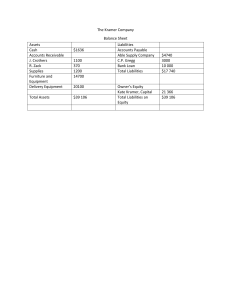
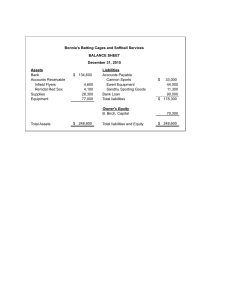
ACC101: Financial Accounting and Reporting 1stSemester: 2022 Preliminary Examination Name: _______________________________ Date: ___________________ Section: ______________________________ Part 1. Multiple Choice 1) 2) 3) 4) The process of IDENTIFYING, RECORDING, and COMMUNICATING economic events of an organization to interested users a. Bookkeeping c. Purchasing b. Accounting d. Engineering The basic storage of information in accounting a. Account Title c. Trial Balance b. Normal Balance d. Account Events that affect the asset, liabilities, equity, income or expenses of a business when identifying transactions a. Journal Entries c. Accountable Event b. Communicating d. Bookkeeping The process of recording accounts or transactions of an entity and normally ends with the preparation of the trial balance. a. Journal Entries b. Communicating 5) 6) 7) c. Accountable Event d. Bookkeeping Information is selected or presented without bias and is not manipulated to increase favorability. a. Completeness c. Verifiability b. Neutrality d. Timeliness Economic resources you control that can provide economic benefits. a. Liabilities c. Equity b. Asset d. Income Increases in assets, or decreases in liabilities, that result in increases in equity. a. Liabilities c. Equity b. Asset d. Income 8) Defined as the difference between assets and liabilities. a. Liabilities c. Net Worth b. Expenses d. Income 9) The concept that views each transaction as having two-fold effect on values. a. Duality c. Journalizing b. Equilibrium d. Posting 10) Represents the reduction of the value of a related account a. Credit c. Contra-account b. Debit d. Depreciation The concept of observing a degree of caution when exercising judgements 11) needed in making accounting estimates. a. Time Period c. Matching b. Prudence d. Separate entity The concept of the business is viewed as a separate person, distinct from its 12) owners. a. Time Period c. Matching b. Prudence d. Separate entity The concept that guides the accountant when applying accounting 13) principles a. Materiality c. Prudence b. Matching d. Separate entity 14) Represents the goods that are held for sale by a business a. Bad debts c. Office supplies b. Inventory d. Equipment 15) Interest incurred but not yet paid. a. Interest expense c. Interest payable b. Prepaid interest d. Interest receivable Part 2. ACCOUNTING EQUATION ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY 1 370,000.00 70,000.00 ? 2 270,000.00 ? 130,000.00 3 ? 180,000.00 330,000.00 4 330,000.00 ? 120,000.00 5 130,000.00 80,000.00 ? 6 780,000.00 150,000.00 ? 7 1,000,000.00 ? 580,000.00 8 ? 330,000.00 170,000.00 9 920,000.00 ? 560,000.00 10 760,000.00 240,000.00 ? ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY + INCOME - EXPENSES 11 690,000.00 130,000.00 320,000.00 270,000.00 ? 12 940,000.00 127,000.00 300,000.00 ? 180,000.00 13 750,000.00 360,000.00 ? 200,000.00 80,000.00 14 680,000.00 ? 300,000.00 210,000.00 70,000.00 15 ? 410,000.00 170,000.00 480,000.00 190,000.00 16 360,000.00 100,000.00 200,000.00 85,000.00 ? 17 1,250,000.00 250,000.00 500,000.00 ? 150,000.00 18 359,000.00 160,000.00 ? 70,000.00 50,000.00 19 697,000.00 ? 200,000.00 300,000.00 600,000.00 20 ? 780,000.00 470,000.00 680,000.00 490,000.00 PART3-Journal Entries: A business had the following transactions during the month. Provide the journal entries to record the transactions. Aug Transaction 1 The owner contributed P500,000 cash to the business. 3 The business purchased inventory worth P150,000 on account. 4 The business purchased office supplies worth P40,000 on account. The business purchased additional inventory worth P200,000 on cash 5 basis. The business purchased an equipment worth P50,000 and paid 50% 6 down payment and the balance due in 30days The business sold goods for P10,000 cash. The cost of the goods sold is 7 P5,000. The business sold goods for P5,000 on account. The cost of goods sold is 8 P2,500. 9 The business paid P40,000 accounts payable. 10 The business collected P5,000 receivable from Aug. 8 transaction 12 The business paid for the balance of the equipment purchased. The business sold goods for P20,000 on a promissory note. The cost of 13 goods sold is P10,000. The business sold goods for P30,000 with 90% down payment and the 14 balance on account with a 10% interest. The cost of goods sold is P15,000. 15 The business paid salaries of P20,000 17 The business was paid P10,000 for an order to be delivered in 3 days. 18 The business collected the receivable from Aug. 13 The business collected the balance from Aug. 14 transaction with the 19 interest. The business delivers the order from Aug. 17 and incurs a delivery fee of 20 P100. The cost of goods sold is P5,000. 25 The business paid utilities for P10,000 27 The business paid the purchased inventory from Aug. 3 transaction 31 The business paid salaries expense of P20,000.