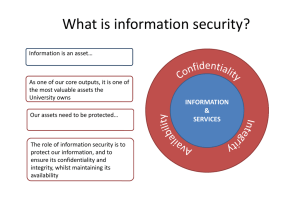
Assignment 1 Information and Assurance Security Submitted by: Geronimo, Zildjian C. Submitted to; Mrs. Evangelista, Jermyn G. Introduction Information assurance and security is the management and protection of knowledge, information, and data. It combines two fields: Information assurance, which focuses on ensuring the availability, integrity, authentication, confidentiality, and non-repudiation of information and systems. Information assurance focuses on gathering data. Information security is about keeping that data safe. In most organizations, these two jobs are combined into one department or even one worker. You’ll need to understand cyber security, database management and security engineering to succeed in this field. Concepts and Terms across Information Security Management Confidentiality is a requirement whose purpose is to keep sensitive information from being disclosed to unauthorized recipients. The secrets might be important for reasons of national security (nuclear weapons data), law enforcement (the identities of undercover drug agents), competitive advantage (manufacturing costs or bidding plans), or personal privacy (credit histories) Integrity is a requirement meant to ensure that information and programs are changed only in a specified and authorized manner. It may be important to keep data consistent (as in double-entry bookkeeping) or to allow data to be changed only in an approved manner (as in withdrawals from a bank account). It may also be necessary to specify the degree of the accuracy of data. Availability is a requirement intended to ensure that systems work promptly and service is not denied to authorized users. From an operational standpoint, this requirement refers to adequate response time and/or guaranteed bandwidth. Network Security Network security encompasses all the steps taken to protect the integrity of a computer network and the data within it. Network security is important because it keeps sensitive data safe from cyber attacks and ensures the network is usable and trustworthy. Computer Security Computer security started becoming increasingly essential since modems were introduced and hackers illegally broke into major computer systems from their homes. This called for the development of advanced computer security techniques that aimed to diminish such threats and attacks in the systems. Threat A threat refers to a new or newly discovered incident that has the potential to harm a system or your company overall. There are three main types of threats: Natural threats, such as floods, hurricanes, or tornadoes Unintentional threats, like an employee mistakenly accessing the wrong information Intentional threats, such as spyware, malware, adware companies, or the actions of a disgruntled employee Vulnerability A vulnerability refers to a known weakness of an asset (resource) that can be exploited by one or more attackers. In other words, it is a known issue that allows an attack to succeed. Risk Risk is defined as the potential for loss or damage when a threat exploits a vulnerability. Examples of risk include: Financial losses Loss of privacy Damage to your reputation Rep Legal implications Even loss of life