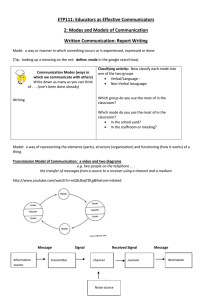
Faculty of Engineering Alexandria University Name: Hany Hamza Mohamed Salah ID: 19016833 Submitted to: Dr. Elsayed Yousef Why did the author choose this cover? The purpose of the book is to provide coverage of digital communication systems. Though the emphasis is on this subject, necessary analog fundamentals are also included since analog waveforms are used to carry digital data and transmit it. The book discusses these techniques in terms of a unified structure, which is the block diagram in the cover letter, and is also included at the beginning of each chapter. Blocks in the diagram are discussed in depth when appropriate to cover the subject of that chapter, so that the student has an idea about the big picture (the whole structure) while also developing in-depth knowledge about some of its elements. Signals and key processing steps are traced from the information source through the transmitter, channel, receiver, and ultimately to the information sink. Signal transformations are organized according to nine functional classes: Formatting and source coding, Baseband signaling, Bandpass signaling, Equalization, Channel coding, Multiplexing and multiple access, Spreading, Encryption, and Synchronization. The block diagram illustrates the flow of a signal in a digital communication system. The upper part is basically the transmitter, and all of the processing steps that the signal goes through, while the lower part is the receiver where all these processes are reversed. The steps are as follows: 1. The input information is converted to binary bits, which are then grouped to form digital messages. 2. Encryption adds a security layer to the data to prevent unauthorized access. 3. Channel encoding adds redundant parts to the bit stream, to make it more resistant to loss of data. 4. Multiplexing and multiple access allows multiple types of data to be sent over the same channel and/or multiple users to be able to 5. 6. 7. 8. access this data, using techniques like frequency division multiplexing and frequency division multiple access. A modulator converts this digital signal to an analog signal that can then travel through a channel, by superimposing the signal on a carrier waveform. Frequency spreading can decrease the risk of interference on the signal, producing a clean signal. The channel carries the information, whether it be a piece of wire or air, in case of wireless data. Synchronization is necessary so that all these processes coordinate with each other, and the transmitter coordinates with the receiver and knows when to send, receive and/or process the signal. All the above steps are then performed in reverse in the receiver, by means of frequency despread, demodulators, decoders and decryptors, to finally reproduce the original signal at the information sink.