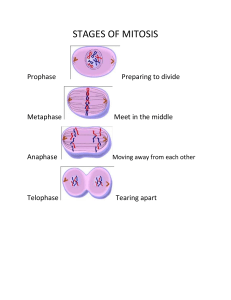
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell divisions in organisms. While both processes share similarities, there are some significant differences between them. Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four genetically diverse haploid cells. In mitosis, the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is the same as in the parent cell, whereas in meiosis, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. Another significant difference between mitosis and meiosis is the purpose they serve in organisms. Mitosis plays a role in growth, development, and tissue repair, while meiosis is critical for sexual reproduction. During meiosis, the process of crossing over and independent assortment ensures genetic diversity in the resulting offspring. The process of mitosis is divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, while meiosis is divided into two rounds. Meiosis I includes the stages of prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I, while meiosis II includes prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. In summary, mitosis produces two genetically identical diploid daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse haploid daughter cells. Mitosis plays a role in growth, development, and repair, while meiosis is critical for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. References: Campbell, N. A., & Reece, J. B. (2005). Biology. Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. Sadava, D. E., Hillis, D. M., Heller, H. C., & Berenbaum, M. R. (2011). Life: the science of biology. Macmillan.