Reactance, Impedance, Power: Electrical Engineering Concepts
advertisement

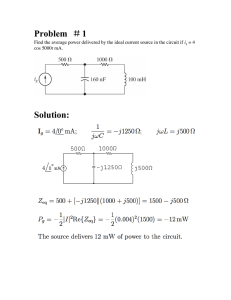
1-7 (computation) 8. Explain what is the ideal value of X. Reactance (X) is the opposition to the flow of current due to its capacitance and inductance. An ideal capacitors and inductors have zero resistance and an ideal resistor has zero reactance. 9. Explain what is the ideal value of Z. Impedance (Z) is the overall opposition of the circuit to current. Ideally, input impedance should be high, at least ten times the output impedance to avoid overloading the source of signal and to reduce the voltage of the signal. On the other hand, output impedance should be low, less than a tenth of the load impedance to ensure that minimal voltage is lost as output current is driven through the output impedance. 10. What is resonance? Electrical resonance occurs when the reactances of circuit elements cancel each other. The impedance between the input and output is almost zero and mathematically, this condition is 𝑋𝐿 = 𝑋𝐶 . 1. What will happen to the apparent power if the reactive power increase? Apparent power is the combination of actual power and reactive power. If the reactive power increases, the apparent power increases as well. 2. How do we increase the reactive power? To increase reactive power, voltage magnitude must be increased. If the field winding voltage is increased, a higher voltage is induced resulting to more reactive power flow. 3. Explain the difference between real, imaginary, and apparent power. The real power, also known as true or active power, is the power consumed by resistive or electric load. Reactive or imaginary power on the other hand is the power released and stored by inductors and capacitors. It opposes the flow of current. Lastly, the apparent power is the vector sum of the real and imaginary power. It is the product of the total voltage and current in the circuit. 4-10 (computation)