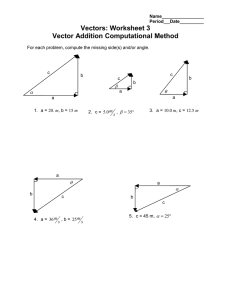
ALL LEARNERS CAN LEARN ACHIEVERS MATHS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ACADEMY(AMSTA) GRADE 11 : PHYSICAL SCIENCES 2021 MECHANIC I : VECTORS IN 2D WORKSHEET # 1 : RESULTANT OF COLLINEAR VECTORS Question 1 1.1Define the following terms : 1.1.1 Vector. 1.1.2 Resultant vector. 1.2 Determine the resultant in EACH of the following cases 1.2.1 (2) (2) (3) 1.2.2 (3) 1.2.3 (3) 1.2.4 (3) [16] WORKSHEET # 2 : RESULTANT OF PERPENDICULAR VECTORS Question 1 Consider the vector diagram below : (7) Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force of F1 and F2. Question 2 For each of the following pairs vectors : 1. Represent them on a Cartesian plane(head-to-tail). 2. Show the Resultant force. 3. Determine the magnitude of the resultant vector using Pythagoras’ Theorem. 4. Determine the direction of the resultant vector using Trig ratios 2.2 F3 = 40N west and F4 =30N south 2.3 F4 =8N North and F5 = 5N west 2.4 F6 = 80N east and F7 =40N south (7) (7) (7) [21] QUESTION 3 Find the resultant in the x-direction, Rx, and y-direction, Ry for the following Forces Sketch Rx and Ry on the cartesian plane. Hence determine the magnitude and direction in each case 3.1 3.2 F1= 2N east,F2=3N east ,F3 =3N north and F4 =10N NORTH 3.3 3.4 F1 = 70N south,F2= 20N north ,F3=35N west ,F4=5west 3.5 • F1 = 4,8 N in the positive x-direction • F2 = 3,2 N in the negative x-direction • F3 = 1,9 N in the positive y-direction • F4 = 2,1 N in the negative y-direction 3.6 • F1 = 2,7 N in the positive x-direction • F2 = 1,4 N in the positive x-direction • F3 = 2,7 N in the negative x-direction • F4 = 1,7 N in the negative y-direction 3.7 F1 = 2,3 N in the positive x-direction • F2 = 4 N in the positive y-direction • F3 = 3,3 N in the negative y-direction • F4 = 2,1 N in the negative y-direction 3.8 • F1 = 2,3 N in the negative x-direction • F2 = 11,7 N in the negative y-direction • F3 = 6,9 N in the negative y-direction • F4 = 1,9 N in the negative y-direction [ WORKSHEET # 2 : RESOLVING A VECTOR INTO ITS COMPONENTS Question 1 1.1 Define the term component of a vector. 1.2 Resolve each of the following vectors into their respective 𝑥 − 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑦 − 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠. In each case show the vector and the components on a Cartesian plane. 1.2.1 F1 = 5000 N E 350 N 1.2.2 F2 = 100N N 600 W 1.2.3 F3 = 50N W 300 S 1.2.4 F4 = 20N S 150 E (2) (7) (7) (7) (7) WORKSHEET # 3 : RESULTANT OF TWO VECTORS THAT ARE NEITHER PERPENDICULAR OR NON-LINEAR Question 1 Force vectors P and Q were drawn to scale on the Cartesian plane shown below. 1.1 Define the term resultant vector. 1.2 Use a calculation to determine each of the following: 1.2.1 the magnitude of Vector P in force units and its direction . 1.3 (2) (5) Use the component method to determine the magnitude and resultant of Vectors P and Q. (7) [14] Question 2 Determine the magnitude and the direction of the resultant vector in each of the following cases. 2.1 (5) 2.2 (9) 2.3 (9) [23] WORKSHEET # 4 : VECTORS AT EQUILBRIUM : 30/04/2021 QUESTION 1 Three forces, F1, F2 and w, act on point O as shown in the diagram below 1.1 1.2 Define the term resultant of forces. The horizontal and vertical components of F2 are equal to 40 N and 42 N respectively. 1.2.1 Explain what is meant by forces at equilibrium 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 (2) 1.2.2 Define the term equilibrant 1.2.3 Prove with calculations that the horizontal components of the forces are in equilibrium. Calculate the magnitude and direction of force W Hence determine the mass of the object. State the triangle rule of three forces at equilibrium. Draw a sketch triangle (not to scale) showing W, F1 and F2 and all the known angles. (2) (2) (2) (5) (3) (2) (3) [14] Question 2 The diagram below shows a rope and pulley arrangement of a device being used to lift an 800 N object. Assume that the ropes are light and inextensible and also that the pulleyis light and frictionless. 2.1 Determine the magnitudes of the tensions T1 and T2 if the system is at equilibrium. (7) 2.2 (3) Represent T1, T2 and Fg in a sketch triangle showing all known angles. [10] Question 3 The diagram below shows a rope and pulley system of a device being used to lift a 122,5 kgcontainer upwards at a constant velocity. Assume that the ropes are light and inextensible, and the pulley is frictionless. 3.1 Calculate the weight of the container. (3) 3.2 The system is moving upwards at a constant velocity as indicated above. 3.3 Draw a vector diagram of all forces acting on the container and indicate the angles (5) represented in the diagram. 3.4 Name and state the Physics Law that systems at equilibrium obey. (3) 3.5 Represent T1, T2 and Fg in a sketch triangle showing all known angles. (3) 3.6 5.1.1 Determine the magnitudes of the forces T1 and T2.(7) [14]