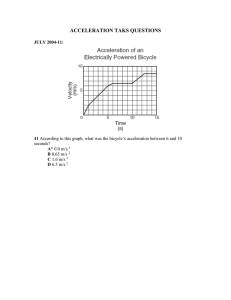
Assignment 2.5 - Explanation for the spreadsheet • Fig 1. Shows the velocity vs time graph of IDC for a 2W and a 3W Figure 1: 2 wheeler Indian Drive cycle • Fig 2. Explains what is the vehicle state in these 108 seconds of drive cycle. Whether the vehicle is accelerating, decelerating, steady state or idling. o Column “acceleration” denotes the vehicle acceleration in that operation. o Column “speed” mentions the starting and ending speed in that operation. o Column “duration of operation” denotes the number of seconds the operation lasted for. o Column “cumulative time” gives the cumulative time (1 to 108 seconds) Figure 2. Figure showing various states of acceleration, deceleration, Idling and steady state at various instances of IDC • Fig 3. Contains all the vehicle specs and other parameters which can be taken as variables. Figure 3. Specs of 2 wheeler given in question • Next job is to expand the drive cycle given in Fig 2. at 1 second interval, so as to compute all the forces at granularity of 1 sec. This is illustrated in fig 4. Highlighted is the operation no 2 of fig 2. Acceleration = 0.65, velocity goes from 0 to 14, duration of 6 sec and cumulative time 22 sec. In this fashion build the entire spreadsheet for 108 seconds. time(s) vel(km/h) dist (meters) vel (m/s) dv/dt = a 0 0 16 0 0 0 0 17 2.3333 0.6481 0.6481 0.6481 18 4.6666 1.2962 1.2962 0.6481 19 7 1.9444 1.9444 0.6481 20 9.3333 2.5925 2.5925 0.6481 21 11.6666 3.2407 3.2407 0.6481 22 14 3.8888 3.8888 0.6481 23 16 4.4444 4.4444 0.5555 24 18 5 5 0.5555 25 20 5.5555 5.5555 0.5555 0 Figure 4. A section of drive cycle. • Next setup a spreadsheet to compute all the traction forces. Take small intervals of ΔT (say 1 second). Figure 5. Spreadsheet derived using IDC Below formulas are used to compute the required forces: ◦ Distance: Vel (m/sec) * ΔT (sec) at each point ◦ Acceleration = ΔVel / ΔT in m/sec2 ◦ Acceleration Force Fa = M * Acceleration (Newtons) ◦ Rolling Resistance Force Fr = M*g*μ ◦ Drag Force FD = 0.5* Cd * ρ* A * v2 ◦ Traction Force Ftrac = Fa +Fr + FD (Newtons) ◦ Traction Torque (Nm) = Ftrac * wheel radius (m) ◦ Ptrac (Watts) = Ftrac* V (Nm/sec) and Ptrac (Watts) = (R * Ftrac) * V with Regeneration Efficiency R, when Ftrac is –ve (Ptrac computation in spreadsheet uses average speed of time instance t and instance (t-1), hence you will find factor of 0.5 in formula realized in spreadsheet.) ◦ Energy (Wh) = Ptrac * ΔT, Integrate to give drive-cycle energy USE MS Excel formulas to realize above equations.