Projectile Motion Worksheet: Physics Problems & Formulas
advertisement

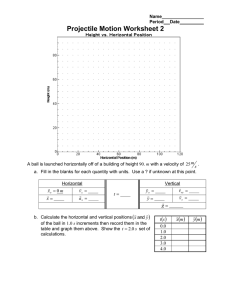
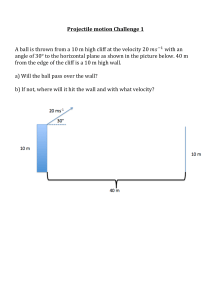
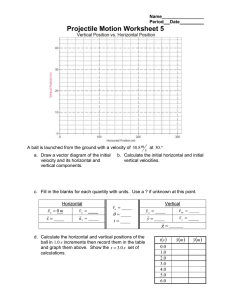
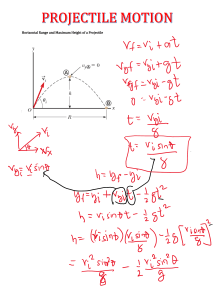
Curvilinear Translation (Projectile Motion) Projectile motion follows a parabolic trajectory. The vertical component of projectile is under constant gravitational acceleration and the horizontal component is at constant velocity. For easy handling, resolve the motion into x and y components and use the formulas in rectilinear translation. vox vo cos v oy vo sin At any point B For the x-component of motion, acceleration is zero (constant velocity), thus a x 0 . v Bx vox x vox t For the y-component of motion, a y g . Notice that the first three formulas that follow are taken from motion with constant acceleration. y v oy t v By v oy gt From x vox t , t x y voy vox 1 2 gt 2 v By voy 2 gy 2 2 1 x x . Substitute t to y v oy t gt 2 . 2 v ox v ox 1 x g 2 vox 2 1 x2 g 2 2 vox x y voy vox x 1 x g y vo sin 2 vo cos 2 vo cos y x tan 2 gx 2 2vo cos 2 2 At point A At the highest point or summit, v Ay 0 . H v oy 2 2g t voy g At point C x R , y 0 , vc vo and v cy v oy vo sin 2 g 2 R t 2voy g 2vo sin g Note: v y is positive if directed upward and negative if directed downward At any point D below the origin O, the sign of y is negative. 1. A projectile is fired horizontally with a speed of 30m/s from the top of a cliff 80m high. a. How long will it take to strike the level ground at the base of the cliff? b. How far from the foot of the cliff will it strike? c. With what velocity will it strike? 2. A stunt flier is moving at 15 m/s parallel to the flat ground 100m below. How large must the distance x from the plane to target be if a sack of flour released from the plane is to strike the target? 3. A baseball is thrown with an initial velocity of 100 m/s at an angle of 30 above the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the baseball attain its original level? 4. A ball is thrown from the top of one building toward a tall building 50m away. The initial velocity of the ball is 20 m/s, 40 above the horizontal. How far above or below its original level will the ball strike the opposite wall? 5a. Find the range x of a gun which fires a shell with muzzle velocity v at an angle of elevation b. Find the angle of elevation of a gun which fires a shell with muzzle velocity of 120 m/s and hit a target on the same level but 1300m distant. 6. A body projected downward at an angle of 30 with the horizontal from the top a building 170m high. Its initial speed is 40 m/s. a. How long will it take before striking the ground? b. How far from the foot of the building will it strike? c. At what angle with the horizontal will it strike? 7. A projectile is fired up the inclined plane at an initial velocity of 15 m/s. The plane is making an angle of 30° from the horizontal. If the projectile was fired at 30° from the incline, compute the maximum height z measured perpendicular to the incline that is reached by the projectile. Neglect air resistance. 8. A bullet is fired at an initial velocity of 150 m/s and an angle of 56° at the top of a 120 m tall building. Neglecting air resistance, determine the following: a. The maximum height above the level ground that can be reached by the bullet. b. The time for the bullet to hit the ground. c. The velocity with which the bullet will hit the ground. 9. A hose lying on the ground shoots a stream of water upward at an angle of 40 to the horizontal. The speed of the water is 20 m/s as it leaves the hose. How high up will it strike a wall which is 8.0m away? 10. A ball is thrown upward at an angle of 30 to the horizontal and lands on the top edge of a building that is 20m away. The top edge is 5.0m above the throwing pint. How fast was the ball thrown? 11. A body projected upward from the level ground at an angle of 50 with the horizontal has an initial speed of 4. m/s. a. How long will it take to hit the ground? b. How far from the starting point will it strike? c. At what angle with the horizontal will it strike? 12. A batter hits a baseball so that it leaves the bat at speed vo 37 m/s at an angle of 53.1 . a. Find the position of the ball and the magnitude and direction of its velocity at t 2s . b. Find the time when the ball reaches the highest point of its flight and find its height h at this point. c. Find the horizontal range R (horizontal distance from the starting point to where the ball hits the ground).