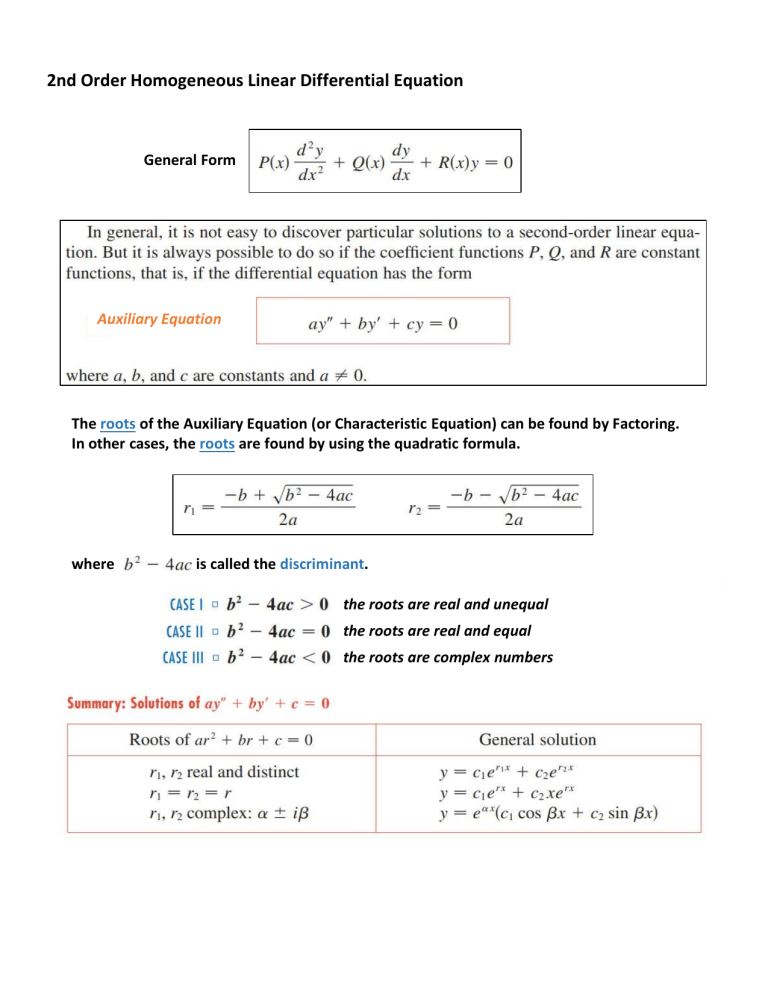
2nd Order Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation General Form Auxiliary Equation The roots of the Auxiliary Equation (or Characteristic Equation) can be found by Factoring. In other cases, the roots are found by using the quadratic formula. where is called the discriminant. the roots are real and unequal the roots are real and equal the roots are complex numbers Determine the General Solution of the 2nd Order Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation. Determine the Solution of the 2nd Order Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation with Initial Value. Answers to Odd Number questions. Intentionally Left Blank 2nd Order Non-Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation General Form Case I: G(t) where G(t) is a polynomial function Case II: G(t) where G(t) is an exponential function Case III: G(t) where G(t) is a cosine/sine function When G(t) is a sum of several functions, solve the particular solutions individually and then add. exponential function polynomial function cosine/sine function Important: 1. Note that Y(t) or the particular solution is only for G(t). 2. Still need to determine the homogeneous solution or the complimentary solution. Final Solution Determine the General Solution of the 2nd Order Non-Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation. Determine the Solution of the 2nd Order Non-Homogeneous Linear DE with Initial Value. Answers to questions.