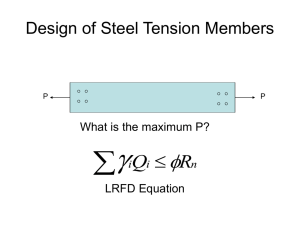
TENSION MEMBERS • Tension members are among the most basic of structural elements • These are axially loaded members stressed in tension and are used in steel structures in various forms • Can be found in: • Bracing system • Trusses • BASIC MODES OF FAILURE • Tensile Yielding • Occurs when the stress in the gross area of the section is large enough to cause excessive deformation. • Tensile Rupture • Occurs when the stress on the effective area of the section is large enough to cause the member to fracture, which usually occurs across a line of bolts where the tension member is weakest. • G ROSS SECTIO N YIELDING LRFD ∅𝑃𝑛 = ∅𝐹𝑦𝐴𝑔 ASD where: 𝐹𝑦𝐴𝑔 𝑃𝑛 = Ω𝑡 Ω𝑡 • ∅ = resistance factor • ∅ = 0.90 • Ω = 1.67 𝐹𝑦 = minimum yield stress 𝐴𝑔 = gross area of the tension member ∅𝑃𝑛 = design capacity • NET SECTION FRACTURE LRFD ∅𝑃𝑛 = ∅𝐹𝑢𝐴𝑒 ASD Where 𝑃𝑛 Ω𝑡 = 𝐹𝑢𝐴𝑒 Ω 𝑡 ∅ = resistance factor • ∅ = 0.75 • Ω = 2.00 • 𝐹𝑢 = minimum tensile stress • 𝐴𝑒 = effective area of the tension member • ∅𝑃𝑛= design capacity • EFFECTIVE NET AREA 𝐴𝑒 = 𝐴 𝑛 𝑈 where: • A𝑒 - effective net area • 𝐴 𝑛 - net area of the tension member • U - shear lag factor • GROSS AREA AND NET AREA • Tension member that is connected by welds, the net area equals the gross area • Net area of a tension member with fasteners that are in is the difference between the gross cross-sectional area and the area of the bolt holes 𝐴𝑛 = 𝐴𝑔 − 𝐴h𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 Where: • 𝐴h𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 = 𝑛 (d𝑏 + 1/8) t • GROSS AREA AND NET AREA • Tension members with a series of holes in a diagonal or zigzag pattern, which might be used when bolt spacing is limited there may exist several possible planes of failure that need to be investigated. • For a failure plane where one or more of the failure planes is at an angle 𝐴𝑛 = 𝐴𝑔 − ∑ 𝑑 𝑡 + ∑ 𝑡 4𝑔 • Where s - Longitudinal center-to-center spacing or pitch between two consecutive holes g - Transverse center-to-center spacing or gage between two consecutive holes • Example 1: • Calculate the net area of the plate shown connected with 3/4” diameter bolts • Example 2: • Calculate the net area of a rolled shape W10 x 49 steel connected with 3/4” diameter bolts (refer to Table 1-1 page 1-26 AISC - SCM) • STAGGERED BOLT CONNECTION • Example 1: • Calculate the net area of the plate shown connected with ¾ ” diameter bolts. • STAGGERED BOLT CONNECTION • Example 2 • Compute 𝐴 𝑛 and 𝐴𝑒 for a 14-in.-wide and 1/2-in. thick plate subject to tensile loading with staggered holes as shown.