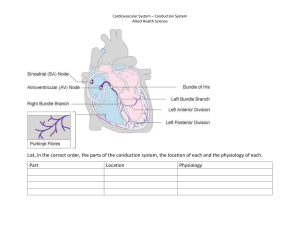
Uploaded by
Mary Jessa Dequiña
General Physiology Course Outline: Cells, Plants, Animals
advertisement
Course Outline in General Physiology (SCI 217) 3 units (3 hours per week) Semester/School Year Offered: 2nd t semester; SY 2021-2022 Course Description: This course discusses concepts which deals with the function of living cells, tissue, and organ, and system of plants and animals Topics Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO) Activity References I. THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE HUMAN BODY ● Atoms, Ions and Chemical Bonds ● Carbohydrates ● Lipids ● Proteins ● Nucleic Acids II. THE CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ● The Prokaryotic Cell - Structure - Function ● The Eukaryotic Cells ● The Plant Cell -Structure and Function of each organelles ● The Animal Cell - Structures and Functions of Animal Cell ● The Similarities and Differences of Plant Cell and Animal Cell III. WATER AND PLANT CELLS At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. identified the levels of organization in living things from atoms to individual. 2. identified the different biomolecules needed for life. 3. described the characteristics of the different biomolecules. 4. stated the importance of each biomolecule in maintaining life. At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. identified the different structures and organelles of a plant cell and their equivalent functions. 2. identified the different structures and organelles of an animal cell and their corresponding functions. 3. compared and contrasted plant cell from an animal cell 4. stated the recent trends and development in the field of Cytology (e.g. stem cell research) At the end of the unit, students must have: Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web LEARNING MODULE ● ● - - The Structure and Properties of Water Water structure Water Transport Processes Passive Transport -osmosis -diffusion Active Transport Primary Active Transport Secondary Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion IV. WATER BALANCE OF PLANTS ● Water in the Soil ● Water absorption by Roots ● Water transport through the Xylem ● Water Movement from the Leaf to the Atmosphere V. PHOTOSYNTHES IS ● - ● - ● Light Reaction Organization of Photosynthetic Apparatus Organization of Light Absorbing Antenna Systems Dark Reaction The Calvin Cycle Regulation of the Calvin Cycle The C2 Oxidative Photosynthetic Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis: Physiological and 1. Identified and described the structure of water. 2. describe water in terms of its properties. 3. described passive transport and its types 4. described active transport. 5. described facilitated diffusion 6. illustrated the different types of transport. source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologi a.vegetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. identified the mechanism of water transport within the plant and between the plant and it environment. 2. described the structure of plants’ roots. 3. described the process of how roots absorb water from the soil. 4. traced water movement from roots to leaf to atmosphere. At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. defined photosynthesis. 2. identified and differentiated the two types of photosynthetic reactions. 3. discussed the different light absorbing antenna systems and their functions in photosynthesis. 4. discussed the C2 oxidative pathway of photosynthesis 5. stated the physiological and ecological considerations of photosynthesis. Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology: Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC VI. Ecological Considerations GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Embryogenesis The Role of Cytokinesis in Pattern Formation Meristems in Plant Development Leaf Development Root Development Cell Differentiation Senescence and Programmed Cell Death At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. defined and described embryogenesis 2. discussed the role of cytokinesis in pattern formation. 3. discussed plant development in terms of meristems, leaf and root development. 4. described the process of cell differentiation. 5. discussed senescence and cell death Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisio logia.vegetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf PLANTS HORMONE Auxin Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Auxin Auxin Transport Physiological Effect of Auxin Gibberellins - Discovery and Effects of Gibberelins on Growth and Development Cytokinins Cell Division and Plant Development Discovery, Identification and Properties of Cytokinins Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Transport of Cytokinins Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Transport of ABA Developmental and Physiological Effects of ABA At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. identified some plants’ hormones. 2. stated the mechanism of hormone-induced plant growth. 3. described the physiological effect of some hormones to plants’ growth and development. 4. described plants’ growth when hormones failed to perform their designated function. Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf VIII. STRESS PHYSIOLOGY ● Water Deficit and Drought Resistance At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. identified the different types of stress that may affect plants’ Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologia.v egetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf - VII. ● ● ● - - ● - - LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) LEARNING MODULE PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC LEARNING MODULE PPT ● Heat Stress and Heat Shock ● Chilling and Freezing ● Salinity Stress ● Oxygen Deficiency ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY I. CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY AND HOMEOSTASIS •Cell parts and functions •Homeostasis •Body’s Regulation Mechanism -Negative feedback mechanism -Positive feedback mechanism II. ANIMAL NUTRITION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION Nutrition • Types of Nutrition • Steps in Nutrition ● Body’s Macronutrient Requirements Digestion ● Invertebrate Digestion • Mechanical Digestion • Chemical Digestion Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines • Steps in Digestion (include parts and function/s of each part) growth. 2. described the effect of heat stress and heat shock, chilling and freezing, salinity stress and oxygen deficiency to plants’ growth and development. 3. identified some plants’ survival mechanism to different types of stress. Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. defined a cell conceptually and operationally. 2. identified the basic cell parts, its organelles and their specific functions. 3. defined homeostasis 4. described how cells maintain balance or homeostasis. 5. described and illustrated body’s feedback mechanism (negative feedback and positive feedback) 6. cited examples of body’s feedback mechanism and describe each. At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. defined nutrition, its types and steps. 2. discussed macronutrient’s role in organisms’ survival. 3. discussed and differentiated the two phases of digestion. 4. identified digestive parts performing mechanical digestion or chemical digestion or both. 5. discussed in details the structural make-up and functions of the digestive structures. 6. stated the roles of accessory organs in digestion. 7. conversed on the importance of controlling digestion. Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) - Mouth - Esophagus - Stomach - Small Intestines •Accessory organs in digestion - Pancreas - Liver - Gall Bladder Metabolism ● Anabolism ● Catabolism III. ANIMAL ORGAN SYSTEM: THE RESPIRATORY AND CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM Circulatory System: •The Heart - Pulmonary and Systemic Circulations •The Blood - Composition - Function •The Blood vessels - Arteries - Capillaries - Veins Respiratory System •The structure of animal (human) respiratory system •Functions •Breathing and the Control of Respiration ● Hemoglobin and Oxygen Transport ● Carbon dioxide transport ● Acid-base balance of the blood Diseases of circulatory and respiratory system IV. ANIMAL ORGAN At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. described the general functions and major components of the circulatory system 2. described the composition of blood plasma and the physical characteristics and functions of the formed elements of the blood. 3. described the structure and pathways of the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 4. compared the structure of an artery and vein and explain how the structure of each type of vessel relates to its function 5. described the general functions and components of the respiratory system 6. explained how inspiration and expiration are accomplished in unforced breathing 7. explained the hemoglobin and oxygen transport in the blood and how they are influenced by blood Ph and temperature. 8. listed the different forms in which carbon dioxide is carried by the blood. Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC At the end of the unit, students must Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) LEARNING SYSTEM: THE URINARY SYSTEM •Organs of Excretion •The Urinary System -Functions •The Urination: Controlling a Reflex •Controlling Kidney Function and Maintaining Homeostasis V. ANIMAL ORGAN SYSTEM: MUSCLE MECHANISMS OF CONTRACTION AND CONTROL •Muscular System -The muscle fiber -Types of muscles -Functions ● Mechanisms of Contraction - Sliding filament theory of contraction - Regulation of contraction ● Contractions of Skeletal Muscles - Twitch, summation and tetanus ● Energy Requirements of Skeletal Muscles - Metabolism of Skeletal Muscles - Slow-and-FastTwitch Fibers - Muscle Fatigue have: 1. listed the functions of kidneys 2. identified the external and internal gross anatomical structure of the kidneys 3. traced the path of blood flow through the kidneys 4. describe the process of glomerular filtration 5. described how kidneys produce dilute and concentrated urine. 6. explained how dialysis is performed and what it accomplishes 7. described the effects of aging to urinary system 8. described how kidneys maintain body’s homeostasis. At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. described the gross structure of skeletal muscles. 2. described and explained the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. 3. listed the events that occur during cross-bridge cycles and described the role of ATP in muscle contraction. 4. explained how tropomyosin and troponin control muscle contraction and relaxation, and describe the role of Ca2+ and sarcoplasmic reticulum in excitation contraction coupling. 5. described the neural pathways involved in muscle contraction 6. explained how slow-twitch, fasttwitch and intermediate fibers differ in structure and function. 7. compared cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle in terms of structure and physiology 8. described the structure of smooth muscles and explained how its contraction is regulated Edition MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) ● Neural Control of Skeletal Muscles - Muscle spindle apparatus - Skeletal muscle reflexes ● Cardiac and Smooth Muscles - Cardiac Muscles - Smooth Muscles VI. ANIMAL ORGAN SYSTEM: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM •Principles of endocrinology •Pituitary and Hypothalamus - Pituitary Hormones - Control of the pituitary •The Thyroid gland - Production and Action of Thyroid Hormones •The Parathyroid gland •The Pancreas - Pancreatic Islets (islets of Langerhans) - Pineal gland - Thymus •The Adrenal Glands - Functions of adrenal cortex - Functions of adrenal medulla - Stress and Adrenal Gland VII. ANIMAL ORGAN SYSTEM: PHYSIOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM •Structure and At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. explained the principles of endocrinology. 2. defined the terms hormone and endocrine glands and describe how chemical transformations in the target cells can activate certain hormones. 3. described the structure of pituitary gland and explain the functional relationship between the pituitary and the hypothalamus. 4. described the productions and actions of the thyroid and parathyroid. 5. explained why the pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland and described the structure and functions of pancreatic islets. 6. described the functions of adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla 7. stated the connection between stress and the adrenal gland. Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. described the structure of a neuron and explain the functional significance of its principal regions Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Taiz,L and Zeiger, E. (2002). Plant Physiology, 3rd Edition, web source: exa.unne.edu.ar/biologica/fisiologi PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology: Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) functions of the neuron - Classification of neurons and nerves - Nuerilemma and myelin sheath - Action Potentials ● The Synapse - Electrical Synapse: Gap Junctions - Chemical Synapses ● Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter - Acetylcholinerase (AChE) - Acetylcholine in the PNS - Acetylcholine in the CNS • The CNS - The Brain: Its parts and Functions - The Spinal Cord and the Nerves: Parts and Functions •The Autonomic Nervous System - Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions - Functions of ANS VIII. REPRODUCTION, CELL DIVISION AND CANCER •Reproductive Organs -Invertebrates and Vertebrates -Human Reproductive structures and disorders •Cell Division -The Cell Cycle 2. classified neurons on the basis of their structure and function 3. described the neurilemma and its functions. 4. explained how a myelin sheath is formed. 5. described the properties of action potentials and explain the significance of the all-or-none law and refractory periods. 6. described ACh as neurotransmitter 7. located the major brain regions and described the structures within each region. 8. described the functions of each region 9. compared the structures and pathways of the autonomic system with those involved in the control of skeletal muscle. 10. described the structure and the general functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. a.vegetal/Plant PhysiologyTaiz2002.pdf At the end of the unit, students must have: 1. described the structures and functions of the reproductive organs of the invertebrate group 2. described and differentiated the structures and functions of male and female reproductive structures 3. described the hormonal changes that occur during puberty. 4. described the stages of spermatogenesis and the functions of Sertoli cells in this Fox, S. (2008). Human Physiology, 10th Edition LEARNING MODULE Reddy, P.B. (2015). Textbook of Animal Physiology web source: https://www.researchgate.net/publica tion/286456096 PPT PRESENTATI ON OF THE TOPIC TOPIC Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) Suggested Reading: Chiras, D. (1999). Human Biology:Health, Homeostasis, and the environment (3rd Edition) -Stages of Cell Cycle -Types of Cell Division and their significance •Understanding Cancer 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. process. described oogenesis and the stages of follicle development through ovulation and the formation of corpus luteum. described the significant events in the cell cycle. differentiated the types of cell division discussed the control of the cell cycle. discussed the status of cancer in the society described some physical and biological agents that may cause cancer. FINAL EXAMINATION CRITERIA FOR GRADING: Learning Modules Developed Topic Presentations Major Exam Individual Portfolio TOTAL 30% 20% 40% 10% 100% OTHER REQUIREMENTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. Learning Modules per topic PPT presentation of each topic Midterm and/or Final exam E-portfolio A, FORMAT FOR LEARNING MODULES: The learning modules must contain the following (per topic): I. II. INTRODUCTION (INCLUDES OBJECTIVES OF THE LESSON) BODY/CONTENT Includes: - Thorough and in-depth discussion of the topic - Clear illustrations of the topic (if needed) III. IV. V. VI. - Proper citations of the pictures used in the module. The source where the picture was taken must be indicated below the picture. - Diagrams/tables or any pictures must be properly labelled DRILL/ACTIVITIES/SHORT EXERCISES EVALUATION SUMMARY OF THE LESSON REFERENCES ALL LEANING MODULES ARE EXPECTED TO BE AT LEAST 80% AUTHENTIC. PLAGIARISM TEST WILL BE DONE UPON SUBMISSION OF THE OUTPUTS AND PLAGIARISM SHOULD NOT EXCEED 20% OF THE TOTAL MANUSCIPT. B. STUDENTS WHO CAN MAKE AND PRESENTED A COMPLETED RESEARCH (PEGAGOGY AND/OR CONTENT) IN ANY NATIONAL OR INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE SHALL BE EXEMPTED IN TAKING THE FINAL EXAM. C. CRITERIA FOR TOPIC PRESENTATIONS (IN PPT FORMAT) 10 pts c.1 The slides built interest in the presentation 20 pts c.2 The slides were clear, logical and organized 10 pts c.3 There were only bullets, no paragraphs. 20 pts c.4 The presentation was well-conceived 20 pts c.5 Information id accurate and includes a complete explanation of the concepts 20 pts c.6. Applications of the lessons are included 100 PTS