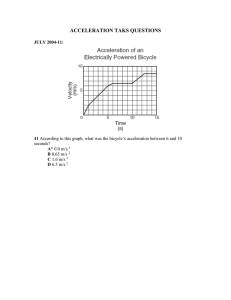
Utilization and Traction (EEN-364) 1. A Train has a schedule speed of 30 Kmph over a level track, distance between stations being 1 km. station stopping time is 20 seconds. Assuming braking retardation of 3 Kmphps. and maximum speed 25 percent greater than average speed, calculate acceleration required to run the service. 2. A train runs average speed of 40 Kmph. Distance between stations is 2 km. Values of acceleration and retardation are 1.5 Kmphps and 2.5 Kmphps respectively. Find the maximum speed of train using trapezoidal speed time curve. 3. A 200 tonne motor coach having 4 motors, each developing 6000 N.M. torque during acceleration, starts from rest. if up gradient is 30 in 1000, gear ratio 4, gear transmission efficiency 90%, wheel radius 45 cm., train resistance 50 N/tonne, addition of rotational inertia 10%, calculate time taken to attain speed of 50 kmph. If line voltage is 3000 V. d.c. and efficiency of motors 85%, find the current taken during notching period. 4. An electric train has quadrilateral speed time curve as follows: A. Uniform acceleration from rest at 2 Kmphps. for 30 seconds B. Coasting for 50 seconds. C. Duration of braking 20 seconds. If train is moving a uniform up gradient of 10%, tractive resistance is 40 N/tonne, rotational inertia effect 10% of dead weight, duration of station stop 15 seconds and overall efficiency of transmission gear and motor as 75%, find the schedule speed and specific energy consumption of run. 5. If in question no 4. instead of up gradient, there is down gradient of 10%. find specific energy output and total energy consumption for 200 tonne train. 6. An electric train weighing 300 tonnes runs 10% upgradient with following speed time curve. A. Uniform acceleration of 1.5 kmphps for 30 seconds. B. Constant speed for 40 seconds. C. Coasting for 30 seconds. D. Braking at 2.5 kmphps to rest. Calculate the specific energy consumption if tractive resistance is 45 N/tonne, rotational inertia effect 10%, overall efficiency of transmission and motor 75%. 7. 400 tonne goods train is to be hauled by a locomotive up a gradient of 20% with acceleration of 1 kmphps. Coefficient of adhesion is 20%, track resistance 40 N/tonne and effective rotating masses 10% of dead weight. Find the weight of locomotive and number of axles, if axle load is not to increase beyond 22 tonne. 8. A locomotive of 100 tonnes can just accelerate train of 500 tonnes with an acceleration of 1 Kmphps upgradient of 10% Adhesive weight of locomotive is 70% of total dead weight, tractive resistance 45 newtons/tonne and rotational inertia 10%. If this locomotive is helped by another locomotive of 130 tonnes with 100% adhesive weight, find out: A. B. C. Trailing weight that can be hauled up the same gradient under same conditions. The maximum gradient, trailing hauled load remaining unchanged. Acceleration if gradient and hauled load remain unchanged.