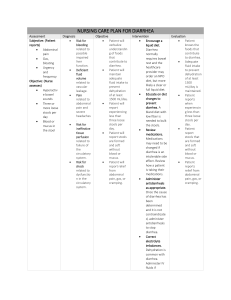
SAN PABLO COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING DRUG STUDY Generic – Brand name Classification/ Indication Generic Name: Cefuroxime Indications: Brand Name: Ceftin, Zinacef Treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible organisms: Respiratory tract infections, Skin and skin structure infections, Bone and joint infections. Meningitis, gynecologic infections, and Lyme disease, septicemia, perioperative prophylaxis. Classification: Therapeutic: antiinfectives Side effects/ Adverse Reaction (Common/Lifethreatening) CNS: SEIZURES (high doses). GI: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILEASSOCIATED DIARRHEA (CDAD), diarrhea, cramps, nausea, vomiting. Derm: rashes, urticaria. Hemat: agranulocytosis, bleeding (qwith cefotetan and cefoxitin), eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, Mechanism of Action Nursing Consideration Patient Teaching Bind to bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death. ● Assess for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool; WBC) at beginning and during therapy. ● Instruct patient to take medication around the clock at evenly spaced times and to finish the medication completely, even if feeling better. Take missed doses as soon as possible unless almost time for next dose; do not double doses. Use calibrated measuring device with liquid preparations. Advise patient that sharing of this medication may be dangerous. Therapeutic Effects: Bactericidal action against susceptible bacteria. Spectrum: Similar to that of first-generation cephalosporins but have activity against several other gram-negative pathogens including: Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinaseproducing strains), Proteus, Providencia, Serratia marcescens, Moraxella catarrhalis. Not active against methicillin resistant ● Before initiating therapy, obtain a history to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response. ● Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results. ● Advise patient to report signs of superinfection (furry overgrowth on the tongue, vaginal itching or discharge, loose or foul-smelling stools) and allergy. ● Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug immediately if these symptoms occur. Keep ● Instruct patient to notify health care professional if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat Pharmacologic: second-generation cephalosporins neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. Local: pain at IM site, phlebitis at IV site. Misc: allergic reactions including ANAPHYLAXIS and SERUM SICKNESS, superinfection. staphylococci or enterococci, epinephrine, an antihistamine, and Active against Borrelia resuscitation equipment close by in the burgdorferi. event of an anaphylactic reaction. ● Monitor bowel function. Diarrhea, abdominal cramping, fever, and bloody stools should be reported to healthcare professionals promptly as a sign of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). May begin up to several wk following cessation of therapy. ● Lab Test Considerations: May cause positive results for Coombs’ test in patients receiving high doses or in neonates whose mothers were given cephalosporins before delivery. ● May cause elevated serum AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, BUN, and serum creatinine. ● May rarely cause leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and eosinophilia. diarrhea without consulting health care professional SAN PABLO COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING DRUG STUDY Generic – Brand name Classification/ Indication Generic Name: Omeprazole Indications: Brand Name: Losec, Olex, PriLOSEC, PriLOSEC Duodenal ulcers (with or without antiinfectives for Helicobacter pylori). Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. Pathologic hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Reduction of risk of GI bleeding in critically ill patients. OTC: Heartburn occurring twice/wk. Classification: Side effects/ Adverse Reaction (Common/Lifethreatening) Adverse Reactions/Side Effects CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, headache, weakness. Mechanism of Action Nursing Consideration Patient Teaching Action Binds to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen. ● Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate. ● Instruct patient to take medication as directed for the full course of therapy, even if feeling better. Take missed doses as soon as remembered but not if almost time for next dose. Do not double doses. Therapeutic Effects: Diminished accumulation of CV: chest pain. GI: acid in the gastric lumen CLOSTRIDIUM with lessened DIFFICILEgastroesophageal reflux. ASSOCIATED Healing of duodenal ulcer. DIARRHEA (CDAD), abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting. F and ● Monitor bowel function. Diarrhea, abdominal cramping, fever, and bloody stools should be reported to health care professional promptly as a sign of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). May begin up to several wk following cessation of therapy. ● Lab Test Considerations: Monitor CBC with differential periodically during therapy. ● May cause increased AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. ● May cause serum gastrin concentrations to increase during the ● May cause occasional drowsiness or dizziness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. ● Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and consult health care professional before taking any new medications, especially St. John’s wort. Therapeutic: antiulcer agents Pharmacologic: proton-pump inhibitors E: hypomagnesemia (especially if treatment duration 3 mo). GU: acute interstitial nephritis. Derm: cutaneous lupus erythematosus, itching, rash. Hemat: vitamin B12 deficiency. MS: bone fracture. Misc: allergic reactions, systemic lupus erythematosus. first 1– 2 wk of therapy. Levels return to normal after discontinuation of omeprazole. ● Monitor INR and prothrombin time in patients taking warfarin. ● Advise patient to avoid alcohol, products containing aspirin or NSAIDs, and foods that may cause an increase in GI irritation. ● May cause hypomagnesemia. Monitor serum magnesium prior to and periodically during therapy. ● Advise patient to report onset of black, tarry stools; diarrhea; abdominal pain; or persistent headache to health care professional promptly. ● May cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors due to increase serum chromogranin A (CgA) levels secondary to drug-induced, decrease gastric acidity. Temporarily stop esomeprazole at least 14 days before assessing CgA levels and consider repeating test if initial CgA levels are high. ● Instruct patient to notify health care professional of onset of black, tarry stools; diarrhea; abdominal pain; or persistent headache or if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. ● Advise female patient to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected or if breast feeding. SAN PABLO COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING DRUG STUDY Generic – Brand name Classification/ Indication Generic Name: Tranexamic acid Indications: Brand Name: Cyklokapron, Lysteda Taken orally, tranexamic acid is indicated for the treatment of hereditary angioedema, cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding in premenopausal females, and other instances of significant bleeding in the context of hyperfibrinolysis. Given intravenously, tranexamic acid is indicated for shortterm use (2-8 days) in patients with hemophilia to prevent or reduce Side effects/ Adverse Reaction (Common/Lifethreatening) Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Hypotension Thromboembolic, e.g., arterial, venous, embolic; Neurologic, e.g., visual impairment, convulsions, headache, mental status changes; myoclonus; Rash Mechanism of Action Nursing Consideration Patient Teaching Tranexamic acid competitively and reversibly inhibits the activation of plasminogen via binding at several distinct sites, including four or five lowaffinity sites and one highaffinity site, the latter of which is involved in its binding to fibrin. The binding of plasminogen to fibrin induces fibrinolysis by occupying the necessary binding sites tranexamic acid prevents this dissolution of fibrin, thereby stabilizing the clot and preventing hemorrhage. ● Monitor blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory status as indicated by severity of bleeding. ● Unusual change in bleeding pattern should be immediately reported to the physician. ● Monitor for overt bleeding every 15– 30 min. ● For women who are taking Tranexamic acid to control heavy bleeding, the medication should only be taken during the menstrual period. ● Monitor neurologic status (pupils, level of consciousness, motor activity) in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. ● Assess for thromboembolic complications. (especially in patients with history). Notify physician of positive Homans’ sign, leg pain hemorrhage, edema, hemoptysis, dyspnea, or chest pain. ● Monitor platelet count and clotting factors prior to and periodically throughout therapy in patients with systemic fibrinolysis. ● Tranexamic Acid should be used with extreme caution in CHILDREN younger than 18 years old; safety and effectiveness in these children have not been confirmed. ● The medication can be taken with or without meals. ● Swallow Tranexamic Acid whole with plenty of liquids. Do bleeding following tooth extraction. ● Stabilize IV catheter to minimize thrombophlebitis. Monitor site closely. Classification: Anti-fibrinolytic, antihemorrhagic ● Instruct patient to notify the nurse immediately if bleeding recurs or if thromboembolic symptoms develop. ● Caution patient to make position changes slowly to avoid orthostatic hypotension. not break, crush, or chew before swallowing. ● If you miss a dose of Tranexamic Acid, take it when you remember, then take your next dose at least 6 hours later. Do not take 2 doses at once. ● Inform the client that he/she should inform the physician immediately if the following severe side effects occur: - Severe allergic reactions such as rash, hives, itching, dyspnea, tightness in the chest, swelling of the mouth, face, lips or tongue - Calf pain, swelling or tenderness. - Chest pain - Confusion - Coughing up blood - Decreased urination. - Severe or persistent headache - Severe or persistent body malaise - Shortness of breath - Slurred speech - Slurred speech Vision changes SAN PABLO COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING DRUG STUDY Generic – Brand name Classification/ Indication Generic Name: Rebamipide Indications: Brand Name: Mucosta Bleeding, erosion, redness, and edema (all signs of gastric mucosal lesions) that occur in acute gastritis and acute exacerbation of chronic gastritis. Classification: Anti-gastric and Anti-ulcer Side effects/ Adverse Reaction (Common/Lifethreatening) Hypersensitivity: Rash, pruritus, drug-eruption-like eczema, other symptoms of hypersensitivity Urticaria Neuropsychiatric: Numbness, Dizziness, Sleepiness Gastrointestinal: Constipation, feeling of abdomen Gastrointestinal enlarged, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, abdominal pain, belching, Mechanism of Action Nursing Consideration Patient Teaching Mucosal Protectant. This is an amino acid derivative of 2-(1H)-quinolinone, which is used to protect the mucosa, heal peptic ulcers, and treat gastritis. The drug's mechanism of action is by enhancing mucosal defenses, scavenging free radicals and transiently activating genes encoding cyclooxygenase-2. ● Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate. ● Instruct patient to take medication as directed for the full course of therapy, even if feeling better. Take missed doses as soon as remembered but not if almost time for next dose. Do not double doses. ● Monitor for any adverse reaction. ● Administer the drug before meals. ● Check the Bp after give the medication. ● Let the patient verbalize discomfort after administration. ● Explain the drug may be taken before meal. ● Instruct patient to take all prescribed drug even if feeling better before drug is finished ● May cause occasional drowsiness or dizziness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. ● Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC taste abnormality, thirst Hepatic: Increased AST (GOT) ALT (GPT), Y-GTP, alkaline phosphatase levels Hematologic Leukopenia, granulocytopenia, Thrombocytopenia Skin: Rash, pruritus, drugeruption-like eczema Other: Menstrual disorders, increased BUN Breast swelling and pain, gynecomastia, levels, edema, feeling of a foreign body I induce lactation, palpitations, fever, facial flushing, numbness of tongue, cough, medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and consult health care professional before taking any new medications, especially St. John’s wort. ● Advise patient to avoid alcohol, products containing aspirin or NSAIDs, and foods that may cause an increase in GI irritation. ● Advise patient to report onset of black, tarry stools; diarrhea; abdominal pain; or persistent headache to health care professional promptly. ● Instruct patient to notify health care professional of onset of black, tarry stools; diarrhea; abdominal pain; or persistent headache or if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. ● Advise female patient to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected or if breast feeding. in the pharynx respiratory distress, alopecia