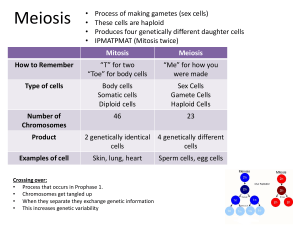
Mitosis and Meiosis What is mitosis? A process where a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Interphase: the cell is preparing for mitosis (cell division by multiplication chromosomes) Stages of mitosis: 01. Prophase : the chromosomes pair up; each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. 02. Prometaphase : the mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores. 03. Metaphase : the chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell(equator). 04. Anaphase : the chromosomes split; pulled to opposite sides of the cell. 05. Telophase : Nuclear membrane begins to form to create two new nuclei; cells begin to separate Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm divides and forms two daughter cells. Questions: 1) What are the purposes of mitosis? Mitosis is important for cell growth, repair and replacement of the cells and asexual reproduction. 2) Mitosis is part of what cycle? Cell cycle 3) What type of cell undergoes mitosis? Somatic cells 4) How does a daughter cell compare to a parent cell after undergoing mitosis? Identical to the parent 5) Does mitosis make haploid or diploid cells? Diploid 6) What n value are the cells which are made by mitosis? 2n (n=23 chromosomes) Facts: ● Makes 2 cells ● Produce somatic cells ● Makes diploid cells ● Divides once ● Produces body cells ● Makes 2n cells ● At the end, a human cell would have 46 chromosomes ● Closely related to asexual reproduction What is meiosis? A process that contributes to variety. Stages of meiosis: 01. Prophase 1 : the nuclear membrane disintegrates and crossing over (recombinations) occurs. This process can lead to genetic variation in daughter cells. 02. Metaphase 1 : the tetrads attach to spindle fibers at their centromeres and line up at the middle cell. 03. Anaphase 1 : the cell membrane begins to construct and tetrads separate. 04. Telophase 1 : nuclear membrane encloses the separated chromatids and two diploid cells are produced. 05. Prophase 2 : the DNA begins to condense and each chromosome pair has a centromere. Don’t have homologous pairs. 06. Metaphase 2 : the chromatids line up at mid-cell and the centrioles are at the poles. 07. Anaphase 2: the chromosomes split and move to opposite sides of the cell. 08.Telophase 2 : four haploid cells are produced and each cell has half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Questions: 1) What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Reproductive sex cells 2) What are the two main types of gametes? Sperm cells and egg cells 3) What are gametes used for? To form zygote(new cells) 4) Does meiosis make haploid or diploid cells? Haploid 5) What n value are the cells which are made by meiosis? n 6) How does a daughter cell compare to the parent cell after undergoing meiosis? Different than the parent 7) What process in prophase 1 of meiosis makes every gamete different? Crossing over (recombination) Facts: ● Divides twice ● Produces gametes ● Makes 4 cells ● Makes haploid cells ● Produces sex cells ● At the end, human chromosomes would have 23 chromosomes ● Closely related to sexual reproduction Compare and contrast: Mitosis Meiosis Comparison 4 stages in total 8 stages in total Produce new cells Happens in somatic cells Happens in germ cells Similar basic steps Purpose is cellular proliferation Purpose is sexual reproduction Start with single parent cell Produce 2 diploid daughter cells Produce 4 haploid daughter cells After interphase, sister chromatid identical Chromosomes numbers remain the same Chromosomes numbers is halved into each daughter cell Begins with interphase, where DNA replicated Genetic variation doesn't change Genetic variation increased A type of cell division In prophase, sister chromatid identical (genetically identical cells) In prophase, sister chromatid crossed over (genetic variations) Produces daughter cells Can be means of sexual reproduction Start of sexual reproduction Daughter cells:diploid 4 genetically different daughter cells: haploid Quizzz: ★ Sperm cells and egg cells have 23 chromosomes so that a fertilized egg can develop into a human. ★ Not all sperm cells are the same when they are produced. ★ Interphase doesn’t happen twice and doesn’t happen after meiosis occurs. ★ Meiosis has the same phase term as mitosis, but PMAT happens twice in meiosis. ★ Homologous: the same size and same genes in the same location ★ The only cells that come from meiosis are sperm and egg. ★ Why would it be important to replicate DNA before a cell divides in mitosis or meiosis? In order for genetic information to be transferred into daughter cells. ★ In mitosis, the two resulting cells are identical to the starting cell and identical to each other. ★ Which cell type is not produced in meiosis? Body cells ★ Mitosis is useful for the creation of new cells which is important for all of the following except generation of gametes. ★ Meiosis makes sperm and egg cells. In humans, sperm and egg cells each have 23 chromosomes. Therefore a fertilized human egg cell would create a cell with 43 chromosomes. ★ In meiosis, the four resulting cells are different from the starting cell and different from each other. Book questions: 01. Why is it important for cells to have a control system to regulate the rate of cellular division? So they won’t grow whenever and however they want (without control) 02. The function of proteins that regulate the cell cycle? Regulator proteins instruct the cell when to grow or divide. 03.Why is cancer an alteration to the cellular cycle? Because it’s characterized by uncontrolled cellular division and growth. 04.How does a cast help the bone heal? The cast provides support for adjusting the bone to its original position, so when the cells begin to grow and divide, they will do so in the correct place. 05. How can you tell if a cell is in prophase 1 or prophase 2? In prophase 1, the cell has 4 chromatids and a crossover takes place. Prophase 2 only has 2 chromatids. 06.What type of reproduction results in offspring with greater genetic variation? Sexual reproduction is the reproduction with greater genetic variation, since it undergoes meiosis, where chromosome crossover takes place to ensure genetic variation. 07. How many chromosomes do the gametes of this organism have? The gametes of this organism will have 4 chromosomes.