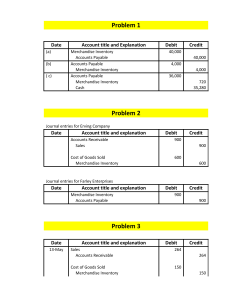
3 Types of Business a.Service – an entity which provides services to customers (ex. Schools, Law firms, Repair shops, etc.) b.Merchandising - purchases goods from merchandise suppliers and sells the same to its customers on their original condition ( ex. Groceries, hardware, drugstores, etc.) c. Manufacturing – an entity that converts raw materials into finished products made for sale to customers (manufacturing of clothing, toys, etc.) NATURE OF MERCHANDISING BUSINESS The merchandise entity purchase inventory and sells the inventory. When the merchandise is sold, revenue is reported as SALES and its cost is recognized as expense called COST OF GOODS SOLD. If Cost of Goods Sold is deducted to Sales it will arrive the amount of GROSS PROFIT. Other Expenses are then deducted to arrive at the NET PROFIT. When the merchandise is unsold at the end of the given period it is called MERCHANDISE INVENTORY. SALES COGS Gross Profit Other Expenses NET PROFIT xx (xx) xx (xx) XX GROSS PROFIT COMPUTATION OF A MERCHANDISING BUSINESS Sales Less: Sales returns and allowances Sales Discount Net Sales Less: Cost of Goods Sold: Merchandise Inventory, beg Add: Purchases xx Freight In xx Total Less: Purchases Returns and Allowances xx Purchase Discount xx Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less: Merchandise Inventory – end Gross Profit xx xx xx (xx) xx xx xx xx xx xx (xx) (xx) xx Accounts to ponder: SALES AND RELATED ACCOUNTS: a. Sales – revenue account – represents the merchandise sold to customers valued at selling price whether for cash or credit b. Sales Returns and Allowances – represents the merchandise returned by customers or the price adjustments allowed for damaged merchandise valued at selling price. This is to be subtracted from sales. c. Sales Discount – This represents the cash discounts granted by the seller to the customers for early payments. d. Freight Out – represents the cost of transporting the merchandise sold to the buyers place. PURCHASES AND RELATED ACCOUNTS: a. Purchases- represents the cost of merchandise purchased from vendors or supplies whether for cash or for credit. b. Purchases Returns and Allowances – represents merchandise returned to vendors/ suppliers or price adjustments for damaged merchandise valued at purchased cost. c. Purchase discount- represents cash discounts granted by the suppliers to the buyers for the early payments of their accounts. d. Freight In – represents the cost of transport ting the merchandise purchased up to the buyer’s place. This is added to the cost of the merchandise purchased by the buyer. e. Merchandise Inventory- Represents the unsold merchandise valued at cost as of a given date. Terms of Transactions Merchandise may be purchased and sold either - Credit terms - Cash on Delivery When goods are sold on account, a period of time is called credit period. Example. If the credit period is 30 days, the payment is expected within 30 days from the invoice date. The credit period is usually described as the net credit period or net terms. The credit period of 30 days is noted as “n/30”. If the invoice is due 10 days after the end of the month, it may be marked “n/10,eom” Cash Discounts – discounts for prompt payment. Cash discounts is designated by such notation as “2/10” which means the buyer may avail of a 2 percent discount if the invoice is paid within 10 days from the invoice date. The period covered by the discount, in this case – 10 days is called discount period. Methods of recording purchases Gross Method – The purchase itself without deduction of cash discounts. Net Method – cash discounts are immediately deducted from purchases and accounts payable Example a. Purchased merchandise 10,000 on account terms, 2/10, n/30 Gross Method Net Method Purchases 10,000 Purchases 9,800 Accounts Payable 10,000 Accounts Payable 9,800 b. Paid the merchandise Accounts Payable 10,000 Accounts Payable 9,800 Cash 9,800 Cash 9,800 Purchase Discount 200 c. If paid after the discount period. Accounts Payable 10,000 Accounts Payable 9,800 Cash 10,000 Purchase Discount Lost 200 Cash 10,000 Cash discounts : Buyer’s viewpoint – purchase discount Seller’s viewpoint – sales discount Example: Assume that June 1- purchased merchandise costing 10,000 terms COD as per invoice 1234 Purchases 10,000 Cash 10,000 June 2 purchased merchandise costing 10,000 on account terms, 2/10, n/30 Purchases 10,000 Accounts Payable 10,000 June 10 Paid the Accounts Payable Accounts Payable 10,000 Cash 9,800 Purchase Discount 200 If the term is 2/EOM, n/30 June 30 Accounts Payable 10,000 Cash 9,800 Purchase Discount 200 June 2 purchased merchandise costing 10,000 on account terms, 2/10, n/30 Purchases 10,000 Accounts Payable 10,000 June 4 Received a credit memorandum from a seller for the merchandise returned 2,000 Accounts Payable 2,000 Purchase Returns and Allowances 2,000 June 12 Paid the Accounts Payable Accounts Payable 8,000 Cash 7,840 Purchase Discount 160 (8,000 *2%) Trade Discounts - Is a special discount (outright deduction) from the list price offered by the seller to the buyer if the order is in large quantity. Example June 1 Purchased merchandise with a list price of 10,000 for cash per invoice 1234 Trade discount 10% and 15% Purchases 7,650 (10,000 * 90% * 85%) Cash 7,650 Trade discount is not recorded June 15, Irene quoted a list price of 2,500 for each 64 GB flash drive, less a trade discount of 20%. If Irene ordered 7 units, the invoice price would be: List Price 2,500 x 7 units 17,500 Less: Trade Discount 20% (3,500) Invoice Price 14,000 ACCOUNTING FOR SALES The merchandise in stock will be sold and new items will be purchased to replace the items sold. Merchandise sales are credited to the SALES account. Sales can be: - Cash - Credit For every sales made, 12% VAT output tax is recorded. The difference between the VAT Output tax and VAT Input tax represents the liability of the business called VAT Payable. Sales Discount – discount granted by the seller for early collection on a credit sale Sales Returns and Allowances – are reduction in sales, resulting from merchandise being returned by the customer or from seller’s reduction in the original sales price. Freight Out or Transportation Out – represents the cost of transporting the merchandise sold from the seller’s place to the buyer’s place which is to be shouldered by the seller. Recording of Sales collection Example: Sold merchandise worth 15,000 per cash sales Cash 15,000 Sales 15,000 Sold merchandise worth 15,000 on credit sales Accounts Receivable 15,000 Sales 15,000 Cash 15,000 Accounts Receivable 15,000 Sold merchandise worth 15,000 on credit sales, 2/10. n/30 Accounts Receivable 15,000 Sales 15,000 Cash 14,700 Sales Discount 300 (15,000 *2%) Accounts Receivable 15,000 INVENTORY SYSTEMS Merchandise Inventory is the key factor in determining the cost of goods sold. Because MI represents the good available for sale. There are two systems available to record events related to merchandise inventory: a. Perpetual Inventory System b. Periodic Inventory System PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEM -under this method, an account called MERCHANDISE INVENTORY is used instead of purchases when journalizing the acquisition of merchandise. - When a sale is made, 2 entries will be made; 1st to record the revenue account called the sales and 2nd to record the cost by charging or debiting to an account called Cost of Goods Sold. -under this method, the inventory account is continuously updated. (maintenance of records which are called (stock cards) if my purchases and sale update mo automatically ang in and out of goods) PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEM -under this method every time a purchase of merchandise is made, it is charged or recorded to an account called PURCHASES. When a sale is made, revenue account called SALES is recorded (credited). -At the end, an inventory( through physical count of the goods unsol) –called merchandise inventory end is made to determine the cost of goods sold. Example: PERIODIC SYSTEM A. Sold merchandise costing 8,000 for 10,000 terms 2/10, n/30 Accounts Receivable 10,000 Sales 10,000 PERPETUAL SYSTEM Accounts Receivable 10,000 Sales 10,000 Cost of Sales 8,000 Inventory 8,000 b. Customer returned merchandise costing P 400 that had been sold on account for 500 (part of the 10,000 sale) Sales Returns and Allowances 500 Sales Returns and Allowances 500 Accounts Receivable 500 Accounts Receivable 500 Inventory 400 Cost of Sales 400 c. Received Payment from customer for merchandise sold above (cash discount taken) Cash 9,310 Cash 9,310 ( 10,000 – 500 -190) Sales Discount 190 Sales Discount 190 (10,000 – 500 x 2%) Accounts Receivable 9,500 Accounts Receivable 9,500 d. Paid 200 freight Transportation In 200 Inventory 200 Cash 200 Cash 200