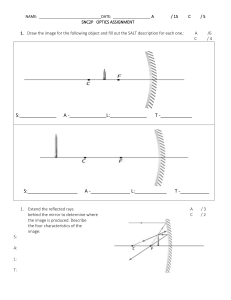
February 28, 2023 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION-2 OUTCOMES By the end of the lesson, students should be able to: • Predict the types of images formed by reflection from a plane mirror and by refraction through a thin convex lens. • Relate the focal length of a lens to the location and magnification of an image. CHARACTERISTICS OF IMAGE IN A PLANE MIRROR 1. The image will be the same size as the object 2. It will be the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. 3. This image is called a virtual image. Law of Reflection Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Drawing an image in a plane mirror Ray diagrams of reflected light from a plane mirror can be drawn according to the guidelines below: • An incident ray is drawn straight from a point on the object to the mirror. A reflected ray is drawn straight away from the mirror. • Additional incident rays are drawn from the same point on the object but at an angle to the mirror. Reflected rays are drawn away from the mirror at the same angles as the incident rays. • Each reflected ray is extended behind the mirror and used to draw the image. Question-1 Draw the image of David in the mirror. 2. Concave mirrors Image in a concave mirror Ray diagrams of reflected light from a curved mirror can be drawn according to the guidelines below: • An incident ray is drawn straight from a point on the object to the mirror. A reflected ray is drawn through the focal point. • A second incident ray is drawn from the same point on the object through the focal point to the mirror. A reflected ray is drawn straight away from the mirror. • The reflected rays are used to draw the image. Types of image in concave mirrors Concave mirrors can form a variety of images, depending on the position of the object in relation to the focal point and the center of curvature of the mirror. 1. An object far away (at infinity) from the mirror forms a real image at the focal point. 2. An object closer to the mirror, just beyond the center of curvature, forms an image between the center of curvature and the focal point. The image is real, inverted, and reduced. 3. An object placed between the center of curvature and the focal point forms an image beyond the center of curvature. This image is real, inverted, and magnified. 4. An object placed between the focal point and the mirror will produce a virtual image (behind the mirror). The image will be magnified and upright. 3. Convex mirrors Image in a convex mirrors Convex mirrors produce only virtual images (behind the mirror) that are upright and smaller than the object. REFRACTION Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. Light changes direction when it passes from one medium to another because it travel with a different speed. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ][10] 1. Draw the image of arrows in the plain mirror. [2] 2. Match words and their place in the diagram. [6] 3. What is refraction. [1] 4. Find the place of images in the mirrors.