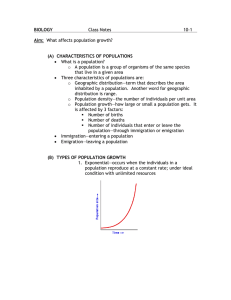
Environmental Science Sec 9.1 Name________________________________ Period______ Matching ____1. Small population size, low growth rate a. transitional ____2. Increasing population size, very high growth rate b. industrial ____3. Large population size, low growth rate c. preindustrial ____4. Decreasing population size, zero or negative d. postindustrial growth rate Multiple Choice ____5. Professionals who study and make predictions about human populations are called? a. Stenographers b. Demographers c. geologists d. populists ____6. The human population doubled from 2 billion to 4 billion in a. 100 years b. 75 years c. 44 years d. 25 years ____7. Which factor contributed most to exponential human population growth? a. More food, better hygiene c. higher fertility rates b. Higher birth rates d. increased immigration Section 9.2 Matching ____8. Housing ____9. Sewage disposal ____10. Fuel supply ____11. Food production 12. The 1991 cholera outbreak in Lima, Peru was caused by a. Lack of clean water b. Inadequate medical care 13. Currently , the fastest growing populations are in a. Europe b. North America a. vegetation b. water c. land c. Widespread malnutrition c. Asia 14. Which of the following is not a strategy that could slow population growth? a. public advertising b. economic incentives c. legal punishments Concept Review -Matching ____ 15. Highest birth rates ____ 16. The distribution of ages in a specific population at a certain time ____ 17. Percentage of member of a group that are likely to survive to a given age ____ 18. Movement of individuals out of a population ____ 19. The study of populations ____ 20. Movement of people into cities from rural areas ____ 21. The basic facilities and services that support a community ____ 22. Land that can be used to grow crops ____ 23. A model that describes how changes in a population may occur ____ 24. Average number of children a woman gives birth to in her lifetime d. Rats and other rodents d. Australia d. limiting education for women a. demography b. age structure c. emigration d. infrastructure e. arable land f. least-developed countries g. survivorship h. demographic transition i. urbanization k. total fertility rate Concept Review - Multiple Choice 25. Some under-developed countries have tried to control population growth by a. increasing fertility rate b. decreasing fertility rate c. increasing emigration d. decreasing emigration 26. Suburban sprawl, over-crowded schools, polluted rivers, and inadequate housing are symptoms of a. stable population size c. declining population size b. overwhelming population growth d. slow population growth 27. Access to adequate food, clean water and safe sewage disposal have resulted in a decline in a. life expectancy b. the birth rate c. the death rate d. infant health 28. According to the theory of demographic transition, populations in Stage 1 tend to a. increase b. decrease c. remain the same d. be large 29. Suburban sprawl results in a. traffic jams b. inadequate infrastructure c. reduction of land for farms and ranches 30. A population’s age structure is represented by a a. population pyramid b. survivorship curve c. total fertility rate d. all of the above d. migration rate 31. What is the main source of energy in the poorest countries? a. coal b. solar collectors c. wood d. nuclear reactors 32. The graph of human population growth since 1200 BCE looks like a. a J-curve b. an S-curve c. a horizontal line 33. Infant mortality rates are least effected by a. average income b. parents’ access to education d. a straight 45 degree line c. clean water d. adequate food 34. Life expectancy in sub-Saharan Africa has declined due to the epidemic of a. tuberculosis b. AIDS c. influenza d. bubonic plague 35. A population will shrink if deaths + emigrants exceeds a. deaths + births c. births + immigrants b. immigration – emigration d. the carrying capacity of a nation 36. Which of the following is NOT part of a community’s infrastructure? a. public water supply b. power plants c. sewer lines d. arable land 37. The movement of individuals between areas is called a. migration b. life expectancy c. survivorship d. urbanization Key – ENVIRO SCIENCE MIXED AND CONCEPT REVIEW 1. C 2.A 3.B 4.D 5.B 6.C 7.A 8.C 9.B 10.A 11.C 12.A 13.C 14.C 15.F 16.B 17.G 18.C 19.A 20.I 21.D 22.E 23.H 24.J 25.B 26.B 27.C 28.C 29.D 30.A 31.C 32.A 33.A 34.B 35.C 36.D 37.A