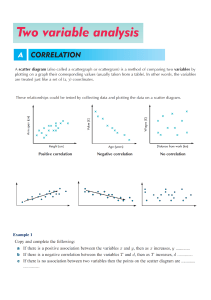
Name: RABAYA, PRINCESS ROCHANNIE L. Course: MTLEd-ICT TYPES OF GRAPHS 1. Bar chart A bar chart, also known as a horizontal column chart, is popular for a reason — it’s easy on the eyes and quickly visualizes data sets. With bar charts, you can quickly identify which bar is the highest or the lowest, including the incremental differences between bars. 2. Line chart Not to be confused with line graphs, you can use a line chart to plot continuous data or data with infinite values. For example, the line chart below highlights the increase in keyword searches for “remote work” across the US from February 1, 2020, to March 22, 2020. pg. 1 3. Area graph An area graph is like a line chart as it also shows changes over time. One difference with these types of graphs is that area graphs can represent volume which is typically filled with color. The area graph example by the BBC below shows a simple comparison of two data sets over a period of time. 4. Scatter plot A scatter plot or a scatter chart helps show the relationship between items based on two different variables and data sets. Dots (or plot data) are plotted in an x-y coordinate system. In some scatter plots, a trend line is added (like in the example below) to a scatter plot. pg. 2 5. Pie chart Pie charts highlight data and statistics in pie-slice format. A pie chart represents numbers in percentages, and the total sum of all pies should equal 100 percent. When considering charts and graphs to employ to visualize data, pie charts are most impactful to your audience if you have a small data set. 6. Pictograph Despite having ‘graph’ in the name, a pictograph doesn’t fall into types of graphs. Instead, a pictograph or a pictogram is a type of chart that uses pictures or icons to represent data. Each icon stands for a certain number of data sets, units or objects. For example, the infographic below contains a pictogram — each human icon represents 10 percent of CEOs. pg. 3 7. Column chart A column chart is ideal for presenting chronological data. Also known as the vertical bar chart, this type of chart works if there are only a few dates to highlight your data set like in the example below. 8. Bubble chart A bubble chart or a bubble plot is a lot like a scatter plot. However, bubble charts have one or two more visual elements (dot size and color) than a scatter plot to represent a third or fourth numeric variable. pg. 4 9. Gauge chart A gauge chart, also known as a dial chart, is an advanced type of chart that shows whether data values fit on a scale of acceptable (good) to not acceptable (bad). For example, you can create a gauge chart to display current sales figures and use your quarterly sales targets as thresholds. Not all charts are able to show data in this way. 10. Stacked Venn A stacked Venn chart is used to showcase overlapping relationships between multiple data sets. This type of graph is a variation of the original Venn diagram, where overlapping shapes or circles illustrate the logical relationships between two or more variables. https://piktochart.com/blog/types-of-graphs/ pg. 5