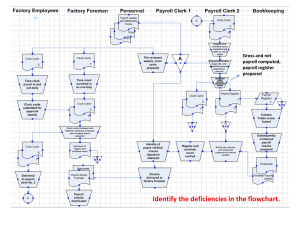
Principles of Cost Accounting, 16th Edition, Edward J. VanDerbeck, ©2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use. Chapter 3 Accounting for Labor Learning Objectives Distinguish between the features of hourly rate and piece-rate plans. Specify procedures for controlling labor costs. Account for labor costs and payroll taxes. Prepare accruals for payroll earnings and taxes. Learning Objectives (cont.) Account for special problems in labor costing. Labor costs issues • How can companies control labor costs in a highly competitive, global environment? • What incentive wage plans can be put into place to ensure that workers are compensated for adding value? • How should bonuses, holiday pay, and vacation pay be accounted for? Factory Payroll costs • Factory payroll costs are divided into two categories: - Direct labor – also known as touch labor, represents payroll costs traced directly to an individual job. - Indirect labor – consists of labor incurred for a variety of jobs related to the production process but not readily traceable to an individual job. Accounting System of a manufacturer • The accounting system of a manufacturer must include the following procedures for recording payroll costs: 1. Recording the hours worked or quantity of output by employees in total and by job, process, or department 2. Analyzing the hours worked by employees to determine how labor time is to be charged. Accounting System of a manufacturer 3. Charging payroll costs to jobs, processes, departments, and factory overhead accounts. 4. Preparing the payroll, which involves computing and recording employee gross earnings, withholdings and deductions, and net earnings. Hourly-rate and piece-rate plans • An hourly-rate plan establishes a definite rate per hour for each employee. • A piece-rate plan bases earnings on the employee’s quantity of production. • Modified wage plans combine some features of the hourly-rate and piece-rate plan. Controlling Labor Cost • The timekeeping and payroll departments have responsibility of maintaining labor records. • The labor time record shows the employee’s time spent on each job, as well as the time spent as indirect labor on machine repair. Controlling Labor Cost Controlling Labor Costs Controlling Labor Costs Labor Costs • Cost accountants examine the labor time records and charge the labor costs to the appropriate jobs or departments and to factory overhead. • A labor cost summary summarizes the direct labor and indirect labor charges to a department for the period. Labor Costs Labor Costs • The labor cost summary becomes the source for making the following general journal entry: Work in Process (Direct Labor) XXX Factory Overhead (Indirect Labor)XXX Payroll XXX Labor Costs Employers’ Payroll Taxes • Payroll taxes imposed on employers include Social Security tax and federal and state unemployment taxes. • Employers must periodically report and pay the following taxes to the appropriate government agencies: • FICA • FUTA • SUTA Payroll Accrual • When the financial statement date does not coincide with the ending date for a payroll period, an accrual for payroll earnings and payroll tax expense should be made. • Employer’s payroll taxes are accrued to avoid understating the expenses and liabilities for the period. Special Labor Cost Problems • Shift premium • Pensions • Bonuses • Vacation and Holiday pay