Alternator Regulation: Synchronous Impedance Method Lab
advertisement

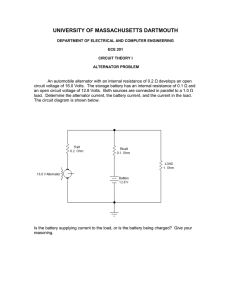
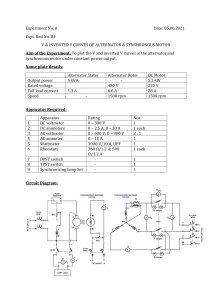
REGULATION OF THREE PHASE ALTERNATOR BY SYNCHRONOUS IMPEDANCE METHOD Aim of the experiment: - To find the regulation of a three phase alternator by synchronous impedance method. Apparatus required: Sl.No. 1 2 3 4 5 Equipment required Ammeter Ammeter Voltmeter Rheostat Rheostat Specifications 0-2A 0-500mA 0-450V 300Ω,2A 38Ω,8.5A Type MI MC MI Quantity 1 1 1 1 1 Circuit Diagram: - 38Ω, 8.5A A S1 1 V 300/2A 220V DC Supply (0-450V) A (0-2A ) M E1 E2 B 2 F1 F2 FF2 ALTERNATOR FIELD 500mA L A + 300,2A 220V DC Supply L - Theory:1. What is regulation of an alternator (a.c generator) The winding of the alternator has some resistance and internal reactance. When this alternator is loaded the output voltage of alternator decreases due to voltage drop taking place in the winding of alternator. In other word if load is thrown off from the generator. Its output voltage will increase. The regulation of alternator is defined as. Regulation = = = 𝑅𝑖𝑠𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑟𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑜𝑓𝑓 𝑁𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑙 𝑓𝑢𝑙𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝐸0 −𝑉 𝑉 𝐸0 −𝑉 𝑉 x100% Where E0 = No load terminal voltage V = Terminal voltage at load While calculating regulation it is assumed that speed and exciting current of alternator is maintained constant as terminal voltage is also function of these quantities. Note: - Changes in voltage depends on load current and power factor. With leading power factor, terminal voltage increases with load and hence regulation will be negative. In practice, regulation (measure of change of voltage) should be as less as possible. 2. Determination of regulation of alternator As Regulation = 𝐸0 −𝑉 𝑉 , we can load an alternator and note voltage at load and at no load. But this method is not possible in case of large machines, as it will not be possible to load them directly. Some other methods therefore are used. Procedure: - Run-1 For open circuit (magnetisation characteristic) a) Keeping alternator excitation zero, start the d.c motor and adjust its speed to rated speed of alternator. b) Increase the excitation of alternator in steps. For each value of excitation current take readings of the terminal voltage. Maintain frequency constant. Run-2 For short circuit characteristic of alternator. a) Reduce the excitation of alternator to zero. b) Remove the voltmeter and connect an ammeter in one line and short circuit the other by a wire. Increase the excitation in steps and note down the value of field current and short circuit current. Field current should be increased very gradually and it should be seen that short circuit current of alternator does not exceed the 125% of full load rated current. 3. Measure the d.c resistance of the alternator armature winding (one phase) by ammeter and voltmeter method. Take the effective resistance as 1.2 times the d.c resistance if taken in hot armature and 1.6 times if taken in cold armature. Observation: Observation for o.c test SL.NO. If V Frequency Speed If Is Observation for s.c test SL.NO. Observation for finding out a.c resistance of alternator winding SL.NO. I V R Mean Reff/ph Report 1. Plot the open circuit and short circuit chart on a common abscissa, (field current) calculate the synchronous impedance to full load current. 2. Draw phasor diagram corresponding to rated current at 0.8 p.f lagging and leading and find the regulation in each case. Discussion and questions 1. Give your comments regarding the accuracy of finding regulations by this method compare merits and demerits with other methods. Questions 1. How can you improve regulation of alternator? 2. Draw vector diagram of alternator at lagging and leading p.f and show that at leading p.f regulation is negative. 3. What are different methods of finding regulation of alternator?