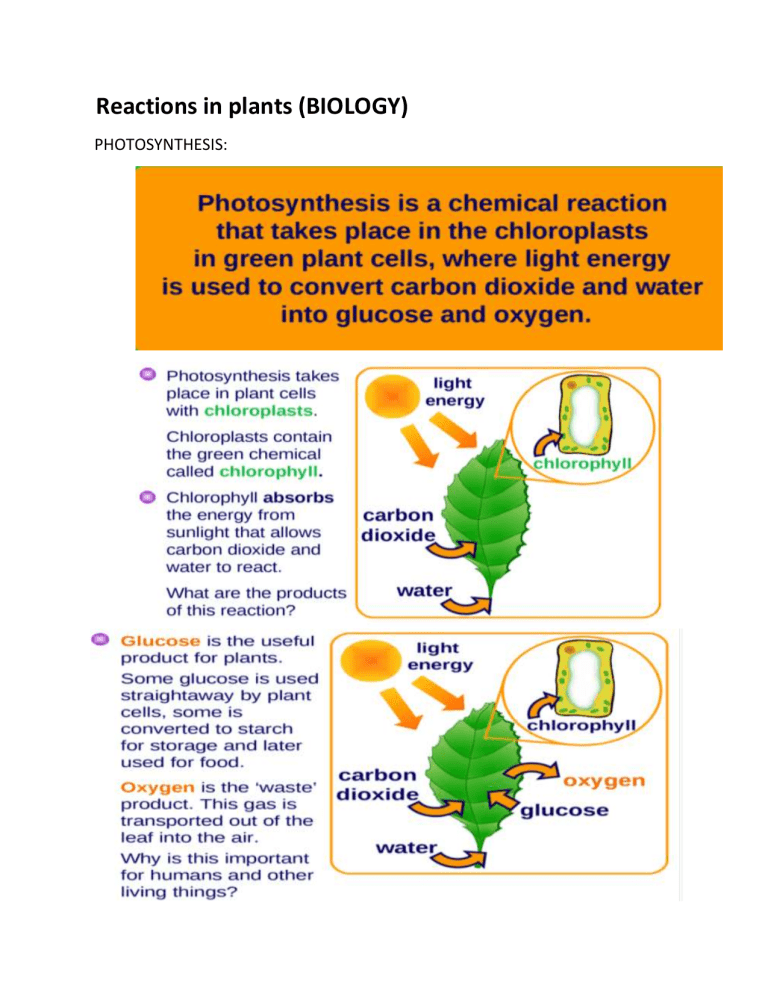
Reactions in plants (BIOLOGY) PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Limiting Factor: A variable that prevents the rate (speed) of a process from becoming any faster. With less light, or a shortage of a raw material, photosynthesis is slower Factors affecting photosynthesis Light intensity Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly - even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide. Increasing the light intensity will boost the rate of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide concentration Even if there is plenty of light, a plant cannot photosynthesise if there is insufficient carbon dioxide. Temperature If it gets too cold, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease. Plants cannot photosynthesise if it gets too hot. If you plot the rate of photosynthesis against the levels of these three limiting factors, you get graphs like the ones shown above. In practice, any one of these factors could limit the rate of photosynthesis. Aerobic Respiration Plant cells need a supply of glucose for energy to help the plant grow and make new substances. The chemical energy stored in the glucose is released by the reaction called aerobic respiration because oxygen from the air is needed for it to work. The word equation and symbol equation for aerobic respiration: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O (+energy) The energy released from glucose is transferred to molecules of ATP, which store energy for a cell until it is needed. Photosynthesis and respiration Respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis only happens when there is light but respiration happens all the time. During the day, a plant produces more oxygen from photosynthesis than it needs for respiration and so oxygen is given off. Glucose is carried to all parts of the plant in the form of sugars dissolved in water. Phloem vessels carry the sugar solution. This is how the roots get glucose for respiration. Roots need oxygen for respiration which they get from the soil.