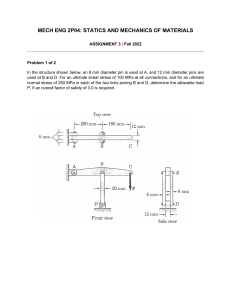
CENG 212 – Mechanics of Materials University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Welcome to the Course! Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 1 CENG 212 – Mechanics of Materials University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. CHAPTER 1: Average Normal and Shear Stresses (Based on Dr. Semih Erhan’s Material) Objectives: • Review important principles of statics. • Principles to determine internal resultant loadings in a body. • Normal and shear stress. • Applications of analysis and design of members subjected to an axial load or direct shear For UoB Students: It is the pre-requisite of : • CENG 311 – Structural Analysis 1 • CENG 341 – Soil Mechanics Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 2 Mechanics University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Mechanics of Materials: is a branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body that is subjected to an external loading. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Important to Understand after this Chapter: • External Loads: (Applied Loads on a body) • Internal Loads: (Internal response to applied loads) • Equilibrium of deformable bodies: (External = Internal/Action = Reaction) • Stresses: (Force per Area) • Strains: (dL/Original L). Those terms are going to be explained further. Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 3 External Loads University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example External Loads: A body is subjected to two types of external loads; surface forces or body forces. • Surface Force: Applied from outside contact. • Body Force: Resulting from mass and movement. • Surface Forces: Distributed over Area Distributed over Line Concentrated Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 4 External Loads University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example External Loads: A body is subjected to two types of external loads; surface forces or body forces. • Surface Force: Applied from outside contact. • Body Force: Resulting from mass and movement. • Body Force : • Own Weight (Gravitational Field) • Electro Magnetic Force (Electro Magnetic Field) • Inertia Loads. Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 5 Internal Loads University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Internal Loads: Loads that are generated in response to the applied surface loads and body loads. • Internal Forces: • Axial Forces: Force Perpendicular to the plane of the section. • Shear Forces: Force Parallel to the plane of the section • Internal Moments: • Bending Moments: Moment in the plane of the section. • Torsion: Moment perpendicular to the plane of the section. Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. 3D General 3D Beam 2D Beam Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 6 Equilibrium University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Equilibrium: Sum of Forces and Moments should be zero. For equilibrium (External), forces and moments are balanced F = 0 M = 0 General procedure for solution is based on two step: i. Draw a free-body diagram to account for all forces acting on the body ii. Apply the equilibrium equations to achieve equilibrium state For equilibrium (Internal Loads) • Draw free body diagram • Calculate support reaction • Choose segment to analyze • Indicate the internal forces (N, V, M) on the segment in positive directions as follows and apply equilibrium. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 7 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Reminder to support Reactions: Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 8 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine resultant loadings acting on cross section at C of the cantilever beam. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 9 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine resultant loadings acting on cross section at C of the cantilever beam. Intensity (w) of loading at C Course: CENG 212 - MoM w 270 = w = 180 N / m 6 9 1 F = ( 180 )( 6 ) = 540 N 2 F acts 1/3 of length 6 m from C = 2 m from C. Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. + ∑ Fx = 0; − Nc = 0 Nc = 0 + ∑ Fy = 0; Vc − 540 N = 0 Vc = 540 N + ∑ Mc = 0; −Mc − 540 N (2 m) = 0 Mc = −1080 N·m Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 10 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: The 500-kg engine is suspended from the crane boom in Figure. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section of the boom at point E. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 11 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. FCD Course: CENG 212 - MoM FCD C Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Ax B Ay Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 12 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. 3 + M A = −500 9.81 (3m) + FCD (2m) = 0 5 FCD = 12262.5 N + Fx = Ax − 4 FCD = 0 5 Ax = 9810 N 3 + Fy = − Ay + FCD − 500 9.81 = 0 5 Ay = 2452.5 N + Fx = 9810 + N E = 0 N E = −9810 N + Fy = −2452.5 − VE = 0 VE = −2452.5N + M = 2452.5 (1m) + M E = 0 M E = −2452.5 N .m Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 13 Statics Review University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at G of the beam shown in Figure. Each joint is pin connected. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh N m Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. N/m m m m Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 14 Statics Review + M E = 900 (4m) + 1500 (10m) − FBC (3m) = 0 University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example FBC= 6200 N + Fy = −1500 − 900 + Ey = 0 Ey = 2400 N + Fx = − Ex + FBC = 0 Ex = 6200 N Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 15 Statics Review 4 FBA = 0 5 FBA= 7750 N + Fx = 6200 − University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. 3 + Fy = FBD − FBA = 0 5 Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. FBD= 4650 N 3 + M E = 1500 (2m) − 7750 (2m) + M G = 0 5 MG = 6300 N.m 3 + Fy = −1500 + 7750 − VG = 0 5 3 + Fx = 7750 + NG = 0 VG = 3150 N.m 5 NG = -6200 N.m Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 16 Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Stress: The force per unit area => The intensity of force. Stress (SIMPLIFIED)/AVERAGE: Average Stress is Force divided by Area. Loads alone: Do not give a full picture as of the effect of loads on the structural components. 100kN 100kN Is more dangerous, because it has a smaller section 100kN 100kN Is less dangerous, because it has a larger section So, stress, which is the force per unit area, is a better measurement. A simplified version is: Stress = Force / Area A more accurate version is: σz = lim ΔFz ΔA →0 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh ΔA 17 Axial Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Axial Stress: Stresses induced by axial forces, which are forces Perpendicular to the section. _ Average Stress Actual Stress Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. 𝜎𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 = 𝑃 𝐴 σz = lim ΔFz ΔA →0 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh ΔA 18 Axial Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Normal Stress: The intensity of the force acting normal to (ΔA) is defined as the normal stress, σ (sigma). _ σz = lim ΔFz ΔA →0 ΔA Tensile stress: Normal force “pulls” or “stretches” the area element ΔA. (We use POSITIVE SIGN for that) Compressive stress: Normal force “pushes” or “compresses” area element ΔA. (We use NEGATIVE SIGN for that) Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Tension Compression 19 Shear Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Shear Stress: Stresses induced by shear forces, which are forces Parallel to the section. _ Average Stress Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. 𝜏𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 = 𝑃 𝐴 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 20 Shear Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Shear Stress: Stresses induced by shear forces, which are forces Parallel to the section. _ Actual Stress Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. τzx = τzy = lim ΔFx ΔA →0 ΔA lim ΔFy ΔA →0 ΔA Shear Stress: The intensity of force acting tangent to ΔA is called the shear stress, τ (tau). Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 21 General Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. • General state of stress: Figure shows the state of stress acting around a chosen point in a body. This state of stress is then characterized by three components acting on each face of the element. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. •Units (SI system) •Unit of stress is pascal (1 Pa = 1 N/m2) •kPa = 103 N/m2 (kilo-pascal) •MPa = 106 N/m2 (mega-pascal) •GPa = 109 N/m2 (giga-pascal) Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 22 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Average normal stress • From equilibrium: we need to add all the “mini forces” from those little areas (dA) + FRz = ∑ Fz ∫ dF = ∫A σ dA P = σA P σ= A Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. σ = average normal stress at any point on cross sectional area P = internal resultant normal force Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh A = x-sectional area of the bar 23 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Maximum average normal stress If internal force P and x-sectional area A are constant along the bar, σ = P/A constant along the bar. • If the bar is subjected to several external loads along its axis and there is a change in x-sectional area we have to find the section where the P/A is maximum. • For such cases, first draw an axial or normal force diagram along bar’s length. Then determine the maximum average normal stress from the plot. • P is positive (+) (Tension) P is negative (-) (Compression) Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 24 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine max. average normal stress in bar when subjected to loading shown if the bar width = 35 mm, thickness = 10 mm Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 25 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Internal Forces: Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Normal force diagram: Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Largest loading area is BC, where PBC = 30 kN Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 26 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Maximum Average normal stress: Note (It is NOT always where the maximum force is!) Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example σBC = PBC A = 30(103) N (35 mm)(10 mm) = 85.7 MPa Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 27 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Example: Determine average compressive stress acting at points A and B if the specific unit weight γst = 80 kN/m3 200 mm Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example 800 mm 100 mm 200 mm 200 mm Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 28 Average Normal Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Free Body Diagram: Course: CENG 212 - MoM Weight of segment AB determined from Wst = γstVst Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. 800 mm + Fz = 0 P − Wst = 0 P − ( 80kN / m3 )( 0.8m )( 0.2m )2 = 0 P = 8.042 kN P 8.042 103 N = = = 0.064 MPa 2 2 A 200 mm Note that stress distribution is uniform in the case of axially loaded member. Therefore, normal stresses at point of A and B are equal. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 29 Average Shear Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. • Shear stress is the stress component that act in the plane of the sectioned area as shown in figure. σz Course: CENG 212 - MoM τzx τzy Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example • Consider the effect of applying a force F acting to the bar as shown below: • If the supports are considered rigid, the bar will deform and fail along the planes identified by AB and CD Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Free body diagram 30 Average Shear Stresses The average shear stress over each section is defined by: University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM V τavg = A τavg = Average shear stress at section. V = Internal shear force at section determined from equations of equilibrium A = Area of section Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example The distribution of average shear stress acting over the sectioned is shown in Figure. (Uniform distribution) Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. This is example of simple or direct shear. The shear is caused by the direct action of applied load F. This type of shear occurs in connections that use, bolts, pins, welded material Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 31 Average Shear Stresses Single, double University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 32 Average Shear Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Single shear Steel and wood joints shown below are examples of single-shear connections, also known as lap joints. For equilibrium, V = F. The average shear stress can be determined on colored section in (d). Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 33 Average Shear Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Double shear The joints shown below are examples of double-shear connections, often called double lap joints. For equilibrium, V = F/2. Apply average shear stress equation to determine average shear stress acting on colored section in (d). Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 34 Average Shear Stresses University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Procedure for analysis Internal shear 1. Section member at the point where the τavg is to be determined 2. Draw free-body diagram 3. Calculate the internal shear force V Average shear stress 1. Determine sectioned area A 2. Compute average shear stress τavg = V/A Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 35 Average Shear Stresses Single Shear University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. 12.5 kN 12.5 kN VB 12.5 103 N B = = = 17.7 MPa 2 AB 30 mm2 4 Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Pin diameter =30 mm VB=12.5 kN Double Shear VA=10.68 kN 21.36 kN Pin diameter =20 mm VA=10.68 kN VA 10.68 103 N A = = = 34MPa 2 AA 2 20 mm 4 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 36 Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine average normal stress and average shear stress acting along (a) section planes a-a, and (b) section plane b-b. (depth and thickness = 40 mm) Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 37 Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Section a-a: Internal loading: Based on free-body diagram, Resultant loading of axial force, P = 800 N Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Fa-a=800 N P=800 N Average stress: P = σ= A 800 N (40 mm)(40 mm) = 0.5 MPa = 500 kPa Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 38 Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Section b-b: Internal loading: Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. ❖ + F + F x y Or directly using x’, y’ axes: = −800 + N sin 60o + V cos 60o = 0 + Fx = N − 800 cos 30o = 0 = V sin 60o − N cos 60o = 0 + Fy = V − 800 sin 30o = 0 N = 692.8N V = 400 N Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 39 Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Solution: Section b-b: Cross section area: Course: CENG 212 - MoM 40 mm Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. x = 40 / sin 60o 60o x A = ( 40mm ) ( 40mm / sin 60o ) 40 mm Average normal stress: = N 692.8 N = = 0.375MPa A ( 40mm )( 40mm / sin 60o ) Average shear stress: = V 400 N = = 0.217 MPa A ( 40mm )( 40mm / sin 60o ) Stress distribution Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 40 Allowable Stress University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. When designing a structural member or mechanical element, the stress in this member or element must be restricted to safe level. This level or value of stress is allowable stress. One method of specifying the allowable stress for a member is to use a number called the factor of safety. The factor of safety (F.S.) is a ratio of the failure stress (σfail) to the allowable load (σallow). F .S . = F .S . = fail allow fail allow allow = allow = fail F .S. fail F .S . Here (σfail) is found from experimental testing of the material, and the factor of safety (F.S.) is selected based on experience. The factor of safety must be greater than 1 in order to avoid the potential for Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 41 failure. Allowable Stress Factor of Safety: Why???? How is it determined? University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example • • • • • • • • Material Uncertainty Loading Uncertainty Analysis Uncertainty # Loading Cycles Type of failure (with warning or without). Importance of the member. Risk to life and property Influence on the function of the structure Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 42 Simple Design Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. By making simplifying assumptions regarding the behavior of the material, the following equations can often be used to analyze or design a simple connection or mechanical element. P = A avg V = A Cross-sectional area of member subjected to normal force A= P allow Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 43 Simple Design Examples Cross-sectional area of a connecter subjected to shear University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 44 Simple Design Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Required area to resist shear caused by axial load The embedded length l of this rod in concrete can be determined using the allowable shear stress of the bonding glue. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 45 Simple Design Examples University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Required area to resist bearing: Bearing stress is normal stress produced by the compression of one surface against another. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh The area of the column base plate B is determined from the allowable bearing stress for the concrete Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 46 Example University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Procedure for analysis 1. Draw internal force diagrams. 2. Determine the section over which the critical forces (maximum forces) is acting. 3. Then use the following formulas to calculate the required area to sustain these loads. A= P A= allow V allow Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 47 Example University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Example: Determine the maximum magnitude P of the load the beam will support if the average shear stress in each pin is not to allowed to exceed 60 MPa. All pins are subjected to double shear as shown, and each has a diameter of 18 mm. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 48 Example Free Body Diagram University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM FBC Ax Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Ay + M A = FBC sin 30o (6) − P (2) − P (4) = 0 FBC = 2 P + F = Ax − 2 P cos30o = 0 x Ax = 1.732 P Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. + F y = Ay − P − P + FBC sin 30o = 0 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Ay = P 49 Example Solution: University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. ❖Note that the shear forces acting on the pins at B and C are: VB = VC = FBC = 2P ❖The force acting on pin A is: VA = Ax 2 + Ay 2 = P 2 + 1.732 P = 2 P ❖All pins are subjected to same force and double shear. 2P V= =P 2 ❖Then P is calculated as: V P allow = 60Mpa = P = 15268 N = 15.3kN A ( 18mm )2 4 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 50 Example University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Example: The two members pinned together at B. If the pins have an allowable shear stress of τallow=90 MPa, and allowable tensile stress of rod CB is (σt)allow=115 MPa. Determine to nearest mm the smallest diameter of pins A and B and the diameter of rod CB necessary to support the load. A Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. C 5 6 kN 4 A B 2m 3 B 1m Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 51 Example Free Body Diagram University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM 6 kN 5 Ax FBC 4 2m Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example 3 1m 3 + M A = FBC (3) − 6 (2) = 0 5 FBC = 6.67 kN Ay + Fx = Ax − FBC 4 =0 5 Ax = −5.32 kN Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. + 3 F = A − 6 + F =0 y y BC 5 Ay = 2 kN Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 52 Example Solution: University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Pin at A: Double Shear VA = 5.322 + 22 = 5.68 kN VA / 2 2.84 103 N AA = = = 31.56 mm 2 allow 90 Mpa d A2 = 31.56 mm 2 d A = 6.3 mm 4 Pin at B: VB = 6.67 kN Single Shear VA 6.67 103 N AB = = = 74.1 mm 2 allow 90 Mpa d B 2 = 74.1 mm 2 d B = 9.7 mm 4 Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 53 Example Diameters of pins: University of Bahrain College of Eng. Civil Eng. Dept. ❖ dA = 7 mm Course: CENG 212 - MoM Instructor: Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh Table of Contents: • Title • Mechanics • Statics Review • Stress • Average N. Stress • Average Sh. Stress • Examples • Allowable Stress • Design Example Book: Mechanics of Materials Hibbeler 9thed. Choose a size larger to nearest millimeter. dB = 10 mm Diameter of rod: PBC 6.67 103 N A= = = 58 mm 2 allow 115Mpa ❖ d BC 2 = 58 mm 2 d BC = 8.59 mm 4 Choose a size larger to nearest millimeter. dBC = 9 mm Dr. Mahmoud Jahjouh 54