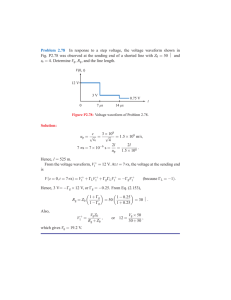
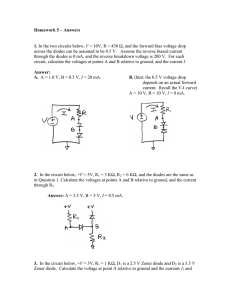
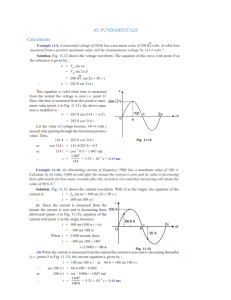
ELTN 1122 – Introduction to Semiconductors (Diode Applications) -Chandika Kiriella Course Outline • Credits: 2 • Lecturer: Mr. Chandika Kiriella • Tutor: Mr. Salith Rathnayaka • Time Allocation: Lectures: 2 hrs/week Tutorials: 1hr/week • Assessments: Continuous Assessments: 30% Final Examination: 70% Learning Outcomes After Completing This Module, the students will be able to: • Explain the operations of different kind of diodes and transistors. • Use diodes and bipolar transistors in simple electronic circuits Recommended Reading: • Introductory Electronic Devices and Circuits, Robert T. Paynter, Pearson Prentice Hall(2006) • Electronic Devices, T.L. Floyd, Pearson Prentice Hall(2008) Introduction • As a simplest semiconductor component, diode has a wide variety of applications in modern electronic systems. • Allows the current flow only in one direction • Can be treated as a one-way switch. • When the voltage applied to the anode is positive with respect to the cathode, the diode is said to be in Forward Bias. If the voltage applied to the diode is greater than the threshold level**,then diode acts as a short circuit and allows the current flow. **threshold level ≈0.7V for Silicon Diodes threshold level ≈0.3V for Germanium Diodes Keep in Mind Half Wave Rectifier Consider the following circuit, Assuming peak voltage of the voltage source is Vm; 𝑉𝑚 𝑅Ω 𝑉𝑅 (a)Draw the voltage variation of voltage source vs. angle. (b)Voltage across R vs. angle. (c)Voltage across D1 vs. angle. (d)Current through the circuit vs. angle. RMS and Average value of a waveform: 𝑉𝑎𝑣𝑔. 1 = 𝑇 𝑡0+𝑇 𝑣(𝑡)𝑑𝑡 𝑡0 (e)Find the RMS value and average value of the voltage in AC voltage source in ‘question1’. (f) Find the RMS value and average value of 𝑉𝑅 in question 1. Full Wave Rectifier By assuming peak value of the supply is Vm, a) Draw the waveform of input voltage vs. angle b) Draw the waveform of output voltage c) Draw the waveforms of current across each semi-conductor device(D1, D2, D3, D4). d) Calculate the average voltage across the load Diode Limiters(Clippers) a) Positive Clipper b) Negative Clipper Question: Draw Vout waveform and mark peak output voltage on it. (Assume the voltage drop of 1N4001 is 0.7V) c) Positive Biased Clipper 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 Fill the below table and draw Vout waveform. (Assume voltage drop of the diode is 0.7V) Vin Vbias + Vin < V bias + Vin > V bias - |Vin| > V bias - |Vin| > V bias Vout Answer: Question: Draw Vout waveform and mark necessary voltages on it. (Assume the voltage drop of diode is 0.7V) d) Negative Biased Clipper 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 If you need to limit any negative voltage level, bias voltage and the diode should be connected as shown above. Draw the output waveform by carefully analyzing the circuit Answer: Questions: (Assume the voltage drop of diode is 0.7V) 1. Draw the output waveform of the positive biased clipper if the diode is turned around (See below figure) 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 2. The circuit shows below comprised of a positive biased clipper with negative biased clipper. Obtain the output voltage waveform