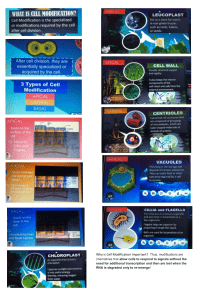
What is transcription and where does it occur? Transcription is the process of converting DNA sequence into mRNA in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell or the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell. During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of double-stranded DNA known as the promoter. The RNA polymerase then synthesizes a single-stranded RNA molecule complementary to one of the DNA strands through base pairing, with the help of nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) that provide the energy required for chain elongation in the growing RNA molecule. As transcription proceeds, a primary transcript is synthesized with the same sequence as the non-template DNA strand with the exception that thymine (T) in DNA is replaced with uracil (U) in RNA. In prokaryotes, transcription occurs in the cytoplasm since there is no nuclear membrane that separates the DNA from the cytoplasm. Therefore, the transcription and translation processes may be coupled, meaning that the mRNA produced is immediately translated into protein. In eukaryotes, however, transcription occurs in the nucleus and is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane. Therefore, the mRNA must be transported from the nucleus, across the nuclear membrane, and into the cytoplasm, where it can then be translated to produce proteins. Transcription is a tightly regulated process as it is the primary way of regulating gene expression. It can be influenced by various factors, including regulatory proteins, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs. Moreover, any error in transcription can lead to mutations that may cause diseases such as cancer, developmental disorders, and genetic diseases. References: 1. Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2014). Molecular biology of the cell (Vol. 6). Garland Science. 2. Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S. L., Matsudaira, P., Baltimore, D., & Darnell, J. (2000). Molecular cell biology (4th ed.). W.H. Freeman. 3. Lewin, B. (2007). Genes (Vol. 3). Jones and Bartlett Publishers.