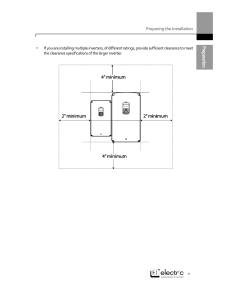
Aviation Safety: Organizational Processes & Human Factors
advertisement
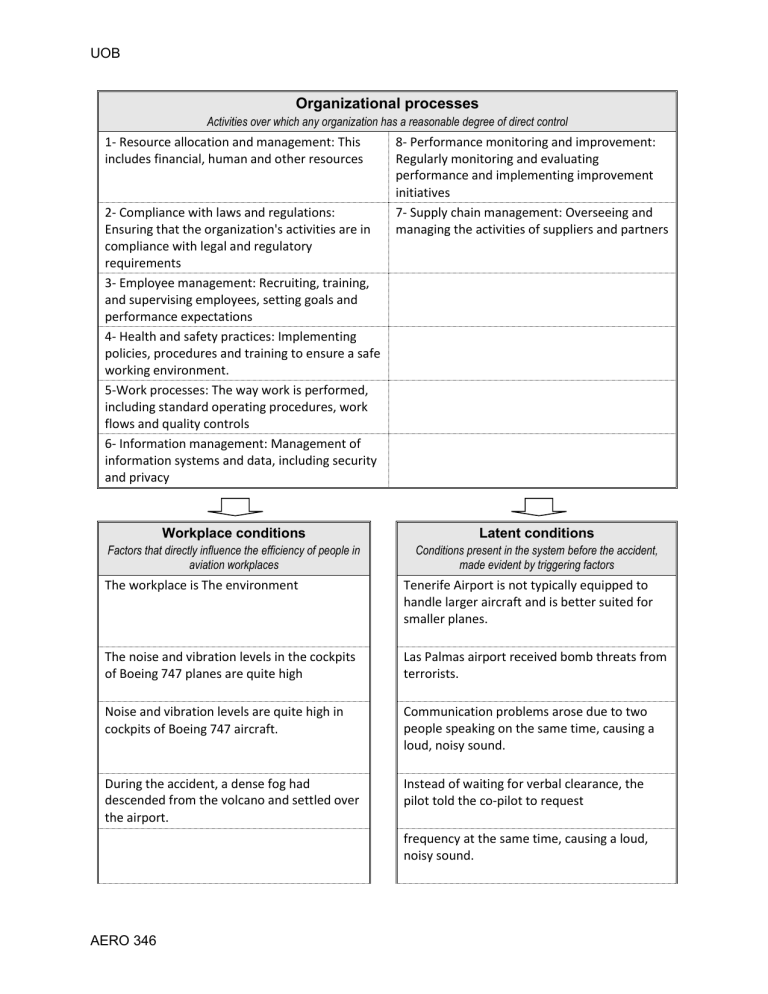
UOB Organizational processes Activities over which any organization has a reasonable degree of direct control 1- Resource allocation and management: This includes financial, human and other resources 2- Compliance with laws and regulations: Ensuring that the organization's activities are in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements 3- Employee management: Recruiting, training, and supervising employees, setting goals and performance expectations 4- Health and safety practices: Implementing policies, procedures and training to ensure a safe working environment. 5-Work processes: The way work is performed, including standard operating procedures, work flows and quality controls 6- Information management: Management of information systems and data, including security and privacy 8- Performance monitoring and improvement: Regularly monitoring and evaluating performance and implementing improvement initiatives 7- Supply chain management: Overseeing and managing the activities of suppliers and partners Workplace conditions Latent conditions Factors that directly influence the efficiency of people in aviation workplaces Conditions present in the system before the accident, made evident by triggering factors The workplace is The environment Tenerife Airport is not typically equipped to handle larger aircraft and is better suited for smaller planes. The noise and vibration levels in the cockpits of Boeing 747 planes are quite high Las Palmas airport received bomb threats from terrorists. Noise and vibration levels are quite high in cockpits of Boeing 747 aircraft. Communication problems arose due to two people speaking on the same time, causing a loud, noisy sound. During the accident, a dense fog had descended from the volcano and settled over the airport. Instead of waiting for verbal clearance, the pilot told the co-pilot to request frequency at the same time, causing a loud, noisy sound. AERO 346 UOB clearance and began the takeoff process by increasing the throttle. There was a management/organizational emphasis on cost and reputation rather than safety culture. The emergency plans and procedures at the airport were not adequate for handling a scenario like this. Active failures Defences Actions or inactions by people (pilots, controllers, maintenance engineers, aerodrome staff, etc.) that have an immediate adverse effect Resources to protect against the risks that organizations involved in production activities must confront The KLM engineer and co-pilot did not intervene when the pilot increased the throttle and took off without receiving clearance from the radar tower. The KLM pilot ignored information suggesting that the Pan Am plane was still on the runway. Pilots should be willing to consider the decisions made by their co-pilots The KLM co-pilot remained silent and did not object to the pilot's actions, believing that the pilot is always right. Communication training can be useful for pilots to enhance their skills in exchanging information with their colleagues and air traffic control. Crew resource management training should be incorporated into a company's culture to minimize failures due to human factors. Air traffic control instructed the Pan Am flight to move from the runway to taxiway 3, but the angle of the taxiway was not suitable for a large Boeing747 to maneuver. The KLM flight engineer questioned the pilot's decision to take off after hearing advice from the traffic tower that the Pan Am flight may not have yet cleared the runway. AERO 346 Stress training may be berleficial for pilots to learn how to manage and cope with stress effectively during flights. Protocols need to be established that mandate that co-pilots possess enough proficiency to challenge the decisions made by their captains. UOB The pilot told the co-pilot to request clearance and immediately began the takeoff process without waiting for verbal clearance. The Pan Am aircraft missed the third taxiway. AERO 346