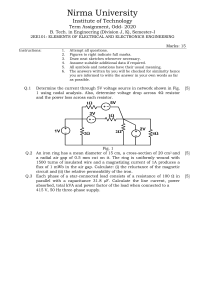
PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. Fig 1.1 shows a circuit diagram. Fig 1.1 a) Which 2 resistors are connected in parallel? (1) b) Calculate: i. The total resistance of the circuit. (3) ii. The current through R1. (1) iii. The potential difference (p.d) across R1. (2) 2. Fig 2.1 shows an electric circuit. Fig 2.1 When switch S is closed the ammeter reading is 3.0 A. Calculate: a) The total resistance of the circuit. (3) b) The current flow through the 3.0 Ω resistor. (2) c) The electromotive force (e.m.f) of the battery. (2) 3. Fig 3.1 shows meter reading before and after using an electric iron for 2 hours. The cost of electricity is 60 thebe per kWh. Fig 3.1 a) Calculate: i. The electrical energy used in kWh. (1) ii. The cost of using the electric iron for 2 hours. (2) 4. Fig 4.1 shows an electric circuit. Fig 4.1 The reading of A3=1.5A a) State the current through i. R2……………… (1) ii. R1……………… (1) b) Calculate the voltage across each resistor. i. Voltage across R1. (2) ii. Voltage across R2. (1) iii. Voltage across R3. (1) 5. Fig 5.1 shows two bulbs connected in a circuit with a battery and two ammeters. Ammeter A reads 2.0 A and ammeter A1 reads 0.5 A. Fig 5.1 Calculate: a) The current through the 2Ω bulb. (2) b) The potential difference across the 6Ω bulb. (2) c) State the potential difference across the battery. (1) 6. Fig 6.1 shows two identical resistors, R1 and R2 connected in parallel to a 12V battery. Fig 6.1 a) The ammeter reading is 3.0 A. i. State the current flowing through R1. (1) ii. Calculate the resistance of R1. (2) b) The circuit is changed so that R1 and R2 are now connected in series with the same ammeter and battery. State and explain how this will affect i. The potential difference across each resistor. Effect:………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Explanation:………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) ii. The ammeter reading. Effect:………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Explanation:……………………………………………………………………………………………………(2) 7. Fig 7.1 shows an electric iron. Fig 7.1 a) State the energy change that takes place when the iron is connected to a socket and switched on. (1) b) Explain why: i. The handle of the iron is made of plastic. (1) ii. The earth is connected to a metal sole. (1) c) The iron transfer 3kWh energy when it is switched on for 2 hrs. Calculate: i. The power input of the iron. (2) ii. The cost of using the iron for 2 hours. The cost of electricity is P0.65 per kWh. (1)