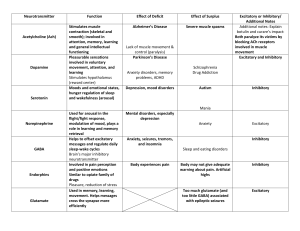
IB Psychology Neuroplasticity and Neurotransmitters You have read about neuroplasticity and neurotransmitters in Sections 3.3 and 3.4 of Chapter 4 of the Pamoja Student Guide 1. SAQs may be asked on any of the terms in the table below. Research their meaning and complete the definition columns. Term neuron Definition Information processing units of the brain that’s responsible for sending and receiving electrochemical signals throughout the body neural networks Technique to stimulate the neuronal changes in the brain neural pruning Process of removing the neurons that are no longer useful agonist Causes a chemical reaction in the brain antagonist Chemical that binds to receptors in brain and prevents an agonist from having a reaction excitatory A type of synapse in which an action potential in a *synapse/neurotransmitter presynaptic neuron increases the probability of an action potential occurring in a postsynaptic cell. inhibitory They block or prevent the chemical message from synapse/neurotransmitter being passed along any farther. * A neurotransmitter acting in an excitatory/inhibitory way results in a synapse that is also excitatory/inhibitory 2. Read about acetylcholine and also about neuroplasticity in the Pamoja Student Guide. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraphs, which will prove useful for your understanding of many of the required terms. Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter that was shown by the researcher Antonova to act as an aid to spatial memory in the hippocampus and the medial temporal lobe. She conducted an experiment using humans that was very similar to Martinez and Kesner’s experiment with humans. Like them, she concluded that ACh is important for spatial memory formation and that the chemical scopolamine acts as an antagonist, reducing the effect of ACh and resulting in slower times when going through a virtual maze. ACh also acts in an antagonist way in the synapse and a reduction in ACh receptors and ACh activity in the medial temporal lobe is one of the first symptoms of alzheimer’s disease . Maguire conducted a quasi-experiment (also described in many texts as a natural experiment) to investigate neuroplasticity in the hippocampus in London taxi-drivers. The researchers demonstrated that there was a positive correlation between the number of years spent driving a taxi and the increased volume of the hippocampal grey matter. This shows that the brain can change In response to ____________________. Draganski investigated structural and functional changes in the brain with a field experiment where participants learnt to juggle, and then stopped juggling. The results showed that while learning a new skill increased the neuronal connections of certain areas of the brain, stopping the learnt activity resulted in neural pruning.