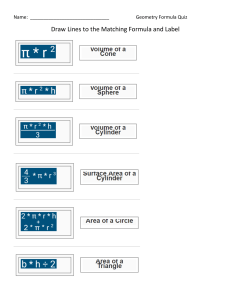
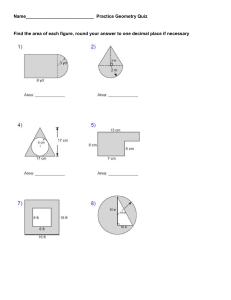
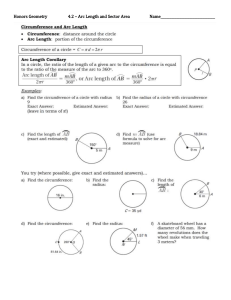
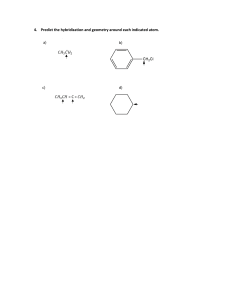
EDMA239- GEOMETRY FOR TEACHERS Course Syllabus: GEOMETRY FOR TEACHERS Instructor: Mohammad Awwad Classes: W 15:20 – 16:35. E-211 F 13:00 – 14:15 E-303 Email: mawwad@bethelehm.edu Office Room No: E-206 Office Ext. : 2032 Office Hours: W 14:00-15:00. E-206 MainTextbook: Elementary Geometry for College Students ; Alexander/Koeberlein's Publisher, Cengage Learning; 6th edition (2014);Language, English; Hardcover, 624 pages . Recommended Supplemental Texts: Geometry and measurement for middle-school teachers A. Cohen, I. Radu, M. Sequin, and C. Woodward Rutgers University, New Brunswick Copyright 2015. Basic Mathematical Skills With Geometry: by James Streeter, Donald Hutchison , Louis Hoelzle . Geometry Tchr. Activity Kit Gr. 6-12 1st Edition by Judith Muschla Palestinian mathematics curriculum at the primary and secondary Grades. Basic Information: A. Purpose statement : Students become aware of creative geometry, activates and materials for teaching geometry. Teaching geometry effectively at middle and secondary grades requires that teachers have a deep and profound understanding. The main goal of this course is to enable students to develop and advanced viewpoint of the geometry that will teach. B. Course description: This course is designed for students who expect to be teaching geometry at the high school or middle school level, but it can be useful for many others as well. This course is listed as an Education course, and you certainly will study mathematics, but not the kind of mathematics you’ve studied before. In this course you will learn the mathematics needed to become an effective teacher. What kind of geometry do teachers need to know? intended for future and practicing teachers. This is a course in how to teach geometry; in addition of that, it is to help you understand the subject and issues in the subject well enough that you can teach the course., This course will be one of the more challenging courses you take as you prepare to become a teacher. Learning goals: Content goals: Students will engage in a thorough development of the concepts of solving problems in geometry. Many students will enter the course with the misconception that mathematics is all about computation and following procedures. Through careful consideration of many type of problems and activates , students will come to understand that mathematics is much more than computation, and more than one approaches to solving any problem. Performance goals: Upon complete of this course students will be prepared to teach geometry by being able to: (1) Demonstrate mathematical creativity and critical thinking by applying geometric understanding to solve a variety of mathematical problems using multiple representations. (2) Improve ability to communicate mathematical ideas appropriately using the language of mathematics. (3) Improve ability to reason mathematically and began developing mathematical proofs. (4) To strengthen knowledge of the relation of geometry to other subjects, their application in society, and relationships within mathematics itself. (5) Increase understanding of the national Palestinian math curriculum relating to geometry. (6) To use technology, such as Geogepra , as an aid in understanding geometry. (7)Analyze development levels of geometric thought. Learning outcomes: - In the scope of knowledge a graduate knows the national curriculum of mathematics in the scope of the school geometry, the teaching objectives and the content knowledge at different education levels (Grade 7,8,9,10). methods of teaching school geometry - substantive and methodical solutions, good practices. -In the scope of skills a graduate can identify typical school exercises with the learning objectives, in particular with the general requirements of the national curriculum . identify the school geometry topics with other learning content topics create didactical situations invoking students' activity and aimed at broadening their interests and at knowledge . recognize typical students' errors and use them in teaching practice Student Assessment: A. Assessment plan: students will assessed and receive regular feedback on their work through the assignment of homework, written and oral communication, group or individual project, in –class examinations, and final exam. B. Methods and criteria: the final grade will be based on the following: 20% home work /class participation 10% Project There will be two exams during the semester, dates to be determined 15% first exam 15% second exam 40% final exam - The project will allow students to teach classes to students at one of the close schools after discussing how to teach and design lesson Plans. Or explore a concept more deeply in a real-world context. This will be due to the middle semester.. Homework's will be assigned regularly to reinforce the advanced mathematical concepts learned in class. Note: All missed exams will be given a grade of zero. Late homework assignments will not be accepted. The only exceptions to this policy will be those absences that are caused by university-approved activities or religious observances for which documentation has been provided to the instructor in advance. The instructor will evaluate unexpected illness or unforeseen catastrophic circumstances on a case-by-case basis and determine whether a make-up is appropriate. Learning Activates: Middle and high school Palestinian mathematical curricula are used as basis in depth study of mathematical geometry content. Many class sessions are developed to dissuasion of mathematical content and skills are necessary in mathematical education of middle school grades. Other class sessions consist of hands on experience in order for the future teachers to learn how to use concrete materials, technology in the development of geometry for middle school grades. Classes : Although I won’t officially take attendance, I expect you to attend all classes. In addition to conducting lectures, discussions, and practice exercises designed to clarify the reading and prepare you for the homework ,I will also be introducing new concepts that are not covered in either the textbooks or the handouts. Because this class is taught in a cooperative inquiry-based format, small groups, and whole class participation is an essential part of the experience for both you and your classmates .Consequently, absences by individual students hurt not only that student, but also the rest of the class. Excessive absences from class will result in a lowering of your overall grade in the course as follows: Number of absences Grade lowered 0-2 3 4 None One point Two points 5 Three points 6 and more Fail The only exceptions to this policy will be those absences that are caused by university approved activities or religious observances for which documentation has been provided to the instructor in advance Academic Integrity: Each student must pursue his or her academic goals honestly and be personally accountable for all submitted work. Representing another person's work as your own is always wrong, whether this is another student's work Cheating: The University’s minimum penalty for cheating or plagiarism is a failure in the course. Cheating or plagiarism can lead to expulsion from the university. It’s not worth it, so don’t do it. Course Content : The following description comes from the original proposal for this course, and reflects the approach I will attempt to take this semester. Detailed course outline: Introduction to geometry and Basic concepts Distances, lines and Angle Relationships Angles Triangles quadrilaterals Similar Triangles Circles Design Geometry class lesson Plan Locus and Concurrence Areas of Polygons and Circles Surfaces and Solids Analytic Geometry Introduction to Trigonometry Geogebra program