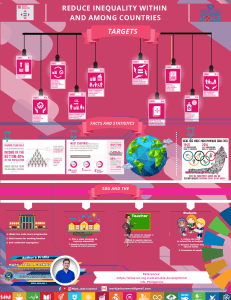
V. Tuon na Sustainable Development Goal A fundamental human right and a significant component of sustainable development is health. In order to guide respective national agendas and policies over the next 15 years, UN member states are expected to utilize a new set of universal goals, targets, and indicators known as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It has 232 different indicators, 169 targets, and 17 ambitions. The guiding principle for achieving these goals was to "Leave No One Behind," which was also the United Nations' adopted motto. The primary focus of this paper is the third Sustainable Development Goal (SDG), "Good Health and Well-Being." The aforementioned goal aims to ensure everyone's health and wellbeing and makes a bold commitment to stop the pandemic and the ongoing spread of communicable diseases. Additionally, it strives to provide everyone with access to affordable, efficient healthcare services as well as medicines and vaccinations that are both safe and effective. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide an ambitious, all-encompassing plan of action for people, the planet, and prosperity while also addressing the imbalances that contribute to poor health and development outcomes. The SDGs recognize the interrelationship of health and development. As a result, we are able to effectively manage health risk reduction in all nations. In the Philippines, the Department of Health (DOH) included in its “Vision for Health” the SDG 3 through initially implementing the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) on September 4, 2005 as one of the SDG’s 2030 targets with the Sin Tax Reform Law. According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, national indicators or goals were developed such as reducing the global maternal mortality ratio, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, and other communicable diseases, strengthen prevention and treatment of substance abuse, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic incidents, achieve universal health coverage, access to sexual and reproductive healthcare services, reduce deaths from contaminations, and research and development of vaccines and medicines for communicable and non-communicable diseases. With these, the WHO is collaborating with Filipino public stakeholders with the purpose of harnessing global knowledge and disseminating information about healthy lifestyle and development. REFERENCES: https://psa.gov.ph/sdg/Philippines/baselinedata/3%20Good%20Health%20and%20W ell-being https://doh.gov.ph/Vision-for-Health https://www.who.int/philippines/our-work