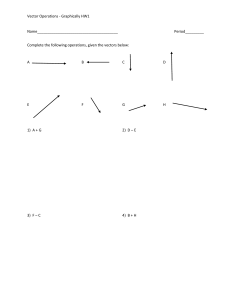
Motion Mechanics - the study of the motion of objects and the forces that cause them. Kinematics is a quantitative description of motion without reference to its physical causes. It describes how the objects move. Dynamics is the study of the relationship between motion and force. It explains why objects move. What is motion? Who is in motion? A. The fast moving car C. The girl riding on a horse B. The man riding in the fast moving car D. The galloping horse E. A man watching the girl . Motion is relative. It depends on where motion is referred to. A body is in motion if it had change position with respect to the reference point. Position – location of an object with respect to some reference point. Reference frame is a physical entity to which motion or position of an object is being referred . Translation is the physical term for straight line motion. Physical Quantities that Describe Motion How far? distance How fast? How long? speed time How far and in what direction? How fast and in what direction? How fast is the rate of change in speed and direction? scalar quantities displacement velocity acceleration Vector quantities SCALARS & VECTORS Scalars Scalars – came from the word “scala” meaning steps or ladder. -quantities which are described by its magnitude alone. Examples include distance, speed, mass, temperature, time, pressure and density. VECTORS Vectors came the word “vehere” meaning to carry. These are quantities which are described by both magnitude and direction. Ex. Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force Graphically, a vector is represented by an arrow. The length of the arrow describes the vector's magnitude head/tip points to the direction. Tail is the origin. Drawing direction Illustrate the directions of Vectors A, B, C, and D. A A is 500 N of E B B is N of W C is 200 S of E 500 450 D is S 200 C D Practice exercise D is W 200 B is 400 N of E N of B D 400 780 C E E is W 200 150 C is 150 S of W A A is 780 S of E Drawing vectors Magnitude: 1 scale = 1 unit Example 1: F = 5.0 N, upward 1 scale = 1.0N Example 2: d = 35 m, East 1 scale = 7.0m 3. F = 12.0 N, 450 NE 1 scale = 3.0N 4. d= 100 km, West 1 scale = 10 km 1. What is the position of the tree with respect to the dog? The tree is 15 m, East of the dog . 2. What is the position of the tree with respect to the house? The tree is 10 m, West of the house. 3. If the dog traveled exactly to the location of the tree, is the dog in motion? Yes, because it had change position with respect to the tree. 4. What is the position of the dog with respect to the house? The dog is 25 m west of the house. 5. What is the total distance travelled by the dog the from its initial position to the house? 6. The total distance travelled by the dog is 25 m. B. Drawing direction: A is W 300 E is 700E N of E N of A 300 D 700 D is East 400 C C is 400 S of W B B is S of E C. Drawing Vectors a) d= 100 km, West 1 scale = 10 km b) d= 20.0 km, 450 South of West 1 scale = 5.0km C) F = 100.0 N is 250 N of W 1 scale = 20.0N 25 0 D) F = 12.0 N 450 North of East 1 scale = 2.0N 45 0 E) v= 24.0 m/s , 350 South of East 1scale = 4.0 m/s 35 0 Additional Activity 1) va= 15 m, 200 North of West 1scale = 3 m 200 2) vb= 36 N , 300 South of East 1scale = 6N 300 3) vc= 28.0 m, 450 North of East 1scale = 4.0m 450 VECTOR ADDITION Resultant is the sum of two vectors A and B. The operation of vector addition as described here can be written as C = A+B Methods of Adding Vectors Graphical Method - adding vectors using graphing devices such as ruler, pencil and protractor. Analytical Method – adding vectors using mathematical equations. Head-to-Tail Method – used in adding 2 or more vectors. Draw the first vector The tail of the next vector is drawn from the head of the first vector. The resultant is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector. Addition of Vectors Determine the resultant of the following vectors: 1.d1 = 300 m, East 3. d1 = 9.0 m, North d2 = 400 m, East d2 = 12.0 m, West 1scale = 100m 1 scale = 3.0 m 2. d1 = 80.0 m, West d2 = 40.0 m, East 1 scale = 10.0m 4. d1 = 5.0m, East d2 = 3.0 m, South d3 = 4.0 m, West 1 scale = 1.0m d1 = 300 m, East 100m 1. dR = d1 + dR = 2. d1 = 80.0 m, West 2. dR = dR = d2 = 400 m, East 1scale = d2 dR = = 700 m, East d2 = 40.0 m, East 1 scale = 10.0m + d1 d2 = dR = 40.0m, W 3. d1 = 25 km, E and d2 =25 km , W dR = + dR = dR = 0 km 4. dR = d1 + d1 = 9.0 m, North d2 d2 = 12.0 m, West dR = 15.0 m, 370 NW 5 dR = d1 5. d1 = 5.0m, East d2 = 3.0 m, South d3 = 4.0 m, West 1 scale = 1.0m + d2 + dR = 3.2 m, 720 SE d3 Analytical addition of Vectors A. For Vectors acting in opposite or the same direction Add the vectors by getting their algebraic sum. B. Addition of Vectors acting at an angle Trigonometric Method – used in adding 2 vectors (drawn at a common point) using trigonometric functions. Component Method – used in adding 2 or more vectors by resolving vectors into their Addition of Vectors Determine the resultant of the following vectors: A. Vectors acting in the same direction d1 = 300 m, East d2 = 400 m, East dR = d1 + d2 = (+300 m) + (+ 400 m ) dR = + 700m = 700 m, East B. Vectors acting in opposite direction d1 = 300 m, West d2 = 400 m, East dR = d1 + d2 dR = (- 300 m) + (+400 m) dR = + 100 m = 100 m, East Determine the resultant of the following vectors acting in other directions: 3. dy = 9.0 m, North dx = 12.0 m, West a) Magnitude of R R = √ x2 + y2 = √ (-12.0m) 2 + (9.0m)2 R = √ 144m2 + 81m2 = √ 225 m2 R = 15 m b) Direction : Ɵ = tan-1 /x÷y/ Ɵ = tan-1 /-12.0m ÷ 9.0 m/ = tan-1 /-1.33333333/ Ɵ = 53.130102350 = 530 North of West dR = 15m, 530 North of West Determine the resultant of the following vectors acting in other directions: 3. dy = 4.0 m, North dx = 3.0 m, East a) Magnitude of R R = √ x2 + y2 = √ (3.0m) 2 + ( 4.0m)2 R = √ 9.0m2 + 16 m2 = √ 25 m2 R = 5.0 m b) Direction : Ɵ = tan-1 /x÷y/ Ɵ = tan-1 / 3.0m ÷ 4.0 m/ = tan-1 /0.75/ Ɵ = 36.869897650 = 370 North of East dR = 5.0m, 370 North of East 4. The boy walks 75 m East, then 50 m North, then 75 m West and finally 50 m South. What is the resultant displacement of the boy? Total displacement : dtotal = sum of dx + sum of dy dtotal = ( 75m, E + 75m, W) + ( 50m, N + 50m, S) Vectors d1 d2 d3 X axis(East and West) + 75m +50m -75m d4 Sum Y axis ( North and South Om dtotal = 0 -50m 0m Terms that describe Motion A d2 = 4.0m d1 =6.0m d3 =3.0m B Distance ,d, refers to the actual length of path taken by an object from its initial position to its final position. It is a scalar quantity. Displacement, d refers to the straight line distance between its initial and final position. It is a vector quantity. It is also known as distance with direction. d1 = 6.0m, East d2 = 4.0 m, South d3 = 3.0 m, East Total distance travelled by the boy = 6.0 m + 4.0 m+3.0 m dtotal = 13.0m Total displacement Sum up vectors along x and along y axis: ∑dx = 6.0 m, East + 3.0 m, East = 9.0 m, East ∑ dy = 4.0 m , South Vectors d1 d2 d3 Sum x y +6.Om -4.Om +3.Om +9.Om -4.Om a) Magnitude of R R = √ x2 + y2 = √ (+9.0m ) 2 + (-4.0m)2 R = √ 81m2 + 16 m2 = √ 97 m2 R = 9.848857802 m = 9.8 m b) Direction : Ɵ = tan-1 /x÷y/ Ɵ = tan-1 /9.0m ÷ -4.0 m/ = tan-1 /-2.25/ Ɵ = 66.037511030 = 660 South of East dR = 9.8 m, 660 South of East Displacement is a vector whose magnitude is the shortest distance from initial to the final position. Example: A child walk 4.0 m, East, then 5.0 m, North, then 4.0 m West and finally 5.0 m South. What is the total distance traveled by the child? What is his total displacement? Total distance = 4.0m + 5.0 m +4.0m + 5.0m dtotal = 18.0 m Total displacement = ∑ x + ∑ y dtotal = (4.0m, E + 4.0m,W) + (5.0m, N + 5.0m, S) dtotal = 0 + 0 = 0 km Example: A car ran 100 meters from point A to point B, then 50 meters from point B to point C, and another 100 meters from point C to point D. What is the total distance travelled? What is its total displacement To solve the total distance travelled you can simply add the length of path from point A to B, B to C and C to D. dtotal = length A to B + length B to C + length C to D dtotal = 100 m + 50 m + 100 m dtotal = 250 m Total displacement : dtotal = sum of dx + sum of dy dtotal = ( 100m, E + 100m, W) + ( 50m, S) Vectors X axis(East and West) d1 d2 +100m -100m d3 Sum dtotal = 50m, South Om Y axis ( North and South -50m -5Om