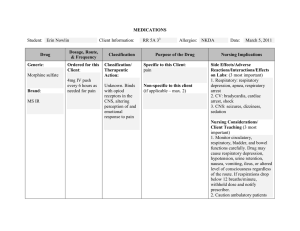
Study Guide Chapter 39: Oxygenation and Perfusion Before you begin reading, review/know the key terms listed at the beginning of the chapter. Be sure to review Chapters 25 (pp ) and 26 (pp ) for additional assessment information and key terms. Learning Objective 1. Describe the principles of respiratory and cardiovascular anatomy and physiology. Figures 39-1, 39-2, 39-3, 39-4, 39-5, 39-6, 39-7 Respiratory system performs its functions through the following terms: (define) Pulmonary ventilation: Respiration: Perfusion: Normal functioning depends on the following: 1) 2) 3) The airway is a pathway for the transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is divided into the upper and lower airways. Describe the organs in each airway and their main functions. STRUCTURE Upper Airway is composed of: ____________, _____________, ____________, __________________ Its main function is: _________, ____________, _______________ inspired air Lower Airway is composed of: (start at trachea and end at alveoli) list below: Its main functions are: _____________, _______________, ______________ Discuss the lungs, including their location, composition, and function. Describe the two phases of the process of ventilation: inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation), and what occurs in each phase. What are the factors that influence the diffusion of gases in the lungs. Describe how oxygen is carried in the body (via plasma and red blood cells). Discuss problems that might exist in ventilation, respiration, or perfusion (hypoxia, hypoventilation). Learning Objective 2. Describe the function and role of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems in oxygenation. An adequately functioning cardiovascular system is vital for exchange of gases. Know the blood flow through the body, back to the heart/lungs – figure 39-6 Name all the structures of the cardiovascular system: Name the Four hollow chambers: __________________ ____________________ What is the function of the upper chambers: What is the function of the lower chambers: Name and discuss the blood vessels and their function: Describe the process of internal respiration: What abnormalities can affect internal respiration? What can improve internal respiration? Learning Objective 3. Describe age-related differences that influence patient-centered care of patients with oxygenation problems. Discuss how nursing care may be tailored to meet age-related respiratory needs. (Refer to Table 39-1: Respiratory Variations in the Life Cycle; Focus on the Older Adult: Nursing Strategies to Address Age-Related Changes in Oxygenation. Learning Objective 4. Identify factors that influence respiratory and cardiovascular function. Discuss the variables that influence respiratory functioning (levels of health, developmental considerations, medications, lifestyle, environment, psychological health). List and define three (3) alterations in respiratory function: 1_______________________________ 2_______________________________ 3_______________________________ Identify specific nursing interventions that might help prevent or alleviate alterations in respiratory function: Learning Objective 5. Perform a cardiopulmonary assessment using appropriate communication interview questions and physical assessment skills. (See Table 39-1). Review Chapter 25 pp (652-70) Skills 25-2 (677-679), 25-3 (680-81), 25-4 (681-686), & Chapter 26 pp (714-721) Skill 26-2 (Peripheral vascular system). Use the nursing process to assess patients for respiratory functioning: Think in terms of: “What do I observe going on with my patient (assess)?” “What questions can I ask to get a better understanding of how my patient feels?” “What alteration in normal respiration is my patient experiencing (diagnose/patient problem)?” “How can I help, what does evidence-based practice tell me I can do to alleviate/prevent the problem/potential problem (planning)?” “How can I intervene (implement the plan)?” “After I have intervened, what was the result (evaluate)? Is the problem solved? If not, what else can I do? Describe the respiratory component of a nursing history and how to perform a physical assessment of the respiratory system. (Refer to Focused Assessment Guide 39-1: Oxygenation for appropriate questions for health history assessment.) Discuss the interviewing techniques used and the types of information obtained in a nursing history. List questions tailored to meet the unique needs of individual adults and older adults. Be sure to take into consideration the variables that affect respiratory functioning discussed in the previous section. What would you say to a patient who has never seen a pulse oximeter? Refer to Skill 39-1: Using a Pulse Oximeter. Describe the type of sounds that may be heard upon percussion and the breath sounds that may be auscultated while listening to a complete respiratory cycle. What differentiates wheezes from rhonchi, crackles, stridor, or friction rubs? (Listen to some examples on Youtube.) Learning Objective 6. List and describe (as if you were explaining to the patient) important diagnostic tests and procedures related to oxygenation and perfusion: (Refer to Box 39-1: Commonly Measured Values from Pulmonary Function Tests; Table 39-2: Common Laboratory Studies Used to Assess Cardiopulmonary Function). What would you say to a patient who has never had: PFT ABG Cardiac Biomarker CBC Sputum Cytologic Study Capnography Thoracentesis What information do these tests give us? Learning Objective 7. Develop nursing diagnoses/patient problems that correctly identify problems that may be treated by independent nursing interventions. Remember, the etiology of the problem directs nursing interventions, and the nurse must determine whether the alteration in respiratory functioning is the problem, is contributing to a different problem, or is a sign or symptom of a problem. List 3 common diagnoses for alterations in respiratory function. 1) 2) 3) Compare/contrast the manifestations (symptoms) a patient may present with each of these diagnoses (patient problems) Learning Objective 8. Discuss safety measures and safe administration of oxygen using different modes of deliver; including for the patient going home with oxygen. Discuss the various types of delivery systems available for administering supplemental oxygen. (Refer to Table 39-4: Oxygen Delivery Systems; Guidelines for Nursing Care 39-2: Transporting a Patient With a Portable Oxygen Cylinder; Skill 39-3: Administering Oxygen by Nasal Cannula; Skill 39-4: Administering Oxygen by Mask) What would you teach a patient regarding the precautions for oxygen administration? (Refer to Teaching Tips 39-1: Using Oxygen at Home; Guidelines for Nursing Care 39-2: Transporting a Patient With a Portable Oxygen Cylinder.) Describe different types of artificial airways and the nurse’s role in providing care for a patient with an artificial airway in place. Discuss types of devices to assist ventilation. (Refer to Table 39-5: Comparison of Chest Drainage Systems; Guidelines for Nursing Care 39-3: Monitoring a Patient With a Chest Tube; Skill 39-2: Suctioning the Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Airways; Skill 395: Providing Care of a Tracheostomy Tube; Skill 39-6: Suctioning a Tracheostomy: Open System.) Review the proper administration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Learning Objective 9. Describe nursing strategies to promote adequate oxygenation and identify their rationale. Review specific nursing interventions to promote adequate respiratory functioning, including teaching about a pollution-free environment, promoting optimal function, promoting comfort, promoting proper breathing, managing chest tubes, promoting and controlling coughing, suctioning the airway, and meeting respiratory needs with medications. Discuss the effects (both active and passive) of cigarette smoking. What environmental controls are being legislated? What are the rights of smokers and nonsmokers? Demonstrate the breathing techniques to promote proper breathing (deep breathing, using incentive spirometry, pursed-lip breathing, abdominal or diaphragmatic breathing). (Refer to Guidelines for Nursing Care 39-1: Teaching Patients to Use an Incentive Spirometer.) Discuss the responsibilities of the nurse when managing chest tubes. (Refer to Guidelines for Nursing Care 39-3: Monitoring a Patient with a Chest Tube) What type of medications can be used to promote coughing, aiding the movement of mucus through the respiratory system, and to control coughing to allow the patient to rest? Review nursing interventions to promote comfort (positioning, adequate fluid, humidified air, chest physiotherapy). What types of inhaled medications administered via nebulizer, metered-dose inhaler, or dry powder inhaler. (Refer to Table 39-3: Selected Medications Used to Improve Respiratory Function) Learning Objective 10. Plan, implement, and evaluate nursing care related to select nursing diagnoses involving oxygenation problems. Everyone involved in the evaluation process needs to identify effective interventions and reasons for any failures in achieving expected outcomes. Adjustments to the nursing care plan should then be made accordingly.