Uploaded by
Genel Yutuc
Grade 8 Science Module: Particle Nature of Matter (Liquid & Gas)
advertisement

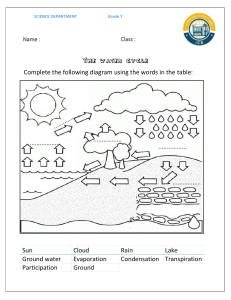
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Regional Office IX, Zamboanga Peninsula 8 SCIENCE Quarter 3 - Module 3 PARTICLE NATURE OF MATTER (Phase Changes Between Liquid and Gas) Name of Learner: ___________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________________ Name of School: ______________________________ Science – Grade 8 Support Material for Independent Learning Engagement (SMILE) Quarter 3 – Module 3: Particle Nature of Matter (Phase Changes Between Liquid and Gas) First Edition, 2021 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for the exploitation of such work for a profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Development Team of the Module Writer: Areen Joy P. Estera Editor: Cherilyn A. Rodriguez Reviewers: Cherilyn A. Rodriguez, Zyhrine P. Mayormita Layout Artist: Oliver A. Manalo Management Team: Virgilio P. Batan Jr. Lourma I. Poculan - Schools Division Superintendent - Asst. Schools Division Superintendent Amelinda D. Montero - Chief Education Supervisor, CID Nur N. Hussien - Chief Education Supervisor, SGOD Ronillo S. Yarag - Education Program Supervisor, LRMS Zyhrine P. Mayormita - Education Program Supervisor, Science Leo Martinno O. Alejo - Project Development Officer II, LRMS Janette A. Zamoras - Public Schools District Supervisor Adrian G. Refugio - School Principal, Zamboanga del Norte NHS Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education – Region IX – Dipolog City Schools Division Office Address: Telefax: E-mail Address: Purok Farmers, Olingan, Dipolog City Zamboanga del Norte, 7100 (065) 212-6986 and (065) 212-5818 dipolog.city@deped.gov.ph What I Need to Know This module was designed and written in a way that suits your understanding and needs. It is here to help you acquire mastery to explain physical changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules (MELC: S8MT-IIIc-d-9). Part of the activities allows you to explore the physical changes of water. The scope of this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. Specifically, this module is about; Lesson 3: Phase Changes between a Liquid and a Gas Specific Objectives: 1. Describe what happens to water when it is left in an open container for some time; 2. Represent through drawings what happens to the particles of water when it is left in an open container; 3. Describe what happens to water when it is left in a closed container for some time; 4. Describe what happens to water when it is heated; 5. Describe what happens to water when it is cooled; 6. Represent through drawings what happens to the particles of water when it is heated and then cooled; and 7. Explain the processes that take place at the submicroscopic (particle) level. What’s In In the previous week, you learned about the particles of matter in different states. Let us check if you can still remember your lessons by answering the activity. Activity 1: Get to Know Me a Little More! The properties of matter are listed below. Choose the properties that correctly describe the state of matter based on the given illustration. Write the properties in the second column of the given table. Lastly, identify the state of matter to complete the table. = Particles are able to move freely to all parts of the container. = Have definite shape and volume = Flows, spreads out and takes the shape of the container = Particles vibrate and are packed closely together in fixed positions = It is compressible. It can occupy small volume or it can expand to occupy a larger one. = Assumes the shape of the portion of the container that it occupies = It is rigid 1 Illustration Properties What State of Matter Am I? Good job! Matter is anything that has mass and volume. It is made up of tiny particles that are moving all the time. These particles have spaces between them. From your previous lesson, you had a better view of how these particles are arranged differently in each state of matter, which are solid, liquid, and gas. Everything you have learned about the states of matter is exactly what you need first to understand our new lesson for this week. What’s New Activity 2: You Raise Me Up! Directions: Decide to either do the simple experiment (at home) or read Scenario 1 in order to answer the activity questions. You can also do both! A. Do the Experiment Materials: ● liquid water, 1 glass ● glass without cover, 1 ● glass with cover, 1 Procedure: 1. Half-fill two (2) identical glasses with liquid water. 2. Label first glass “A” and set it aside. 3. Label second glass “B,” cover it and set it aside. 4. Place in direct sunlight the two glasses of water: uncovered (A) and with cover (B). 5. Observe what happens the next day. 2 B. Scenario 1 Juan and Pedro are neighbors and best buddies. One day they decided to play basketball. While playing under the heat of the sun, Juan signaled for a time-out to have a water break. While having their break, Juan and Pedro respectfully asked Aling Marya if they can have a glass of water for each one of them. They finished the first glass of water and asked for another one. After drinking half of their respective second glass of water, Juan left his glass of water uncovered while Pedro covered his glass of water before they left to play again. Here are important things you need to consider: ✔ Juan’s glass of water is half full and uncovered. ✔ Pedro’s glass of water is half full and covered. ✔ Both glasses of water were placed under the heat of the sun. Activity Questions: Did you perform the experiment? Did you simply read the story of Juan and Pedro? Either way, you will have to answer the questions. 1. Describe what happened to the water in a glass with a cover. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. Describe what happened to the water in a glass that is uncovered. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. What do you think happened to the volume of the water inside the glass which is covered and the one that is uncovered? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. Where do you think the water goes? Describe the process by writing or by drawing your description. Label and use arrows to indicate what is in your drawing. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5. What do you think will happen if you are going to heat the water in a glass with a cover? Explain your answer. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3 Activity 3: Serve it Hot or Cold? Directions: Read the following scenarios carefully. Perhaps you have already encountered almost the same situations at home. All you just need is a little curiosity, keen observation, and the courage to ask questions. All of these will always help you learn something new. C. Scenario 2 Mang Kulas always drinks his hot coffee early in the morning. One day he asked his grandson Jun-Jun to boil water for his coffee. Jun-Jun obediently filled the kettle with one (1) cup of tap water and mounted it on top of a cooking stove, and set it to medium heat. After a while, Jun-Jun noticed that bubbles were formed, and some vapor escaped out of the kettle beak. He decided that the water inside is already boiling and turned off the cooking stove. He then carefully poured the hot water into a clean cup. To his surprise, the amount of water before and after boiling was not the same. Jun-Jun wondered how it was possible. Nevertheless, Jun-Jun continued preparing the coffee and served it to his grandfather with a smile. Based on the scenario you’ve just read, answer the following questions. 1. What did Jun-Jun observe when he decided that the water inside the kettle is boiling? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 2. Write a description or draw a cartoon to show how the particles of water behave as they are heated. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What do you think is the reason why Jun-Jun was able to observe what happened to the water inside the kettle? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 4. If Jun-Jun kept the water boiling for more than 10 minutes, what do you think will happen to the amount of water inside the kettle? Why? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. Where did the water go? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 6. Can you explain by illustration how the water changes from liquid to gas? What is happening to the particles of water? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4 D. Scenario 3 The next day, Jun-Jun boiled water again for his grandfather’s coffee. Since his grandfather was still on their farm, he covered the cup of hot water and set it aside. It took a while for his grandfather to be home, and the cup of hot water had turned cold already. Based on Scenario 3, answer the following questions. 1. Describe what must have been observed by Jun-Jun on the inside of the cup cover? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where does the water under cover of the cup come from? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain by illustration how the water changes from gas to liquid. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 4. Describe what might have happened to the particles of water. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ How did you find the activities? Was it fun? Were you able to share all your observations? Were you able to draw all your observations? You just did a good job on doing your activities. You are now ready to learn the reasons behind your observations. What is it Particles are always in motion based on the particle model of the atom. The principle is presented at a submicroscopic level of the activities that you just had. We are focused on the particles of water that we refer to as molecules that have kinetic energy that differs from one another. Some molecules have higher kinetic energy than others, making them move faster compared to the molecules that have lower kinetic energy (see Figure 1). At room temperature, some molecules of water have enough amount of kinetic energy to break the attraction between the molecules close to them. Once the attraction is broken, these molecules will escape from the surface and will move into the air. Thus, changing the phase from liquid to gas. This process is what we call HYPERLINK evaporation. As evaporation takes place, the water molecules with lower Source: average kinetic energy "https://www.google.com/search?q=molecules+in+ will not be able to escape and will be left in the liquid phase. evaporation&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwiUuYmViJruAhWP Figure 1. Motion of molecules during Evaporation inzosBHVJiD_EQ2sub-microscopic level. cCegQIABAA&oq=molecules+in+evapora&gs_lcp=CgNp It is important to take note that evaporation in an bWcQARgAMgIIADoHCAAQsQMQQzoFCAAQsQM6BAgAEEM6Cg open container differs from evaporation in a container that is covered. In an open container, once gAELEDEIMBEEM6CAgAELEDEIMBOgYIABAFEB5QgFJY7ZUB the molecules have enough energy to break the attraction between neighboring molecules, they YL6cAWgJcAB4BIAB1gKIAeQykgEIMC4yMy44LjOYAQCgAQ GqAQtnd3Mtd2l6LWltZ7ABAMABAQ&sclient=img&ei=V4 can freely escape into the air once they transform into its gaseous phase. On the other hand, in a L_X9SxOY-dr7wP0sS9iA8&bih=772&biw=1517" \l closed container, not all of the molecules can escape into the air outside the container because "imgrc=WYBviM4Aq-9S5M&imgdii=9-Gli6A-9lQFAM" some (in vapor form) may be trapped on the cover. molecules in evaporation - Google Search 5 In scenario 2, Jun-Jun observed that after boiling, the amount of water decreased. What is the possible reason for this? As temperature increases, water molecules will gain more energy, making them move faster. Water molecules will have the energy to break the attraction of nearby molecules. These molecules will escape to its gaseous phase in the process of evaporation. Evaporation and formation of gas can happen even below the surface of the liquid. That explains the formation of bubbles that rise to the surface, and escape into the air seen as steam or vapor. Jun-Jun may have seen both bubbles and steam and made him decide that the water is already boiled. The observation in the activities you had can be better explained in Figure 2. Recall your lessons in math to read and understand the graph shown. The graph is composed of the y-axis (vertical) where the temperature in 0C is indicated, and the x-axis (horizontal), where time is indicated. Drinking water (liquid) lies between above 0oC and below 100 oC and is represented by the letter A segment (dark). When the temperature reaches 100 oC the water (liquid) starts to boil. At this point, evaporation takes place. Once the temperature continues to increase, water molecules start to become vapor (gas). On the other hand, at 100 oC, condensation may also take place when the temperature of the water starts to decrease. So when boiled water in a cup is covered, some of Figure 2. Change of Liquid to Gas the vapor cannot escape and turns back into a liquid through the process of condensation since the temperature is slowly starting to decrease. In Scenario 3, Jun-Jun observed that droplets formed under cover of the cup. Where did the droplets come from? Liquid water that changes into its gaseous phase is called water vapor. The water vapor rises, and some molecules touch the cover of the cup. The cover is cooler than the boiling water, so some of the heat energy of the vapor molecules are transferred into the cover, in effect cooling the water vapor. If the particles lose enough energy, the attraction between them can overcome their motion, which will make them attract with each other again, making them go back to the liquid phase. The droplets under cover of the cup result from the process called condensation (see Figure 3). Not all of the water molecules change from liquid to gas. There is still water in their liquid state that was left. Some of them might not have enough energy to overcome the forces of attraction of the nearby molecules. Moreover, some of the water molecules escape and turn into vapor, some hit the surface of the liquid, and if these molecules do not have enough energy to overcome the attraction, they will stay and remain in the liquid state. The condensation process is exactly the Source: HYPERLINK "https://www.google.com/search?q=condensation+in+a+close reverse of the evaporation process. Figure 3. Motion of molecules during Have you experienced waking up early in the +container&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwik2ZCVjpruAhVZAaYKHegLBuQ Condensation in sub-microscopic level. Q2morning and observed fog around you? Or droplets of water cCegQIABAA&oq=condensation+in+a+close+container&gs_lcp=C gNpbWcQA1DXon a leaf early in the morning without rain the other night? What about opening your packed lunch at noon and seeingglY1_oJYMuCCmgAcAB4AIABrAKIAawCkgEDMy0xmAEAoAEBqgELZ3dzL Xdpei1pbWfAAQE&sclient=img&ei=ooj_X6SAKdmCmAXol5igDg&bih droplets of water under cover of the container of your food?=772&biw=1517" \l "imgrc=0RwcHZQn5DO8FM" condensation in a close container - Google Search And of course, while drinking your cold drinks, you see droplets of water outside the glass. These are examples of condensation. 6 What’s More Activity 4. What is Essential is Invisible to the Naked Eye Directions: Below are cooking pans A and B being heated. A is uncovered while B is covered. Show what happens to the molecules of water inside each pan by drawing. Also, label what kind of process is taking place. Make a short description below each cooking pan. Cooking Pan A Cooking Pan B _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ What I Have Learned Activity 5. 4-Pics 1-Word Direction: What have all these pictures in common? Identify the specific word that links the four pictures. 7 What I Can Do Activity 6: True or False Direction: Read each statement below and decide whether it is TRUE or FALSE. Indicate a checkmark (✔) if the statement is TRUE and an (X) mark if the statement is FALSE. _______1. Evaporation of water is a physical change. _______2. Condensation of water is a physical change. _______3. Drinking water (l), ice (s), steam (g) are all the same substance. _______4. In the process of physical change the substance changes its physical appearance but not its composition. _______5. When drinking water (liquid) is boiled, surface particles start to evaporate and turn into its gaseous state. This process is NOT an example of a physical change. Assessment Direction: Write your answers (letters) clearly on the space provided before the number. _____1. What do you call the molecules that escaped from the liquid and go into the gaseous phase? A. Condense C. Vapor B. Fog D. Water _____2. When a gas is cooled, the motion of the particles slows down. If the particles lose enough energy, their attraction for each other can overcome their motion and cause them to associate with one another to become liquid. What do you call this process? A. Condensation C. Freezing B. Evaporation D. Melting _____3. Which of the following statements is NOT true? A. Condensation process is an example of physical change. B. Evaporation is responsible for ground-water fog. C. Evaporation process is an example of physical change. D. Enough kinetic energy breaks the attraction of nearby molecules allowing evaporation to take place at room temperature. 8 _____4. When the temperature rises and water starts to boil, the molecules gain more energy. What do you call this type of energy as they move faster? A. Electrical Energy C. Kinetic Energy B. Potential Energy D. Mechanical Energy _____5. Which of the following scenarios will at MOST increase the rate of evaporation? A. Glass of water covered and placed under the heat of the sun. B. Glass of water covered and exposed to high heat. C. Glass of water uncovered and placed under the heat of the sun. D. Glass of water uncovered and exposed to high heat. _____6. The following are factors that may affect the evaporation process EXCEPT? A. Heat of the Sun C. Kinetic Energy B. Increase temperature D. Potential Energy _____7. Which of the following situation/s is/are physical change? I. Liquid turns to Gas II. Volume of Water decreases after heating III. Water evaporates IV. Water condenses A. I & II only C. All of the situations given B. All situations EXCEPT IV D. None of the situations given Ana conducted an experiment. She poured 10-mL of water into a 50-mL beaker. She covered and labeled it “A”. She set it aside. She also poured another 10-mL of water into another 50-mL beaker and labeled it “B”. This time she did not cover it. She kept it that way within 24 hours. A B Based on the experiment Anna conducted, answer questions number 8 & 9. _____8. Which of the following is possible to happen? A. Water in a 50-mL beaker “A” decreased in volume. B. Water in a 50-mL beaker “B” decreased in volume. C. Water in a 50-mL beaker “A” increased in volume. D. Water in a 50-mL beaker “B” increased in volume. _____9. What do you think is the reason behind this? A. Condensation happen C. Freezing happen B. Evaporation happen D. Melting happen _____10. Which of the following best describes the illustration below? A. Water condenses C. Water freezes B. Water evaporates D. Water melts _____11. Which of the following statements about the evaporation process is not true? A. The rate of evaporation is fast during rainy days. B. Evaporation happens only on the surface of a liquid. C. All molecules of a liquid take part in the process of evaporation. D. Evaporation and condensation are opposite processes. 9 For numbers 12 - 14 refer to the graph that represents the temperature changes of water as it is heated. _____12. Which figure best describes the arrangement of molecules in line A? A. C. B. D. _____13. What will be the arrangement of molecules in line C? _____14. Which of the following statements is TRUE in situation C? I. Either evaporation or condensation takes place depending on the temperature. II. Liquid evaporates when temperature continues to increase. III. Gas condenses when temperature continues to decrease. IV. Neither evaporation nor condensation will happen. A. B. C. D. I, II & III only I, II & IV only All of the situations are TRUE. None of the given statements are TRUE 10 _____15. Which of the following statements is false? A. Evaporation is the process when a liquid turns into a gas. B. Condensation is the process when a gas turns into a liquid. C. Evaporation and condensation retain the identity of a material. D. Evaporation and condensation are exactly the opposite of each other. Additional Activities Activity 8: The Cycle of Water Directions: Below is an illustration of the water cycle. Evaporation and condensation are part of the processes involved in it. In one whole sheet of paper, make your own illustration and connect what you have learned this week to the cycle of water. You may draw or describe or in any way that can help you explain better what you have learned. Please see attached rubric for guidance. Rubric CATEGORY Presentation 4 The output clearly communicates the idea 3 The output communicates some of the ideas 2 The output indirectly communicates the idea Creativity and Originality All of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used reflect an exceptional degree of ingenuity in the creation All of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used were accurate and related to the lesson Most of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used reflect an exceptional degree of ingenuity in the creation Most of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used were accurate and related to the lesson Words, descriptions, and illustrations used were copied from the designs and idea of others Accuracy and Relevance to the Content TOTAL 11 Some of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used were accurate and related to the lesson 1 The output does not sufficiently communicate the idea Words, descriptions, and illustrations used were not from the student Some of the words, descriptions, and illustrations used were neither accurate nor related to the lesson SCORE Answer Key Gr8Q3 Module 3 Activity 1. Get to Know me a Little More! SOLID`: 1. Have definite shape and volume 2. Particles vibrate in fixed positions 3. It is rigid LIQUID: 1. Flows, spread out and takes the shape of the container 2. Assumes the shape of the portion of the container that it occupies GAS: 1. 2. Particles are able to move freely to all parts of the container It is compressible. If can occupy a larger one. Activity 2. You Raise Me Up! (Answers may vary) 1. >Droplets under the cover >Smaller amount of water compared to the original amount of water 2. Very small amount of water is left 3. With Cover: small of amount of water Without cover: Very low amount of water 4. >It becomes a vapor >It evaporates 5. There will be droplets under the cover Activity 3. Serve it Hot or Cold? Scenario 2 (Answers may vary) 1. Water is boiling bubbles and steam are both visible 2. The molecules move faster 3. The molecules gain high amount of energy breaking the attractions from nearby molecules. 4. Amount of water will decreased because the water will evaporate. 5. It goes into the air. It turns into is gaseous state. Scenario 3 (Answers may vary) 1. There are droplets 2. Those are water in its gaseous state the returns back to its liquid state 3. Change from Liquid to Gas 4. When heated, water molecules become a vapor but since the cup is covered the vapor in gaseous state is trapped and Goes back to its liquid the state again 12 Activity 4. What’s More Molecules have high KE breaking the attraction with other molecule. Liquid changes to gas. Evaporation takes place. Molecules have high KE breaking the attraction with other molecules. Liquid changes to gas. However, some of the molecules are trapped because of the cover. Evaporation takes place but condensation will soon occur once the temp. drops. Droplets will be seen under The cover. Activity 5: 4 Pics 1 Word 1. 2. 3. 4. Condensation Molecules Vapor Evaporation Activity 6: True or False 1. √ 2. √ 3. √ 4. √ 5. x Assessment 1. C 2. B 3. B 4. C 5. D 6. D 7. C 8. B 9. B 10. B 11. A 12. B 13. D 14. A 15. C 13 References (Khan Academy). (No date). Tissues, organs, & organ systems. Retrieved from https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-biology/hs-human-bodysystems/hs-body-structure-and-homeostasis/a/tissues-organs-organ-systems (Study Jams). (No date). The Human Body. Retrieved from http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/science/humanbody/human-body.m (Byjus The Learning App). (No date). Parts of a Compound Microscope. Retrieved from https://byjus.com/biology/study-of-the-parts-of-acompound-microscope/ (Laboratory Info). (2020). Compound Microscope-Types, Parts, Diagrams, Functions, and Uses. Retrieved from https://laboratoryinfo.com/compoundmicroscope/ (Studylib). (No date). Lab: The Compound Microscope. Retrieved fromhttps://studylib.net/doc/6826165/st220_mi croscopelab_istructions Chemistry the Central Science (2002) Brown et., al. 8 th Edition. Image credit: modified from Levels of structural organization of the human body by OpenStax College, Anatomy & Physiology, CC BY 4.0 ( organization of the human body) Department of Education (2017). Science 8 Learner’s Material. First Edition. Department of Education-Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR) Department of Education (2017). Science 8 Teachers Guide. First Edition. Department of Education-Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR) Image Credit: evaporation - Google Search boiling water - Google Search condensation in a close container - Google Search